鎖定鋼板結合縫合錨固定治療NeerⅡB型鎖骨遠端骨折
胡曉川 林輝陽 向明 陳杭 楊國勇
?
·論著·
鎖定鋼板結合縫合錨固定治療NeerⅡB型鎖骨遠端骨折
胡曉川 林輝陽 向明 陳杭 楊國勇
目的 探討應用2.4 mm鎖定鋼板結合縫合錨固定治療不穩定型NeerⅡB型鎖骨遠端骨折的方法及臨床療效。方法 回顧性分析2011年1月至2013年12月收治并獲完整隨訪的16例不穩定型NeerⅡB型鎖骨遠端骨折患者臨床資料,其中男性12 例,女性4例,年齡23~65歲,平均35歲。致傷原因:跌傷4例,自行車摔傷2例,電動自行車摔傷4例,交通事故傷6例,均為新鮮閉合骨折,無神經、血管損傷。受傷至手術時間3~12 d,平均5 d。沿皮膚Langer線的縱切口,采用2.4 mm L形橈骨遠端鎖定鋼板切開復位內固定結合縫合錨增強喙鎖穩定性手術治療。結果 術后切口均Ⅰ期愈合。16例患者均獲隨訪,隨訪時間12~18個月,平均15個月。X線片示骨折均愈合,愈合時間6~12周,平均8周。隨訪期間無內固定物失效、斷裂、移位情況發生。末次隨訪時Constant肩關節功能評分為86~100分,平均94分。疼痛視覺模擬評分為0~2分,平均0.2分。結論 對于不穩定型NeerⅡB型鎖骨遠端骨折,應用2.4 mm L形橈骨遠端鎖定鋼板內固定結合縫合錨增強喙鎖穩定性,術后早期進行活動鍛煉,可獲滿意療效,是一種可行的有效方法。
肩關節;鎖骨骨折,遠端; 鎖定鋼板;縫合錨;內固定
鎖骨遠端骨折占所有鎖骨骨折的10%~30%[1]。大多數鎖骨遠端骨折為無或輕度移位的穩定型骨折(NeerⅠ型和NeerⅢ型),通常保守治療即可獲得滿意的療效。然而對于不穩定型NeerⅡB型鎖骨遠端骨折,治療尚存在爭議,非手術治療骨折不愈合率高,手術治療有發生并發癥的潛在風險,多數學者仍主張手術治療。眾多的手術方法可供選擇,各有優缺點,尚無金標準,且與內固定物相關的并發癥較常見[2-4]。
近年來,有學者將橈骨遠端鎖定鋼板應用于NeerⅡ型鎖骨遠端骨折的手術治療[5-9],骨折愈合率高、并發癥少,早期結果令人鼓舞,但報道較少,尚未形成公認的手術方法。我們回顧性分析2011年1月至2013年12月,采用2.4 mm L形橈骨遠端鎖定鋼板內固定結合縫合錨增強喙鎖穩定性手術治療16例不穩定型NeerⅡB型鎖骨遠端骨折患者的臨床資料,以期為該類型骨折的手術方法選擇提供參考,現報道如下。
資 料 與 方 法
一、一般資料
本組患者16例,男性12例,女性4例;年齡23~65歲,平均35歲。左側6例,右側10例。致傷原因:跌傷4例,自行車摔傷2例,電動自行車摔傷4例,交通事故傷6例,均為新鮮閉合骨折,無神經、血管損傷。術前均行鎖骨正軸位X線,肩關節CT平掃+骨三維重建檢查明確為不穩定型NeerⅡB型鎖骨遠端骨折。受傷至手術時間3~12 d,平均5 d。
二、手術方法
