風濕性疾病相關性間質性肺病患者的臨床特點分析
唐開獎,宋星慧,蔣 茵,韋陽妙,覃玉花
?
·診治分析·
風濕性疾病相關性間質性肺病患者的臨床特點分析
唐開獎,宋星慧,蔣 茵,韋陽妙,覃玉花
目的分析風濕性疾病相關性間質性肺病(RD-ILD)患者的臨床特點,提高臨床對該病的認識。方法選擇2013年1月—2014年6月在廣西醫科大學第四附屬醫院風濕免疫科確診的風濕性疾病(RD)患者513例,統計其間質性肺病(ILD)發生情況,回顧性分析RD-ILD患者原發病、胸部高分辨率CT檢查結果、肺功能檢查結果及血氣分析結果。結果本組513例RD患者發生ILD 87例(占17.0%)。原發病:系統性硬化34例(占39.0%)、類風濕關節炎21例(占24.1%)、干燥綜合征16例(占18.4%)、系統性紅斑狼瘡8例(占9.2%)、肌炎/皮肌炎5例(占5.7%)、其他3例(占3.4%)。胸部高分辨率CT檢查結果顯示,25例(28.7%)為普通型間質性肺炎(UIP),62例(71.3%)為非UIP,其中類風濕關節炎患者UIP發生率最高,為42.9%。肺功能檢查結果顯示,肺功能正常16例(占18.4%),限制性通氣功能障礙47例(占54.0%),阻塞性通氣功能障礙2例(占2.3%),混合性通氣功能障礙4例(占4.6%),彌散功能障礙60例(占69.0%)。血氣分析結果顯示,正常42例(占48.2%)、低氧血癥27例(占31.3%)、Ⅰ型呼吸衰竭15例(占17.2%)、Ⅱ型呼吸衰竭3例(占3.4%)。結論RD患者ILD發生率較高,其中以系統性硬化、類風濕關節炎及干燥綜合征患者多見,RD-ILD患者肺功能障礙主要表現為彌散功能障礙和限制性通氣功能障礙,常伴有低氧血癥及Ⅰ型呼吸衰竭。
風濕性疾病;肺炎,間質性;臨床特點
唐開獎,宋星慧,蔣茵,等.風濕性疾病相關性間質性肺病患者的臨床特點分析[J].實用心腦肺血管病雜志,2016,24(2):109-111.[www.syxnf.net]
Tang KJ,Song XH,Jiang Y,et al.Clinical characteristics of rheumatic disease-related interstitial lung disease[J].Practical Journal of Cardiac Cerebral Pneumal and Vascular Disease,2016,24(2):109-111.
近年來,隨著高分辨率CT的普及,間質性肺病(interstitial lung disease,ILD) 越來越受到人們的關注。ILD是指急、慢性肺間質病變導致肺泡壁、肺泡腔發生不同程度的炎癥及纖維素性滲出,以彌漫性肺實質、肺泡炎癥和間質纖維化為基本病理改變,以活動性呼吸困難、胸片示彌漫陰影、限制性通氣障礙、彌散功能降低和低氧血癥為臨床表現的不同類疾病群構成的臨床病理實體的總稱。風濕性疾病(rheumatic disease,RD)是一組多系統損害的自身免疫性疾病,臨床表現多樣,是引起ILD的常見原因,但部分RD-ILD患者起病隱匿。為了提高臨床醫師對RD-ILD的診斷水平,本研究回顧性分析了87例RD-ILD患者的臨床資料,并分析該類患者的臨床特點,現報道如下。
