霍爾推力器加速通道-空心陰極耦合區物理研究進展
孟天航,寧中喜,于達仁
(哈爾濱工業大學,能源科學與工程學院,150001哈爾濱)
?
霍爾推力器加速通道-空心陰極耦合區物理研究進展
孟天航,寧中喜,于達仁
(哈爾濱工業大學,能源科學與工程學院,150001哈爾濱)
摘要:重點介紹霍爾推力器耦合區物理過程的研究現狀.霍爾推力器的耦合區連接陰極與通道內等離子體,控制通道入口電子參數,也通過耦合環境影響陰極自身的電子發射特性.由于耦合區處于推力器外部的負梯度弱磁場區,導致耦合區發生的物理過程十分復雜.分別從種子電子向通道內傳導、羽流中和過程、等離子體橋電子的E×B漂移和耦合環境中的陰極放電等方面討論了耦合區的參數分布和影響因素,總結了耦合區的特點,指出了目前研究的難點與不足,并對后續研究給出了建議.
關鍵詞:霍爾推力器;空心陰極;耦合; E×B放電;電子傳導
霍爾推力器由陶瓷加速通道和外部的空心陰極兩部分構成,二者是一直以來研究的重點.加速通道與陰極之間還存在一個區域,負責二者的電荷與能量交換,稱為耦合區.近年來發現,該區域內物理過程也會影響整體性能.特別是陰極安裝位置和角度,對推力器性能有較顯著的影響.已見報的測試結果中,推力增量最大達到25 mN(6 kW推力器),效率增加5%,比沖增量70 s[1].物理層面上,該區域內的電子傳導路徑、壓降形成機理、振蕩模式等與霍爾推力器尚未解決的異常電子傳導、陰極異常腐蝕等問題有著密切的聯系,相關機制需要深入研究.
耦合區早期的研究主要是為了優化陰極安裝位置,許多單位做了大量的枚舉法試驗[1-12],希望得到一個普適性結論.但研究結果表明,不同的推力器最優安裝位置及角度并不相同.例如,有的推力器最優位置在外磁極邊緣,最優安裝角為平行于推力器軸線[2];有的則在盡可能遠處,45°角安裝[1];還有的在中間位置[13].此外,還發現了陰極位置和推力偏心[14]、陰極腐蝕[15]和推力器電磁波譜[16-20]等存在復雜關系.從這些非單調的趨勢可以看出,陰極的安裝位置并不是簡單的遠近或內置外置的問題,而是與陰極當地的磁場、離子束流如何匹配的問題[21-26].安裝位置的優化方法,還是應該回歸耦合區E×B放電物理過程的研究.然而,由于以往推力器和陰極在設計時很少關注二者交界區的問題,導致目前耦合區物理盲點較多,許多現象還無法解釋.
本文介紹耦合區的研究現狀,回顧和分析取得的重要研究結論,總結遇到的主要問題,并對需要繼續關注的問題給出建議.
1 霍爾推力器耦合區物理過程分析

圖1 等離子體橋亮線
從幾何上劃分,耦合區一般是指陰極出口和通道出口之間的等離子體區域.該區域中,陰極發射出的電子束在磁場作用下彎曲,形成從陰極出口連接至內磁極端面上的一條亮線(圖1) ;同時,在E× B場中進行漂移,形成一個扇面結構(圖2).該發光扇面是通常所稱的等離子體橋,它是電子傳導至通道內和羽流下游的主要通道.

圖2 等離子體橋扇面
與等離子體橋相關的電子軌跡十分復雜,現實的做法是統計電子的分布和波動特性.該區域可歸納出:電子向通道內傳導,羽流中和過程,等離子體橋電子的E×B漂移以及耦合環境中的陰極放電等4個過程.首先介紹等離子體參數分布,包括電子密度和電子溫度的分布,之后簡述相關影響因素的研究結果.
1.1種子電子向通道內傳導
1.1.1參數分布
Khartov[27]等發現,電子在陰極出口處密度最高,等效電子溫度最低,在靠近通道出口或向羽流下游遷移過程中等效電子溫度會逐漸升高.電子能量分布(EEDF)從麥氏分布逐漸變為非麥分布,快電子組分逐漸增加,如圖3所示.