全身麻醉聯合臂叢神經阻滯麻醉下,患者取45°沙灘椅位,患肩墊高。沿皮膚Langer線(皮膚彈力纖維走形線),切口從肩鎖關節內側1.5~2.0 cm向前至喙突,長約6.0 cm。顯露三角肌、斜方肌筋膜,沿鎖骨長軸切開筋膜顯露骨折端,術中注意保持肩鎖韌帶完整性,保護三角肌和斜方肌止點。從胸大肌內側緣鈍性分離進入,將三角肌拉向外側,即可顯露喙突基底,小心分離,避免損傷臨近血管神經,充分暴露喙突基底,探查喙鎖韌帶的完整性。清理骨折端,于鎖骨近折端遠側前1/3處相距1.0 cm鉆2個骨孔;將1枚5.0 mm縫合錨(Mitek Fastinrc,Depuy或Twinx,Smith&Nephew)固定于喙突基底,將縫合錨釘尾的兩股2號不可吸收線穿過骨孔。向上托起患肢,向前下推壓近折端,向內推患肩,復位骨折后,將縫合錨尾線打結固定。以1枚1.5 mm克氏針經或不經肩峰結合點狀復位鉗臨時固定,C臂機透視確認骨折復位、錨釘位置滿意。
將1枚2.4 mm橈骨遠端直形或斜L形鎖定加壓鋼板(瑞士Synthes公司或山東威高骨科材料有限公司)置于鎖骨遠端上方。使用細針頭確定肩鎖關節間隙,在確保最遠端螺釘不會進入肩鎖關節間隙后,再置入螺釘,遠端3~4枚螺釘,近端2~3枚螺釘。若遠折端骨塊足夠大,可以用1枚2.4 mm皮質骨螺釘行拉力螺釘固定。必要時可以用2號不可吸收線縫合,加強固定。對于斷裂的喙鎖韌帶不作特殊處理。仔細修復三角肌及斜方肌筋膜。術中活動患肢判斷骨折固定的穩定性。
三、術后處理
術后頸腕吊帶制動患肢6周,術后即刻活動肘關節、腕關節及手指,術后2周開始仰臥位肩關節被動前屈上舉,外旋功能鍛煉,術后6周開始肩關節主動輔助功能鍛煉,待X線片示有明顯的骨折愈合征象后開始肩關節肌力訓練。建議患者術后6個月內避免從事接觸性體育活動。
四、療效評定標準
于術后第4、6、8、12周,第6、9、12個月隨訪,之后每隔6個月定期隨訪。拍鎖骨正軸位X線片,觀察骨折愈合情況,內固定物有無失效、斷裂、移位等。采用Constant肩關節功能評分[10]評價肩關節功能,疼痛視覺模擬評分(visual analogu scale,VAS)評價疼痛程度。
結 果
術后切口均Ⅰ期愈合,無血管及神經損傷、感染等并發癥發生。16例患者均獲隨訪,隨訪時間12~18個月,平均15.0個月;X線片示骨折均愈合,愈合時間6~12周,平均8周。隨訪期間無內固定物失效、斷裂、移位情況發生。末次隨訪時Constant肩關節功能評分為86~100分,平均94分。VAS評分為0~2分,平均0.2分。10例患者于術后12~18個月取出內固定物,見圖1,2。
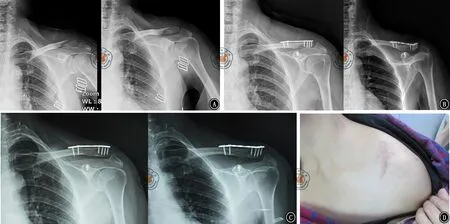
圖1 患者,女性,47歲,左側NeerⅡB型鎖骨遠端骨折。A為術前鎖骨正軸位X線片;B為術后即刻鎖骨正軸位X線片;C為術后12個月鎖骨正軸位X線片;D為手術切口
討 論
一、病理表現與分型
Neer[11]基于骨折線與喙鎖韌帶和肩鎖關節的關系,將鎖骨遠端骨折分為3型:Ⅰ型為喙鎖韌帶外側骨折,肩鎖韌帶完整,通常無明顯移位或輕度移位;Ⅱ型為喙鎖韌帶內側骨折,其中根據韌帶完整度分為ⅡA型(錐狀韌帶與斜方韌帶完整,附著于骨折遠端)和ⅡB型(錐狀韌帶撕裂,斜方韌帶完整);Ⅲ型為喙鎖韌帶外側骨折,累及肩鎖關節面。
