1,25-二羥基維生素D3對高氧環境中肺腺癌細胞凋亡的影響及機制
張有辰,金正勇,許東元
(1延邊大學附屬醫院,吉林延吉133000;2延邊大學形態實驗中心)
?
1,25-二羥基維生素D3對高氧環境中肺腺癌細胞凋亡的影響及機制
張有辰1,金正勇1,許東元2
(1延邊大學附屬醫院,吉林延吉133000;2延邊大學形態實驗中心)
目的觀察1,25-二羥基維生素D3[1,25(OH)2VitD3]對高氧環境中人肺腺癌A549細胞凋亡的影響,并探討其機制。方法取對數生長期A549細胞,隨機分為5組。A組于37 ℃、5% CO2飽和濕度培養箱中培養,不處理;B組于高氧環境中培養,不處理;C、D、E組于高氧環境中培養,并分別加入終濃度為0.1、1、10 μmol/L的1,25(OH)2VitD3處理48 h。流式細胞儀檢測凋亡細胞數并計算細胞凋亡指數,Western blot法檢測細胞中的Bcl-2、Bax蛋白。結果A、B、C、D、E組細胞凋亡指數分別為2.45±0.91、40.83±4.96、42.65±4.85、63.43±5.61、76.47±5.94,A組與其他四組比較P均<0.05,B、C組比較P>0.05,D、E組與B、C組比較P均<0.05,D、E組比較P<0.05。與A組比較,B、C、D、E組Bcl-2蛋白表達及Bcl-2/Bax值均下降,而Bax蛋白表達均增高,P均<0.05。B、C組Bcl-2、Bax蛋白表達及Bcl-2/Bax值比較,P均>0.05。與B、C組比較,D、E組Bcl-2蛋白表達及Bcl-2/Bax值下降,而Bax蛋白表達增高,P均<0.05。與D組比較,E組Bcl-2蛋白表達及Bcl-2/Bax值下降(P均<0.05),而Bax蛋白表達變化不明顯(P>0.05)。結論1,25(OH)2VitD3可促進高氧環境中肺腺癌A549細胞凋亡,可能與其調節Bcl-2/Bax平衡有關。
肺腫瘤;A549細胞;1,25-二羥基維生素D3;高氧;細胞增殖;細胞凋亡;Bcl-2蛋白;Bax蛋白
肺癌作為最常見的惡性腫瘤之一,居癌癥死亡首位[1]。氧氣吸入廣泛應用于肺癌的治療,高氧可迅速提高血氧含量,改善或糾正組織缺氧,防止或減輕缺氧性損害的發生、發展。研究表明,高氧可誘導乳腺癌、肺癌、結腸癌等多種腫瘤細胞的凋亡,增強腫瘤細胞對放化療的敏感性[2]。近年研究發現,紫外線照射可促進維生素D合成,減少肺癌的發生率[3]。1,25-二羥基維生素D3[1,25(OH)2VitD3]作為固醇類激素,可從食物及藥物中獲取并被人體吸收利用。研究報道,1,25(OH)2VitD3能抑制肺腺癌細胞增生,調控細胞周期,促進細胞凋亡[4]。但1,25(OH)2VitD3對高氧環境中肺腺癌的細胞凋亡是否有影響,尚需進一步研究。2015年3月~2016年1月,我們觀察了1,25(OH)2VitD3對高氧環境中肺腺癌A549細胞凋亡的影響,并探討其可能的機制,為肺癌的綜合治療提供實驗依據。
1 材料與方法
1.1材料1,25(OH)2VitD3購自美國Sigma公司,A549細胞由延邊大學醫學院形態學實驗中心提供;Annexin V-FITC/PI試劑盒購自美國BD公司,流式細胞儀(BD FACSVerse公司);凋亡調控相關抗體(Bcl-2,Bax)購自Santa Cruz公司,四甲基偶氮唑鹽(MTT)購自GIBCO公司,DMEM/HIGH GLUCOSE培養液購自Thermo scientific公司,胎牛血清購自Thermo Fisher scientific公司,胰蛋白酶-EDTA消化液購自Solarbio公司,SDS-PAGE凝膠制備試劑盒購自Solarbio公司;紫外分光光度計(eppndorf BioPhotometer公司),細胞培養箱(STIK公司),電泳儀(BIO-RAD公司)。
1.2方法
1.2.1細胞培養及分組處理將A549細胞復蘇后,于37 ℃、5% CO2飽和濕度培養箱中進行常規培養。取對數生長期細胞,隨機分為5組,每組設9個平行復孔。A組仍于37 ℃、5%CO2飽和濕度培養箱中用含5%胎牛血清的DMEM培養液常規培養,不處理;B組于高氧培養箱(即向封閉培養箱內通入O2、CO2及N2混合氣30 min,流量5 L/min,當測得氧濃度為80%~85%時封閉培養箱)中培養48 h,培養液同A組,不處理;C、D、E組于高氧培養箱中培養,待細胞融合至40%~50%,分別給予0.1、1、10 μmol/L的1,25(OH)2VitD3處理48 h。