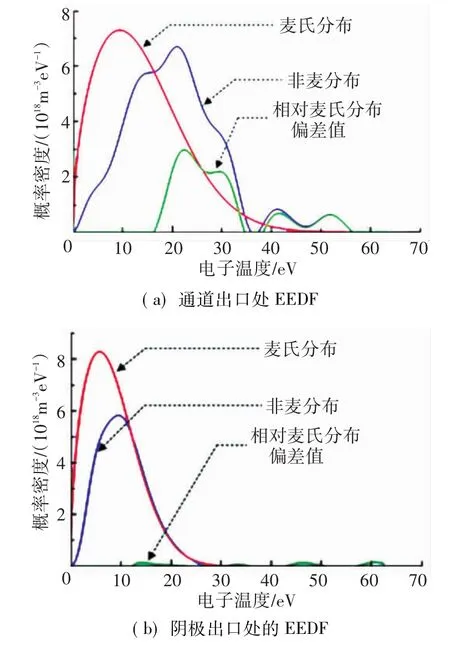
圖3 不同位置處的電子溫度分布函數[27]
1.1.2影響因素分析
種子電子的傳導過程受振蕩、壁面碰撞和陰極位置影響較大.Smith等[28]對近場區電子軌跡進行了蒙特卡洛模擬,結果(表1)表明,外磁極壁面處碰撞、磁場不對稱性和庫倫碰撞會增強種子電子向通道內傳導.耦合區內可測得的螺旋振蕩也有相似的作用,從該模擬可以看出,電子的擴散系數在螺旋振蕩算例中有所增加,但其機理還不明確.有觀點認為[29-30],是螺旋振蕩所產生的周向電場漂移Eφ×B增強了種子電子的傳導.此外,還發現種子電子電流值對陰極位置、角度和發射的電子電流擴散角十分敏感.這些參數微小的調節會引起種子電子電流值劇烈的變化.
Raitses等[31]發現,種子電子和中和電子的傳導過程還與真空背壓有關.過去一直認為真空背壓主要提供粒子反流.而Raitses認為,背壓還影響種子電子傳導的阻抗.背壓升高,碰撞頻率增高,傳導阻抗減小,有利于減小耦合電壓,提高電壓利用率.在其實驗中還發現,背壓超過某一臨界,耦合區內的螺旋振蕩會消失.
此外,Alberede等[32]還觀察到通道出口空間電勢、電子密度跟隨羽流離子密度波動而波動的現象.Alberede認為,當離子密度出現波動時,相應的陰極與出口間電勢分布會改變,使陰極發射的電子具有不同的作用:離子密度谷值來臨時,相應的會有一部分電子作為種子電子向陽極傳導;但離子密度峰值來臨時,陰極發射的電子主要用于中和這部分離子.

表1 種子電子電流影響因素數值模擬結果[28]
1.2羽流中和過程
1.2.1參數分布
Alberede的研究[32]引出了一個暗含的問題:種子電子和中和電子是否有交界? Morozov等[33]曾提出“中和機制轉換區域”的概念:該區域中離子由被閉環漂移的電子中和轉換成被陰極發射的電子中和.但當時并未找到直接的實驗證據.
如果假設閉環漂移電子向陽極遷移,而中和電子向羽流遷移,則該轉換區域將會是電子電流的分流區域.可以通過分析電子分流過程,來近似表征中和機制的轉換過程.
近年有一些實驗現象似乎是分流過程的痕跡.首先,Bugrova等[34]與Bacal等[35]的研究表明,通道內與通道外電子凈通量方向相反.從電荷守恒角度,需要存在一個電子注入區;從速度場連續性角度,需要存在一個零凈通量區.陰極出口區電子的流線分布[36]見圖4.

圖4 耦合放電近陰極區825 nm光強分布[36]
耦合區內阻抗(與陰極負)軸向分布[37]見圖5.由4、5可以看出,陰極羽流確實發生了分流過程.特別是通道與近場區模擬出的電子流線分布[38](圖6)顯示,存在電子通量散度大于零的區域.