二、治療方法
大多數鎖骨遠端骨折為無或輕度移位的穩定型骨折(NeerⅠ型和NeerⅢ型),采用頸腕吊帶制動4~6周,2周后疼痛緩解后即可開始肩關節功能鍛煉,可獲得滿意的療效。然而對于不穩定型鎖骨遠端骨折(NeerⅡB型)的治療尚存在爭議。由于遠折端較小,常為粉碎性骨折,喙鎖韌帶撕裂,導致水平和垂直方向的不穩定,斜方肌和胸鎖乳突肌牽拉近折端向上后移位,加上胸肌和上肢重力的作用,常導致骨折端較大的分離[12-13]。非手術治療難以對骨折進行復位和固定,骨折不愈合率達到30%[12]。
盡管有臨床研究報道非手術和手術治療的遠期肩關節功能差異不大,骨不愈合對肩部最終功能和肌力無太大影響,且手術治療有發生并發癥的潛在風險,從而對手術的指征提出了質疑[14-15],但多數學者仍主張手術治療。文獻報道了眾多的手術方法包括:鎖骨鉤鋼板、鎖骨遠端解剖鎖定鋼板、經肩峰克氏針、Knowles針、喙鎖螺釘固定、張力帶縫線、改良Weaver-Dunn術、Endo-button、縫合錨、雙鋼板及關節鏡技術等,各有優缺點,尚無金標準,且內固定物相關的并發癥較常見,如骨折不愈合、內置物失效斷裂移位、復位丟失、肩峰骨折、肩峰下骨侵蝕、肩峰撞擊、鋼板周圍鎖骨骨折等[2-4,16-17]。
三、方法和療效
近年來,有學者將橈骨遠端鎖定鋼板應用于NeerⅡ型鎖骨遠端骨折的手術治療,骨折愈合率高、并發癥少,早期結果令人鼓舞。Kalamaras等[5]于2008年,首次報道將2.4 mm橈骨遠端鎖定鋼板應用于9例Neer Ⅱ型鎖骨遠端骨折,采用鎖骨前方平行于鎖骨的皮膚切口,其中6例采用掌側T形鋼板(需塑形),3例采用L形鋼板,6例采用了不可吸收線環繞喙突和鎖骨遠端技術增強。8例患者獲得隨訪10~19個月,骨折均愈合(6~16周),1例出現傷口感染,Constant評分均為優。并指出該技術無肩鎖關節的干擾和醫源性的肩袖損傷和撞擊,鋼板低切跡不需要常規取出鋼板,固定穩定,允許早期活動,愈合率高。
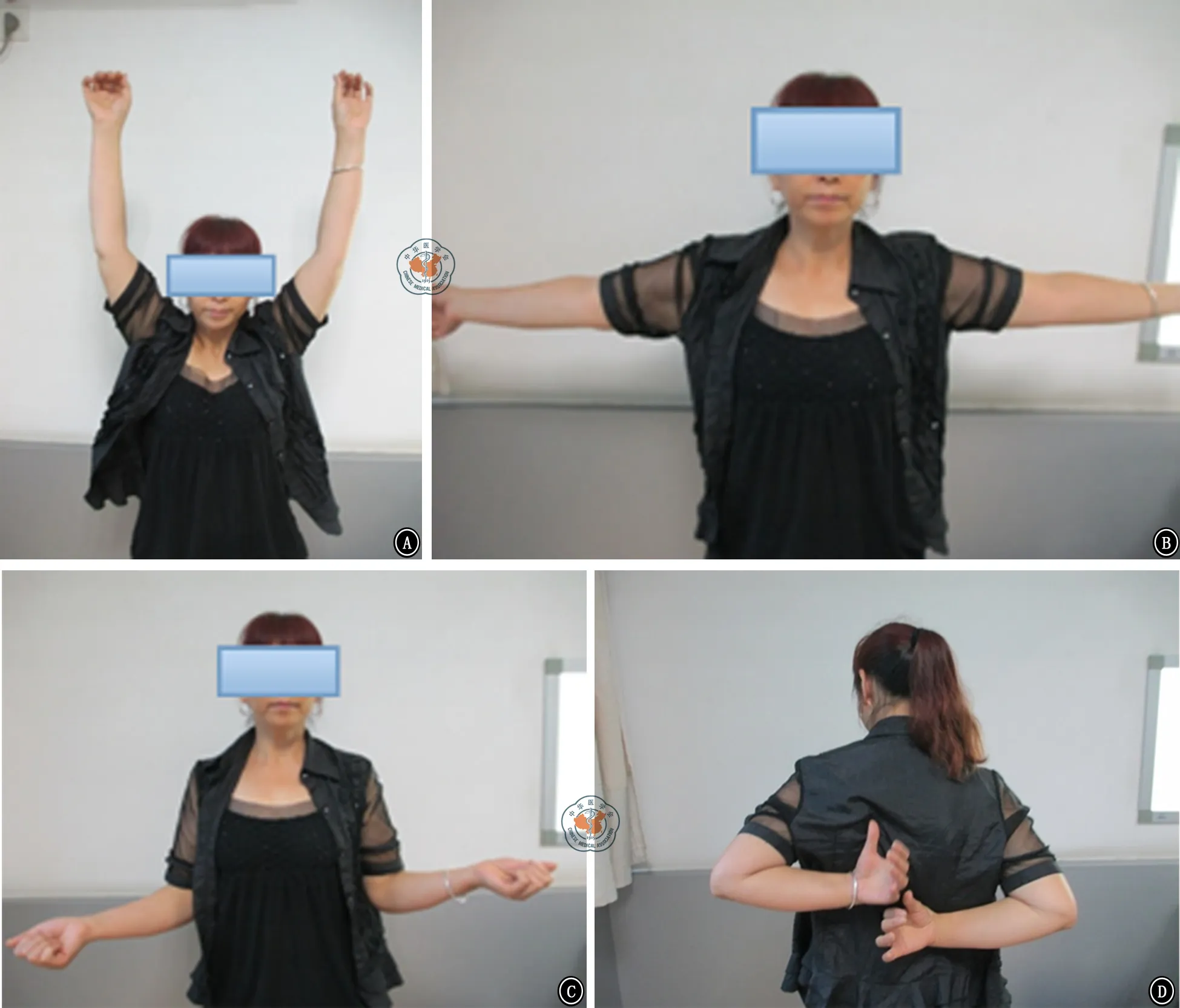
圖2 患者術后12個月肩關節功能。A為肩關節前屈上舉;B為肩關節外展;C為肩關節外旋;D肩關節內旋
Herrmann等[6]于2009年報道了8例Neer ⅡB型鎖骨遠端骨折,橫行皮膚切口,如果三角肌筋膜無創傷性撕脫需從鎖骨上切斷以顯露喙突基底,喙突基底置入1~2枚縫合錨,復位骨折后以1塊3.5 mm橈骨遠端鎖定鋼板固定骨折,必要時以2.0 mm皮質骨螺釘固定大骨折塊,縫合錨縫線環繞鎖骨和鋼板打結增強喙鎖間穩定性,重建喙鎖韌帶功能。7例患者獲得平均8.3個月(4~16個月)隨訪,無術中和術后早期并發癥,6周內骨折均愈合,臨床或X線片均無垂直或水平方向的不穩定征象,Constant評分5例為優,2例為良。