1.2.2細胞凋亡檢測采用流式細胞術。取各組細胞,加入胰蛋白酶-EDTA消化液,PBS洗滌。取100 μL的Binding Buffer懸浮細胞,加入5 μL Annexin V-FITC混勻,后加入5 μL的Propidium Iodide混勻,室溫避光反應15 min,流式細胞儀檢測凋亡細胞數。細胞凋亡指數=凋亡細胞數/總細胞數×100。以上步驟重復10次,取平均值。
1.2.3細胞Bcl-2、Bax蛋白檢測采用Western blot法。取各組細胞,用胰蛋白酶-EDTA消化液消化,用PBS洗滌細胞2次。加入RIPA細胞裂解液和蛋白酶抑制劑,充分攪勻,離心抽提液;提取蛋白樣本以8%聚丙烯酰胺凝膠進行還原性SDS-PAGE電泳,半干式轉膜(PVDF膜),300 mA恒流40 min。封閉液封閉后,PVDF膜過夜;PBS-T緩沖液中充分振蕩清洗,分別滴加Bcl-2、Bax蛋白一、二抗(稀釋比例均為1∶2 000);ECM顯色,X線膠片顯影、定影。將膠片進行掃描或拍照,用ImageJ2軟件處理系統分析目標條帶的灰度值,以此表示目的蛋白的表達量。以上步驟重復10次,取平均值。
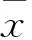
2 結果
2.1各組細胞凋亡指數比較A、B、C、D、E組細胞凋亡指數分別為2.45±0.91、40.83±4.96、42.65±4.85、63.43±5.61、76.47±5.94,A組與其他四組比較P均<0.05,B、C組比較P>0.05,D、E組與B、C組比較P均<0.05,D、E組比較P均<0.05。
2.2各組細胞Bcl-2、Bax蛋白表達比較見表1。

表1 各組細胞Bcl-2、Bax蛋白表達及Bcl-2/Bax值比較
注:與A組比較,*P<0.05;與B組比較,#P<0.05;與C組比較,△P<0.05;與D組比較,▽P<0.05。
3 討論
VitD3可用于低鈣血癥、佝僂病、骨軟化癥及嬰兒手足搐搦癥等多種疾病的治療,其不僅能提高人體對鈣、磷的吸收,還能使血漿鈣、磷水平達到飽和程度[5]。近期研究發現,1,25(OH)2VitD3對乳腺癌、前列腺癌有強效抗癌活性[6],補充高劑量VitD3可減少結直腸癌發病并延緩病情惡化[7],提示VitD3可抑制多種腫瘤的發生、發展,對腫瘤細胞有殺傷作用[8];并且,紫外線照射強的地區與日光照射差的地區對比,癌癥發病率明顯降低[9,10]。研究表明,高氧可抑制A549細胞增殖[11,12],1,25(OH)2VitD3對肺癌細胞的增殖、血管新生具有明顯抑制作用[13,14]。但是,1,25(OH)2VitD3對高氧環境肺癌細胞凋亡的影響尚不清楚。本研究結果表明,B、C、D、E組細胞凋亡指數高于A組細胞,D、E組細胞凋亡指數高于B、C組,E組高于D組,提示高氧可促進A549細胞凋亡,1,25(OH)2VitD3能夠增強高氧引起的A549細胞凋亡,高劑量1,25(OH)2VitD3作用更明顯。
Bax和Bcl-2與大部分細胞凋亡有密切關系,在凋亡的線粒體通路中,Bax和Bcl-2蛋白起著主要作用。Bax為促凋亡因子,Bcl-2為抑制凋亡因子,兩者形成異聚體,改變線粒體膜的滲透性[15]。本研究結果顯示,各組細胞Bax蛋白表達變化不大,但Bcl-2蛋白表達及Bcl-2/Bax值明顯降低,高劑量1, 25(OH)2VitD3作用后變化更明顯。這可能是由于大量的氧氣在細胞內堆積,可產生對細胞有害的活性氧物質,并抑制Bcl-2的形成,增加了線粒體對凋亡因素的敏感性,使細胞凋亡的速度變快[16,17]。胡萍萍等[18]實驗表明,VitD可促使p38磷酸化水平上調。活化的p38 MAPK信號途徑作用于Bcl-2,使Bcl-2/Bax二聚體解聚,促進細胞色素 C釋放,使pro-Caspase3轉換為活性Caspase3,最終導致細胞凋亡。由此我們推測,1,25(OH)2VitD3也可能通過p38途徑使Bcl-2蛋白失活,解除Bcl-2抑制細胞凋亡的作用,最終增強高氧誘導的A549肺癌細胞凋亡。
綜上所述,1,25(OH)2VitD3可促進高氧環境中A549細胞凋亡,其作用機制可能與調節Bcl-2/Bax平衡有關,為今后研究肺癌的防治提供了新的方向。