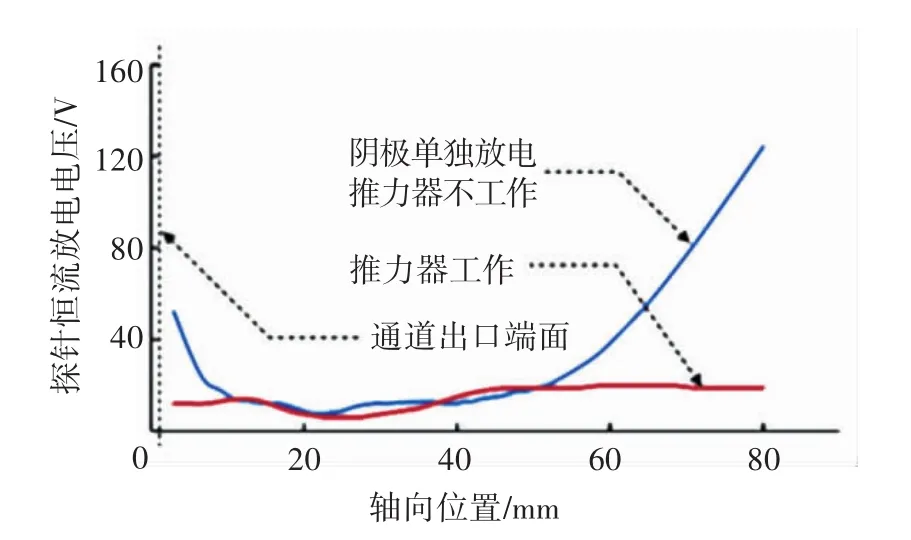
圖5 等離子體橋軸向阻抗分布[37]
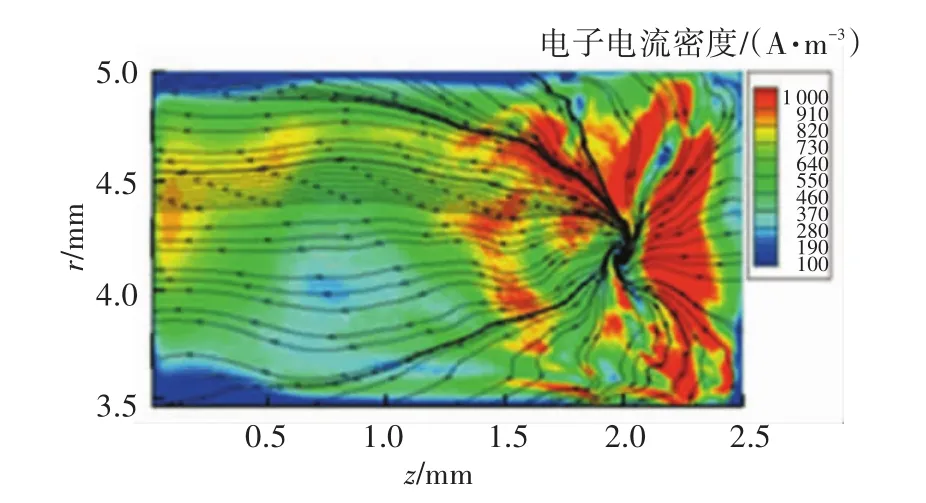
圖6 通道與近場區電子通量分布[38]
中和過程一直延伸至遠場區.Sekerak等[39]所測量的參數分布中,空間電勢從出口向外逐漸下降,電子溫度逐漸降低;電子數密度顯示,羽流會逐漸向中軸線聚攏.此外,羽流中電子具有較強的定向性,宏觀速度與離子束流方向基本一致.Bacal[35]認為,陰極中和離子束流過程中會從后者獲得能量.
1.2.2影響因素分析
實驗測量到近場區存在多種振蕩.這些振蕩會影響電導特性,從而影響中和過程.例如,1.1.2節已經敘述的電位和電子密度跟隨離子浪涌呈周期性變化.除了這種由于低頻振蕩引起的軸向離子浪涌以外,Knoll等[40]還測量到周向1~10 MHz的螺旋振蕩、周向80~100 MHz的螺旋振蕩、軸向1~5 MHz離子振蕩(圖7),甚至是2.2~2.4 GHz的振蕩(圖8)、遠場區周向16~28 kHz的螺旋振蕩[39,41].伴隨這些振蕩,Dannenmayer等[42]測量到EEDF,特別是高能尾部的組分會周期性增減.高能尾部周期性增減對加速通道內的深層次影響還不清楚.

圖7 近場區離子電流振蕩頻率與α角的關系[40]

圖8 近場區離子電流振蕩頻譜[40]
WU和Walker等[13]發現,陰極位置對中和過程影響也很大.實驗中,測量到推力器羽流電位高于殼體兩翼磁感線包絡區的電位.Walker認為,中和電子需要跨越兩翼的磁感線去中和離子束流,其路徑看似與推力器內部無關,但沿程碰撞引起的振蕩最終會被耦合進電源中,從而影響推力器性能.因此,陰極在外磁路中的位置會影響中和電子的路徑,從而影響放電穩定性.
1.3等離子體橋電子的E×B漂移
1.3.1參數分布
與霍爾推力器等漂移假設不符,耦合區表現出比較明顯的周向不均勻性.Khartov等[27]的實驗中,電子溫度在周向上不均勻,在陰極通道圓周上的對頂點處電子溫度比陰極出口高.Smith[30]的模擬中,電子密度在等離子體橋E×B漂移下游1/4π~1/2π范圍內較高(圖9).與之對應的是該圓周角范圍內較低的離子通量[43](圖10),以及朝向陰極的離子速度分量[14].目前,尚不清楚這種周向不對稱性會對霍爾推力器放電過程產生哪些深層次的影響.