Hohmann等[7]于2012年,報道了31例Neer Ⅱ型鎖骨遠端骨折,鎖骨前方橫行皮膚切口,鈍性分離三角肌顯露喙突,置入TightRope縫線裝置,鎖骨上方以2.4 mm橈骨遠端鎖定鋼板固定,喙鎖韌帶以TightRope縫線增強。29例獲得隨訪,骨折愈合時間平均(6.3±4.1)周,1例出現傷口感染,1例出現骨折不愈合和鋼板斷裂,Constant評分24例優,5例良。并指出不可吸收線環繞鎖骨和喙突技術有縫線侵蝕喙突骨質的潛在風險,TightRope系統的優點在于可避免骨質侵蝕,因為縫線是系在鈕扣上而不是在鎖骨和喙突上。
龔偉華等[8]于2009年報道了9例NeerⅡ型鎖骨遠端骨折,采用肩峰弧形切口,鎖骨上方以橈骨遠端鎖定鋼板(未報告型號)固定,因選用的病例喙鎖韌帶并非完全撕裂,原始移位不甚明顯,術中檢查LCP完全能滿足骨折固定的需要,未修補喙鎖韌帶。隨訪3~14個月,傷口均I期愈合,無內固定并發癥。骨折愈合時間為8~10周,平均9.1周。無骨折延遲愈合、不愈合及畸形愈合。按照Constant肩關節功能評分:患側為84~94分,平均90分;同期健側為90~97分,平均95分。
最近,朱彤等[9]比較了橈骨遠端T形鎖定鋼板與鎖骨鉤鋼板治療NeerⅡ型鎖骨遠端骨折的療效。鎖骨表面橫行切口,采用橈骨遠端T形鎖定鋼板(未報告鋼板的大小)預彎后置于鎖骨遠端表面,所有患者均未行斷裂喙鎖韌帶修復術。術后隨訪中未發現鋼板斷裂和骨折不愈合。結果顯示橈骨遠端T形鎖定鋼板治療效果明顯優于鎖骨鉤鋼板,前者可避免對肩峰周圍軟組織的侵襲損害。
四、注意事項與技巧
本組患者均采用2.4 mm L形橈骨遠端鎖定鋼板結合縫合錨治療NeerⅡB型鎖骨遠端骨折,療效滿意,與文獻報道的結果相似,無骨折延遲愈合、不愈合,無感染,無內固定物失效、斷裂、移位情況發生,但方法有一些不同之處。基于本組資料并結合有關文獻,我們有如下體會和建議:(1)可選擇橫切口或縱切口,均可滿足充分顯露的需要,沿皮膚Langer線的縱切口具有以下優點[3]:①瘢痕小,切口方向與皮紋線方向一致,可以較大程度減少術后傷口的皮膚攣縮,從而減小瘢痕的面積,且容易用服裝掩蓋;②避免鎖骨上神經損傷,減少術后麻木。因此,我們推薦采用縱切口,不建議常規采用上述文獻采用的橫切口。(2)因NeerⅡB型骨折肩鎖韌帶完整,故術中無須暴露肩鎖關節,避免醫源性破壞肩鎖關節穩定性和骨折端血運。(3)基于NeerⅡB型骨折主要特點:遠端骨折塊通常較小且粉碎,主要為松質骨,不穩定、移位大的主要原因是錐狀韌帶的斷裂,2.4 mm鎖骨鋼板螺釘的把持力和強度均有限。因此,我們不建議單獨應用該鋼板,推薦結合縫合錨增強喙鎖間穩定性,避免鋼板失效,通常1枚縫合錨已足夠。已有實驗表明,使用縫合錨固定代替喙鎖韌帶的功能,其強度同喙鎖韌帶相似[18]。(4)喙突縫合錨的置入:我們推薦從胸大肌內側緣(胸三角的外側邊)鈍性分離進入,將三角肌拉向外側,即可顯露喙突基底,但須小心分離和牽拉,避免損傷臨近的血管神經。不建議分離三角肌或剝離三角肌筋膜,因其會加重軟組織的損傷和破壞骨折端的血運。鎖骨骨孔位于喙突上方鎖骨前中1/3,靠后可能會阻礙隨后鋼板的放置。縫合錨應盡量置入喙突基底的中心,以提供最大的錨定力,避免其拔出。(5)復位:基于NeerⅡB型骨折的移位特點:近折端向后上移位,遠折端下外移位,復位時需向上托起患肢,向前下推壓近折端,向內推患肩。