Twist蛋白在結直腸癌中的表達水平及其促進癌癥發展的機制研究
王琳
(河南省鄭州人民醫院放療科,河南鄭州450000)
?
Twist蛋白在結直腸癌中的表達水平及其促進癌癥發展的機制研究
王琳
(河南省鄭州人民醫院放療科,河南鄭州450000)
摘要:目的研究Twist蛋白在結直腸癌中的表達水平,其對結直腸癌細胞的增殖以及侵襲能力的影響,并探討其促進癌癥發展具體的機制。方法經結腸鏡活檢取20例患者組織和20例正常人的標本,采用實時定量PCR的方法檢測了Twist的mRNA表達水平。采用脂質轉染法對結直腸癌細胞系CT-26細胞進行RNA干擾,采用CCK-8法及transwell法觀察干擾Twist后對結直腸癌細胞的增殖以及侵襲能力的影響;采用RT-PCR以及Western blot檢測了CT-26細胞中MMP-9的mRNA及蛋白水平。結果Twist在結直腸癌組織中的mRNA水平顯著高于對應癌旁組織以及對照組(P<0.05);在伴有淋巴結轉移的癌組織中Twist mRNA的表達水平顯著高于無淋巴結轉移的組織(P<0.05);與轉染對照組比較,Twist siRNA轉染的CT-26細胞增殖水平及遷徙能力均顯著降低(P<0.05);干擾Twist的CT-26細胞能夠顯著降低金屬蛋白酶MMP-9 mRNA及蛋白的水平。結論Twist蛋白能夠增加結直腸癌癌細胞的增殖及遷徙能力,其影響機制可能與金屬蛋白酶MMP-9有關。
關鍵詞:Twist蛋白;結直腸癌;MMP-9;增殖;侵襲;機制
結直腸癌(colorectal cancer,CRC)是常見的消化道惡性腫瘤,目前,我國結直腸癌的發病率居第3位,其病死率居第4位,且該病的患者群逐漸趨向年輕化[1]。因此,深入探討結直腸癌發病及轉移的分子機制,尋找新的治療靶點,對治療結直腸癌具有重要的意義。Twist蛋白是堿性螺旋-環-螺旋家族的轉錄因子之一,已有大量的研究表明,其在促進上皮-間質轉變,參與實體腫瘤的遠處器官轉移及癌旁結節形成中發揮重要的作用[2-5]。國外學者Valdés-Mor等發現,Twist過度表達與男性原發性大腸癌的淋巴結浸潤密切相關[6],然而至今,結直腸癌癌患者中Twist的表達水平以及其對結直腸癌癌細胞的增殖及遷移影響的研究尚無報道。因此,本研究旨在探討Twist在結直腸癌組織中的表達情況,并從體外通過低表達結直腸癌細胞系中的Twist水平來探討其影響結直腸癌遷移的分子機制。
1 資料與方法
1.1臨床資料
所有結直腸癌組織來源于2013年8月-2014 年1月來鄭州人民醫院就醫患者的手術切除標本。癌變組共20例,其中,男性11例,女性9例;年齡57~73歲,平均(62.2±6.6)歲。所有組織標本經術后病理學證實為結直腸癌,分別取結直腸癌及對應腫瘤邊緣2~6 cm處癌旁組織進實驗分析。對照組取同期醫院檢查的正常20例人群結直腸黏膜組織,其中,男性12例,女性8例,年齡60~72歲,平均(63.52±7.53)歲。
1.2結直腸癌組織以及血漿標本總RNA提取及逆轉錄反應(PT-PCR)
