miR-200c增加H2228細胞對克唑替尼和紫杉醇及順鉑敏感性的研究
高海祥,曹 磊
?
·論著·
miR-200c增加H2228細胞對克唑替尼和紫杉醇及順鉑敏感性的研究
高海祥,曹 磊
背景 miR-200c可以增加腫瘤細胞對紫杉醇、順鉑的敏感性及表皮生長因子受體(EGFR)陽性肺癌細胞對分子靶向藥物厄洛替尼、吉非替尼及阿法替尼的敏感性,但其是否可以增加棘皮動物微管相關(guān)樣蛋白4(EML4)-間變性淋巴瘤激酶(ALK)融合基因陽性肺腺癌細胞(ALK陽性肺癌細胞)對克唑替尼、紫杉醇和順鉑的敏感性尚無相關(guān)研究。目的 觀察miR-200c是否可以增加H2228細胞對克唑替尼、紫杉醇及順鉑的敏感性,并探討其機制。方法 2014年2月—2015年5月,培養(yǎng)H2228細胞并進行轉(zhuǎn)染,根據(jù)轉(zhuǎn)染物的不同,將細胞分為增強轉(zhuǎn)染組(轉(zhuǎn)染miR-200c mimics)、增強對照組(轉(zhuǎn)染miR-200c mimics陰性對照)、抑制轉(zhuǎn)染組(轉(zhuǎn)染miR-200c inhibitor)、抑制對照組(轉(zhuǎn)染miR-200c inhibitor陰性對照)。采用實時熒光定量PCR法(Real-time PCR法)檢測H2228細胞中miR-200c基因表達水平,MTT法檢測不同濃度抗腫瘤藥物〔克唑替尼(50、100、200 nmol/L)、紫杉醇(6.25、12.50、25.00 nmol/L)、順鉑(25、50、100 nmol/L)〕作用下H2228細胞增殖水平,Transwell法檢測H2228細胞遷移率,Real-time PCR法檢測增強轉(zhuǎn)染組、增強對照組H2228細胞中E-鈣黏蛋白、N-鈣黏蛋白、波狀蛋白、CD24mRNA表達水平,Western blotting法檢測增強轉(zhuǎn)染組、增強對照組H2228細胞中E-鈣黏蛋白、N-鈣黏蛋白、波狀蛋白、CD24表達水平。結(jié)果 增強轉(zhuǎn)染組H2228細胞中miR-200c基因表達水平高于增強對照組(P<0.05)。抑制轉(zhuǎn)染組H2228細胞中miR-200c基因表達水平低于抑制對照組(P<0.05)。增強轉(zhuǎn)染組各濃度抗腫瘤藥物作用下H2228細胞增殖水平均低于增強對照組(P<0.05)。抑制轉(zhuǎn)染組各濃度抗腫瘤藥物作用下H2228細胞增殖水平均高于抑制對照組(P<0.05)。增強轉(zhuǎn)染組H2228細胞遷移率小于增強對照組(P<0.05)。抑制轉(zhuǎn)染組H2228細胞遷移率大于抑制對照組(P<0.05)。增強轉(zhuǎn)染組H2228細胞中E-鈣黏蛋白及其mRNA表達水平高于增強對照組,N-鈣黏蛋白、波狀蛋白、CD24及其mRNA表達水平低于增強對照組(P<0.05)。結(jié)論 miR-200c可以通過使肺癌細胞發(fā)生間質(zhì)-上皮轉(zhuǎn)變(MET)而增加H2228細胞對克唑替尼、紫杉醇及順鉑的敏感性。
抗藥性,腫瘤;H2228;miR-200c;克唑替尼;紫杉醇;順鉑
高海祥,曹磊.miR-200c增加H2228細胞對克唑替尼和紫杉醇及順鉑敏感性的研究[J].中國全科醫(yī)學,2016,19(36):4478-4483.[www.chinagp.net]
GAO H X,CAO L.Effect of increased H2228 cells through miR-200c on sensitivity of crizotinib,paclitaxel and cisplatin[J].Chinese General Practice,2016,19(36):4478-4483.