1 資料與方法
1.1一般資料選擇2013年1月—2014年6月在廣西醫科大學第四附屬醫院風濕免疫科確診的RD患者513例,均為住院期間經各項檢查明確診斷為RD或既往確診為RD,行胸部高分辨率CT檢查顯示ILD患者87例(占17.0%);并排除可能造成ILD的慢性阻塞性肺疾病(COPD)及系統性血管炎等其他疾病患者。
1.2方法回顧性分析87例RD-ILD患者的臨床資料,并分析患者的原發病、胸部高分辨率CT檢查結果、肺功能檢查結果及血氣分析結果。(1)根據高分辨率CT檢查結果分為普通型間質性肺炎(usual interstitial pneumonia,UIP)和非UIP,其中UIP指病變分布以胸膜下、基底部為主,可見網格狀陰影,蜂窩樣表現明顯,可伴或不伴有牽拉性支氣管擴張[1];非UIP指病變分布以上、中肺野為主,支氣管血管周圍病變明顯,可見明顯的磨玻璃影,較多的小結節影,散在的囊性影,彌漫性馬賽克征/氣體分布不均,可見支氣管肺段或葉實變。(2)肺功能檢測:阻塞性通氣功能障礙表現為肺活量正常或減低,第一秒用力呼氣容積(FEV1)/用力肺活量(FVC)減低,殘氣量增高,肺總量正常或增高,殘總比明顯增高;限制性通氣功能障礙表現為肺活量減低,FEV1/FVC正常或增高,殘氣量減低,肺總量減低,殘總比正常或輕度增高;混合性通氣功能障礙為阻塞性通氣功能障礙和限制性通氣功能障礙二者兼而有之;彌散性功能障礙表現為明顯的通氣/血流比例失調。(3)血氣分析結果,低氧血癥:動脈血氧分壓(PaO2)<80 mm Hg(1 mm Hg=0.133 kPa),但未達到呼吸衰竭標準;Ⅰ型呼吸衰竭:PaO2<60 mm Hg,動脈血二氧化碳分壓(PaCO2)正常或輕度下降;Ⅱ型呼吸衰竭:PaO2<60 mm Hg,伴PaCO2>50 mm Hg。
2 結果
2.1一般資料與原發病分布87例患者中男30例(34.5%),女57例(65.5%);年齡18~76歲,平均年齡(59.4±11.8)歲。原發病:系統性硬化34例(占39.0%)、類風濕關節炎21例(占24.1%)、干燥綜合征16例(占18.4%)、系統性紅斑狼瘡8例(占9.2%)、肌炎/皮肌炎5例(占5.7%)、其他3例(占3.4%)。
2.2胸部高分辨率CT檢查結果胸部高分辨率CT檢查結果顯示,25例(28.7%)為UIP,62例(71.3%)為非UIP,其中類風濕關節炎患者UIP發生率最高,為42.9%,見表1。
表187例RD-ILD患者胸部高分辨率CT檢查結果(例)
Table 1Chest high-resolution CT examination results of the 87 patients with RD-ILD
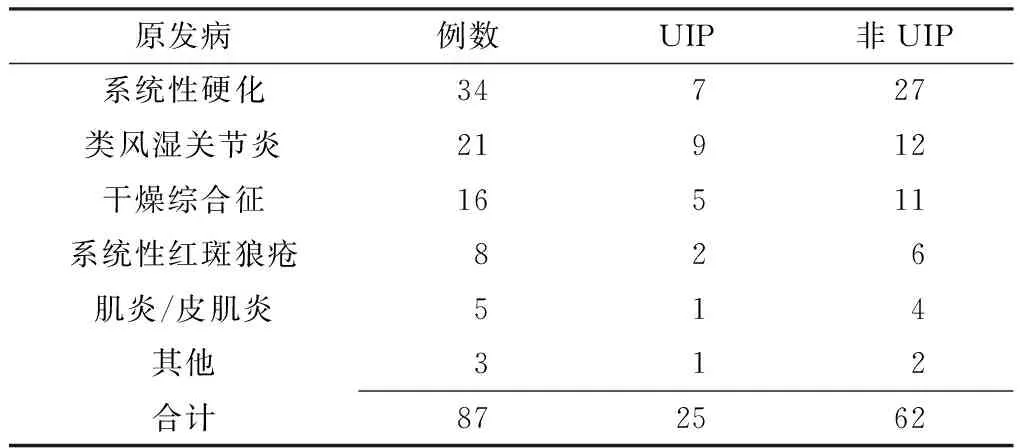
原發病例數UIP非UIP系統性硬化34727類風濕關節炎21912干燥綜合征16511系統性紅斑狼瘡826肌炎/皮肌炎514其他312合計872562
注:UIP=普通型間質性肺炎