[1] Park S, Nam BH, Yang HR, et al. Individualized risk prediction model for lung cancer in Korean men[J]. PLoS One, 2013,8(2):e54823.
[2] 韓俊慶.高氧液靜脈輸注在腫瘤放療增敏應用中的研究現狀[J].實用癌癥雜志,2011,26(5):548-550.
[3] 蔣普,蔣迎九.1,25二羥基維生素D3對肺癌的抑制作用[J].檢驗醫學與臨床,2013,10(8):998-1000.
[4] 胡志勇,周逸鵬,黎書煒,等.1,25-二羥基維生素D3增強卡鉑對人肺癌A549細胞的殺傷效果[J].腫瘤防治研究,2013,40(2):125-130.
[5] Trautvetter U, Neef N, Leiterer M,et al. Effect of calcium phosphate and vitamin D3 supplementation on bone remodelling and metabolism of calcium, phosphorus, magnesium and iron[J]. Nutr J, 2014,13(1):1-9.
[6] Swami S, Krishnan AV, Wang JY, et al.Dietary vitamin D3 and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 (calcitriol) exhibit equivalent anticancer activity in mouse xenograft models of breast and prostate cancer[J]. Endocrinology, 2012,153(6):2576-2587.
[7] Muindi JR, Adjei AA, Wu ZR, et al. Serum vitamin D metabolites in colorectal cancer patients receiving cholecalciferol supplementation: correlation with polymorphisms in the vitamin D genes[J]. Horm Cancer, 2013,4(4):242-250.
[8] Marshall DT, Savage SJ, Garrett-Mayer E, et al.Vitamin D3 supplementation at 4000 international units per day for one year results in a decrease of positive cores at repeat biopsy in subjects with low-risk prostate cancer under active surveillance[J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2012,97(7):2315-2324.
[9] Hill NT, Gracia-Maldonado GH, Leonard MK, et al. Role of vitamin D3 in modulation of ΔNp63α expression during UVB induced tumor formation in SKH-1 mice[J].PLoS One, 2014,9(9):e107052.
[10] Cheng TY, Goodman GE, Thornquist MD, et al.Estimated intake of vitamin D and its interaction with vitamin A on lung cancer risk among smokers[J]. Int J Cancer, 2014,135(9): 2135-2145.
[11] 金貞愛,趙以坤,金正勇,等.胰島素樣生長因子-1對高氧誘導的A549細胞凋亡的影響[J].中國當代兒科雜志,2013,15(6):490-493.