2016年CHEN等[1]研究顯示,肺癌是男性最常見的惡性腫瘤,是女性第二位高發(fā)的惡性腫瘤,而在病死率中,無論是男性還是女性,肺癌均為癌癥相關(guān)病死率的第一位。在肺癌的治療上,第三代含鉑聯(lián)合化療(PBC)具有良好的治療效果,可以使70%~80%接受一線化療的患者臨床獲益,但晚期肺癌患者總生存期(OS)較差,為8~10個月;與PBC相比,分子靶向藥物治療極大地提高了患者治療有效率和OS[2]。研究顯示,應用厄洛替尼前后患者的OS存在明顯差異(17.6個月與27.2個月)[3],但是,無論是化療藥物還是分子靶向藥物,耐藥的發(fā)生不可避免[4],因此,尋找一種可以提高化療、分子靶向藥物治療敏感性的方法,延緩耐藥的發(fā)生也是解決腫瘤耐藥的新途徑。多項研究表明,miR-200c可以增加紫杉醇、順鉑及分子靶向藥物厄洛替尼、吉非替尼及阿法替尼對表皮生長因子受體(EGFR)陽性肺癌細胞的抑制作用,甚至可以增加EGFR野生型肺癌細胞對厄洛替尼的敏感性[5-8]。但是,miR-200c是否可以增加克唑替尼對棘皮動物微管相關(guān)樣蛋白4(EML4)-間變性淋巴瘤激酶(ALK)融合基因陽性肺腺癌細胞(ALK陽性肺癌細胞)的抑制作用,目前尚無相關(guān)報道。基于此,本研究將miR-200c轉(zhuǎn)染ALK陽性肺癌細胞H2228細胞,觀察轉(zhuǎn)染前后細胞對紫杉醇、順鉑及克唑替尼敏感性的變化。
1 材料與方法
1.1 實驗材料 H2228細胞株為ALK陽性肺癌細胞,購于ATCC(American Type Culture Collection)公司。
1.2 主要試劑及儀器 ALK抑制劑克唑替尼購自美國Sigma-Aldrich公司;miR-200c mimics、miR-200c inhibitor及相應陰性對照購自美國invitrogen公司;RPMI 1640培養(yǎng)基、胎牛血清、胰蛋白酶以及MTT溶液購自美國Gibco公司;鼠抗人E-鈣黏蛋白、N-鈣黏蛋白、波狀蛋白、CD24單克隆抗體購自美國Abcam公司;辣根過氧化物酶(HRP)標記抗鼠和兔的二抗購自美國Fementas公司。
1.3 實驗方法
1.3.1 細胞培養(yǎng)與轉(zhuǎn)染 2014年2月—2015年5月,將肺腺癌H2228細胞株從液氮中取出,迅速置于37 ℃水浴箱中解凍后移至離心管中,添加RPMI 1640培養(yǎng)基,輕輕吹打細胞,800 r/min離心5 min(離心半徑3 cm),去上清液,完全培養(yǎng)液重懸細胞,調(diào)整至合適的細胞密度并接種于培養(yǎng)瓶中,放入37 ℃、5% CO2細胞培養(yǎng)箱中培養(yǎng),次日更換1次培養(yǎng)液,磷酸鹽緩沖液(PBS)清洗,0.25%胰蛋白酶消化傳代。取對數(shù)生長期H2228細胞接種在6孔板中,每孔中加入不含抗生素的培養(yǎng)液,調(diào)整細胞密度并于37 ℃培養(yǎng)箱中培養(yǎng),使細胞貼壁生長,密度達80%左右進行轉(zhuǎn)染。將細胞接種于96孔板中,根據(jù)轉(zhuǎn)染物的不同,將細胞分為增強轉(zhuǎn)染組(轉(zhuǎn)染miR-200c mimics)、增強對照組(轉(zhuǎn)染miR-200c mimics陰性對照)、抑制轉(zhuǎn)染組(轉(zhuǎn)染miR-200c inhibitor)、抑制對照組(轉(zhuǎn)染miR-200c inhibitor陰性對照)。轉(zhuǎn)染方法:將A、B液混合形成mimics-lipofectamine 2000復合物,加入細胞培養(yǎng)基中,來回輕柔搖晃細胞培養(yǎng)基,然后放入培養(yǎng)箱中,放置4~6 h換液,換成含有血清和雙抗的培養(yǎng)基,繼續(xù)培養(yǎng)或進行傳代。
