基于MapReduce的隱私保護的關聯規則挖掘算法的研究
熊富蕊 桑應朋


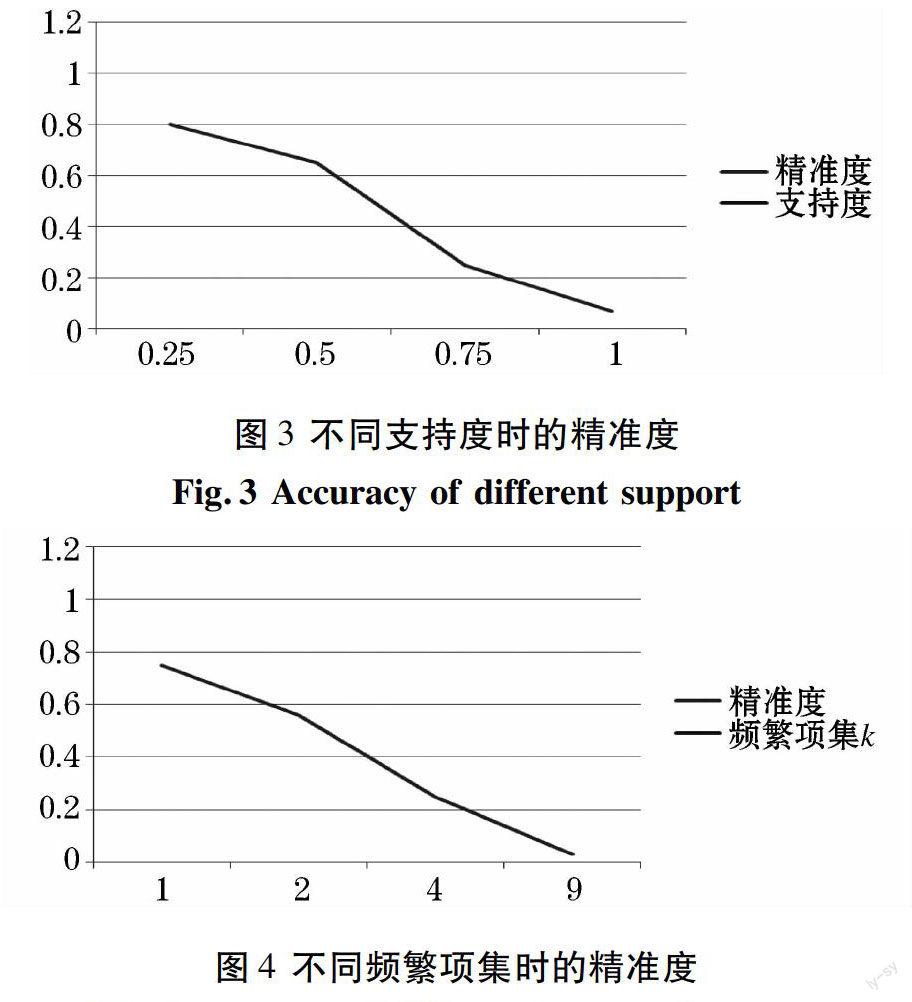
摘要:主要針對關聯規則中的Apriori算法在執行過程中產生大量候選集和重復掃描數據庫會使串行算法的時間復雜度高和執行率低的缺點,提出了一種基于MapReduce的并行關聯規則挖掘算法,對傳統的關聯規則算法進行并行優化。在Hadoop平臺上進行了單機測試和集群測試。分析得出基于MapReduce的關聯規則算法克服了串行算法產生大量候選集和重復掃描數據庫的兩大缺點,從而提高了執行效率。此外,針對目前數據隱私泄露的嚴重現象,在進行并行化的數據挖掘之前,使用加隨機數的方法來保護數據的隱私,并驗證了保護數據在關聯規則挖掘中保留了高可用性。
關鍵字:MapReduce;Apriori;Hadoop;隱私保護
中圖分類號:TP391 文獻標識碼 A文章編號:2095-2163(2015)06-
Abstract:The main disadvantage of Apriori algorithm for association rule mining is that it produces large amounts of candidate sets and database scannings during execution, making the serial algorithm having high time complexity and low implementation rate. This paper proposes a new algorithm based on MapReduce,which optimizes the traditional association rule algorithm in a parallel way.Simulations based on the hadoop platform are performed on one single machine and clusters. The results demonstrate that our new algorithm based on MapReduce overcomes the disadvantage of the serial algorithm.Whats more, considering the serious phenomenon of data privacy leaking, the paper uses randomization to protect data privacy before they are mined, and shows the randomized data keep a high utiltity for association rule mining.
