丙戊酸鈉與順鉑聯合應用對人骨肉瘤細胞株U-2 OS增殖、凋亡的影響及其作用機制
閆抗,夏斯龍,王業華
(1徐州醫學院研究生學院,江蘇徐州 221000;2徐州醫學院附屬醫院)
?
丙戊酸鈉與順鉑聯合應用對人骨肉瘤細胞株U-2 OS增殖、凋亡的影響及其作用機制
閆抗1,夏斯龍1,王業華2
(1徐州醫學院研究生學院,江蘇徐州 221000;2徐州醫學院附屬醫院)
摘要:目的觀察丙戊酸鈉(VPA)與順鉑(DDP)聯合應用對人骨肉瘤細胞株U-2 OS增殖、凋亡的影響,并探討其可能機制。方法 培養U-2 OS細胞,分為A、B、C、D組,A組加入35 mmol/L VPA+20 mg/L DDP,B組加入35 mmol/L VPA,C組加入20 mg/L DDP,D組未加任何藥物。CCK-8法檢測細胞增殖,流式細胞儀檢測細胞周期及凋亡,RT-PCR法檢測細胞凋亡相關基因(Caspase-3、Fas)。結果與D組比較,A、B、C組細胞存活率降低,G0/G1期細胞增加,凋亡率及Fas、Caspase-3相對表達量升高;與C組比較,A組細胞存活率降低,G0/G1期細胞增加,凋亡率及Fas、Caspase-3相對表達量升高;P均<0.05。結論 VPA聯合DDP可抑制U-2 OS細胞增殖,促進其凋亡,且較單用VPA或DDP作用更為明顯;其機制可能與Fas、Caspase-3表達上調有關。
關鍵詞:骨肉瘤;丙戊酸鈉;順鉑
骨肉瘤是青少年常見的惡性骨腫瘤,在小兒骨惡性腫瘤中最多見[1]。順鉑(DDP)是臨床常用的化療藥物,但由于耐藥性及不良反應等因素限制其療效的進一步發揮。丙戊酸鈉(VPA)屬于短鏈脂肪酸家族,是臨床廣泛應用的廣譜抗癲癇藥,屬于組蛋白去乙酰化酶抑制劑(HDACi)[2],具有抑制組蛋白去乙酰化活性的作用。研究[3]表明,VPA在體內外均可通過誘導細胞周期停滯,以促進細胞凋亡和分化,進而抑制多種腫瘤細胞的生長和增殖,其潛在的抗腫瘤作用越來越受到關注。2014年6月~2015年6月,我們觀察了VPA與DDP聯合應用對人骨肉瘤細胞U-2 OS增殖、凋亡的影響,并探討其可能機制,旨在為骨肉瘤的治療藥物選擇提供新的思路。
1材料與方法
1.1細胞株和試劑細胞株:人骨肉瘤細胞株U-2 OS(上海中科學院細胞庫),用含有10%胎牛血清的1640培養液在37 ℃、5%CO2條件下培養。主要試劑:VPA,DDP,胎牛血清,改良型1640培養基,細胞周期檢測試劑盒,Annexin V-FITC/PI細胞凋亡檢測試劑盒,TRIzol試劑盒,Fas,Caspase-3,內參β-actin。
1.2VPA藥物濃度篩選及U-2OS細胞分組、干預 ①VPA藥物濃度篩選實驗:分別用5、10、20、40 mmol/L共4個濃度分別處理細胞24、48 h,計算24 h的藥物半數抑制濃度IC50[4],并以此濃度作為下述聯合用藥實驗中VPA濃度。②VPA、DDP聯合用藥實驗:設A、B、C、D組,其中VPA濃度為VPA藥物半數抑制濃度IC50,即35 mmol/L,DDP濃度為20 mg/L。
1.3U-2 OS細胞增殖檢測取對數生長期U-2 OS細胞,常規消化,計數,調整細胞密度按5 000/孔,接種于96孔培養板,待細胞生長約70%后加藥。A組加入35 mmol/L VPA+20 mg/L DDP,B組加入35 mmol/L VPA,C組加入20 mg/L DDP,A、B、C組為實驗組;D組未加任何藥物(對照組)。每個濃度設5個平行復孔,處理結束后加入CCK-8,輕搖,37 ℃孵育2 h,采用酶聯免疫檢測儀測定培養24、48 h每孔在450 nm波長處的吸光度(OD)。取5孔OD值的平均值,計算各組細胞的存活率,細胞存活率(%)=(A實驗組/A對照組)×100%。
1.4U-2 OS細胞周期、凋亡檢測取對數生長期U-2 OS細胞常規消化后計數,調整細胞密度按3×105/孔,接種于6孔培養板,待細胞生長約70%后加藥。各組藥物干預同上,藥物作用細胞24 h后用不含EDTA的胰酶消化收集,用PBS洗滌細胞2次。①細胞周期測定:PBS洗滌后,調整細胞濃度為1×106/mL,取1 mL單細胞懸液,離心,去除上清,在細胞中加入體積分數為70%冷乙醇500 μL固定,4 ℃保存,過夜后用PBS洗去固定液;加入100 μL RNase A,37 ℃水浴30 min,再加入400 μL的PI染色混勻,4 ℃避光30 min,上機檢測記錄激發波長488 nm處紅色熒光,記錄G0/G1期細胞數。②細胞凋亡率測定:PBS洗滌后,加入500 μL的Binding Buffer懸浮細胞,加入5 μL的Annexin V-FITC混勻,后加入5 μL的Propidium Iodide,混勻;室溫、避光、反應5~15 min;流式細胞儀檢測細胞凋亡率。