1.3.2 實時熒光定量PCR法(Real-time PCR法)檢測H2228細胞中miR-200c基因表達水平 取各組對數(shù)生長期H2228細胞,TRIZOL法提取H2228細胞的總RNA,將miRNA反轉(zhuǎn)錄為cDNA,參照Real-time PCR說明書檢測miR-200c基因表達水平。PCR擴增反應體系:SYBR Premix Ex Taq(2×)5 μl、PCR 正向引物(10 μmol/L)0.2 μl、PCR 反向引物(10 μmol/L)0.2 μl、DNA模板1 μl、雙蒸水(ddH2O)3.6 μl;PCR反應條件:95 ℃預變性2 min,95 ℃變性15 s,60 ℃退火60 s,共40個循環(huán)。miR-200c上游引物:5′-CAGTGCGTGTCGTGGAGT-3′,下游引物:5′-GGCCTAATACTGCCGGGTAAT-3′;U6上游引物:5′-CGCTTCACGAATTTGCGTGTCAT-3′,下游引物:5′-GCTTCGGCAGCACATATACTAAAAT-3′。擴增完畢后,以U6為內(nèi)參照基因,得到miR-200c基因表達水平。實驗重復3次。
1.3.3 MTT法檢測不同濃度抗腫瘤藥物(克唑替尼、紫杉醇、順鉑)作用下H2228細胞增殖水平 取各組對數(shù)生長期的H2228細胞,胰蛋白酶消化,培養(yǎng)液稀釋細胞懸液,并接種到96孔板,200 μl/孔,每組細胞均設(shè)置空白調(diào)零孔(不含細胞的完全培養(yǎng)基)。于37 ℃ 5% CO2培養(yǎng)箱中培養(yǎng)24 h。取出96孔板,吸去舊培養(yǎng)基,PBS洗滌2次,將細胞分別加入不同濃度的待測藥物中(克唑替尼:50、100、200 nmol/L;紫杉醇:6.25、12.50、25.00 nmol/L;順鉑:25、50、100 nmol/L),于37 ℃ 5% CO2培養(yǎng)箱中培養(yǎng)44 h。取出96孔板,每孔加MTT溶液(5 mg/ml)20 μl,繼續(xù)孵育4 h,終止培養(yǎng),每孔加150 μl二甲基亞砜(DMSO),脫色搖床低速震蕩10 min,溶解結(jié)晶物。采用酶聯(lián)免疫檢測儀于490 nm波長處檢測各孔吸光度值(OD值),即H2228細胞增殖水平。實驗重復3次。
1.3.4 Transwell法檢測H2228細胞遷移率 將Transwell小室置入無菌的24孔板中。各組取對數(shù)生長期H2228細胞,用含0.1%胎牛血清的McCoy′s 5A培養(yǎng)基懸浮,計數(shù),稀釋至密度為1×106/ml,每個上室中分別加入200 μl細胞懸液。24孔板下室中均加入600 μl含有30%胎牛血清的McCoy′s 5A培養(yǎng)基。37 ℃ 5% CO2培養(yǎng)箱中繼續(xù)培養(yǎng)48 h后棄去孔中培養(yǎng)液,PBS洗滌2次,將4 ℃ 4%甲醛溶液500 μl/孔加入下室,固定30 min,用棉簽輕輕擦掉上層未遷移細胞,再用0.1%龍膽紫500 μl染色20 min,清水洗滌3遍以上。顯微鏡下隨機選取5個視野(×400)觀察細胞,計數(shù)并采集圖像,計算H2228細胞遷移率。實驗重復3次。
1.3.5 Real-time PCR法檢測增強轉(zhuǎn)染組、增強對照組H2228細胞中E-鈣黏蛋白、N-鈣黏蛋白、波狀蛋白、CD24mRNA表達水平 操作方法同Real-time PCR法檢測miR-200c基因表達水平。E-鈣黏蛋白上游引物:5′-TGGACAGGGAGGATTTTGAG-3′,下游引物:5′-ACCTGAGGCTTTGGATTCCT-3′;N-鈣黏蛋白上游引物:5′-CCACAGCTCCACCATATGACT-3′,下游引物:5′-CCCCAGTCGTTCAGGTAATC-3′;波狀蛋白上游引物:5′-AGTGCCTGGAACGTCAGATG-3′,下游引物:5′-CAGCAGCTTCCTGTAGGTGG-3′;CD24上游引物:5′-AGAGATAACCCTGCCCGAGG-3′,下游引物:5′-GTCTAGCAGGATGCTGGGTG-3′;內(nèi)參GAPDH上游引物:5′-CGGATTTGGTCGTATTGGG-3′,下游引物:5′-TGCTGGAAGATGGTGATGGGATT-3′。實驗重復3次。