Keywords: MapReduce;Apriori;Hadoop;Privacy_Preserving
0 引言
隨著各行各業的快速發展,大量的數據開始出現和累積。然而,如何從這些數據中,提取出所需要的有用信息,則已成為時下研究關注、且矚目的一個焦點問題。作為一個分析工具,數據挖掘可以從大量數據集中發現有趣、有用的信息。現如今數據挖掘的技術已經開始用于商業用途,藉此提高商業價值。數據挖掘主要分為三大領域:分類分析、聚類分析和關聯規則分析。尤其是,關聯規則分析已經獲得了數據挖掘中比較重要的領域地址,具體實現主要分為兩步:發現頻繁項目集和生成關聯規則。關聯規則中的一種基本算法就是Apriori算法。該算法在執行過程中會產生大量的候選集,并且還要多次重復掃描數據庫。由此可知,隨著數據的逐漸增加,有如Apriori這樣的傳統挖掘算法已經不能快速有效地分析獲取有用的信息。基于以上背景所述,本文提出了一種新的基于MapReduce的并行關聯規則的算法。此外,隨著挖掘技術的不斷進步,使得一些敏感、有用的信息相繼公開,這就增加了原始數據的風險性。因此,基于隱私保護[1-2]的需求,本文即在數據挖掘前使用了添加隨機數的方法,從而實現對數據隱私的保護。
1 國內外研究現狀
現在國內外已經應用很多方法解決關聯規則挖掘算法[3-6]。隨著大量數據的產生,各種并行關聯規則算法也隨即陸續提出。例如:CD (Count Distribution) CaD(Candidate Distribution) and DD (Data Distribution)[7-8],這些算法可以運用于云計算環境。但是算法卻都具有缺乏同步性的缺點。
文獻[9]針對Apriori算法產生大量候選項集的缺點,提出了一種頻繁模式算法(FP),是一種不用生成候選項目集,實現Apriori的算法。可以快速構建挖掘模型,是一種高效的關聯規則算法。
文獻[10-13]提出了基于MapReduce的Apriori并行算法,利用Hadoop平臺的多個節點并行運算的Apriori算法。可以有效地實施并行化,但仍會產生大量候選項集。
2 基礎理論概述
2.1關聯規則挖掘和Apriori算法
設I={i1,i2…,im}是項的集合。給定一個交易數據庫D,其中每個事務T是I的非空子集,即,每一個交易都與一個唯一的標識符TID(Transaction ID)對應。關聯規則在D中的支持度(support)是D中事務同時包含A、B的百分比,即P(A∪B);置信度(confidence)是D中事務已經包含A的情況下,包含B的百分比,即P(B|A)。如果滿足最小支持度閾值和最小置信度閾值,則認為關聯規則是有趣的[14]。關聯規則的挖掘分為兩個步驟:
(1)找出所有滿足最小支持度的頻繁項集;
(2)由頻繁項集產生滿足最少支持度和最少置信度的強關聯規則。
Apriori算法是最具影響的一類關聯規則挖掘算法,使用一種逐層搜索的迭代方法。其具體實現過程為:首先,找出1-項集的集合(L1),用L1去找頻繁2項集L2。依次下去,直至不能找到頻繁k項集。每尋獲一個LK都需要掃描一次數據庫。所以,需要多次重復掃描數據庫導致時間復雜度較高和執行效率降低。偽代碼如下[15]:
輸入:交易數據庫D,最小支持度min_sup。
輸出:頻繁集L
L1=find_frequent_1_itemset(D);//產生1-頻繁集
for(k=2;Lk-1!=?;k++){
Ck=apriori_gen(Lk-1,min_sup);//產生k-候選集
for each transaction t in D{
Ct=subset(Ck,t);//獲得事務t包含的候選項集
for each candidate c in Ct
c.count++; }
Lk={c∈Ck|c.count>=min_sup}; }
L=?kLk;
Procedure apriori_gen(Lk-1:frequent(k-1)-itemset;min_sup:support)
Foreach itemset l1 in Lk-1
Foreach itemset l2 in Lk-1
If( (l1 [1]=l2 [1])&&( l1 [2]=l2 [2])&& …&&(l1 [k-1]then{ c = l1 link l2 // 連接步:產生候選
if has_infrequent_subset(c, Lk-1) then