1.5U-2 OS細胞形態學觀察倒置相差顯微鏡觀察各組細胞經藥物處理24 h后細胞形態學變化。
1.6U-2 OS細胞Fas、Caspase-3檢測細胞處理及分組與“1.4”方法相同,藥物作用24 h后用TRIzol、氯仿、異丙醇等試劑提取各組細胞總RNA,按照TIANScript RT Kit(cDNA第一鏈合成試劑盒)說明書逆轉錄成cDNA,然后按2×Taq Master Mix說明書進行PCR擴增,擴增后的DNA用2%瓊脂糖凝膠進行電泳。采用凝膠成像系統對條帶進行照相,Image J進行灰度值分析。
2結果
2.1各組細胞存活率、G0/G1期細胞、細胞凋亡率比較細胞存活率、G0/G1期細胞、細胞凋亡率比較見表1。
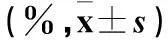
表1 各組細胞存活率、G0/G1期細胞、細胞凋亡率比較
注:與D組比較,*P<0.05;與C組比較,△P<0.05。
2.2各組細胞形態學變化D組U-2 OS細胞增殖良好;B、C組細胞數量減少,部分細胞由梭形變小、變圓,細胞質內顆粒增粗、增多,少量細胞脫落、裂解,可見少量凋亡小體,呈典型凋亡形態改變;A組細胞密度更低,凋亡現象更加明顯。
2.3各組細胞Fas、Caspase-3相對表達量比較細胞Fas、Caspase-3相對表達量比較見表2。
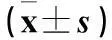
表2 各組細胞Fas、Caspase-3相對表達量比較
注:與D組比較,*P<0.05;與C組比較,△P<0.05。
3討論
骨肉瘤患者預后差,單純手術治愈率僅15%~20%,約50%的患者術后復發。隨著新輔助化療技術的應用,骨肉瘤患者的5年生存率有所提高[5],但在臨床治療過程中發現其對臨床常用抗腫瘤藥物如鉑類、多柔比星、甲氨蝶呤等逐漸產生耐藥性[6],甚至是多重耐藥,這對骨肉瘤的治療效果造成極大的影響。
DDP是癌癥化療方案中的重要組分[7],但細胞耐藥性及不良反應限制其應用,因此設計與DDP的聯合用藥以增強DDP的化療效果成為臨床關注的熱點[8]。有研究表明,HDACi能有效抑制腫瘤細胞增殖,其與多種化療藥物聯用可有效增加抑癌效果。VPA是一種八碳支鏈的脂肪酸鈉鹽,屬于HDACi,作為傳統的抗癲癇藥物,其不良反應輕,患者可長期使用,在抗癲癇治療時表現出很強的組蛋白去乙酰化酶抑制劑活性。已有研究[9~11]表明,VPA對肺癌、淋巴瘤、肝癌等多種腫瘤細胞有抑制作用。然而,VPA聯合DDP是否具有協同抗骨肉瘤作用鮮有報道。本研究顯示,與D組比較,A、B、C組細胞存活率降低,凋亡率升高;與C組比較,A組細胞存活率降低,凋亡率升高。提示VPA聯合DDP可抑制U-2 OS細胞存活,促進其凋亡,VPA聯合DDP具有較強的協同抑癌活性,且較單用VPA或DDP作用更明顯。
細胞凋亡是多種基因調控的結果,Fas基因作為重要的凋亡基因[12],其表達的蛋白是誘導細胞程序性死亡的信號分子,在正常細胞內可通過信號轉導途徑逐級放大死亡信號,通過相應的受體傳導至細胞核內部,引起核內轉錄基因的改變,從而啟動凋亡程序。近年研究[13]表明,Fas在骨肉瘤中的表達與肺轉移的發生呈負相關,提示通過改變Fas表達可以調整骨肉瘤細胞的侵襲能力。Caspase是由Caspase基因家族轉錄表達的一類具有酶切作用的蛋白質,目前發現有14種,Caspase-3為主要的凋亡執行蛋白[14],被上游分子激活后能分解細胞的骨架蛋白、細胞器等結構,參與細胞凋亡的具體執行過程。本研究顯示,A、B、C組Fas和Caspase-3相對表達量較D組升高,A組Fas和Caspase-3相對表達量較C組升高,表明VPA聯合DDP可促進Fas、Caspase-3表達,且較單用VPA或DDP作用更為明顯。
總之,VPA聯合DDP可抑制U-2 OS細胞存活,促進其凋亡,且較單用VPA或DDP作用更為明顯;其作用機制可能與Fas、Caspase-3表達上調有關。
參考文獻:
[1] Samimi MA, Mirkheshti N, Pazouki A. Assessing the percent of necrosis after neoadjuvant chemotherapy with 24hr infusional cisplatin/3 days doxorubicin intermittent with ifosfamide-doxorubicin for osteosarcoma[J]. Int J Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Res, 2014,8(1):5-8.