1.3.6 Western blotting法檢測增強轉(zhuǎn)染組、增強對照組H2228細胞中E-鈣黏蛋白、N-鈣黏蛋白、波狀蛋白、CD24表達水平 取各組對數(shù)生長期H2228細胞,提取總蛋白,采用含有蛋白酶抑制劑的蛋白裂解液(RIPA)裂解細胞,4 ℃ 12 000×g離心30 min,取上清液總蛋白;采用BCA法測定蛋白質(zhì)濃度;蛋白樣品100 ℃水浴變性,按次序上樣至電泳道,十二烷基硫酸鈉-聚丙烯酰胺凝膠電泳(SDS-PAGE)并轉(zhuǎn)印到聚偏二氟乙烯(PVDF)膜上,將PVDF膜放入含有一抗(鼠抗人E-鈣黏蛋白、N-鈣黏蛋白、波狀蛋白、CD24單克隆抗體)的封閉稀釋液中,4 ℃靜置孵育過夜。TBST洗膜3次,加入HRP標記抗鼠和兔的二抗稀釋液,室溫下反應1~2 h或4 ℃反應過夜,再次TBST洗膜,增強化學發(fā)光法使蛋白條帶發(fā)光并在X線片上曝光顯影,計算E-鈣黏蛋白、N-鈣黏蛋白、波狀蛋白、CD24表達水平。實驗重復3次。
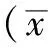
2 結(jié)果
2.1miR-200c基因表達水平 增強轉(zhuǎn)染組H2228細胞中miR-200c基因表達水平(310.7±19.8)高于增強對照組(1.0±0.1),差異有統(tǒng)計學意義(t=-27.225,P=0.001)。抑制轉(zhuǎn)染組H2228細胞中miR-200c基因表達水平(0.3±0.0)低于抑制對照組(1.0±0.2),差異有統(tǒng)計學意義(t=5.393,P=0.033)。
2.2 不同濃度抗腫瘤藥物(克唑替尼、紫杉醇、順鉑)作用下H2228細胞增殖水平 增強轉(zhuǎn)染組各濃度抗腫瘤藥物(克唑替尼、紫杉醇、順鉑)作用下H2228細胞增殖水平均低于增強對照組,差異有統(tǒng)計學意義(P<0.05,見表1)。抑制轉(zhuǎn)染組各濃度抗腫瘤藥物(克唑替尼、紫杉醇、順鉑)作用下H2228細胞增殖水平均高于抑制對照組,差異有統(tǒng)計學意義(P<0.05,見表2)。
2.3H2228細胞遷移率 增強轉(zhuǎn)染組H2228細胞遷移率(31.0±2.6)小于增強對照組(54.7±3.5),差異有統(tǒng)計學意義(t=16.289,P=0.004)。抑制轉(zhuǎn)染組H2228細胞遷移率(79.7±6.7)大于抑制對照組(53.3±6.0),差異有統(tǒng)計學意義(t=-8.021,P=0.015,見圖1,本文圖1彩圖見本刊官網(wǎng)www.chinagp.net電子期刊相應文章附件)。
2.4 增強轉(zhuǎn)染組、增強對照組H2228細胞中E-鈣黏蛋白、N-鈣黏蛋白、波狀蛋白、CD24mRNA表達水平 增強轉(zhuǎn)染組H2228細胞中E-鈣黏蛋白mRNA表達水平高于增強對照組,N-鈣黏蛋白、波狀蛋白、CD24mRNA表達水平低于增強對照組,差異有統(tǒng)計學意義(P<0.05,見表3)。
Table 3 Comparison of the mRNA expression levels of E-cadherin,N-cadherin,corrugated protein,and CD24in H2228 cells in enhanced transfection group and enhanced control group
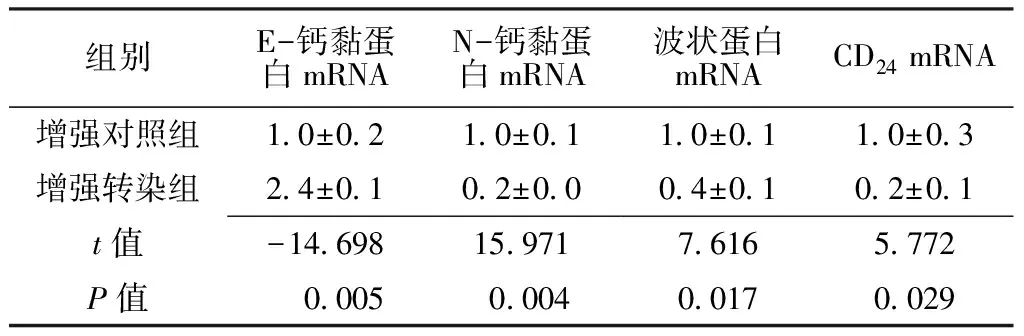
組別E-鈣黏蛋白mRNAN-鈣黏蛋白mRNA波狀蛋白mRNACD24mRNA增強對照組10±0210±0110±0110±03增強轉(zhuǎn)染組24±0102±0004±0102±01t值-146981597176165772P值0005000400170029
Table1ComparisonofcellproliferationlevelsofH2228undertheeffectofantineoplasticdrugs(crizotinib,paclitaxelandcisplatin)inenhancedtransfectiongroupandenhancedcontrolgroup
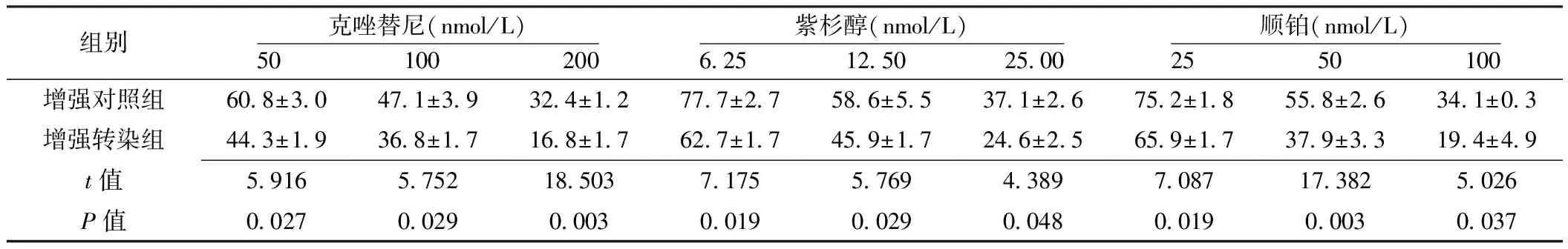
組別克唑替尼(nmol/L)50 100 200紫杉醇(nmol/L)625 1250 2500順鉑(nmol/L)25 50 100增強對照組608±30471±39324±12777±27586±55371±26752±18558±26341±03增強轉(zhuǎn)染組443±19368±17168±17627±17459±17246±25659±17379±33194±49t值59165752185037175576943897087173825026P值002700290003001900290048001900030037
