鹽霉素對人鼻咽癌CNE2/DDP細胞順鉑耐藥的影響及其機制
陳冬杰,廖雪陽,陳可緒,李毅斌,汪森明
(南方醫科大學珠江醫院,廣州510282)
鹽霉素對人鼻咽癌CNE2/DDP細胞順鉑耐藥的影響及其機制
陳冬杰,廖雪陽,陳可緒,李毅斌,汪森明
(南方醫科大學珠江醫院,廣州510282)
目的 探討鹽霉素對人鼻咽癌CNE2/DDP細胞順鉑耐藥的影響及其可能的作用機制。方法將人鼻咽癌CNE2/DDP細胞隨機分為四組,分別加入2 μg/mL順鉑(順鉑組)、8 μmol/L鹽霉素(鹽霉素組)、2 μg/mL順鉑和8 μmol/L鹽霉素(聯合組)、0.1%二甲基亞砜(對照組)進行處理。采用CCK-8法檢測各組細胞增殖抑制率,流式細胞術檢測細胞凋亡率,Western blotting法檢測Wnt/β-catenin信號通路(β-catenin、p-LRP6)、mTORc1信號通路(P70S6K、p-P70S6K、S6、p-S6)相關蛋白相對表達量,熒光分光光度法檢測caspase3、caspase9活性。結果與對照組比較,順鉑組、鹽霉素組、聯合組細胞增殖抑制率、凋亡率和caspase3、caspase9活性均升高(P均<0.05);順鉑組、鹽霉素組和聯合組上述指標均逐漸升高,兩兩比較P均<0.05。β-catenin、p-LRP6、p-P70S6K、p-S6蛋白相對表達量:順鉑組和對照組均高于鹽霉素組和聯合組(P均<0.05),順鉑組與對照組、鹽霉素組與聯合組比較差異均無統計學意義(P均>0.05)。P70S6K、S6蛋白相對表達量:各組比較差異均無統計學意義(P均>0.05)。結論鹽霉素可以逆轉人鼻咽癌CNE2/DDP細胞的順鉑耐藥;激活caspase活性、抑制Wnt/β-catenin和mTORc1信號通路可能是其作用機制。
鼻咽癌;鹽霉素;順鉑;耐藥;細胞凋亡
鼻咽癌是致死率最高的頭頸部腫瘤[1,2],放療是惟一可能治愈早期鼻咽癌的方法[3],聯合放化療是局部晚期鼻咽癌的標準治療方法[4]。順鉑是中晚期鼻咽癌常用的化療藥物之一,但部分患者治療過程中會對順鉑產生耐藥性,大大降低了療效[5,6]。鹽霉素是一種選擇性乳腺癌干細胞抑制物,可抑制多種腫瘤細胞的增殖和分化[7]。2015年4月~2016年1月,我們觀察了鹽霉素對人鼻咽癌CNE2/DDP細胞順鉑耐藥的影響,現分析結果并探討其可能的作用機制。
1 材料與方法
1.1 材料 人鼻咽癌CNE2/DDP細胞由南方醫科大學腫瘤研究所饋贈,采用含10%胎牛血清的RMPI 1640培養基于37 ℃、5% CO2培養箱中進行培養。藥物及試劑:順鉑由珠江醫院腫瘤中心提供,鹽霉素購于美國Sigma公司,均溶于二甲基亞砜(DMSO)中,于-20 ℃冰箱中避光保存。抗p-LRP6(Ser1490) 抗體購于英國Abcam公司,抗S6抗體、抗p-S6(Ser235/236)、抗P70S6K抗體、抗p-P70S6K(Thr389)抗體、抗β-catenin抗體、抗GADPH抗體均購于美國Affinity公司。
1.2 細胞增殖抑制率檢測 采用CCK-8法。取對數生長期的CNE2/DDP細胞,調整細胞密度為5×104個/mL,接種于96孔板中,每孔加入細胞懸液100 μL,培養24 h,隨機分為順鉑組、鹽霉素組、聯合組和對照組。取出溶于DMSO的順鉑和鹽霉素,采用RMPI 1640培養基將其濃度調整為2 μg/mL和8 μmol/L。順鉑組加入含2 μg/mL順鉑的培養基100 μL,鹽霉素組加入含8 μmol/L鹽霉素的培養基100 μL,聯合組加入含2 μg/mL順鉑及8 μmol/L鹽霉素的培養基100 μL,對照組加入含0.1% DMSO的培養基100 μL,每組設置5個復孔。作用48 h后終止培養,每孔中加入預先配好的CCK-8試劑,繼續放入孵育箱中培養2 h。取出培養板,酶標儀450 nm波長下測定各孔光密度值(OD值),實驗重復3次。細胞增殖抑制率=(1-實驗組OD值/對照組OD值)×100%。