克氏針和點狀復位鉗有助于維持復位。復位后應先將縫合錨縫線打結穩定近折端,然后再用鋼板固定遠近折端。(6)因鎖骨遠端呈向后的弧形,而近折端有縫合錨線結的阻礙,通常選擇拐角向后的L形鋼板,再根據具體骨折形態選擇直L形或斜L形鋼板,使遠端有3~4枚螺釘,近端有2~3枚螺釘固定。(7)使用細針頭確定肩鎖關節間隙,有助于確保鋼板最遠端螺釘不會進入肩鎖關節間隙。(8)鋼板遠端螺釘要獲得足夠把持力需要骨折塊足夠的骨量和較好的骨質量。如果遠折端小、嚴重粉碎、骨質疏松,難以有效復位鋼板內固定,術前、術中應做好轉變手術方式的準備。年輕患者為了盡可能保留鎖骨遠端,可選擇龔曉峰等[19]報道的縫合錨結合骨折端縫線環扎技術。老年患者可選擇鎖骨遠端切除改良Weaver-Dunn術[12]。(9)應仔細修復三角肌及斜方肌筋膜,因為其有助于喙鎖關節前后向的穩定[19]。
綜上所述,對于NeerⅡB型鎖骨遠端骨折,應用2.4 mm L形橈骨遠端鎖定鋼板結合縫合錨增強喙鎖間穩定性,術后早期活動鍛煉,可獲滿意療效,是一種可行的有效方法。但由于本組病例數較少,且隨訪時間較短,還需要更大樣本量和更長期的隨訪觀察以明確療效。
[1] Robinson CM, Cairns DA. Primary nonoperative treatment of displaced lateral fractures of the clavicle[J]. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 2004, 86(4): 778-782.
[2] Banerjee R, Waterman B, Padalecki J, et al. Management of distal clavicle fractures[J]. J Am Acad Orthop Surg, 2011, 19(7): 392-401.
[3] 胡孫君,俞光榮,張世民.鎖骨遠端骨折的治療[J].中華創傷骨科雜志,2008,10(1):85-88.
[4] 吳曉明,高偉,李凡,等.鎖骨鉤鋼板內固定術后并發癥分析與防治對策[J].中華骨科雜志,2012,32(4):331-338.
[5] Kalamaras M, Cutbush K, Robinson M. A method for internal fixation of unstable distal clavicle fractures: early observations using a new technique[J]. J Shoulder Elbow Surg, 2008, 17(1): 60-62.
[6] Herrmann S, Schmidmaier G, Greiner S. Stabilisation of vertical unstable distal clavicular fractures (Neer 2b) using locking T-plates and suture anchors[J]. Injury, 2009, 40(3): 236-239.