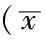
Table2ComparisonofcellproliferationlevelsofH2228undertheeffectofantineoplasticdrugs(crizotinib,paclitaxelandcisplatin)ininhibitorytransfectiongroupandinhibitorycontrolgroup
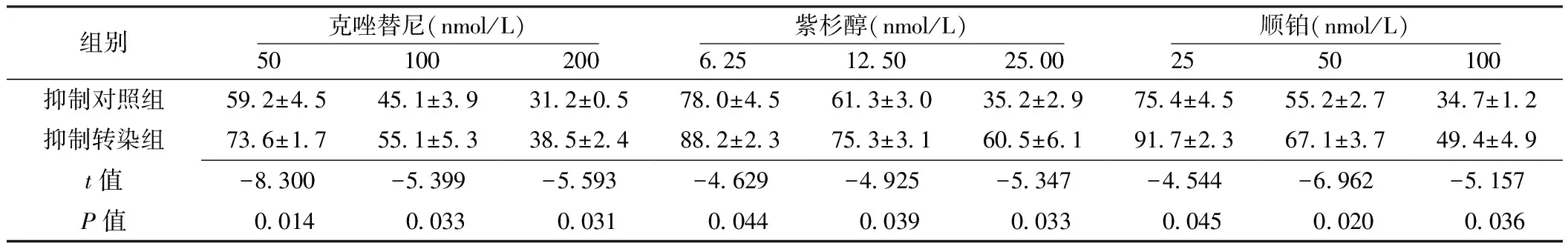
組別克唑替尼(nmol/L)50 100 200紫杉醇(nmol/L)625 1250 2500順鉑(nmol/L)25 50 100抑制對照組592±45451±39312±05780±45613±30352±29754±45552±27347±12抑制轉(zhuǎn)染組736±17551±53385±24882±23753±31605±61917±23671±37494±49t值-8300-5399-5593-4629-4925-5347-4544-6962-5157P值001400330031004400390033004500200036
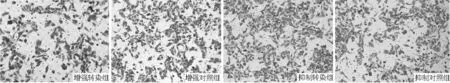
圖1 Transwell法檢測H2228細胞遷移率
2.5 增強轉(zhuǎn)染組、增強對照組H2228細胞中E-鈣黏蛋白、N-鈣黏蛋白、波狀蛋白、CD24表達水平 增強轉(zhuǎn)染組H2228細胞中E-鈣黏蛋白表達水平高于增強對照組,N-鈣黏蛋白、波狀蛋白、CD24表達水平低于增強對照組,差異有統(tǒng)計學意義(P<0.05,見表4、圖2)。
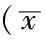
Table 4 Comparison of the expression levels of E-cadherin,N-cadherin,corrugated protein,and CD24in H2228 cells in enhanced transfection group and enhanced control group
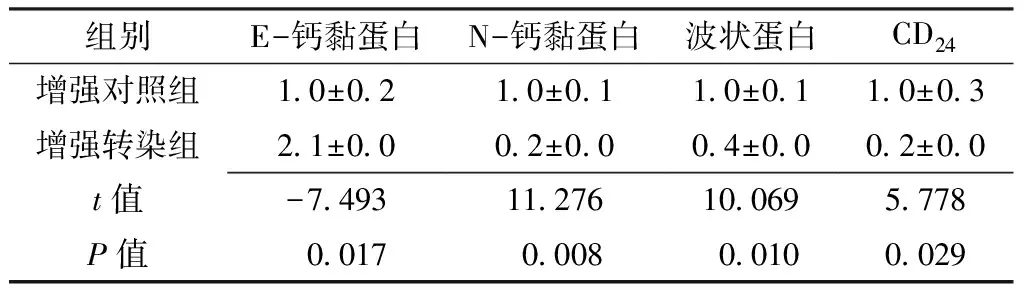
組別E-鈣黏蛋白N-鈣黏蛋白波狀蛋白CD24增強對照組10±0210±0110±0110±03增強轉(zhuǎn)染組21±0002±0004±0002±00t值-749311276100695778P值0017000800100029
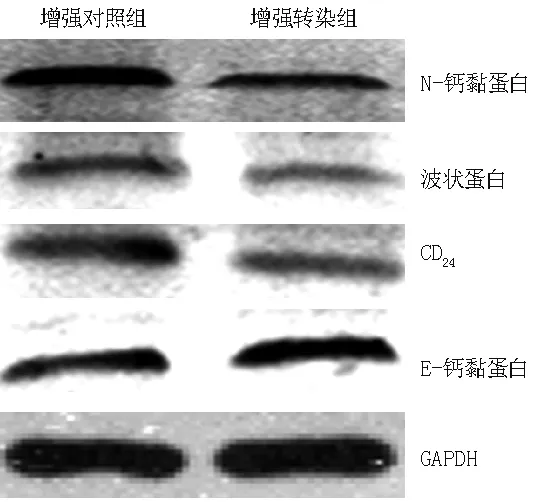
圖2 Western blotting法檢測增強轉(zhuǎn)染組、增強對照組H2228細胞中E-鈣黏蛋白、N-鈣黏蛋白、波狀蛋白、CD24表達水平的SDS-PAGE圖
Figure 2 SDS-PAGE of the expression levels of E-cadherin,N-cadherin,corrugated protein,and CD24in H2228 cells in enhanced transfection group and enhanced control group by Western blotting method
3 討論
miRNA-200c是目前研究較多的微小RNA(microRNAs,簡稱miRNAs)之一,miRNAs是一類進化上高度保守的內(nèi)源性非編碼單鏈小RNA,其可以調(diào)節(jié)機體細胞的發(fā)育、分化、增殖、代謝及凋亡等關(guān)鍵環(huán)節(jié)[9]。多項研究表明,miR-200c與多種腫瘤相關(guān),被認為是具有治療潛力的腫瘤標志物[10],其不僅與肺癌的發(fā)生發(fā)展密切相關(guān)[11-12],還可以增強腫瘤細胞對放療的敏感性[13-14],同時增強多種化療藥物對腫瘤細胞的抑制作用,甚至增加分子靶向藥物EGFR-酪氨酸激酶抑制劑(TKI)對EGFR突變型肺癌的抗腫瘤活性[5-8]。本研究旨在檢測miR-200c 是否可以增加ALK-TKI藥物克唑替尼及化療藥物紫杉醇、順鉑對ALK陽性肺癌細胞的抗腫瘤活性并進一步探討其機制,為臨床應用提供理論基礎(chǔ)。