1.3 細胞凋亡率檢測 采用流式細胞術。取對數生長期CNE2/DDP細胞,調整細胞密度為1.5×105個/mL,接種于6孔板中,每孔1 mL,培養24 h。順鉑組加入含2 μg/mL順鉑的培養基2 mL,鹽霉素組加入含8 μmol/L鹽霉素的培養基2 mL,聯合組加入含2 μg/mL順鉑及8 μmol/L鹽霉素的培養基2 mL,對照組加入含0.1% DMSO的培養基2 mL。作用48 h后終止培養,將舊培養液轉移至10 mL離心管內。收集各孔細胞并轉移至舊培養液所在離心管中,采用胰酶進行消化(已去除EDTA),1 000 r/min離心5 min,去上清。收集細胞,采用4 ℃預冷的PBS洗滌3次,1 000 r/min離心5 min,棄上清。400 μL Binding Buffer懸浮細胞,加入5 μL Annexin V-FITC混勻,加入5 μL Propidium Iodide混勻。在室溫、避光條件下反應10 min,上流式細胞儀檢測細胞凋亡率,實驗重復3次。
1.4 Wnt/β-catenin、mTORc1信號通路相關蛋白表達檢測 參照1.3的方法進行接種及分組處理,作用48 h后采用4 ℃預冷的PBS進行洗滌,棄上清。每孔加入200 μL RIPA裂解液,冰上裂解20~30 min。將裂解的細胞收集至EP管中,于4 ℃條件下1 200 r/min離心20 min,將含蛋白的上清轉移到新的EP管中。采用SDS-PAGE凝膠電泳分離,電泳濕轉至PVDF膜,轉移至4 ℃冰箱中,5% BSA封閉2 h,加入一抗孵育過夜。PBS洗滌PVDF膜3次,每次15 min;加入HRP標記的二抗,室溫下孵育1 h;PBS洗滌3次,每次15 min。進行ECL化學發光反應及曝光,以GADPH作為對照,實驗重復3次。Wnt/β-catenin信號通路(β-catenin、p-LRP6)、mTORc1信號通路(P70S6K、p-P70S6K、S6、p-S6)蛋白相對表達量以目的蛋白灰度值與GADPH灰度值的比值表示。
1.5 caspase3、caspase9活性檢測 采用熒光分光光度法。參照1.3的方法進行接種及分組處理,作用48 h后,收集細胞。冰上裂解30 min,4 ℃條件下1 200 r/min離心1 min,取上清置于EP管。加入相應的caspase底物,充分混勻后,加入96孔板中,避光孵育4 h。每組設置3個復孔,以酶標儀405 nm波長下各孔OD值表示caspase3、caspase9活性。實驗重復3次。

2 結果
2.1 各組細胞增殖抑制率和凋亡率比較 與對照組比較,順鉑組、鹽霉素組、聯合組細胞增殖抑制率和凋亡率均升高(P均<0.05)。順鉑組、鹽霉素組和聯合組細胞增殖抑制率和凋亡率均逐漸升高,兩兩比較P均<0.05。見表1。

表1 各組細胞增殖抑制率和凋亡率比較
注:與對照組比較,*P<0.05;與順鉑組比較,#P<0.05;與鹽霉素組比較,△P<0.05。
2.2 各組Wnt/β-catenin信號通路相關蛋白表達比較 順鉑組和對照組 β-catenin、p-LRP6蛋白相對表達量均高于鹽霉素組和聯合組(P均<0.05);順鉑組和對照組比較、鹽霉素組和聯合組比較差異均無統計學意義(P均>0.05)。見表2。
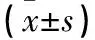
表2 各組Wnt/β-catenin信號通路相關蛋白相對表達量比較
注:與對照組比較,*P<0.05;與順鉑組比較,#P<0.05。