delete c; // 剪枝步:刪除非頻繁候選
else add c to Ck; }
Return Ck;
Procedure has_infrequent_subset(c:candidatek-itemset;
Lk-1 :frequent(k-1)-itemsets)
For each (k-1)-subset s of c
If s?Lk-1 then
Return true;
Return false;
2.2Hadoop平臺
Hadoop是一個開發和運行處理大規模數據的軟件平臺,是Appach的一個基于java語言推出的開源軟件框架,可以實現在大量計算機組成的集群中對海量數據進行分布式計算[16]。Hadoop的框架最核心的設計就是:HDFS和MapReduce。在此,對其分述如下。
HDFS(Hadoop Distributed File System)是一個分布式文件系統,由一個名稱節點(NameNode)和N個數據節點(DataNode)組成,每個節點均是一臺普通的計算機。NameNode 是一個通常在 HDFS 實例中的單獨機器上運行的軟件,具體負責管理文件系統名稱空間和控制外部客戶機的訪問。NameNode 決定是否將文件映射到 DataNode 上的復制塊上。Hadoop 集群包含一個 NameNode 和大量 DataNode。DataNode 響應來自 HDFS 客戶機的讀寫請求。同時還響應來自 NameNode 的創建、刪除和復制塊的命令[17]。
MapReduce是一種并行編程模型,其基于HDFS拓展實現,可用于大規模數據集的并行計算。MapReduce編程模型的原理是:MapReduce 以函數方式提供了 Map 和 Reduce 來進行分布式計算。Map 相對獨立且并行運行,對存儲系統中的文件按行處理,處理后產生鍵值(key/value)對。Reduce則以 Map 的輸出作為輸入,相同鍵值的記錄匯聚到同一 reduce,再對這組記錄進行操作,相應將產生新的key/value對集合[18]。
3 基于Mapruduce的隱私保護的關聯規則挖掘算法
該算法的思想是:首先通過加隨機數的方式對原始的數據D進行保護,得到變換后的數據D1。然后使用mapreduce的分布式編程原理,將原始數據集按行劃分為多個小數據集,分布到三個節點上。稍后每個節點對輸入的數據塊分配一個map,通過map函數執行,并采用一種改進的Apriori算法計算滿足最小支持度的候選項目集。最后使用reduce函數獲得頻繁項目集,再將得到的數據集存放在HDFS上。主要實現步驟為:
(1)在每個節點上對原始數據D添加隨機數變成D1。
(2)第一階段:
在每個節點上用map函數對數據進行操作,分割的整個數據集作為輸入,產生鍵值對
Struct hashnode{
Map mapnode;
Boolean isleafnode;
List items;
}
在datanode上用reduce函數對map輸出結果進行整合。將結果返回給namenode節點。Reduce函數輸出結果為key/value對,key代表頻繁1項集元素,value為出現該鍵值的次數。并且將結果存儲在HDFS中。生成1頻繁項目集。
(2)第二階段:直接從HDFS中取出數據,此時的數據已經不是最初數據庫中的原始數據,而是前一階段產生的1頻繁項目集,這樣就大大的縮減了候選項集的數目。此后再通過map/reduce函數重復以上的步驟,依次找到2頻繁項目集、k頻繁項目集。
(1)-(3)偽代碼如下:
Map task:
輸入:改變后分割數據D2
輸出:對,key代表頻繁項目集的元素
map(object, D2)
C=G-Apriori(D2)
Foreach itemset item in C
Out(item,one);
End foreach
End map
End
Reduce task
輸入:
參考文獻:
[1]ZHU Jianming, ZHANG Ning, LI Zhanyu Li. A new privacy preserving association rule mining algorithm based on hybrid partial hiding strategy[J]. Bulgarian Acadmeny Of Sciences,2013,13(special issue):41-50.