本研究結(jié)果顯示,增強轉(zhuǎn)染組H2228細胞中miR-200c基因表達水平高于增強對照組,抑制轉(zhuǎn)染組H2228細胞中miR-200c基因表達水平低于抑制對照組,增強轉(zhuǎn)染組各濃度抗腫瘤藥物(克唑替尼、紫杉醇、順鉑)作用下H2228細胞增殖水平均低于增強對照組,抑制轉(zhuǎn)染組各濃度抗腫瘤藥物(克唑替尼、紫杉醇、順鉑)作用下H2228細胞增殖水平均高于抑制對照組,說明克唑替尼、紫杉醇及順鉑對高表達miR-200c細胞的抑制作用明顯增強,而對低表達miR-200c細胞的抑制作用則明顯減弱,表明miR-200c可以增加H2228細胞對分子靶向藥物克唑替尼及常規(guī)化療藥物紫杉醇和順鉑的敏感性,這與既往研究結(jié)果相似[5-7]。
有文獻報道,E-鈣黏蛋白是上皮細胞的特征性分子學標志物,而N-鈣黏蛋白、波狀蛋白是間質(zhì)細胞的特征性分子學標志物,通過調(diào)節(jié)這些分子學標志物可以誘發(fā)細胞發(fā)生上皮及間質(zhì)之間的相互轉(zhuǎn)化[15]。CD24為腫瘤細胞上皮-間質(zhì)轉(zhuǎn)變(EMT)表型及干細胞表型的特征性分子標志物[16]。本研究結(jié)果顯示,增強轉(zhuǎn)染組H2228細胞遷移率小于增強對照組,抑制轉(zhuǎn)染組H2228細胞遷移率大于抑制對照組,說明miR-200c抑制了細胞的遷移活性,表明過表達miR-200c后,細胞有間質(zhì)-上皮轉(zhuǎn)變(MET)可能,為進一步證實,本研究組檢測了增強轉(zhuǎn)染組、增強對照組H2228細胞中E-鈣黏蛋白、N-鈣黏蛋白、波狀蛋白、CD24及其mRNA表達水平,結(jié)果顯示,增強轉(zhuǎn)染組H2228細胞中E-鈣黏蛋白及其mRNA表達水平高于增強對照組,N-鈣黏蛋白、波狀蛋白、CD24及其mRNA表達水平低于增強對照組。
多項研究顯示,腫瘤細胞對抗腫瘤藥物敏感性降低的過程有趨向間質(zhì)化的表現(xiàn),通過對耐藥細胞的研究發(fā)現(xiàn),多種耐藥細胞發(fā)生了EMT表現(xiàn):阿霉素體外誘導乳腺癌細胞發(fā)生EMT,而且該細胞表現(xiàn)出侵襲轉(zhuǎn)移能力增強和多藥耐藥現(xiàn)象[17],耐5-氟尿嘧啶的乳腺癌細胞株也觀察到了耐藥細胞的EMT現(xiàn)象[18],此外,耐厄洛替尼、吉非替尼及克唑替尼的肺癌細胞也發(fā)生了不同性質(zhì)的EMT改變[19-21]。因此,逆轉(zhuǎn)癌細胞EMT的變化,可以增加癌細胞對化療藥物及分子靶向藥物的敏感性[5-6,21]。miR-200c最主要功能之一是調(diào)節(jié)細胞上皮及間質(zhì)轉(zhuǎn)變的病理生理過程即EMT和MET。EMT和MET是兩個可逆的、相反的過程,miR-200c通過直接調(diào)節(jié)E盒結(jié)合鋅指蛋白-1(ZEB1)及其下游基因E-鈣黏蛋白來調(diào)節(jié)EMT及MET之間的轉(zhuǎn)變,從而進一步調(diào)節(jié)腫瘤多方面的生物學特征[22]。
本研究尚有不足之處,目前人工調(diào)節(jié)miRNA變化的體內(nèi)試驗還鮮有報道[13]。miR-200c可以調(diào)節(jié)多種細胞因子而增加肺癌治療效果,但只是停留在細胞或動物實驗水平上,臨床上肺癌患者并無明顯受益,如何將miR-200c應用于臨床或通過調(diào)節(jié)miR-200c上下通路而改變其表達尚待進一步研究及論證,隨著miR-200c研究的進一步深入,相信miR-200c將在腫瘤的早期診斷、治療及預后的判斷方面有更加廣泛的前景。
綜上所述,miR-200c通過使細胞發(fā)生MET改變而增加H2228細胞對克唑替尼、紫杉醇及順鉑的敏感性。
作者貢獻:高海祥進行實驗設(shè)計與實施、資料收集整理、撰寫論文并對文章負責;曹磊進行實驗實施、評估、質(zhì)量控制及審校。
本文無利益沖突。
[1]CHEN W,ZHENG R,BAADE P D,et al.Cancer statistics in China,2015[J].CA Cancer J Clin,2016,66(2):115-132.