圖9 通道出口(r,φ)平面電子密度的分布[30]

圖10 (0,π)圓周角內羽流離子通量分布[43]
1.3.2影響因素分析
E×B漂移過程與很多參數有關.首先,耦合區的周向不對稱性與陰極流量有關,流量較大時,偏陰極一側離子通量較大[36](圖11).其次,通道出口處電子密度的周向對稱性受放電電壓影響較大,通道出口處的單探針測量表明,電壓升高,近陰極區電子溫度升高,且周向更不均勻[27].此外,周向對稱性與勵磁電流的正反有關,推力器勵磁電流反向前后,可以肉眼觀察到等離子體橋扇面也反向做E×B漂移,與此同時通道束流也一定程度上發生了偏斜[37](圖12).最后需要指出,周向不均勻性不單指等離子體橋漂移扇面引起的不對稱,還包括由于振蕩引起的密度與電位的周向塊區(圖13).實驗中這些振蕩的色散關系比較雜亂,已知的驅動因素有電離[44]、磁場梯度[45],甚至是電子混合過程[33],且仍在不斷挖掘.

圖11 耦合區陰極所在(r,z)平面內525 nm光強分布[36]

圖12 磁場反向前后羽流離子電流徑向分布[37]
1.4耦合環境中的陰極放電
實驗表明陰極放電特性受耦合環境(如磁場、電場和背壓等)影響較大.已有研究結果包括:磁場降低了三極管放電的電壓(圖14),改變了內腔放電氣壓[25](圖15),將陰極電勢降內的電位振蕩幅值減小了一個數量級[23],并降低了陰極羽流內離子的速度[46](圖16).這些現象充分體現了有磁場的陰極放電特性與三極管放電的差異性.陰極外部供氣后推力器推力增大[10](圖17),又說明近陰極區物理過程的干預會對下游產生影響.因此,在研究耦合區內物理過程時,掌握耦合場中陰極電子源的特性是必要的.

圖13 推力器通道內電位周向分布模擬結果[38]

圖14 軸向磁場強度對陰極放電電壓的影響[25]
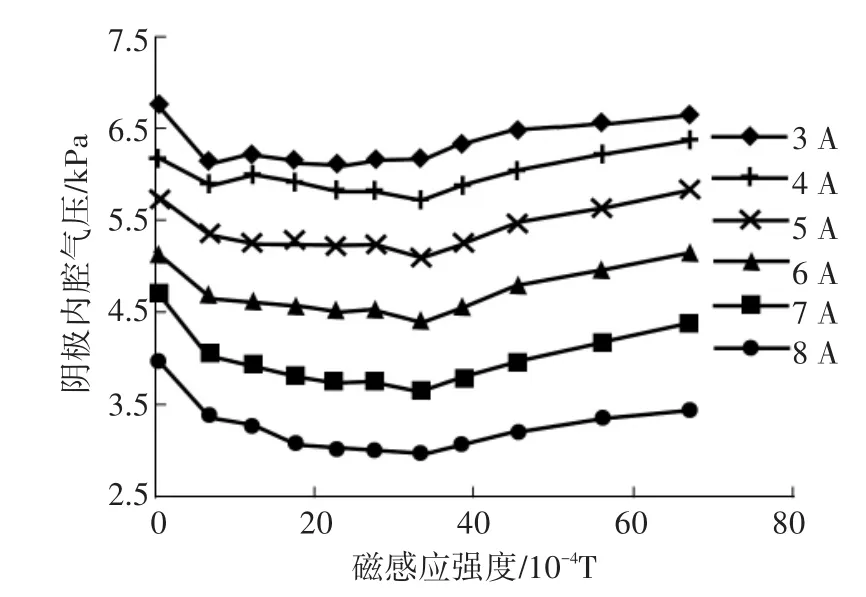
圖15 軸向磁場強度對陰極內腔氣壓的影響[25]

圖16 磁場對陰極出口區離子速度分布的影響[46]
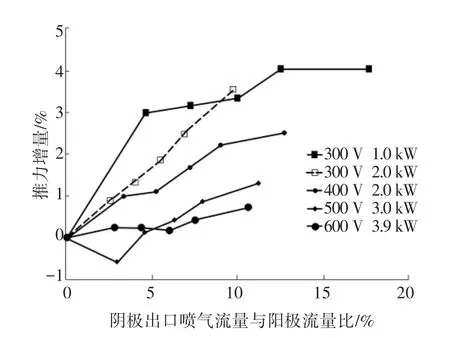
圖17 陰極出口噴冷氣對推力器推力的影響[10]
2 耦合區參數分布特點總結
本文介紹了霍爾推力器-陰極耦合區的研究現狀,總結了耦合區參數分布特點和已發現的影響因素.耦合區有如下幾個特點:
1)軸不對稱性.把三維物理過程視為軸對稱是霍爾推力器的一個基礎性假設.耦合區可能是唯一一個不滿足該假設的區域.