取結直腸癌及對應癌旁組織約100 mg組織后,加入1 ml的Trizol(美國Invitrogen公司)充分勻漿,將抽提的總RNA溶于30μl DEPC水溶液。提取的總RNA經紫外分光光度計進行定量分析,并采用Femantes逆轉錄試劑盒進行逆轉錄,cDNA產物-20℃冰箱保存備用。熒光定量PCR試劑盒購自美國Roche公司,本實驗使用美國ABI公司的7300型號Real-Time PCR儀器進行擴增,PCR反應條件:95℃變性20 s,然后60℃20 s和70℃1 s進行40個循環,使用2-ΔΔCt法進行相對定量分析結果。RT-PCR序列:基質金屬蛋白酶-9(matrix metalloprotein 9,MMP-9):正向引物:CGCAGACATCGTCATCCAGT,反向引物:GGATTGGCCTTGGAAGATGA;Twist:正向引物:CACGCAGTCGCTGAACGA,反向引物:GACCTGGTACAGGAAGTCGATGT;GAPDH:正向引物:AACTGGGACGACATGGAGAA,反向引物:ATACCCCTCGTAGATGGGCA。
1.3細胞轉染
小鼠大腸癌細胞CT-26細胞采用完全DMEM培養液培養,待匯合度達到50%~60%左右。采用脂質體Lipofectamine?2000(美國Invitrogen公司)對小鼠大腸癌細胞CT-26細胞中Twist進行小RNA干擾,Twist的siRNA靶向序列為5'-GGUACAUCGACUUCCUGUATT;對照序列為5'-UCAUAAGUG AUGCUGGAGCTT[7]。待干擾48 h后,采用RT-PCR技術驗證轉染效率。
1.4細胞遷移實驗
取對數生長期的結腸癌細胞并調整細胞密度至2×105~3×105個/ml,按0.1 ml/孔加入到transwell小室的上層,小室下層加入l ml的10%血清的培養液。培養24 h時間后,對已遷移至小室下層的細胞進行計數(×200倍)。
1.5CCK-8試劑檢測細胞增殖
按CCK-8試劑(上海前塵生物科技有限公司)說明書進行分析。分別收集未處理組和轉染組的24 h,48 h和72 h后的CT-26細胞,加入終濃度為10%的CCK-8試劑,于37℃培養箱中繼續孵育3 h,然后測定450 nm的光密度(optical density,OD)值。
1.6免疫印跡法(Western blot)檢測蛋白水平
細胞收取后,加入1×SDS細胞裂解液,進行SDS-PAGE電泳,110 V電壓轉膜100 min,37℃封閉后,加兔抗人的MMP-9(美國Biolegend公司)4℃孵育過夜后,HRP標記的小鼠抗兔二抗(南京生興生物公司)(1∶1 000稀釋)37℃孵育50 min,內參蛋白選用美國Sigma公司的抗人β-actin(1∶5 000稀釋),孵育后用PBS-T洗膜3次,進行免疫印跡化學發光(ECL)檢測。
1.7統計學方法
所有數據采用SPSS 19.0統計軟件進行分析。計量資料以均數±標準差(±s)表示,均通過正態性檢驗。兩組間比較采用兩獨立樣本t檢驗,多組間比較為單因素方差分析+兩兩多重比較(LSD-t檢驗)。多時點資料的比較則為單因素重復測量方差分析。P<0.05為差異有統計學意義。
2 結果
2.1結直腸癌組織及對應癌旁中Twist mRNA表達水平