2.3 各組mTORc1信號通路相關蛋白表達比較 各組P70S6K、S6蛋白相對表達量比較差異均無統計學意義(P均>0.05)。順鉑組和對照組p-P70S6K、p-S6蛋白相對表達量均高于鹽霉素組和聯合組(P均<0.05);順鉑組和對照組比較、鹽霉素組和聯合組比較差異均無統計學意義(P均>0.05)。見表3。
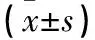
表3 各組mTORc1信號通路相關蛋白相對表達量比較
注:與對照組比較,*P<0.05;與順鉑組比較,#P<0.05。
2.4 各組caspase3、caspase9活性比較 與對照組比較,順鉑組、鹽霉素組和聯合組caspase3、caspase9活性均升高(P均<0.05)。鹽霉素組、順鉑組和聯合組caspase3、caspase9活性均逐漸升高,兩兩比較P均<0.05。見表4。
3 討論
在鼻咽癌的治療中,逆轉順鉑耐藥性藥物的研究為當前熱點。鹽霉素可抑制多種腫瘤細胞,包括肝癌[8]、乳腺癌[9]、胰腺癌[10]、前列腺癌[11]、腸癌[12]、鼻咽癌[13]等,但其對鼻咽癌細胞的作用及其對順鉑耐藥性影響的報道較少。前期研究顯示,順鉑作用于CNE2/DDP細胞的IC50為5.93 μg/mL,鹽霉素為10 μmol/L,結合相關參考文獻,本研究分別選取低于兩種藥物IC50的濃度為工作濃度,分別為2 μg/mL、8 μmol/L[13,14]。本研究結果顯示,聯合組細胞增殖抑制率和凋亡率均明顯高于順鉑組、鹽霉素組。提示鹽霉素能提高CNE2/DDP細胞對順鉑的敏感性,并逆轉其對順鉑的耐藥性;鹽霉素聯合順鉑可能成為鼻咽癌順鉑耐藥患者的一種新的治療方案。
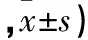
表4 各組caspase3、caspase9活性比較(OD值
注:與對照組比較,*P<0.05;與順鉑組比較,#P<0.05;與鹽霉素組比較,△P<0.05。
研究表明,鹽霉素對鼻咽癌細胞的抑制作用可能與其抑制Wnt/β-catenin信號通路有關,但具體的機制并未完全清楚[14]。Wnt/β-catenin、mTORc1信號通路均與腫瘤的增殖和侵襲密切相關,且兩條通路之間可能存在交叉[15~19]。因此能夠同時抑制Wnt/β-catenin信號通路及mTORc1信號通路的物質有可能成為新型的抗腫瘤藥物。LRP6是Wnt/β-catenin信號通路中的關鍵Wnt協同受體,LRP6的磷酸化在Wnt/β-catenin信號通路的激活過程中起關鍵作用[20,21]。本研究發現,順鉑組和對照組 β-catenin、p-LRP6、p-P70S6K、p-S6蛋白相對表達量均高于鹽霉素組和聯合組,而順鉑組和對照組比較、鹽霉素組和聯合組比較差異均無統計學意義。提示鹽霉素可同時抑制Wnt/β-catenin與mTORc1信號通路,而順鉑無此作用;鹽霉素提高CNE2/DDP細胞的順鉑敏感性、逆轉其耐藥性的作用機制可能與其抑制Wnt/β-catenin與mTORc1信號通路有關。本研究鹽霉素組、順鉑組和聯合組caspase3、caspase9活性逐漸升高,說明caspase的激活可能是鹽霉素作用的另一種相關機制。
綜上所述,鹽霉素可以逆轉人鼻咽癌CNE2/DDP細胞的順鉑耐藥性;激活caspase活性、抑制Wnt/β-catenin和mTORc1信號通路可能是其作用機制。
[1] Lee AW, Ma BB, Ng WT, et al. Management of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: current practice and future perspective[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2015,33(29): 3356-3364.