[7] Hohmann E, Hansen T, Tetsworth K. Treatment of neer type II fractures of the lateral clavicle using distal radius locking plates combined with TightRope augmentation of the coraco-clavicular ligaments[J]. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg, 2012, 132(10): 1415-1421.
[8] 龔偉華,孫月華,俞超,等.鎖定加壓鋼板在鎖骨遠端骨折中的應用[J].中華手外科雜志,2009,25(6):346-347.
[9] 朱彤,傅智軼,胡小鵬,等.橈骨遠端T形鎖定鋼板與鎖骨鉤鋼板治療NeerⅡ型鎖骨遠端骨折的療效比較[J].中華創傷骨科雜志,2014,16(1):76-78.
[10] Constant CR, Murley AH. A clinical method of functional assessment of the shoulder[J]. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1987,(214): 160-164.
[11] Neer CS 2nd. Fractures of the distal third of the clavicle[J]. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1968,(58):43-50.
[12] Anderson K. Evaluation and treatment of distal clavicle fractures[J]. Clin Sports Med, 2003,22(2):319-326.
[13] Lee YS, Lau MJ, Tseng YC, et al. Comparison of the efficacy of hook plate versus tension band wire in the treatment of unstable fractures of the distal clavicle[J]. Int Orthop, 2009, 33(5): 1401-1405.
[14] Rokito AS, Zuckerman JD, Shaari JM, et al. A comparison of nonoperative and operative treatment of type II distal clavicle fractures[J]. Bull Hosp Jt Dis, 2003, 61(1/2): 32-39.