2)近壁面過程的貢獻較小.與加速通道和陰極不同,耦合區幾乎是一個開放的空間,缺乏壁面約束,因此相對于等離子體-壁面相互作用,一些不穩定性的影響更加突出[47].
3)動力學特征.電子從陰極發射之后,經歷了由麥氏分布、各向同性向非麥分布、各向異性過渡的過程,導致使用普通的流體或是粒子方法描述耦合區都有可能失準,正如噴氣推進實驗室在近陰極區遇到的困難一樣[48-50].
3 展望
3.1物理層面
耦合區的研究已經進入到了電子傳導層面,但耦合區的特殊性導致該區域很難直接套用加速通道內部或空心陰極內部的成熟結論.又由于以往不太重視這種交界區的問題,導致許多現象還缺乏合理的解釋.針對已發現的現象,但不僅限于這些現象,建議在物理層面上,未來研究應關注如下問題:
1)陰極電子源在耦合環境中的特性.陰極處于電子傳導的源頭,它下游物理過程的描述需要陰極特性作為鋪墊.以往陰極設計不考慮這些問題,相關機理認識還很有限.
2)耦合區內振蕩的成因及影響.以往研究振蕩問題多集中在加速通道內部,對出口以外的振蕩問題,例如近陰極區振蕩[51]、微波輻射[30,33]、對整體動力學的影響[32,,46]等問題,還沒有深入討論過.
3)周向不對稱性的影響.漂移扇面的周向不對稱性可能引發的連鎖反應,例如對加速通道內部對稱性的影響以及對振蕩的貢獻[52]等,還未評估過.
4)適應耦合區的研究手段.包含非接觸式診斷方法、瞬態測量方法以及適合耦合區特點的模型和算法.
3.2工程層面
在實際工程應用層面上,建議留意如下問題:
1)大型推力器的耦合區優化.大推力器加速通道和陰極的關鍵尺寸、工作特性和主導效應與中小推力器存在較大差異[53-54],可能需要單獨研究大型推力器的耦合問題.
2)壽命后期耦合問題.壽命后期加速通道與陰極工作特性的漂移,可能在后期伴生出新的物理效應[55-56],相關的認識有助于進一步了解壽命演化過程.
3)微波輻射問題.了解耦合區微波輻射的發射特性,有助于減小霍爾推力器對航天器整體的通訊干擾.
參考文獻
[1]MCDONALD M S,GALLIMORE A D.Cathode position and orientation effects on cathode coupling in a 6-kW hall thruster[C/OL].[2015-11-23].http: / /erps.spacegrant.org/uploads/images/images/iepc_articledownload_1988-2007/2009index/IEPC-2009-113.pdf.
[2]TILLEY D L,de GRYS K H,MYERS R M.Hall thrustercathode coupling[C]/ / Proceedings of 35th Joint Propulsion Conference&Exhibit.Reston: AIAA,1999: 1-10.
[3]CARPENTER C.Comparison of on-orbit and ground based hollow cathode operation[C]/ / Proceedings of38th Joint Propulsion Conference&Exhibit.Reston: AIAA,2002: 1-11.
[4]BEAL B E,GALLIMORE A D.Effects of cathode configuration on hall thruster cluster plume properties[J].Journal of Propulsion and Power,2007,23(4) : 836-844.DOI: 10.2514/1.24636.
[5]SOMMERVILLE J D,KING L B.Effect of cathode position on hall-effect thruster performance and cathode coupling voltage[C]/ / Proceedings of 43rd Joint Propulsion Conference&Exhibit.Reston: AIAA,2007: 1-11.
[6]SOMMERVILLE J D,KING L B.Effect of cathode position on hall-effect thruster performance and near-fieldplume properties[C]/ / 44th Joint Propulsion Conference&Exhibit.Reston: AIAA,2008: 1-20.
[7]SOMMERVILLE J D,KING L B.Hall-effect thrustercathode coupling part I: efficiency improvements from an extended outer pole[C]/ / 45th Joint Propulsion Conference&Exhibit.Reston: AIAA,2009: 1-14.
[8]SOMMERVILLE J D,KING L B.Hall-effect thruster-cathode coupling,part II: ion beam and near-field plume [J]/ /Journal of Propulsion and Power,2011,27(4) : 754-767.