[2] Perez CA, Devineni VR, Marcial-Vega V, et al. Carcinoma of the nasopharynx: factors affecting prognosis[J]. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 1992,23(2):271-280.
[3] Chen MY, Chen YS, Hu LJ, et al. The end-of-treatment telephone response and prognosis of post-radiotherapy nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients in southern China[J]. Int J Clin Exp Med, 2015,8(9):16564-16570.
[4] Chua ML, Wee JT, Hui EP. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma[J]. Lancet, 2016,6736(15):1-13.
[5] Gottschalk S, Heslop HE, Rooney CM. Adoptive immunotherapy for EBV-associated malignancies[J]. Leuk Lymphoma, 2005,46(1):1-10.
[6] 陳磊,鄭樹艷,黃永望.PPAR-γ對人鼻咽癌CNE1/DDP細胞順鉑耐藥性的逆轉作用及其機制探討[J].山東醫藥,2014,54(40):10-12,15.
[7] Gupta PB, Onder TT, Jiang G, et al. Identification of selective inhibitors of cancer stem cells by high-throughput screening[J]. Cell, 2009,138(4):645-659.
[8] Wang F, He L, Dai WQ, et al. Salinomycin inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells in vitro and in vivo[J]. PLoS One, 2012,7(12):e50638.
[9] Lu Y, Ma W, Mao J, et al. Salinomycin exerts anticancer effects on human breast carcinoma MCF-7 cancer stem cells via modulation of Hedgehog signaling[J]. Chem Biol Interact, 2015,228(6):100-107.
[10] Lu Y, Ma W, Mao J, et al. Salinomycin inhibits growth of pancreatic cancer and cancer cell migration by disruption of actin stress fiber integrity[J]. Cancer Lett, 2015,358(2):161-169.
[11] Lu W, Li Y. Salinomycin suppresses LRP6 expression and inhibits both Wnt/beta-catenin and mTORC1 signaling in breast and prostate cancer cells[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2014,115(10):1799-1807.
[12] Zou ZZ, Nie PP, Li YW, et al. Synergistic induction of apoptosis by salinomycin and gefitinib through lysosomal and mitochondrial dependent pathway overcomes gefitinib resistance in colorectal cancer[J]. Oncotarget, 2015,7(1):1-17.
[13] Wu D, Zhang Y, Huang J, et al. Salinomycin inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell in vitro and suppresses tumor growth in vivo[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2014,443(2):712-717.
[14] 姜潤德,張立新,岳文,等.人鼻咽癌順鉑耐藥細胞系(CNE2/DDP)的建立及耐藥相關基因的篩選[J].癌癥,2003,22(4):337-345.
[15] Bensouda Y, Kaikani W, Ahbeddou N, et al. Treatment for metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma[J]. Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis, 2011,128(2):79-85.
[16] Gupta PB, Onder TT, Jiang G, et al. Identification of selective inhibitors of cancer stem cells by high-throughput screening[J]. Cell, 2009,138(4):645-659.
[17] Fuchs D, Heinold A, Opelz G, et al. Salinomycin induces apoptosis and overcomes apoptosis resistance in human cancer cells[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2009,390(3):743-749.
[18] Zhi QM, Chen XH, Ji J, et al. Salinomycin can effectively kill ALDH (high) stem-like cells on gastric cancer[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2011,65(7):509-515.
[19] Lee HG, Lee JM, Shin SJ, et al. Salinomycin inhibited cell proliferation and induced apoptosis in human uterine leiomyoma cells[J]. Obstet Gynecol Sci, 2014,57(6):501-506.
[20] Schenk M, Aykut B, Teske C, et al. Salinomycin inhibits growth of pancreatic cancer and cancer cell migration by disruption of actin stress fiber integrity[J]. Cancer Lett, 2015,358(2):161-169.