3組的Twist mRNA表達水平,整體比較差異有統計學意義(F=128.590,P=0.000)。與正常組織比較,結直腸癌癌旁組織中Twist mRNA水平顯著增高,差異有統計學意義(t =4.547,P=0.000);與癌旁組織比較,結直腸癌組織中Twist mRNA的表達水平顯著增高,差異有統計學意義(t =11.045,P = 0.000),見表1。
表1 結直腸癌及對應癌旁組織中Twist mRNA表達水平(n=20,±s)
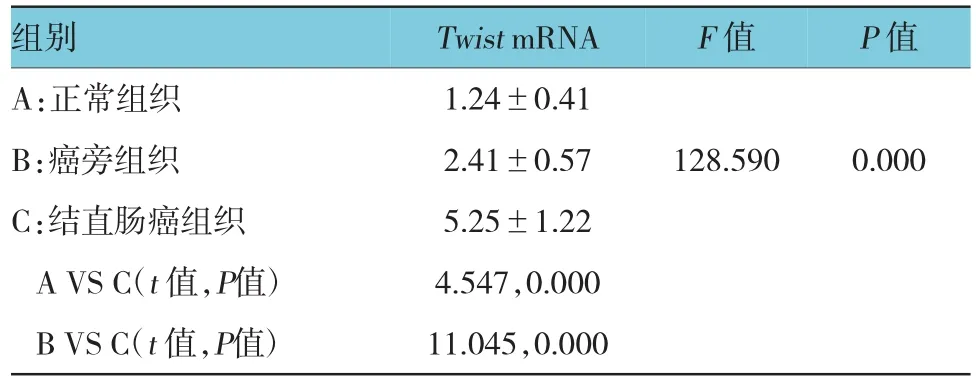
表1 結直腸癌及對應癌旁組織中Twist mRNA表達水平(n=20,±s)
組別 TwistmRNA F值 P值A:正常組織 1.24±0.41 B:癌旁組織 2.41±0.57 128.590 0.000 C:結直腸癌組織 5.25±1.22 A VS C(t值,P值) 4.547,0.000 B VS C(t值,P值) 11.045,0.000
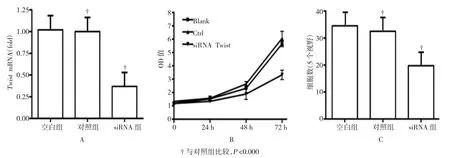
圖1 低表達Twist對結直腸癌細胞增殖及侵襲的影響
表2 低表達Twist對結直腸癌細胞增殖及侵襲的影響(n=6,±s)

表2 低表達Twist對結直腸癌細胞增殖及侵襲的影響(n=6,±s)
注:整體比較為單因素方差分析,兩兩比較為LSD檢驗
組別 TwistmRNA OD450 nm 細胞數0 h 24 h 48 h 72 h A:空白組 1.03±0.18 1.12±0.06 1.41±0.11 2.27±0.16 5.92±0.18 34.0±2.6 B:對照組 0.98±0.19 1.14±0.06 1.52±0.17 2.52±0.51 6.18±0.61 32.6±4.6 C:siRNA組 0.35±0.06 1.09±0.05 1.20±0.16 1.83±0.40 3.25±0.41 18.9±1.8 F值P值35.556 0.000 1.213 0.325 7.136 0.007 4.848 0.024 82.439 0.000 35.556 0.000 A VS B(LSD-t值,P值) 0.588,0.565 0.474,0.642 1.269,0.224 1.148,0.269 1.013,0.327 0.588,0.565 A VS C(LSD-t值,P值) 7.579,0.000 1.048,0.311 2.448,0.027 1.932,0.072 10.579,0.000 7.579,0.000 B VS C(LSD-t值,P值) 6.991,0.000 1.522,0.149 3.716,0.002 3.081,0.008 11.592,0.000 6.991,0.000
2.2Twist mRNA表達與淋巴結轉移及Duckes分期的關系
所有患者中,無淋巴結轉移8例(Dukes A/B期),而具有淋巴結轉移12例(Dukes C/D期)。Twist mRNA的表達水平在Dukes C/D期組織中的表達水平為(3.01±0.51),顯著高于Dukes A/B期的(1.29±0.31),差異具有統計學意義(t =8.505,P= 0.000)。