[9]ALBAREDE L,LAGO V,LASGORCEIX P,et al.Correlation between hollow cathode operating conditions and hall thruster (SPT100-ML) performances[C]/ / Proceedings of 38th Propulsion Conference&Exhibit.Reston: AIAA,2002: 1-12.
[10]KAMHAWI H,HUANG W,HAAG T.Investigation of the effects of cathode flow fraction and position on the performance and operation of the high voltage hall accelerator[C]/ / Proceedings of 50th Joint Propulsion Conference.Reston: AIAA,2014: 1-13.
[11]張巖,康小錄.空心陰極對霍爾推力器性能的影響研究[C]/ /第八屆中國電推進技術學術研討會論文集.北京:中國宇航學會,2012: 198-203.
[12]MIYASAKA T,ASATO K,FURUTA D,et al.Characteristics of side by side operation of hall thruster[C/OL].[2015-11-23].http: / /erps.spacegrant.org/uploads/images/ 2015Presentations/IEPC-2015-70_ISTS-2015-b-70.pdf.
[13]WALKER J A,FRIEMAN J D,WALKER M,et al.Hall effect thruster electrical interaction with a conductive vacuum chamber[C]/ / Proceedings of 50th Joint Propulsion Conference.Reston: AIAA,2014: DOI: 10.2514/6.2014-3817.
[14]BOURGEOIS G,MAZOUFFRE S,SADEGHI N.Unexpected transverse velocity component of Xe+ ions near the exit plane of a hall thruster[J].Physics of Plasmas,2010,17(113502) : 1-7.DOI: 10.1063/1.3507308.
[15]KIM V,ARKHIPOV A,BISHAEV A,et al.Investigation of the “back”and“radial”ion flows in the vicinity of the stationary plasma thruster exit plane[C/OL].[2015-11-23].http: / /erps.spacegrant.org/uploads/images/ 2015Presentations/IEPC-2015-247_ISTS-2015-b-247.pdf.
[16]LOYAN A,TITOV M,RYBALOV O,et al.Middle power hall effect thrusters with centrally located cathode[C/OL].[2015-11-23].http: / /erps.spacegrant.org/uploads/ images/images/iepc _ articledownload _ 1988-2007/ 2013index/oi1pcpmn.pdf
[17]JAMESON K K.Investigations on hollow cathode effects on total thruster efficiency of a 6-kW hall thruster[D].Los Angeles: University of California Los Angeles,2009.
[18]JAMESON K K,GOEBEL D M,HOFER R,et al.Cathode coupling in hall thrusters[C/OL].(2007-09-05)[2015-11-23].http: / /erps.spacegrant.org/uploads/ images/images/iepc _ articledownload _ 1988-2007/ 2007index/ IEPC-2007-278.pdf.
[19]GOEBEL D M,JAMESON KK,HOFER R.Hall thruster cathode flow impact on coupling voltage and cathode life [J].Journal of Propulsion and Power,2012,28 (2) : 355-363.DOI: 10.2514/1.B34275.
[20]BEITING E J,COX W A,DIAMANT K D,et al.Busek BHT-1500 external vs.center cathode EMC study[C/OL].[2015-11-23].http: / /erps.spacegrant.org/uploads/ images/ 015Presentations/ EPC-2015-124_ISTS-2015-b-124.pdf.
[21]SOMMERVILLE J D.Hall-effect thruster-cathode coupling: the effect of cathode position and magnetic field topology [D].Hughton: Michigan Technical University,2009.
[22]孟天航,寧中喜,于達仁.電推進空心陰極實驗的磁場環境等效[C]/ /中國第十屆電推進學術研討會論文集.上海:中國宇航學會,2014: 1-4.
[23]FARNELL C,WILLIAMS J D,FARNELL C.Comparison of hollow cathode discharge plasma configurations[C/OL].[2015-11-23].http: / /erps.spacegrant.org/uploads/ images/images/iepc _ articledownload _ 1988-2007/2009 index/IEPC-2009-016.pdf.
[24]GOEBEL D M,JAMESON KK,KATZ I,et al.Potential fluctuations and energetic ion production in hollow cathode discharges[J].Physics of Plasmas,2007,14(103508) : 1-16.DOI: 10.1063/1.2784460.
[25]MENG Tianhang,NING Zhongxi,YU Daren.Influence of background magnetic field on hollow cathode discharge characteristics[C/OL].[2015-11-23].http: / /erps.spacegrant.org/uploads/images/2015Presentations/IEPC-2015-77_ISTS-2015-b-77.pdf.
[26]GEORGIN M,DUROT C,GALLIMORE A D.Preliminary measurements of time resolved ion velocity distributions near a hollow cathode[C/OL].[2015-11-23].http: / / erps.spacegrant.org/uploads/images/2015 Presentations/ IEPC-2015-106_ISTS-2015-b-106.pdf.