[2]ZHANG J W,ZHAO Y Y,GUO Y,et al.The impact of both platinum-based chemotherapy and EGFR-TKIs on overall survival of advanced non-small cell lung cancer[J].Chin J Cancer,2014,33(2):105-114.
[3]TAKANO T,FUKUI T,OHE Y,et al.EGFR mutations predict survival benefit from gefitinib in patients with advanced lung adenocarcinoma:a historical comparison of patients treated before and after gefitinib approval in Japan[J].J Clin Oncol,2008,26(34):5589-5595.
[4]IACONO D,CHIARI R,METRO G,et al.Future options for ALK-positive non-small cell lung cancer[J].Lung Cancer,2015,87(3):211-219.
[5]CEPPI P,MUDDULURU G,KUMARSWAMY R,et al.Loss of miR-200c expression induces an aggressive,invasive,and chemoresistant phenotype in non-small cell lung cancer[J].Mol Cancer Res,2010,8(9):1207-1216.
[6]胡麗麗,尹燕軍,鐘文娟,等.miR-200c增強肺癌A549細胞對紫杉醇及吉非替尼的敏感度及相關(guān)機制[J].腫瘤防治研究,2015,42(8):760-764. HU L L,YIN Y J,ZHONG W J,et al.miR-200c Enhances sensitivity of lung cancer cell A549 to paclitaxel and gefitinib and related mechanism[J].Cancer Research on Prevention and Treatment,2015,42(8):760-764.
[7]ZHANG H H,ZHANG Z Y,CHE C L,et al.Array analysis for potential biomarker of gemcitabine identification in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines[J].Int J Clin Exp Pathol,2013,6(9):1734-1746.
[8]LI J,LI X,REN S,et al.miR-200c overexpression is associated with better efficacy of EGFR-TKIs in non-small cell lung cancer patients with EGFR wild-type[J].Oncotarget,2014,5(17):7902-7916.
[9]SHEN J,STASS S A,JIANG F.MicroRNAs as potential biomarkers in human solid tumors[J].Cancer Lett,2013,329(2):125-136.
[10]KUMAR S,NAG A,MANDAL C C.A comprehensive review on miR-200c,a promising cancer biomarker with therapeutic potentia[J].Curr Drug Targets,2015,16(12):1381-1403.
[11]LI J,TAN Q,YAN M,et al.miRNA-200c inhibits invasion and metastasis of human non-small cell lung cancer by directly targeting ubiquitin specific peptidase 25[J].Mol Cancer,2014,13:166.DOI:10.1186/1476-4598-13-166.
[12]TEJERO R,NAVARRO A,CAMPAYO M,et al.miR-141 and miR-200c as markers of overall survival in early stage non-small cell lung cancer adenocarcinoma[J].PLoS One,2014,9(7):e101899.
[13]CORTEZ M A,VALDECANAS D,ZHANG X,et al.Therapeutic delivery of miR-200c enhances radiosensitivity in lung cancer[J].Mol Ther,2014,22(8):1494-1503.
[14]SHI L,ZHANG S,WU H,et al.miR-200c increases the radiosensitivity of non-small-cell lung cancer cell line A549 by targeting VEGF-VEGFR2 pathway[J].PLoS One,2013,8(10):e78344.
[15]LEE J M,DEDHAR S,KALLURI R,et al.The epithelial-mesenchymal transition:new insights in signaling,development,and disease[J].J Cell Biol,2006,172(7):973-981.
[16]MIMEAULT M,BATRA S K.Molecular biomarkers of cancer stem/progenitor cells associated with progression,metastases,and treatment resistance of aggressive cancers[J].Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev,2014,23(2):234-254.
[17]COCHRANE D R,SPOELSTRA N S,HOWE E N,et al.MicroRNA-200c mitigates invasiveness and restores sensitivity to microtubule-targeting chemotherapeutic agents[J].Mol Cancer Ther,2009,8(5):1055-1066.
[18]ZHANG W,FENG M,ZHENG G,et al.Chemoresistance to 5-fluorouracil induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition via up-regulation of Snail in MCF7 human breast cancer cells[J].Biochem Biophys Res Commun,2012,417(2):679-685.