2.3肺功能檢查結果肺功能檢查結果顯示,肺功能正常16例(占18.4%),限制性通氣功能障礙47例(占54.0%),阻塞性通氣功能障礙2例(占2.3%),混合性通氣功能障礙4例(占4.6%),彌散功能障礙60例(占69.0%),見表2。
表287例RD-ILD患者肺功能檢查結果(例)
Table 2Pulmonary function examination results of the 87 patients with RD-ILD
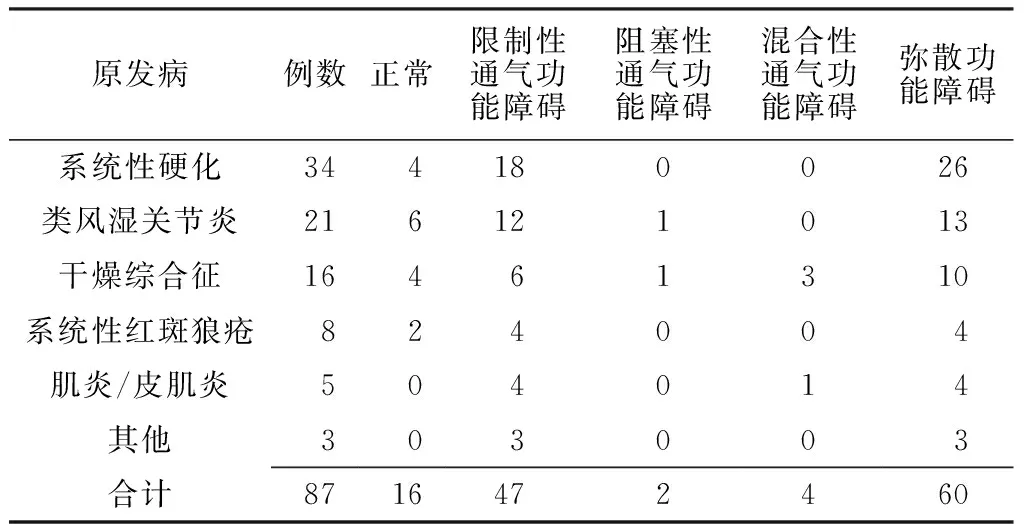
原發病例數正常限制性通氣功能障礙阻塞性通氣功能障礙混合性通氣功能障礙彌散功能障礙系統性硬化344180026類風濕關節炎216121013干燥綜合征16461310系統性紅斑狼瘡824004肌炎/皮肌炎504014其他303003合計8716472460
2.4血氣分析結果血氣分析結果顯示,正常42例(占48.2%)、低氧血癥27例(占31.3%)、Ⅰ型呼吸衰竭15例(占17.2%)、Ⅱ型呼吸衰竭3例(占3.4%),見表3。
表387例RD-ILD患者血氣分析結果(例)
Table 3Blood-gas analysis examination results of the 87 patients with RD-ILD
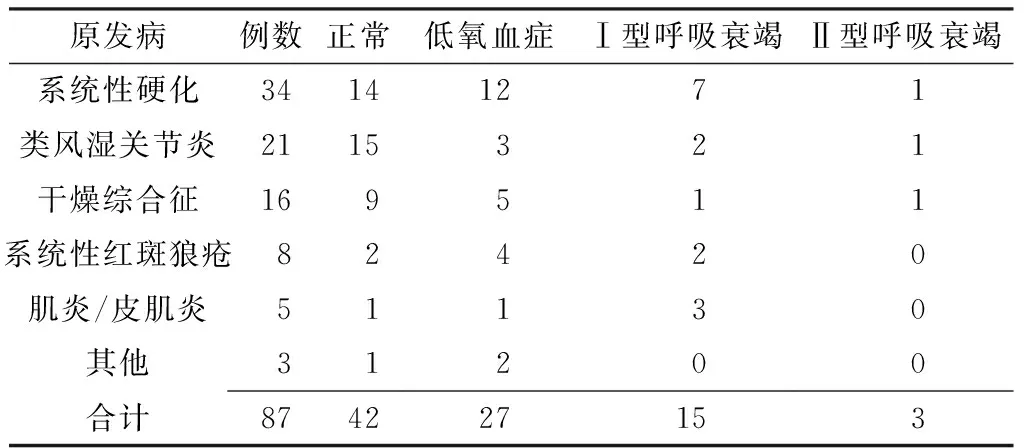
原發病例數正常低氧血癥Ⅰ型呼吸衰竭Ⅱ型呼吸衰竭系統性硬化34141271類風濕關節炎2115321干燥綜合征169511系統性紅斑狼瘡82420肌炎/皮肌炎51130其他31200合計874227153
3 討論
RD是指一類累及多系統的自身免疫性疾病,包括系統性紅斑狼瘡、類風濕關節炎、干燥綜合征、系統性硬化、肌炎/皮肌炎等。肺臟含有豐富的膠原纖維和血管,是RD較易侵犯的臟器。ILD是風濕免疫性疾病所致肺部病變中出現頻率最高的并發癥,其可以是RD的首發癥狀,影響RD的預后,亦可以是引起肺動脈高壓的主要原因之一。本研究結果顯示,本組RD患者ILD發生率為17.0%,且引起ILD的最常見RD為系統性硬化、類風濕關節炎及干燥綜合征,與既往研究結果基本一致[2]。Bouros等[3]研究結果顯示,70%~75%的系統性硬化患者并發ILD;5%~10%的肌炎/皮肌炎患者并發ILD,與張烜等[4]研究結果基本相符。
美國胸科學會/歐洲呼吸學會認為,特發性ILD的疾病分型可用于RD-ILD[5]。ILD的病理分型與疾病發展的自然病程、對激素的反應及疾病預后關系密切[6],其中UIP是唯一可根據臨床表現、胸部高分辨率CT檢查即可診斷的ILD病理分型,其他病理分型須經過肺病理活檢方可診斷[1]。本研究分析了RD-ILD患者的胸部高分辨率CT檢查結果,結果顯示,類風濕關節炎患者UIP發生率最高,其次是系統性硬化和干燥綜合征、肌炎/皮肌炎患者,與國外研究基本一致[7]。有臨床研究顯示,UIP患者較其他病理分型患者預后較差,糖皮質激素治療效果不佳,因此明確RD-ILD病理分型對制定治療方案具有重要意義。