[27]KHARTOV S,NAZARENKO I P,PERESLAVTSEV A A.Plasma parameters investigation in the near cathode zone of the SPT discharge[C/OL].(2007-09-05)[2015-11-23].http: / /erps.spacegrant.org/uploads/ images/images/ iepc_ articledownload_1988-2007/2007index/IEPC-2007-006.pdf.
[28]SMITH A W,CAPPELLI M A.On the role of fluctuations,cathode placement,and collisions on the transport of electrons in the near-field of hall thrusters[J].Physics of Plasmas,2010,17(093501) : 1-11.DOI: 10.1063/1.3479827.
[29]MCDONALD M S,BELLANT C K,St.PIERRE B A,et al.Measurement of cross-field electron current in a hall thruster due to rotating spoke instabilities[C]/ / Proceedings of 47th Joint Propulsion Conference&Exhibit.Reston: AIAA,2011: 1-22.
[30]ELLISON C L,RAITSES Y,FISCH N J.Cross-field electron transport induced by a rotating spoke in a cylindrical hall thruster[J].Physics of Plasmas,2012,19(013503) : 1-8.DOI: 10.1063/1.3671920.
[31]RAITSES Y,KAGANOVICH I,SMOLYAKOV A.Effects of the gas pressure on low frequency oscillations in E×B discharges.[C/OL].[2015-11-23].http: / /erps.spacegrant.org/uploads/images/2015Presentations/IEPC-2015-307_ISTS-2015-b-307.pdf.
[32]ALBARèDE L,VIAL V,LAZURENKO A,et al.Hollow cathode stationary and dynamic behavior: in diode regime and with a hall thruster[C].Proceedings of the 4th International Spacecraft Propulsion Conference.Sardinia: ESA,2004: 1-11.
[33]MOROZOV A I,SAVELYEV V V.Fundamentals of stationary plasma thruster theory[J].Reviews of Plasma Physics,2000,21: 203-382.DOI: 10.1007/978-1-4615-4309-1.
[34]BUGROVA A I,MOROZOV A I,KHARCHEVNIKOV V K.Experimental Investigation of near wall conductivity [J].Soviet Journal of Plasma Physics,1990,16(12) : 849-856.
[35]BACAL M,PERESLAVTSEV AA,TANGUY M,et al.Electron density and energy distribution function in the plume of a hall-type thruster[J].Review of Scientific Instruments,2002,73(2) : 931-933.DOI: 10.1063/1.1431404.
[36]ALBARèDE L,LAGO V,LASGORCEIX P,et al.Interaction of a hollow cathode stream with a hall thruster [C/OL].[2015-11-23].http: / /erps.spacegrant.org/ uploads/images/images/ iepc _ articledownload _ 1988-2007/2003index/0333-0303iepc-full.pdf.
[37]孟天航.空心陰極-霍爾推力器耦合特性研究[D].哈爾濱:哈爾濱工業大學,2014.
[38]TACCOGNA F,MINELLI P.Assessment of fluctuationinduced and wall-induced anomalous electron transport in HET[C/OL].[2015-11-23].http: / /erps.spacegrant.org/uploads/images/2015Presentations/IEPC-2015-418_ ISTS-2015-b-418.pdf.
[39]SEKERAK M,MCDONALD M,HOFER R,et al.Hall thruster plume measurements from high-speed dual Langmuir probes with ion saturation reference[C]/ / IEEE Aerospace Conference.Piscataway: IEEE,2013:1-16.
[40]KNOLL A,THOMAS C,GASCON N,et al.Experimental investigation of high frequency plasma oscillations within hall thrusters[C]/ / Proceedings of 42nd Joint Propulsion Conference&Exhibit.Reston: AIAA,2006: 1-7.
[41]SMITH A W,CAPPELLI M A.Time and space-correlated plasma potential measurements in the near field of a coaxial hall plasma discharge[J].Physics of Plasmas,2009,16 (073504) : 1-12.DOI: 10.1063/1.3155097.
[42]DANNENMAYER K,MAZOUFFRE S,KUDRNA P,et al.The time-varying electron energy distribution function in the plume of a hall thruster[J].Plasma Sources Science and Technology,2014,23 (065001) : 1-9.DOI: 10.1088/0963-0252/23/6/065001.
[43]XU K G,WALKER M.Effect of external cathodeazimuthal position on hall-effect thruster plume and diagnostics[J].Journal of Propulsion and Power,2014,30(2) : 506-513.DOI: 10.2514/1.B34980.
