發(fā)酵方式對(duì)玉米粉加工特性及淀粉精細(xì)結(jié)構(gòu)的影響

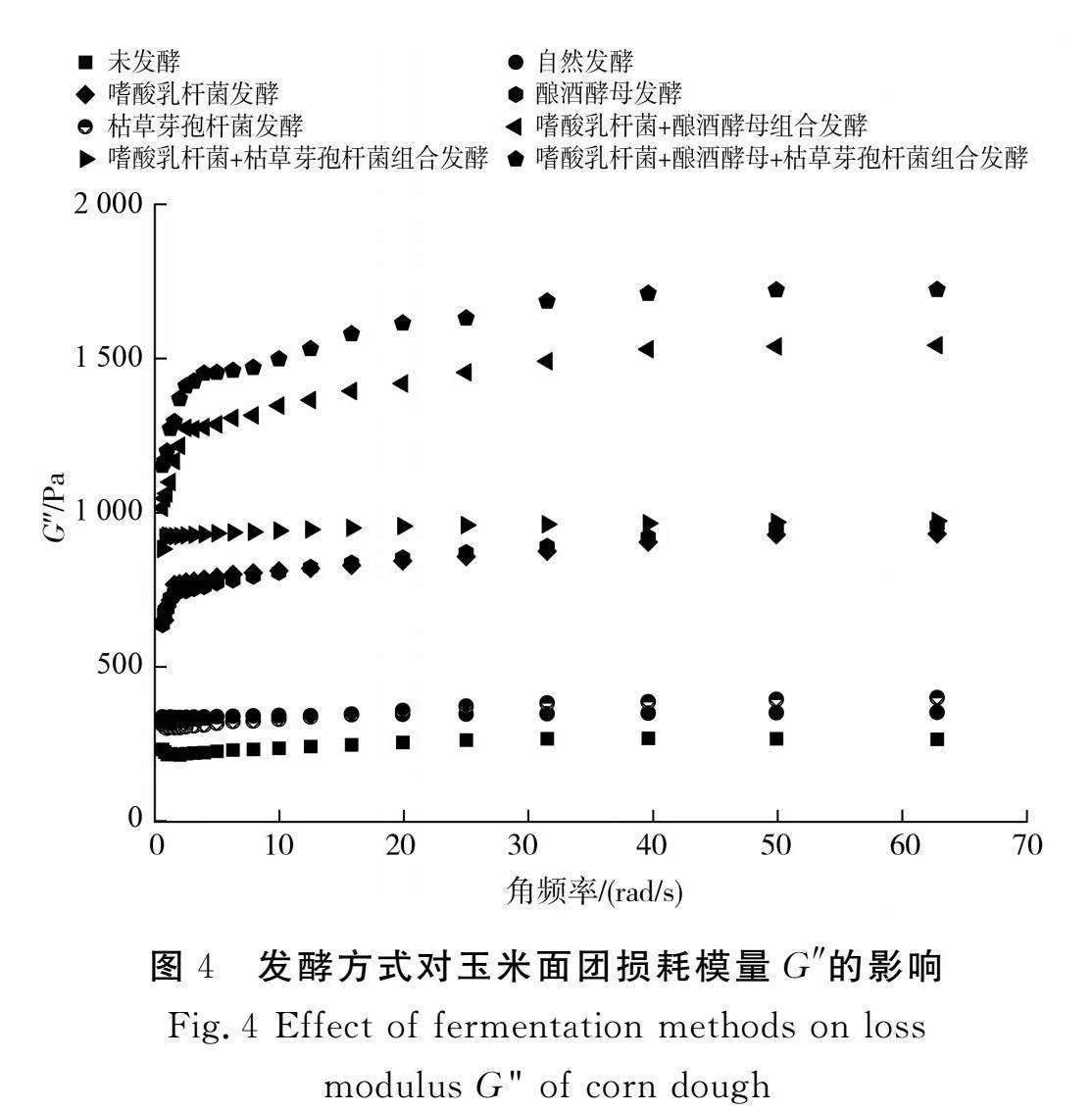

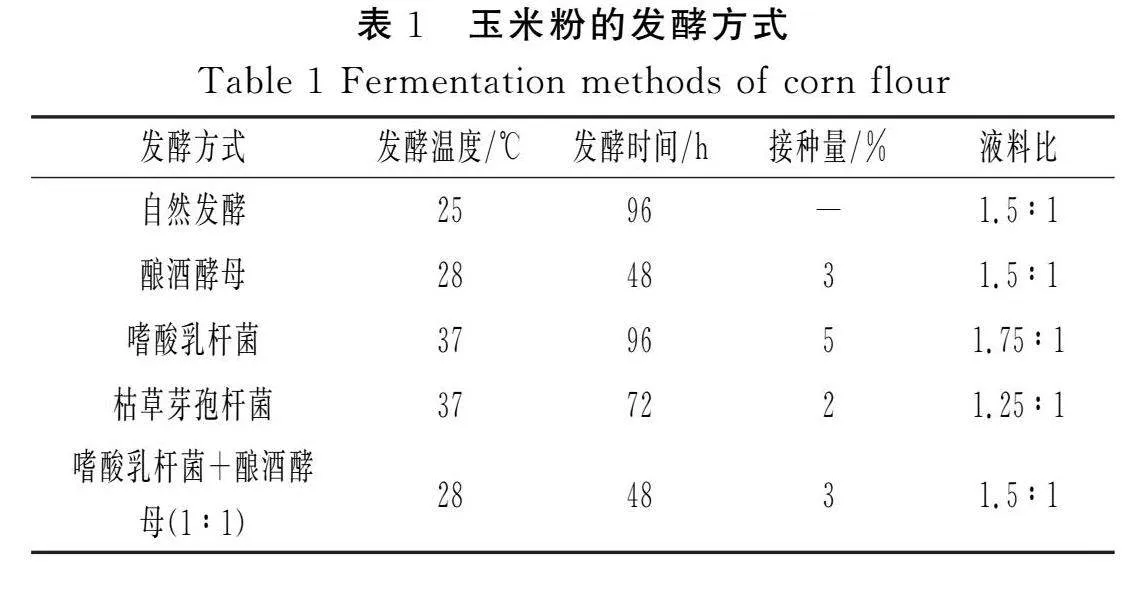
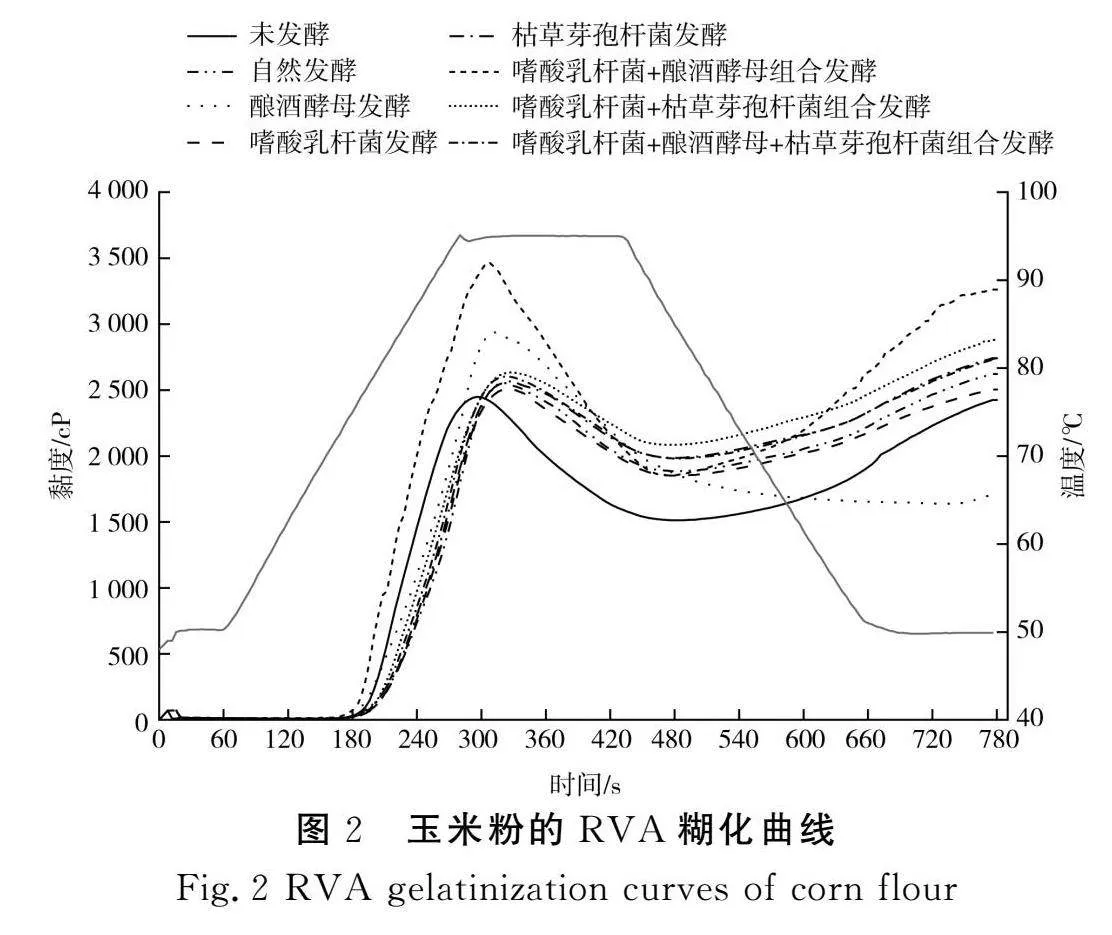
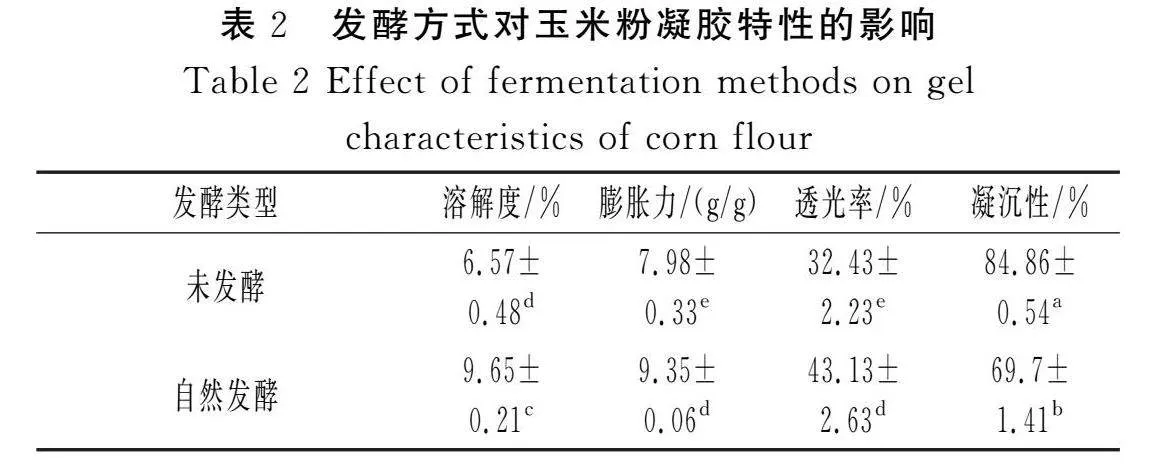

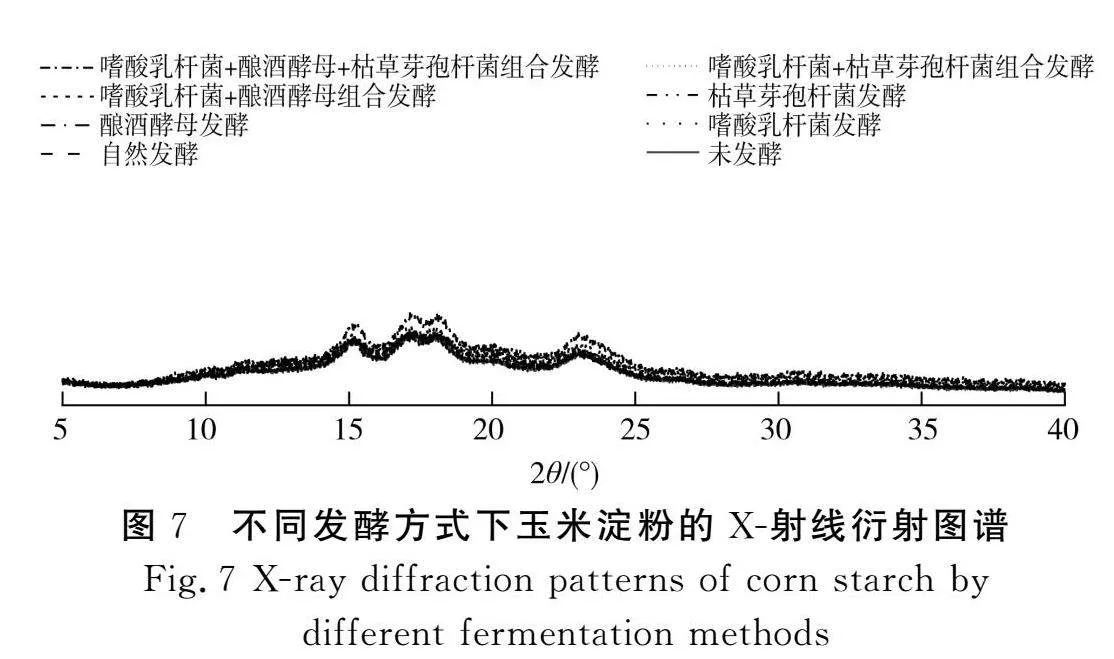
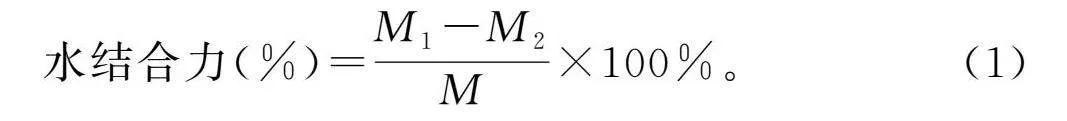
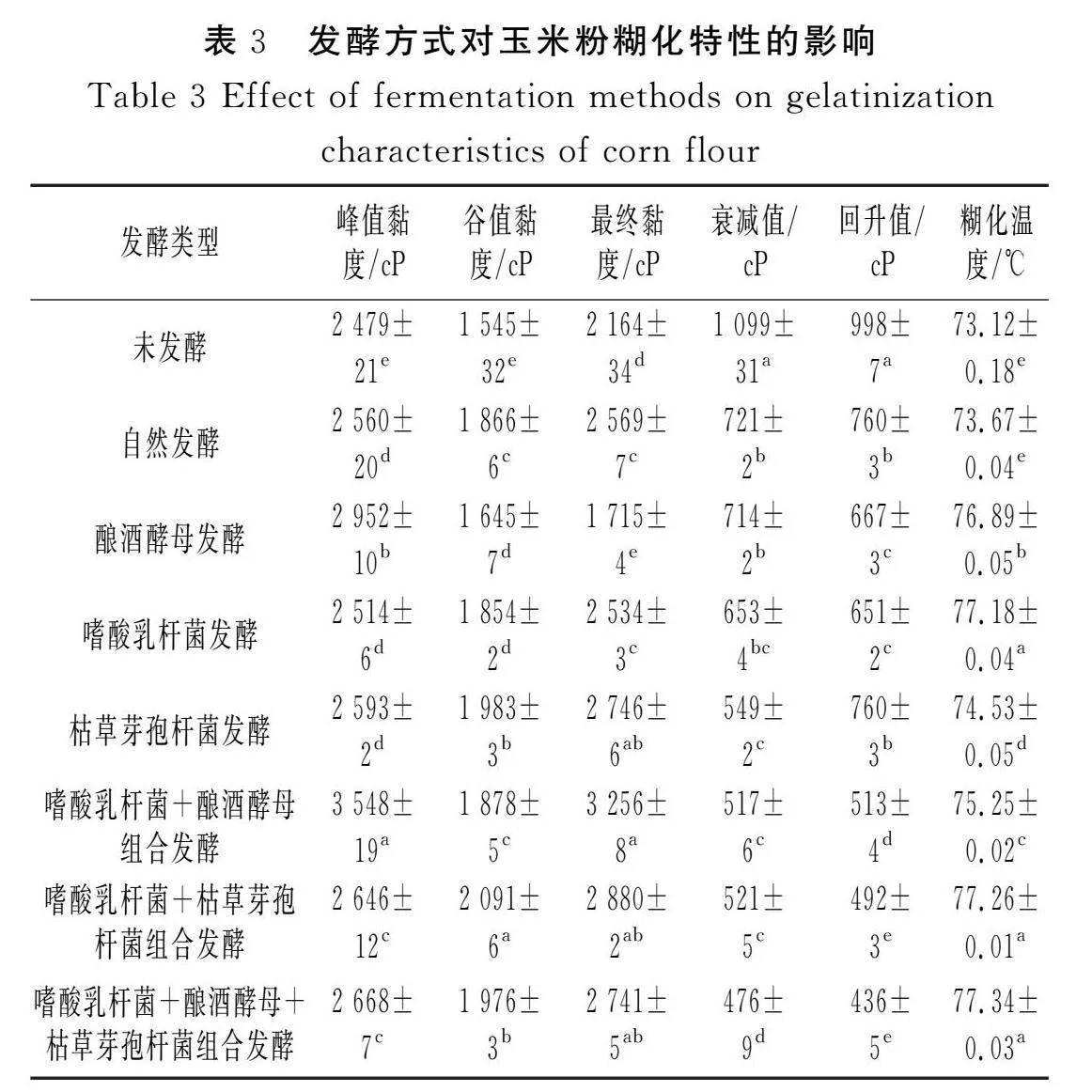
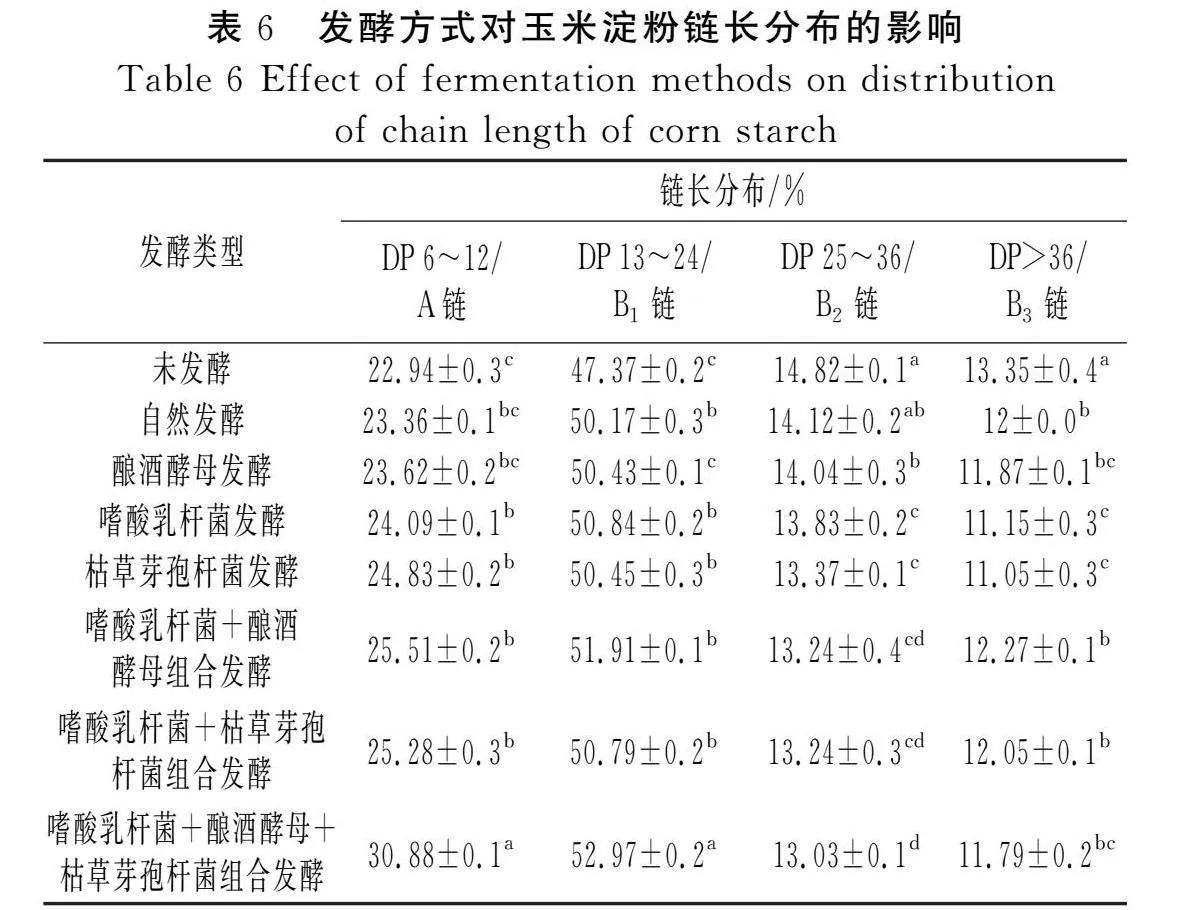