[19]CHUNG J H,RHO J K,XU X,et al.Clinical and molecular evidences of epithelial to mesenchymal transition in acquired resistance to EGFR-TKIs[J].Lung Cancer,2011,73(2):176-182.
[20]SUDA K,TOMIZAWA K,FUJII M,et al.Epithelial to mesenchymal transitionin an epidermal growth factor receptor-mutant lung cancer cell line with acquired resistance to erlotinib[J].J Thorac Oncol,2011,6(7):1152-1161.
[21]KIM H R,KIM W S,CHOI Y J,et al.Epithelial-mesenchymal transition leads to crizotinib resistance in H2228 lung cancer cells with EML4-ALK translocation[J].Mol Oncol,2013,7(6):1093-1102.
[22]KORPAL M,ELL B J,BUFFA F M,et al.Direct targeting of Sec23a by miR-200s influences cancer cell secretome and promotes metastatic colonization[J].Nat Med,2011,17(9):1101-1108.
(本文編輯:崔麗紅)
Effect of Increased H2228 Cells through miR-200c on Sensitivity of Crizotinib,Paclitaxel and Cisplatin
GAO Hai-xiang,CAO Lei.
The First Department of Pulmonology Disease,Hebei General Hospital,Shijiazhuang 050051,China
GAO Hai-xiang,the First Department of Pulmonology Disease,Hebei General Hospital,Shijiazhuang 050051,China;E-mail:gaohaixiang0801@163.com
Background The miR-200c can increase the sensitivity of tumor cells on paclitaxel and cisplatin,and the sensitivity of positive lung carcinoma cells in epidermal growth factor receptor(EGFR) on molecular targeted drug such as erlotinib hydrochloride tablets,gefitinib and afatinib.However,there are no related studies on whether it can increase the sensitivity of echinodermata microtubule-associated protein-like 4(EML4)-anaplastic lymphoma kinase(ALK) fusion gene positive lung adenocarcinoma cells on crizotinib,paclitaxel and cisplatin.Objective To observe whether miR-200c can increase the sensitivity of H2228 cells on crizotinib,paclitaxel and cisplatin,and to explore its mechanism.Methods From February 2014 to May 2015,H2228 cells were cultured and transfected.According to the different transfectants,the cells were divided into enhanced transfection group(transfected with miR-200c mimics),enhanced control group(transfected miR-200c mimics negative control),inhibitory transfection group(transfected with miR-200c inhibitor) and inhibitory control group(transfected with miR-200c inhibitor negative control).The real-time fluorescence quantification PCR method was used to detect the expression level of miR-200c gene in H2228 cells,MTT assay was performed to measure the proliferation level of H2228 cells under antineoplastic drugs〔ketazidine(50,100,200 mmol/L),paclitaxel(6.25,12.50,25.00 mmol/L) and cisplatin(25,50,100 nmol/L)〕 of different concentrations,Transwell assay was used to measure the migration rate of H2228 cells,Real-time PCR method was applied to detect the expression level of E-cadherin,N-cadherin,corrugated protein and CD24mRNA in H2228 cells in transfection group and enhanced control group,Western blotting was used to measure the expression levels of E-cadherin,N-cadherin,corrugated protein and CD24in H2228 cells in enhanced transfection group and enhanced control group.Results The gene expression level of miR-200c in H2228 cells in enhanced transfection group was significantly higher than that in the enhanced control group(P<0.05).The gene expression level of miR-200c in H2228 cells in inhibitory transfection group was significantly lower than that in inhibitory control group(P<0.05).The cell proliferation level of H2228 under the effect of antineoplastic drugs of different concentrations in enhanced transfection group was lower than that in enhanced control group(P<0.05).The proliferation level of H2228 cells under the effect of the effect of antineoplastic drugs of different concentrations in inhibitory transfection group was higher than that in inhibitory control group(P<0.05).The migration rate of H2228 cells in enhanced transfection group was greater than that in enhanced control group(P<0.05).The migration rate of H2228 cells in inhibitory transfection group was greater than that in the inhibitory control group(P<0.05).The expression level of E-cadherin and its mRNA in H2228 cells in enhanced transfection group was higher than that in enhancedcontrol group,and the expression level of N-cadherin,corrugated protein,CD24and their mRNA was lower than that in enhanced control group(P<0.05).Conclusion Through the mesenchymal epithelial transiton in lung carcinoma cells,miR-200c can enhance the sensitivity of H2228 cells on crizotinib,paclitaxel and cisplatin.
Drug resistance,neoplasm;H2228;miR-200c;Crizotinib;Paclitaxel;Cisplatin
河北省2016年度醫(yī)學科學研究重點課題計劃項目(20160065)
050051 河北省石家莊市,河北省人民醫(yī)院呼吸一科(高海祥),呼吸二科(曹磊)
高海祥,050051 河北省石家莊市,河北省人民醫(yī)院呼吸一科;E-mail:gaohaixiang0801@163.com
R 915 R 979.19
A
10.3969/j.issn.1007-9572.2016.36.015
2016-07-05;
2016-10-13)