2.3siRNA干擾Twist對CT-26細胞的增殖及侵襲功能的影響
經CT-26細胞轉染后,3組Twist siRNA水平,24 h后450 nm的OD值及5視野的細胞計數整體比較差異均有統計學意義(P<0.05)。CT-26細胞轉染Twist siRNA后,Twist mRNA水平與對照組比較顯著降低(P<0.05),見圖1A;CCK-8法結果顯示,與對照組比較,CT-26細胞干擾Twist基因72 h后的增殖能力顯著降低(P <0.05),見圖1B;進一步實驗結果顯示,CT-26細胞轉染Twist siRNA后,transwell小室下層細胞數量與對照組比較顯著減少(P< 0.05),見圖1C。此外,對轉染Twist siRNA后的CT26細胞的CCK-8法檢測結果,進行多時間點重復測量分析發現,各時間點間差異有統計學意義(P<0.05),見表2。
2.4CT-26細胞干擾Twist對MMP-9的mRNA和蛋白表達影響
3組的MMP-9 mRNA表達水平,整體比較差異有統計學意義(F=39.381,P=0.000)。與對照組比較,干擾Twist的CT-26細胞能顯著降低MMP-9 mRNA的水平,差異有統計學意義(t =7.365,P = 0.000),見表3,圖2A;并能顯著降低MMP-9蛋白的水平,見圖2B。
表3 低表達Twist對CT-26細胞遷徙基因MMP-9 mRNA及蛋白水平影響(n=6,±s)
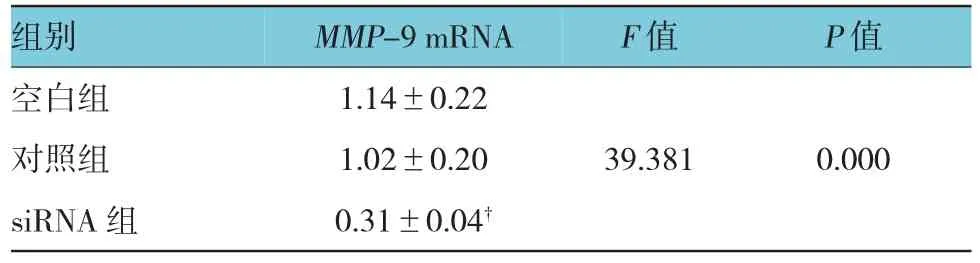
表3 低表達Twist對CT-26細胞遷徙基因MMP-9 mRNA及蛋白水平影響(n=6,±s)
注:整體比較為單因素方差分析,兩兩比較為LSD檢驗;?與對照組比較,t=7.365,P=0.000
組別 MMP-9 mRNA F值 P值空白組 1.14±0.22對照組 1.02±0.20 39.381 0.000 siRNA組 0.31±0.04?
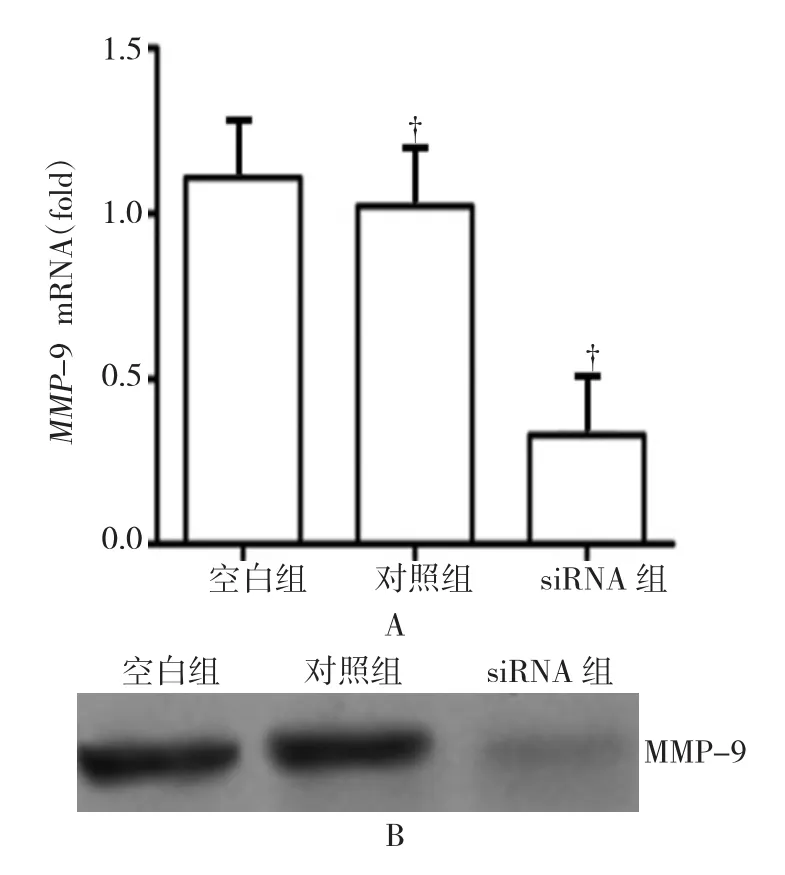
圖2 低表達Twist對CT-26細胞遷徙基因MMP-9 mRNA及蛋白水平影響
3 討論
結直腸癌是消化道最常見的惡性腫瘤之一,且近年來,全世界結直腸癌的發病率和死亡率呈現逐年上升的趨勢[8]。因此,研究結直腸癌發病的細胞學及分子學機制對其預防和治療有著極大的臨床意義。Twist是一種最早在果蠅的受精卵中被發現的基因,由于果蠅胚胎Twist基因缺失后的發育呈一種“扭曲”的現象,表現為原腸胚形成受阻、中胚層發育障礙而導致胚胎發育的末期死亡,從而將該基因命名為“Twist”[9]。近年來,越來越多的研究認為Twist基因參與上皮-間質轉變過程中的調控,其在卵巢癌、胰腺癌等腫瘤細胞發生及其侵襲和轉移中均發揮十分重要的功能[10-12]。然而目前,Twist在結直腸癌中的表達水平以及其對結直腸癌細胞的增殖以及侵襲能力的影響機制尚不完全明了。