[15] Nordqvist A, Petersson C, Redlund-Johnell I. The natural course of lateral clavicle fracture. 15(11-21)year follow-up of 110 cases[J].Acta Orthop Scand, 1993, 64(1): 87-91.
[16] 陳曉峰,李曉林.鎖骨遠端骨折的治療進展[J].中華創傷骨科雜志,2012,14(9):810-813.
[17] Takase K, Kono R, Yamamoto K. Arthroscopic stabilization for Neer type 2 fracture of the distal clavicle fracture[J]. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg, 2012, 132(3): 399-403.
[18] Harris RI, Wallace AL, Harper GD, et al. Structural properties of the intact and the reconstructed coracoclavicular ligament complex[J]. Am J Sports Med, 2000, 28(1): 103-108.
[19] 龔曉峰,姜春巖,王滿宜.應用縫合錨固定治療不穩定型鎖骨遠端骨折[J].中華骨科雜志,2005,25(6):382-384.
(本文編輯:李靜)
Locking plate combined with suture anchor for treatment of NeerⅡ B distal clavicular fractures
HuXiaochuan,LinHuiyang,XiangMing,ChenHang,YangGuoyong.
DepartmentofUpperExtremity,SichuanOrthopaedicHospital,Chengdu610041,China
Correspondingauthor:XiangMing,Email:josceph_xm@sina.com
Background The cases of distal clavicular fracture account for about 10%-30% of all clavicular fracture cases. Most of distal clavicular fracture cases are stable fracture cases without fracture or with minor fractures (Neer I type and Neer Ⅲ type), for which satisfactory curative effects can be achieved through conservative treatment in general. However, there are disputes over treatment methods for the cases of instable Neer ⅡB type distal clavicular fractures. The non-operative therapy is featured by high fracture nonunion rate, while operative treatment involves potential risk of complications. The majority of scholars still advocate operative treatment. Many operation methods are optional and have their own advantages and disadvantages. However, there is no gold standard for operative treatment at present, and the complications related to internal fixtures are frequent.In recent years, some scholars have applied the distal radius locking plate in the operative treatment of Neer Ⅱ type distal clavicular fracture, featuring high fracture union rate, less complications and encouraging early results. However, there are few research reports, and no generally accepted operation method has been formed. During the period from January 2011 to December 12, 2013, our department adopted 2.4 mm L-shaped distal radius locking plate for internal fixation in combination with suture anchor with enhanced coracoclavicular stability in the operative treatment of 16 patients with instable Neer ⅡB type distal clavicular fractures. We hereby make retrospective analysis on the clinical data of these patients, in order to provide references for selecting the operation method for this type of fracture.Methods (1) General materials:This groups includes 12 male cases and 4 female cases; they are aged 23-65, with average age of 35 years. There are 6 cases of left side fracture and 10 cases of right side fracture; The injury causes: 4 cases of falling injury, 2 cases of bicycle injury, 4 cases of electric bicycle injury and 6 cases of traffic accident injury. All these cases suffer from fresh closed fracture, without nerve and vascular injury. Prior to operation, our department performed X-ray examination on clavicular orthoaxis position, CT plan scanning on shoulder joint+ three-dimensional bone reconstruction on these cases and thus made clear that they suffer from instable NeerⅡB type distal clavicular fracture. The duration from injury to operation is 3-12 d, with average duration of 5 d. (2) Operative method:Under general anesthesia in combination with brachial plexus block anesthesia, allow the patient to lie on 45° beach chair position, and raise the shoulder of patient; Perform skin incision along the Langer line of skin (spandex running line of skin), incise forwards from 1.5-2.0 cm inner side of acromioclavicular joint to coracoid, with incision length of about 6.0 cm. Expose deltoid fascia and inclined and square muscle fascia, incise the fasciae along the long axis of clavicle to expose the fracture ends. In the operation, pay attention to keeping the integrity of acromioclavicular ligament and protecting the insertions of deltoid and musculus trapezius.Perform blunt separation from the medial margin of pectoralis major muscle, enter the musculus pectoralis major, pull the deltoid outwards, so that the coracoid base can be exposed. Make separation carefully, avoid causing injury to adjacent vascular nerves, sufficiently