本組87例RD-ILD患者均行肺功能檢查及血氣分析,結果顯示,RD-ILD患者肺功能的主要表現為彌散功能障礙和限制性通氣功能障礙,且彌散功能障礙是反映ILD最靈敏的肺功能指標,與既往研究結果相一致[8-9];本組RD-ILD患者的主要血氣分析表現為低氧血癥和Ⅰ型呼吸衰竭,且阻塞性通氣功能障礙、Ⅱ型呼吸衰竭患者均有長期吸煙史,考慮可能存在吸煙導致的小氣道病變,與Afeltra等[10]研究結果相一致。肺功能檢查及血氣分析診斷RD-ILD雖無特異性,但有助于評價患者病情嚴重程度、對治療的反應及預后判斷。目前,激素及免疫抑制劑仍是治療RD-ILD的重要方法[2,11],但大多數ILD患者不適合長期應用糖皮質激素,且對免疫抑制劑的反應仍不清楚,因此主張根據RD-LID患者的病理分型、RD活動情況及肺動脈高壓[12]制定治療方案,但仍需依靠影像學檢查、肺功能檢查、血氣分析、肺泡灌洗液(BALF)及肺病理活檢等。
綜上所述,RD患者ILD發生率較高,其中以系統性硬化、類風濕關節炎及干燥綜合征患者多見,RD-ILD患者肺功能障礙主要表現為彌散功能障礙和限制性通氣功能障礙,常伴有低氧血癥及Ⅰ型呼吸衰竭。
[1]Travis WD,Costabel U,Hansell DM,et al.An official American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society Statement:Update of the International Multidisciplinary Classification of the Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias[J].Am J Respir Crit Care Med,2013,188(6):733-748.
[2]Strange C,Highland KB.Interstitial lung disease in the patient who has connective tissue disease[J].Clin Chest Med,2004,25(3):549-559.
[3]Bouros D,Wells AU,Nicholson AG,et al.Histopathologic subsets of fibrosing alveolitis in patients with systemic sclerosis and their relationship to outcome[J].Am J Respir Crit Care Med,2002,165(12):1581-1586.
[4]張烜,董怡,張奉春,等.結締組織病中肺動脈高壓臨床特點分析[J].中華風濕病學雜志,1999,3(1):5-7.
[5]Veeraraghavan S,Nicholson AG,Wells AU.Lung fibrosis:new classifications and therapy[J].Curr 0pin Rheumatol,2001,13(6):500-504.
[6]李海云,鄭毅.結締組織病合并間質性肺疾病的研究進展[J].中華風濕病學雜志,2005,9(7):438-441.