[12] 蔡成,常立文,李文斌,等.SiRNA抑制高氧暴露下A549細胞硫氧還蛋白-2表達及其與肺細胞代謝和凋亡的關系[J].臨床兒科雜志,2012,30(4):377-381.
[13] 李彪,王旭,曹洪明,等.維生素D及其在肺癌中的研究進展[J].中國老年學雜志,2015,35(7):1999-2001.
[14] 高衛衛,李培,施毅.維生素D對免疫系統的調節作用[J].中華哮喘雜志,2013,7(4):43-46.
[15] 沈曉詠,呂帆真,武韞,等.bcl-2,bax和p53在小細胞肺癌中的表達及對細胞凋亡的影響[J].四川醫學,2013,34(7):915-917.
[16] 童偉,劉永煜,玉寒冰,等.環氧合酶-2抑制劑對非小細胞肺癌A549細胞Bcl-2和Bax表達的影響[J].解剖科學進展,2015,21(6):639-641.
[17] 姚星宇,石有,賈麗秋,等.馬鈴薯提取物對非小細胞肺癌細胞凋亡、增殖的影響及機制探討[J].山東醫藥,2015,55(42):13-15.
[18] 胡萍萍,房棟,陳淼.1,25-二羥基維生素D3增強多柔比星對胃癌細胞株的殺傷作用[J].腫瘤,2011,31(4):304-309.
Effects of 1,25(OH)2VitD3on hyperoxia-induced apoptosis of lung adenocarcinoma cells
ZHANGYouchen1,JINZhengyong,XUDongyuan
(1AffiliatedHospitalofYanbianUniversity,Yanji133000,China)
Objective To observe the effects of 1, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3[1,25(OH)2VitD3]on the apoptosis of human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells in the high oxygen environment and to explore its mechanism. MethodsA549 cells in the logarithmic phase were randomly divided into five groups: groups A, B, C, D and F. Cells in the group A were cultured at 37 ℃, 5% CO2humidified incubator, and were not processed; cells in the group B were cultured in high-oxygen environment, and were not processed; cells in the groups C, D and E were cultured in high oxygen environment, and then were treated with 0.1, 1 and 10 μmol/L of 1,25 (OH)2VitD3for 48 h. Apoptotic cells were detected by flow cytometry, and the Bcl-2, Bax protein was detected by Western blotting.ResultsThe apoptosis indexes of groups A, B, C, D and E group were 2.45±0.91, 40.83±4.96, 42.65±4.85, 63.43±5.61 and 76.47±5.94, respectively. Significant difference was found between group A and groups B, C, D and E, allP<0.05; no significant difference was found between group B and group C,P>0.05; significant difference was found between groups D, E and groups B, C, allP<0.05; and significant difference was found between group D and group,P<0.05. Compared with group A, the Bcl-2 protein expression and Bcl-2/Bax value were decreased, but the Bax protein expression was increased in the groups B, C, D and E (allP<0.05). No significant difference was found in the Bcl-2, Bax protein expression and Bcl-2/Bax value between group B and group C, allP>0.05. Compared with group B and group C, the Bcl-2 protein expression and Bcl-2/Bax value were decreased, but the Bax protein expression was increased in the groups D and E (allP<0.05). Compared with group D, the Bcl-2 protein expression and Bcl-2/Bax value were decreased (allP<0.05), and the Bax protein expression did not change in the group E (P>0.05).Conclusion1,25(OH)2VitD3may promote the apoptosis of lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells in a high oxygen environment by regulating Bcl-2/Bax balance.
lung neoplasms; A549 cells; 1, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3; hyperoxia; cell proliferation; apoptosis; Bcl-2 protein; Bax protein
國家自然科學基金資助項目(81160083)。
張有辰(1987-),女,博士研究生,主要研究方向為呼吸系統疾病。E-mail: zangyoujin123@163.com
簡介:許東元(1974-),男,副教授,主要研究方向為組織修復與再生。E-mail: dyxu@ybu.edu.com
10.3969/j.issn.1002-266X.2016.22.004
R734.2
A
1002-266X(2016)22-0012-03
2016-01-12)