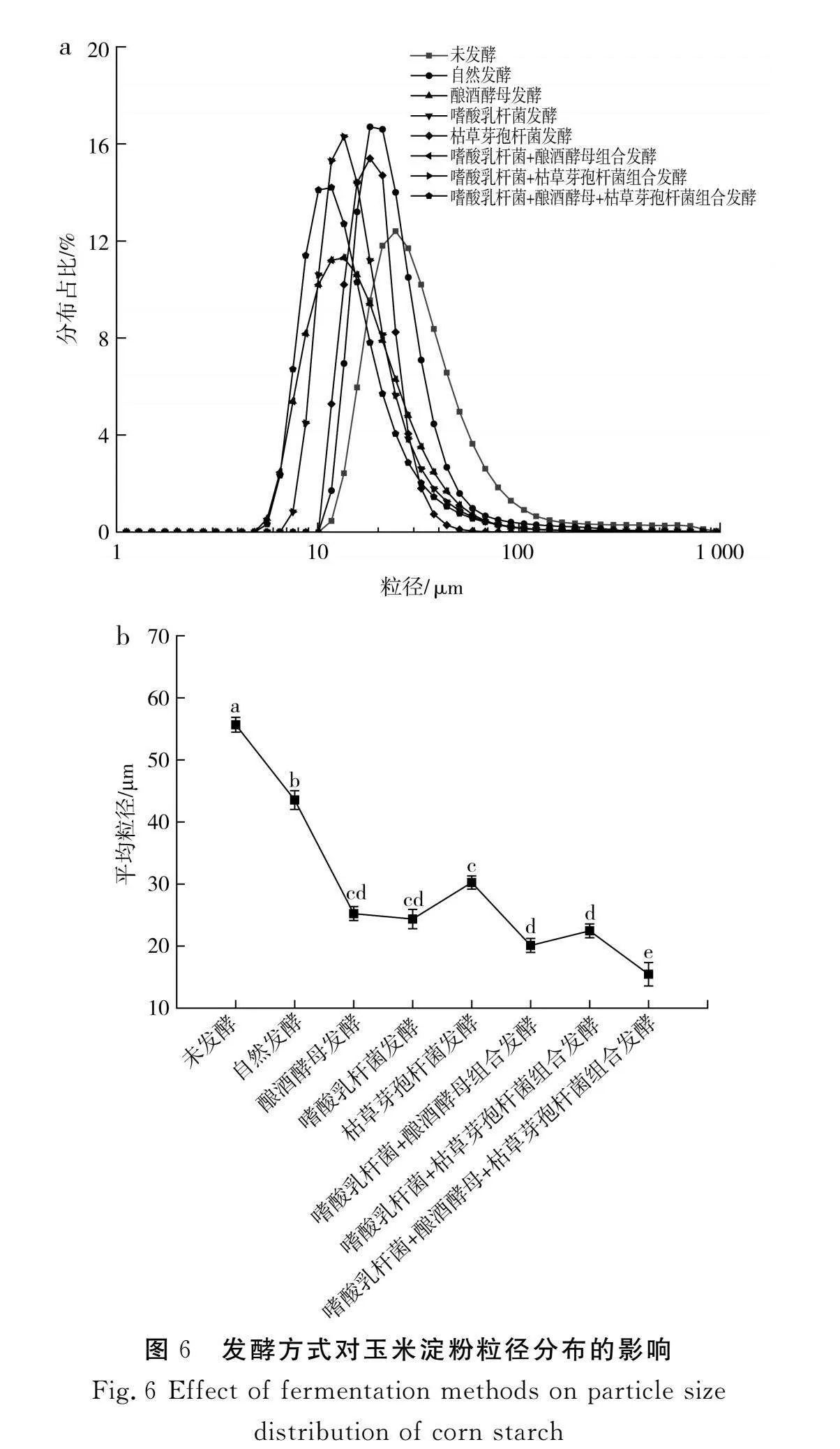
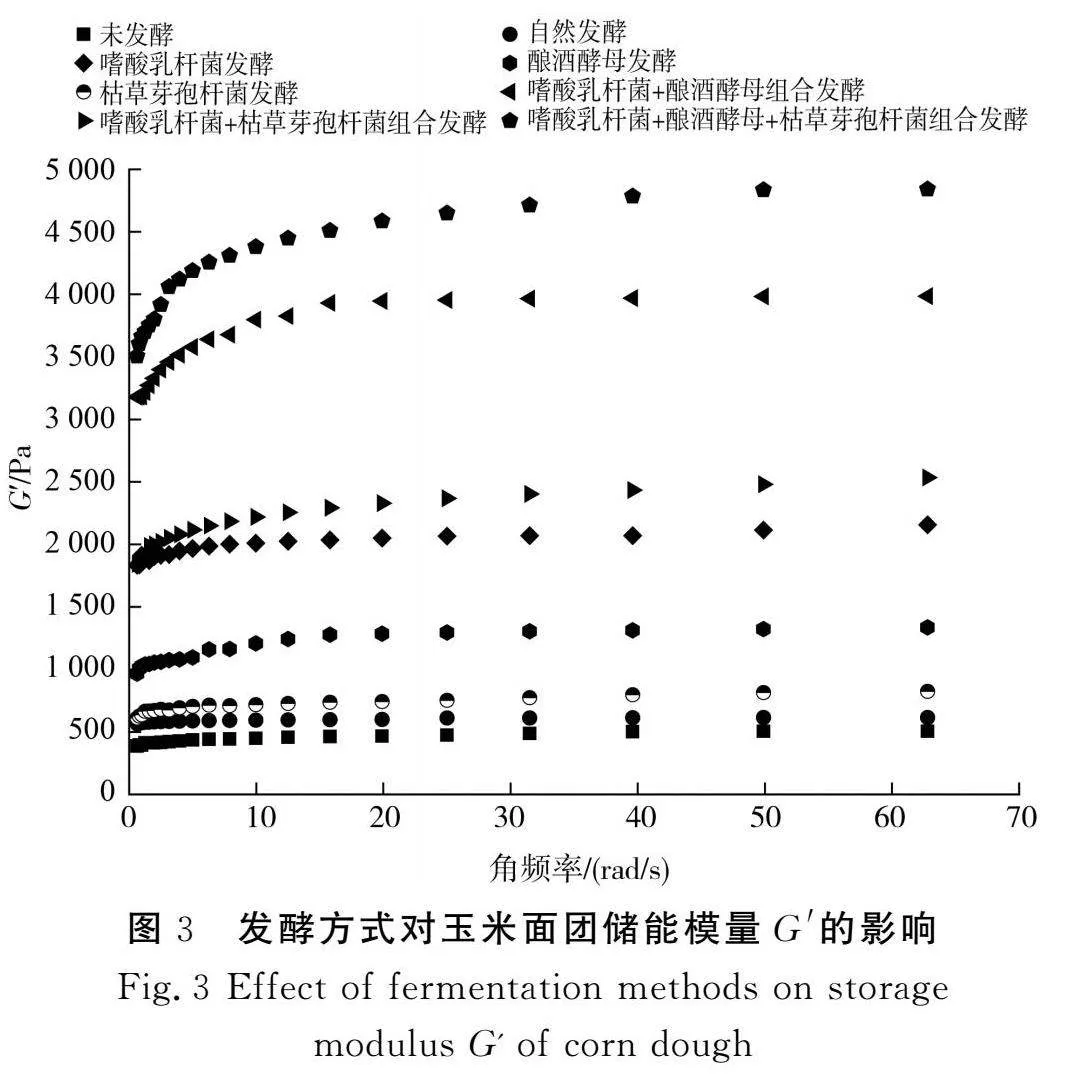

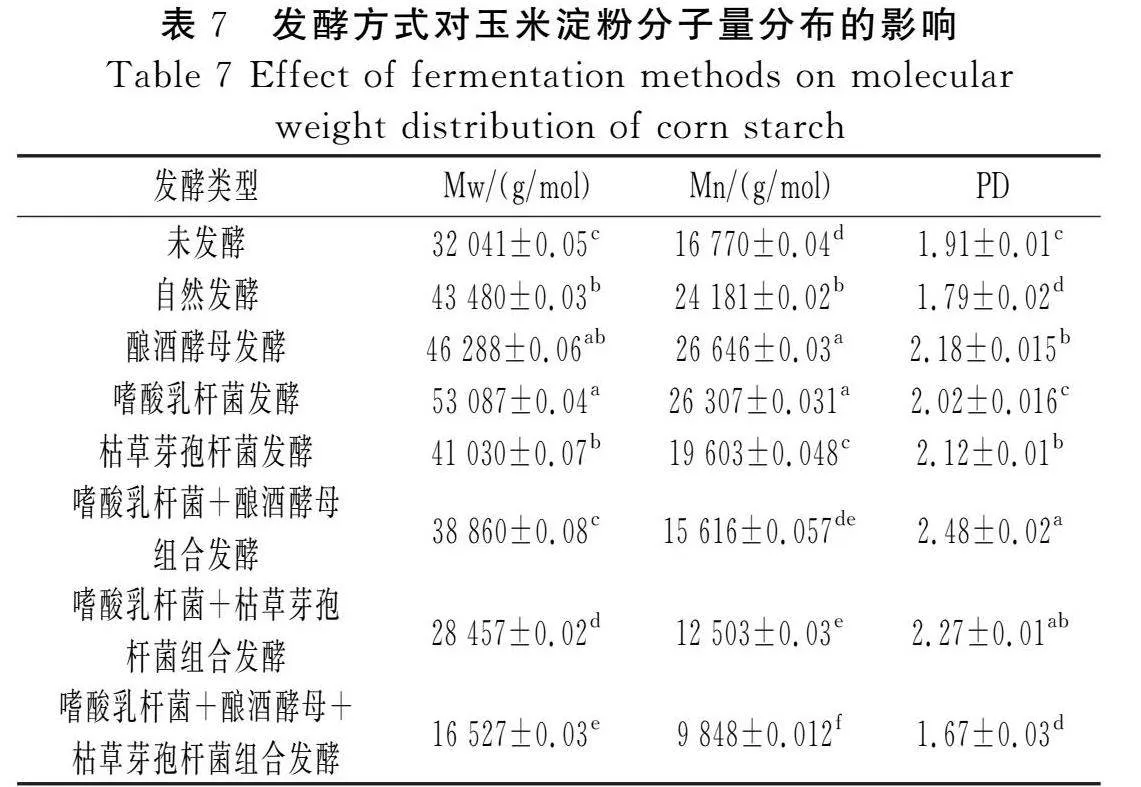
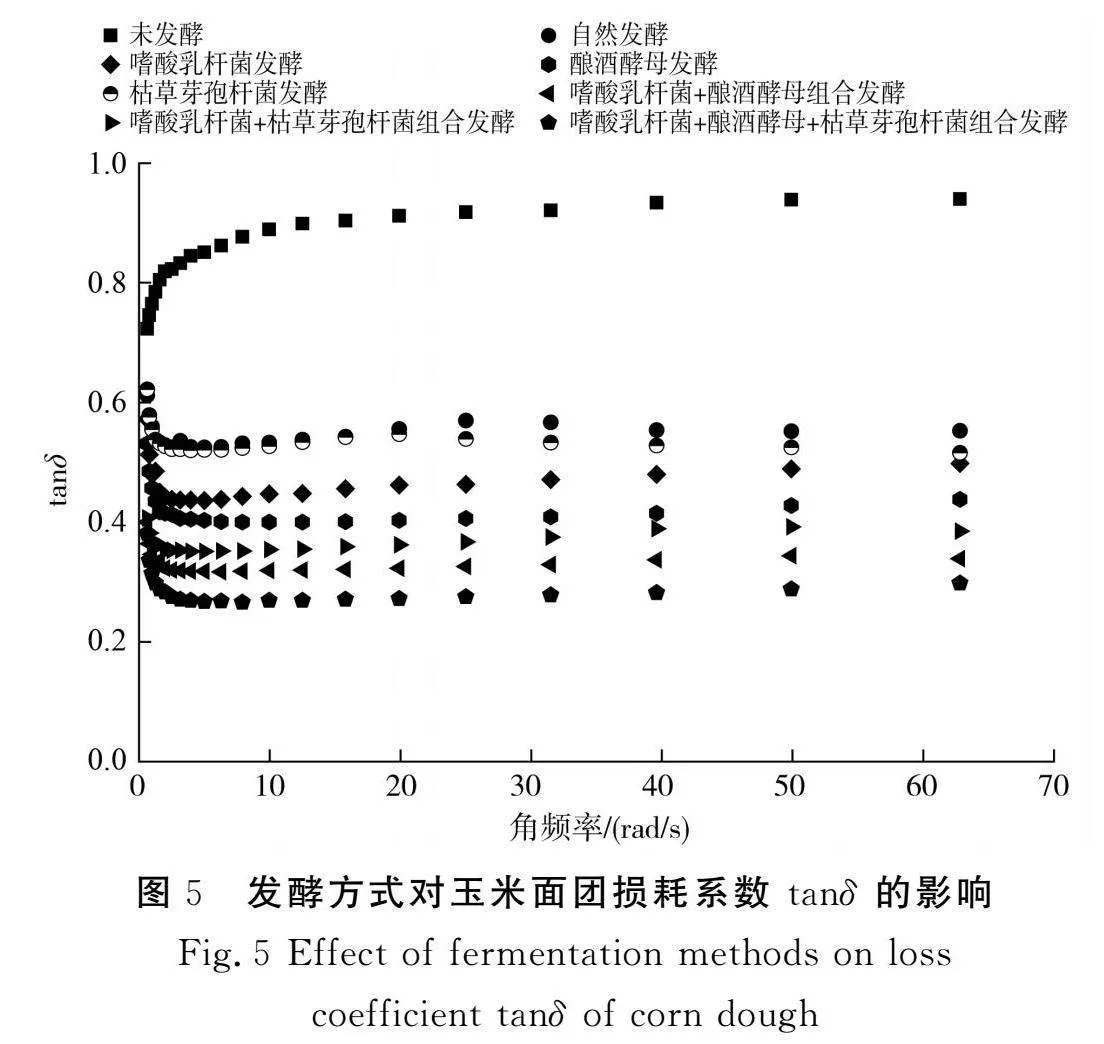
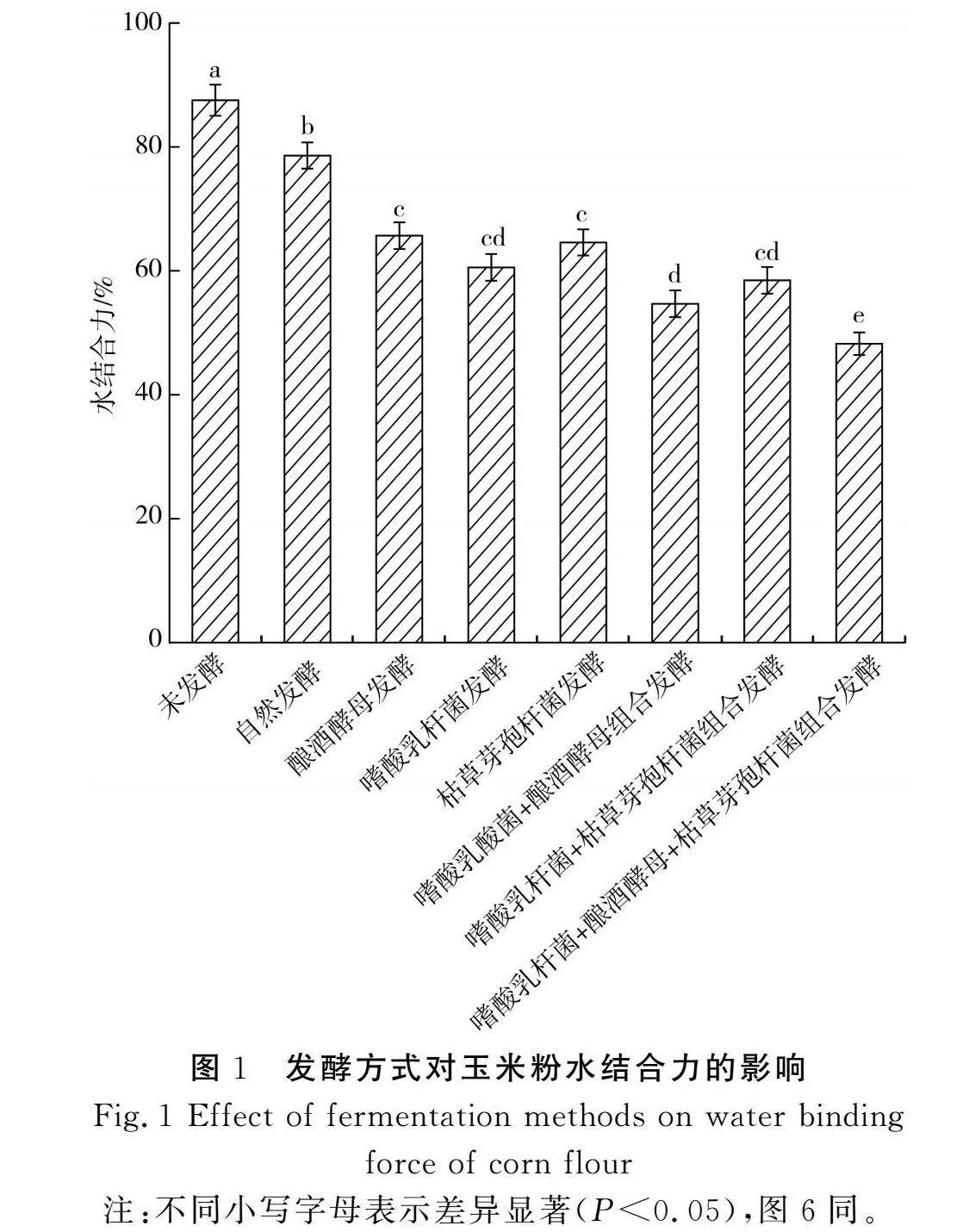

摘要:為進(jìn)一步探究如何通過發(fā)酵改善玉米粉的品質(zhì),推進(jìn)玉米在食品行業(yè)的發(fā)展,該研究以玉米碴為原料,對(duì)自然發(fā)酵、嗜酸乳桿菌、釀酒酵母和枯草芽孢桿菌以單一及組合發(fā)酵方式下玉米粉的加工特性進(jìn)行研究,并對(duì)淀粉精細(xì)結(jié)構(gòu)進(jìn)行相關(guān)性分析。