[2] Giannini G, Cabri W, Fattorusso C, et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitors in the treatment of cancer: overview and perspectives[J]. Future Med Chem, 2012,4(11):1439-1460.
[4] 趙斌,葛金芳,朱娟娟,等.小議在MTT法測細胞增殖抑制率中IC50的計算方法[J].安徽醫藥,2007,11(9):834-836.
[5] Bacci G, Rocca M, Salone M, et al. High grade osteosarcoma of the extremities with lung metastases at presentation: treatment with neoadjuvant chemotherapy and simultaneous resection of primary and metastatic lesions[J]. J Surg Oncol, 2008,98(6):415-420.
[6] Wang J, LI G. Mechanisms of methotrexate resistance in osteosarcoma cell lines and strategies for overcoming this resistance[J]. Oncol Lett, 2015,9(2):940-944.
[7] Chiu TJ, Wang JW, Chen YJ, et al. Intraarterial cisplatin and intravenous adriamycin in nonmetastatic osteosarcoma of the extremities: a single institution experience in Taiwan[J]. Chang Gung Med J, 2009,32(1):72-80.
[8] Quattrini I, Conti A, Pazzaglia L, et al. Metformin inhibits growth and sensitizes osteosarcoma cell lines to cisplatin through cell cycle modulation[J]. Oncol Rep, 2014,31(1):370-375.
[9] Gavrilov V, Lavrenkov K, Ariad S, et al. Sodium valproate, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, enhances the efficacy of vinorelbine-cisplatin-based chemoradiation in non-small cell lung cancer cells[J]. Anticancer Res, 2014,34(11):6565-6572.
[10] Zheng Z, Cheng S, Wu W, et al. c-FLIP is involved in tumor progression of peripheral T-cell lymphoma and targeted by histone deacetylase inhibitors[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2014,7(1):88.
[11] Matsuda Y, Wakai T, Kubota M, et al. Valproic acid overcomes transforming growth factor-beta-mediated sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Int J Clin Exp Pathol, 2014,7(4):1299-1313.
[12] 陳楷,呂書軍,付東,等.骨肉瘤凋亡與耐藥相關機制的研究進展[J].中國骨與關節雜志,2015,4(1):45-49.
[13] Rao-Bindal K, Koshkina NV, Stewart J, et al. The histone deacetylase inhibitor, MS-275 (entinostat), downregulates c-FLIP, sensitizes osteosarcoma cells to FasL, and induces the regression of osteosarcoma lung metastases[J]. Curr Cancer Drug Targets, 2013,13(4):411-422.
[14] 張巍.細胞凋亡與腫瘤化療的研究進展[J].醫學綜述,2013,19(3):451-453.
Effect and mechanism of sodium valproate combined with cisplatin on proliferation and apoptosis of human osteosarcoma cell line U-2 OS
YANKang1,XIASilong,WANGYehua
(1GraduateSchoolofXuzhouMedicalCollege,Xuzhou221000,China)
Abstract:ObjectiveTo investigate the effect and mechanism of the sodium valproate (VPA) combined with cisplatin (DDP) on proliferation and apoptosis of human osteosarcoma cell line U-2 OS. MethodsThe osteosarcoma U-2 OS cells were cultured in vitro and were divided into groups A, B, C and D. The groups A, B and C were separately treated with 35 mmol/L VPA+20 mg/L DDP, 35 mmol/L VPA and 20 mg/L DDP, and the group D was not treated. The proliferation was assayed by CCK-8. The cell cycle and apoptosis were analyzed by flow cytometry (FCM). The gene expression of Fas and Caspase-3 was detected by RT-PCR. ResultsCompared with group D, the cell viabilities of groups A, B and C were decreased, the cells in the G0/G1phase were increased, the apoptosis rate and the expression levels of Fas and Caspase-3 genes were increased; compared with group C, the cell viability of the group A decreased, the cells in the G0/G1phase were increased, the apoptosis rate and the expression levels of Fas and Caspase-3 genes increased. The difference was statistically significant (all P<0.05).Conclusions VPA combined with DDP could inhibit the cell proliferation and induce to apoptosis of human osteosarcoma U-2 OS, and the effect is more obvious than that of using only one of them. The mechanism may be closely related to the up-regulated expression of Fas and Caspase-3.
Key words:osteosarcoma; sodium valproate; cisplatin
(收稿日期:2015-09-23)
作者簡介:第一閆抗(1990-),男,碩士在讀,主要研究方向為創傷外科。E-mail: xzmcyankang@163.com
中圖分類號:R738.1
文獻標志碼:A
文章編號:1002-266X(2016)03-0011-03
doi:10.3969/j.issn.1002-266X.2016.03.004
通信作者簡介:王業華(1966-),男,博士,主任醫師,主要研究方向為創傷外科。E-mail: 736283162@qq.com