[21] 姜元芹,顏志平,賴世佳,等. uPARAP、MMP9、VEGF在鼻咽癌中的表達及其意義[J].臨床軍醫雜志,2009,37(4):651-653.
·作者·編者·讀者·
一些常用詞匯可直接用縮寫
胎牛血清(FBS) 體質量指數(BMI) 天冬氨酸轉氨酶(AST)
磷酸鹽緩沖液(PBS) 總膽固醇(TC) 人類免疫缺陷病毒(HIV)
變異系數(CV) 甘油三酯(TG) 甲型肝炎病毒(HAV)
磁共振成像(MRI) 低密度脂蛋白膽固醇(LDL-C) 乙型肝炎病毒(HBV)
血紅蛋白(Hb) 高密度脂蛋白膽固醇(HDL-C) 丙型肝炎病毒(HCV)
核因子-κB(NF-κB) 重癥監護病房(ICU) 酶聯免疫吸附測定(ELISA)
逆轉錄—聚合酶鏈反應(RT-PCR) 嚴重急性呼吸綜合征(SARS) 動脈血氧分壓(PaO2)
腫瘤壞死因子(TNF) 動脈血二氧化碳分壓(PaCO2) 干擾素(IFN)
凝血酶時間(TT) 一氧化氮(NO) 白細胞介素(IL)
Effect of salinomycin on cisplatin resistance of human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells CNE2/DDP and its mechanisms
CHENDongjie,LIAOXueyang,CHENKexu,LIYibin,WANGSenming
(ZhujiangHospitalofSouthernMedicalUniversity,Guangzhou510282,China)
Objective To investigate the effect of salinomycin on the cisplatin resistance of human nasopharyngeal carcinoma CNE2/DDP cells and its possible mechanisms. Methods CNE2/DDP cells were randomly divided into four groups, which were separately treated with 2 μg/mL cisplatin (cisplatin group), 8 μmmol/L salinomycin (salinomycin group), 8 μmmol/L salinomycin + 2 μg/mL cisplatin (combination group) and 0.1%DMSO (control group). Inhibitory rate of proliferation was assessed by the Cell Counting Kit 8. Apoptosis rate was measured by flow cytometry. Caspases3 and caspase9 activity was assessed by a colorimetric assay utilizing specific substrates. The protein expression of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway (β-catenin and p-LRP6) as well as mTORc1 signaling pathway (P70S6K, p-P70S6K, S6, and p-S6) was evaluated by Western blotting. Results Compared with the control group, the inhibitory rate, apoptosis rate, Caspase-3/9 activity were increased in the cisplatin group, salinomycin group, and combination group (allP<0.05). Indexes mentioned above were increased the most in the combination group while salinomycin group ranked the second and cisplatin group ranked the third (allP<0.05). The expression of β-catenin, p-LRP6, p-P70S6K, and p-S6: the salinomycin group and combination group was decreased as compared with the cisplatin group and control group (allP<0.05). Meanwhile, no significant differences were found between salinomycin group and combination group as well as between the cisplatin group and control group (allP>0.05). No significant difference was found in the expression of P70S6K and S6 between these four groups (allP>0.05). Conclusion Salinomycin can reverse the cisplatin resistance of human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells CNE2/DDP which is possibly mediated by improving caspases activity and inhibiting both Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway and mTORC1 signaling pathway.
nasopharyngeal carcinoma; salinomycin; cisplatin; drug resistance; apoptosis
廣州市科技計劃項目(2011Y2-00019-3)。
陳冬杰(1988-),男,碩士在讀,研究方向為鹽霉素的抗腫瘤作用。E-mail: 15913106573@163.com
汪森明(1955-),男,主任醫師,博士生導師,研究方向為腫瘤內科治療、惡性腫瘤介入治療、射頻消融治療。E-mail: wsenming@126.com
10.3969/j.issn.1002-266X.2016.48.006
R739.6
A
1002-266X(2016)48-0020-04
2016-03-29)