結(jié)果表明,與未發(fā)酵相比,發(fā)酵使玉米粉的水結(jié)合力、凝沉性、衰減值和回升值顯著降低(Plt;0.05),玉米粉的凝膠強(qiáng)度和黏度顯著提高(Plt;0.05),與單菌發(fā)酵相比,組合發(fā)酵對(duì)玉米粉的理化特性影響更顯著(Plt;0.05),發(fā)酵后玉米面團(tuán)的黏彈性提高(Plt;0.05),硬度降低(Plt;0.05),且嗜酸乳桿菌+釀酒酵母組合發(fā)酵后玉米面團(tuán)的黏彈性最高,嗜酸乳桿菌+釀酒酵母+枯草芽孢桿菌組合發(fā)酵后玉米面團(tuán)的彈性最大;對(duì)其淀粉精細(xì)結(jié)構(gòu)進(jìn)行分析,結(jié)果表明發(fā)酵后淀粉的粒徑和結(jié)晶度顯著降低(Plt;0.05),單菌發(fā)酵的淀粉Mw和Mn增加,組合發(fā)酵的淀粉Mw和Mn減少;發(fā)酵后的淀粉A和B1鏈分布較廣。菌種組合發(fā)酵對(duì)玉米粉加工特性和淀粉結(jié)構(gòu)的影響較大,為玉米粉的深加工提供了參考。
關(guān)鍵詞:發(fā)酵;精細(xì)結(jié)構(gòu);玉米粉;加工特性;嗜酸乳桿菌;釀酒酵母;枯草芽孢桿菌
中圖分類號(hào):TS213.4""""""文獻(xiàn)標(biāo)志碼:A"""""文章編號(hào):1000-9973(2025)02-0093-08
Effect of Fermentation Methods on Processing Characteristics and
Starch Fine Structure of Corn Flour