expose the coracoid base, and explore the integrity of coracoclavicular ligament. Clean the fracture end, on the position 1/3 before distal side of clavicular fracture end, drill two bone holes at interval of 1.0 cm; Fix one 5.0 mm suture anchor (Mitek FASTIN RC, Depuy or Twinx,Smith & Nephew) on coracoid base, and allow two strands of No.2 non-absorbable sutures for stitching anchor tail to pass through the bone holes. Hold up the affected limbs, push and press the proximal fracture end forwards and downwards, and push the affected shoulder inwards; After reduction of bone fracture, knot and fix the suture anchor tail line. Use one 1.5 mm kirschner wire in combination with reduction forceps to perform temporary fixation through acromion or not through acromion; Through C arm X-ray machine perspective, validate fracture reduction and satisfactory position of anchor rivet.Place one 2.4 mm distal radius straight-shaped or inclined L-shaped locking compression plate (provided by Switzerland Synthes Company or Shandong Weigao Orthopedics material Co.,Ltd) above the distal clavicular. Use a fine needle to determine the acromioclavicular joint clearance; After having ensured that the screws at the furthest end will unlikely enter the acromioclavicular joint clearance, place the screws, with 3-4 screws placed at distal end and 2-3 screws at the proximal end. If the bone block at the distal fracture end is big enough, one 2.4 mm cortical bone screw is used to perform lag screw fixation. When necessary, No.2 non-absorbable suture can be used for stitching and enhancing fixation. No special treatment is made for fractured coracoclavicular ligament. The deltoid fascia and inclined and square muscle fascia are carefully repaired. Move the affected limbs during operation, so as go judge the stability of facture fixation. (3) Postoperative treatment:After operation, use neck-wrist strap to rest the affected limbs for 6 weeks, then immediately exercise elbow joint, wrist joint and finger. At 2 weeks after operation, start passive functional exercises of shoulder joint (including forward bending, uplifting and outward rotation) on supine position; At 6 weeks after operation, start the exercise of active and auxiliary functions of shoulder joint; After obvious fracture union sign has been confirmed through X-ray film examination, start the training on muscle strength of shoulder joint. It is suggested that the patient should avoid contact physical sports in 6 months after operation. (4) Evaluation criteria for curative effects:Respectively make follow-up visit at 4, 6, 8 and 12 weeks after operation, in the sixth, ninth and twelfth months after operation, and then make regular follow-up visit at interval of 6 months; Make X-ray photography on the orthoaxis position of clavicular, observe the fracture union and verify whether there is malfunction, fracture or displacement of internal fixture. Adopt shoulder joint function score such as Constant to evaluate the functions of shoulder joint, and adopt visual analogue pain scale (VAS) to evaluate the pain degree.Results All the postoperative incisions were healed up at Phase I, without occurrence of such complications as vascular injury, nerve injury and infection. All 16 cases obtained follow-up visits, with follow-up survey period of 12-18 months and average period of 15.0 months. As shown in X-ray film, 16 cases of fracture were healed without exception, with healing time of 6~12 weeks and average healing time of 8 weeks. During the follow-up period, there was no malfunction, fracture or displacement of fixture. In the final follow-up visit, the Constant shoulder joint function score was 86-100 points, with average score of 94 points.VAS was 0-2 points, with average value of 0.2 points. For 10 cases, internal fixtures were taken out in 12-18 months after operation.Conclusions For unstable Neer type ⅡB distal clavicular fractures, using 2.4 mm L shape locking compression plate designed for distal radius for open reduction and internal fixation combined with suture anchor augmentation of the coraco-clavicular stability, and early active mobilization can obtain good functional results,it is a feasible and effective method.
Shoulder joint;Clavicular fractures,distal;Locking plate;Suture anchor;Internal fixation
10.3877/cma.j.issn.2095-5790.2015.04.002
公益性行業科研專項(201302007)
610041成都,四川省骨科醫院上肢科
向明,Email: josceph_xm@sina.com
2015-03-31)