[2]AGRAWAL D, AGGARWAL C C. On the design and quantification of privacy preserving data mining algorithms[C]// PODS '01 Proceedings of the twentieth ACM SIGMOD-SIGACT-SIGART symposium on Principles of databases,New York:ACM,2002:247-255.
[3]TOIVONEN H.Sampling large databases for association rules[C]// Intl.Conf.on Very Large Databases,Bombay,India:ACM,1996:134–145.
[4]SAVASERE A ,OMIECINSKI E , SHAMKANT B. Et al. An efficient algorithm for Mining Association Rules in Large Databases[C]// Proceedings of the 21th International Conference on Very Large Data Bases, San Francisco:Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc,1995 :432-444.
[5]FANG Min , SHIVAKUMAR N ,GARCIA-MOLINA H ,et al. Ullman, computing iceberg queries efficiently[C]//Proceedings of the 24rd International Conference on Very Large Data Bases,New York:Morgan Kaufmann,1998:299-310.
[6]QURESHI Z,BANSAL J, BANSAL S. A survey on association rule mining in Cloud Computing[J].International Journal of Emerging Technology and Advanced Engineering,2013,3(4):2250-2459.
[7]ASHRAFI M Z, TANIAR D, SMITH K. ODAM: An optimized distributed association rule mining algorithm[J]. Distributed Systems Online IEEE, 2004, 5(3):1.
[8]LI L, ZHANG M. The strategy of mining association rule based on Cloud Computing[J]. IEEE, 2011, 52(1391):475-478.
[9] SANJEEV R, GUPTA P. Implementing improved algorithm
over APRIORI data mining association rule algorithm[J].IJCST,2012,3(1):2250-2459.
[10] CHEN SY, LI Jiahong Li, LIN Kechung Lin, et al.
Using MapReduce framework for mining association rules[C]//
Springer Science+Business Media Dordrecht,TaiWan:NSC,2013:723-731.
[11] RIONDATO M, DEBRABANT J A, FONSECA R, et al. PARMA: a parallel randomized algorithm for approximate association rules mining in MapReduce[C]// Proceedings of the 21st ACM international conference on Information and knowledge management,New York:ACM, 2012:85-94.
[12] YANG Xinyue, LIU Zhen, FU Yan. MapReduce as a programming model for 1ssociation rules algorithm on hadoop[C]// 3rd International Conference on Information Sciences and Interaction Sciences. Chengdu: IEEE,2010:99-102.
[13]LI N, ZENG L, HE Q, et al. Parallel implementation of Apriori Algorithm based on MapReduce[C]// Proceedings of the 2012 13th ACIS International Conference on Software Engineering, Artificial Intelligence, Networking and ParallelDistributed Computing. USA:IEEE Computer Society,2012:236-241.
[14]LIN Xueyan. MR-Apriori:Association rules algorithm based on MapReduce[A]. IEEE Beijing Section.Proceedings of 2014 IEEE 5th International Conference on Software Engineering and Service Science[C].Beijing:IEEE Beijing Section,2014:4.
[15]ZHANG CS, LI ZY, ZHENG DS. An improved algorithm for Apriori. Fourth[C]// Proceedings of the 1st International Workshop on Education Technology and Computer Science, ETCS 2009,v1,Wuhan:IEEE,2009:995-998.
[16]孫趙旭,謝曉蘭,周國清,等. 基于Hadoop的Apriori算法與實現[J]. 桂林理工大學學報,2014(3):584-588.
[17]郝曉飛,譚躍生,王靜宇. Hadoop平臺上Apriori算法并行化研究與實現[J]. 計算機與現代化,2013(3):1-4+8.
[18]LIN M Y, LEE P Y, HSUEH S C. Apriori-based frequent itemset mining algorithms on MapReduce[C]// Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Ubiquitous Information Management and Communication,New York:ACM,2012:20-22.