[44]JANES G W,LOWDER R S.Anomalous electron diffusion and ion acceleration in a low-density plasma[J].The Physics of Fluids,1966,9(6) : 1115-1123.DOI: 10.1063/1.1761810.
[45]LITVAK A A,FISCH N J.Rayleigh instability in hall thrusters[J].Physics of Plasmas,2004,11(4) : 1379-1383.DOI: 10.1063/1.1647565.
[46]GEORGIN M,DUROT C,GALLIMORE A D.Preliminary measurements of time resolved ion velocity distributions near a hollow cathode[C/OL].[2015-11-23].http: / / erps.spacegrant.org/uploads/images/2015 Presentations/ IEPC-2015-106_ISTS-2015-b-106.pdf.
[47]HUISMANN T D.Improving hall thruster plume simulation through refined characterization of near-field plasma properties[D].Ann Arbor: University of Michigan,2011.
[48]CHOI M,BOYD I D.Numerical simulation of the cathode plume of a hall thruster[C]/ / Proceedings of 50th Joint Propulsion Conference.Reston: AIAA,2014: 1-15.
[49]CHOI M,BOYD I D.Numerical simulation of keeper erosion in a 6-kW laboratory hall thruster[C/OL].[2015-11-23].http: / /erps.spacegrant.org/uploads/images/ 2015Presentations/IEPC-2015-16_ISTS-2015-b-16.pdf.
[50]ORTEGAA L,MIKELLIDES I G.The importance of the cathode plume and its interactions with the ion beam in numerical simulations of hall thrusters[C/OL].[2015-11-23].http: / /erps.spacegrant.org/uploads/images/2015 Presentations/IEPC-2015-310_ISTS-2015-b-310.pdf.
[51]MATLOCK T S,DODSON C A,GOEBEL D M,et al.Measurements of transport due to low frequency oscillations in a rotating hollow cathode plasma[C/OL].[2015-11-23].http: / /erps.spacegrant.org/uploads/images/ 2015 Presentations/ IEPC-2015-137_ISTS-2015-b-137.pdf.
[52]LAZURENKO A,VIAL V,PRIOUL M,et al.Experimental investigation of high-frequency drifting perturbations in hall thrusters[J].Physics of Plasmas,2005,12(013501) : 1-10.DOI: 10.1063/1.1818698.
[53]DALE E T,GALLIMOREA D.High-speed image analysis and filtered imaging of nested hall thruster oscillations[C/OL].[2015-11-23].http: / /erps.spacegrant.org/uploads/images/ 2015Presentations/IEPC-2015-285_ISTS-2015-b-285.pdf.
[54]JORNS B A,MIKELLIDES I G,GOEBEL D M.Investigation of energetic ions in a 100-a hollow cathode [C]/ / Proceedings of 50th Joint Propulsion Conference.Reston: AIAA,2014.DOI: 10.2514/6.2014-3826.
[55]JACK T M,PATTERSON S W.The effect of the keeper electrode on hollow cathode characteristics[C]/ / Proceedings of 36th Joint Propulsion Conference&Exhibit.Reston: AIAA,2000: 1-13.
[56]BRUKHTI V I,KIRDYASHEV K P.Evolution of rf instability in a steady-state plasma accelerator[J].Technical Physics Letters,1997,23 (5) : 391.DOI: 10.1134/1.1261691.
(編輯楊波)
Research status of physics in the coupling area between hall thruster acceleration channel and hollow cathode
MENG Tianhang,NING Zhongxi,YU Daren
(Harbin Institute of Technology,School of Energy Science and Engineering,150001 Harbin,China)
Abstract:This article introduced the research status of the physics of coupling zone in Hall thrusters.The coupling zone is the area that links hollow cathode and Hall thruster channel.It determines the electron parameters on the inlet of the channel and the discharge characteristics of the hollow cathode.With negative-gradient weak magnetic field in this area,the local physics are highly complicated.The article chose four different facets to discuss the parameter distribution and influencing factors of this area: the transport of seed electrons towards the anode,the process of ion beam neutralization,the E×B drift of plasma bridge electrons and the hollow cathode discharge in coupling environment.By summarizing the characteristics of this area,the difficulties and shortcomings of current studies were analyzed and suggestions for further studies were given.
Keywords:hall thruster; hollow cathode; coupling; E×B discharge; electron transport
通信作者:于達仁,yudaren@ hit.edu.cn.
作者簡介:孟天航(1989—),男,博士研究生;于達仁(1966—),男,長江學者特聘教授.
基金項目:國家自然科學基金(61571166).
收稿日期:2015-11-23.
doi:10.11918/j.issn.0367-6234.2016.01.002
中圖分類號:O539,V439
文獻標志碼:A
文章編號:0367-6234(2016) 01-0013-08