[7]Kim EJ,Collard HR,King TE Jr.Rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease:the relevance of histopathologic and radiographic pattern[J].Chest,2009,136(5):1397-1405.
[8]鄭捷,潘萌,丁曉敏,等.應用一氧化碳彌散功能檢測結締組織病患者肺間質病變的意義[J].中華結核和呼吸雜志,2002,25(7):396-398.
[9]宋玉,蘇新明,李振華,等.結締組織病患者肺功能降低相關因素的探討[J].中華風濕病學雜志,2004,8(9):519-521.
[10]Afeltra A,Zennaro D,Garzia P,et al.Prevalence of interstitial lung involvement in patients with connective tissue diseases assessed with high-resolution computed tomography[J].Scand J Rheumatol,2006,35(5):388-394.
[11]Kowal-Bielecka O,Kowal K,Rojewska J,et al.Cyclophosphamide reduces neutrophilic alveolitis in patients with scleroderma lung disease:a retrospective analysis of serial bronchoalveolar lavage investigations[J].Ann Rheum Dis,2005,64(9):1343-1346.
[12]Vassallo R,Thomas CF.Advances in the treatment of rheumatic interstitial lung disease[J].Curr Opin Rheumatol,2004,16(3):186-191.
(本文編輯:謝武英)
Clinical Characteristics of Rheumatic Disease-related Interstitial Lung Disease
TANGKai-jiang,SONGXing-hui,JIANGYin,etal.
DepartmentofRheumatology,theFourthAffiliatedHospitalofGuangxiMedicalUniversity,Liuzhou545005,China
ObjectiveTo analyze the clinical characteristics of rheumatic disease-related interstitial lung disease(RD-ILD),to improve the understanding of clinicians.MethodsFrom January 2013 to June 2014,a total of 513 patients with rheumatic disease was collected in the Department of Rheumatology,the Fourth Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University,the incidence of RD-ILD was recorded,and primary illness,chest high-resolution CT examination results,pulmonary function examination results and blood-gas analysis examination results of patients with RD-ILD were retrospectively analyzed.ResultsOf the 513 cases,a total of 87 cases occurred RD-ILD(accounting for 17.0%).The primary illness included 34 cases with systemic sclerosis(accounting for 39.0%),21 cases with rheumatoid arthritis(accounting for 24.1%),16 cases with sicca syndrome(accounting for 18.4%),8 cases with systemic lupus erythematosus(accounting for 9.2%),5 cases with myositis or dermatomyositis(accounting for 5.7%),3 cases with other illness(accounting for 3.4%).Chest high-resolution CT examination results showed that,25 cases were usual interstitial pneumonia(accounting for 28.7%),other 62 cases were unusual interstitial pneumonia(accounting for 71.3%),and of the 25 cases with usual interstitial pneumonia,9 cases were rheumatoid arthritis(accounting for 42.9%).Pulmonary function examination results showed that,16 cases were normal(accounting for 18.4%),47 cases occurred restrictive ventilatory dysfunction(accounting for 54.0%),2 cases occurred obstructive ventilatory dysfunction(accounting for 2.3%),4 cases occurred mixed ventilatory dysfunction(accounting for 4.6%),60 cases occurred diffusion dysfunction(accounting for 69.0%).Blood-gas analysis examination results showed that,42 cases were normal(accounting for 48.2%),27 cases occurred hyoxemia(accounting for 31.3%),15 cases occurred type Ⅰ respiratory failure(accounting for 17.2%),3 cases occurred type Ⅱ respiratory failure(3.4%).ConclusionThe incidence of RD-ILD is relatively high in patients with rheumatic disease,the major primary illness includes systemic sclerosis,rheumatoid arthritis and sicca syndrome,the major pulmonary dysfunction includes diffusion dysfunction and restrictive ventilatory dysfunction,and the major complications includes hyoxemia and type Ⅰ respiratory failure.
Rheumatism diseases;Pneumonia,interstitial;Clinical characteristics
545005廣西柳州市,廣西醫科大學第四附屬醫院風濕免疫科
宋星慧,545005廣西柳州市,廣西醫科大學第四附屬醫院風濕免疫科;E-mail:huihui3012@qq.com
R 593.21 R 563.13
B
10.3969/j.issn.1008-5971.2016.02.033
2015-09-26;
2016-01-25)