本研究發現,Twist在結直腸癌癌組織以及癌旁組織中mRNA水平顯著高于正常黏膜組織,且癌組織中表達更高;此外,Twist在伴有淋巴結轉移的癌組織中其表達水平高于無淋巴結轉移的癌組織,說明Twist具有潛在的促進結腸癌的發病以及對結腸癌的轉移有著一定的促進功能。這與Sasaki等人研究的在人食管鱗狀細胞癌中Twist高表達,并參與癌癥轉移結果一致[5]。為了進一步觀察Twist對結直腸癌癌細胞的增殖及遷移能力的影響,筆者通過siRNA干擾技術對結直腸癌癌細胞系CT-26細胞系低表達Twist。結果發現,結直腸癌癌細胞Twist低表達后,癌細胞的增殖及侵襲能力也相應降低,提示了Twist對結腸癌的細胞增殖以及轉移具有重要的促進作用。惡性腫瘤發生浸潤轉移重要的步驟之一是腫瘤細胞對基質的降解,而MMP-9已被證實參與多種腫瘤的浸潤轉移[13-15]。為了進一步探討Twist影響結直腸癌癌細胞遷移的機制,筆者檢測了siRNA干擾Twist水平后的MMP-9的表達,結果發現Twist低表達后能夠顯著抑制MMP-9的表達水平,從而提示Twist可能通過促進MMP-9的表達來增加癌細胞遷移能力,這與Li等在人腹膜間皮細胞中高表達Twist后可以增加細胞的遷移能力的結果一致[16]。
綜上所述,Twist可能通過促進MMP-9的表達增加癌癥的遷移,其在結直腸癌的發生、發展中發揮著及其重要的作用。臨床中Twist的檢測對結腸癌的診斷及預后可能具有一定的指導意義。
參考文獻:
[1]趙亮,丁彥青.結直腸癌轉移機制研究進展[J].浙江大學學報:醫學版, 2014, 43(4): 486-493.
[2] Qin Q, Xu Y, He T, et al. Normal and disease-related biological functions of Twist1 and underlying molecular mechanisms[J]. CellRes, 2012, 22(1): 90-106.
[3] Yang MH, Chen CL, Chau GY, et al. Comprehensive analysis of the independent effect of twist and snail in promoting metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Hepatology, 2009, 50(5): 1464-1474.
[4] Zhang Z, Xie D, Li X, et al. Significance of TWIST expression and its association with E-cadherin in bladder cancer[J]. Hum Pathol, 2007, 38(4): 598-606.
[5] Sasaki K, Natsugoe S, Ishigami S, et al. Significance of Twist expression and its association with E-cadherin in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2009, 28: 158.
[6] Valdés-Mora F, G仵mez del Pulgar T, Bandrés E, et al. TWIST1 overexpression is associated with nodal invasion and male sex in primary colorectal cancer[J]. Annals of Surgical Oncology, 2009, 16(1): 78-87.
[7] Yu W, Kamara H, Svoboda KK. The role of twist during palate development[J]. Dev Dyn, 2008, 237(10): 2716-2725.
[8] Brenner H, Kloor M, Pox CP. Colorectal cancer[J]. Lancet, 2014, 383(9927): 1490-1502.
[9] Simpson P. Maternal-Zygotic gene interactions during formation of the dorsoventral pattern in drosophila embryos[J]. Genetics, 1983, 105(3): 615-632.
[10] Roesch A. TWIST and switch' metastasis [J]. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res, 2014, 27(2): 157-158.
[11] Wang T, Li Y, Tuerhanjiang A, et al. Correlation of Twist upregulation and senescence bypass during the progression and metastasis of cervical cancer[J]. Front Med, 2014, 8(1): 106-112.
[12] Nuti SV, Mor G, Li P, et al. TWIST and ovarian cancer stem cells: implications for chemoresistance and metastasis[J]. Oncotarget, 2014, 5(17): 7260-7271.
[13] Xu C, Hu DM, Zhu Q. eEF1A2 promotes cell migration, invasion and metastasis in pancreatic cancer by upregulating MMP-9 expression through Akt activation[J]. Clin Exp Metastasis, 2013, 30(7): 933-944.
[14] Li X, Yang Z, Song W, et al. Overexpression of Bmi-1 contributes to the invasion and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by increasing the expression of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)2, MMP-9 and vascular endothelial growth factor via the PTEN/PI3K/Akt pathway[J]. Int J Oncol, 2013, 43: 793-802.
[15] Hsin CH, Wu BC, Chuang CY, et al. Selaginella tamariscina extract suppresses TPA-induced invasion and metastasis through inhibition of MMP-9 in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma HONE-1 cells [J]. BMC Complement Altern Med, 2013, 13: 234.
[16] Li C, Ren Y, Jia X, et al. Twist overexpression promoted epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of human peritoneal mesothelial cells under high glucose[J]. Nephrol Dial Transplant, 2012, 27: 4119-4124.
(張蕾編輯)
論著
Expression of Twist protein in colorectal cancer and mechanism of its cancer promoting effect
Lin Wang
(Department of Radiotherapy, Zhengzhou People's Hospital, Zhengzhou, Henan 450000, China)
Abstract:Objective To explore the expression of Twist protein in colorectal cancer and its impact on the proliferation and invasion of colorectal cancer cells, and to clarify the mechanism of its cancer promoting effect. Methods Twenty tissue specimens were selected from colorectal cancer patients and normal people through colonoscopy biopsy, respectively, then the expression of Twist mRNA was detected through real time quantitative PCR method. The colorectal cancer cell line CT-26 cell was RNA interfered by lipid transfection method, and was observed the impact of Twist after interference on the proliferation and invasion of colorectal cancer cells by CCK-8 method and transwell method, and the expression of mRNA and protein of MMP-9 in CT-26 cell were detected by RT-PCR and Western blot method. Results The expression of Twist mRNA in colorectal cancer tissues was significantly higher than in para-carcinoma tissues the control group (P< 0.05). The expression of Twist mRNA in colorectal cancer tissues with lymph node metastasis was significantly higher than in colorectal cancer tissues without lymph node metastasis (P< 0.05). Compared with transfection control group, the proliferation and migration ability of CT-26 cells transfected by Twist siRNA were significantly decreased (P < 0.05). CT-26 cells interfering Twist reduced the expression of mRNA and protein of metal protease MMP-9. Conclusions Twist protein strengthens the proliferation and migration ability of colorectal cancer cells, and the mechanism may relate with metal protease MMP-9.
Keywords:twist protein; colorectal cancer; MMP-9; proliferation; invasion; mechanism
收稿日期:2015-11-06
文章編號:1005-8982(2016)08-0028-05
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1005-8982.2016.08.006
中圖分類號:R735.3
文獻標識碼:A