HAN Chun-ran, YA Han-qin, NA Zhi-guo*, NIU Ji-chao, LIU Si-qi, LIU Tong
(Key Laboratory of Cereal Food and Cereal Resources in Heilongjiang Province, College of Food
Engineering, Harbin University of Commerce, Harbin 150028, China)
Abstract: In order to further investigate how to improve the quality of corn flour by fermentation and promote the development of corn in the food industry, in this study, with corn grit as the raw material, the processing characteristics of corn flour by natural fermentation, single or combined fermentation of Lactobacillus acidophilus, Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Bacillus subtilis are investigated, and the correlation analysis of the starch fine structure is conducted. The results show that compared with unfermented corn flour, fermentation significantly reduces the water binding force, coagulability, attenuation value and retrogradation value of corn flour (Plt;0.05), and significantly increases the gel strength and viscosity of corn flour (Plt;0.05). Compared with single strain fermentation, combined fermentation has more significant effects on the physicochemical properties of corn flour (Plt;0.05). After fermentation, the viscoelasticity of the corn dough increases (Plt;0.05) and the hardness decreases (Plt;0.05), and after the combined fermentation of Lactobacillus acidophilus+Saccharomyces cerevisiae, the viscoelasticity of the corn dough is the highest. The combined fermentation of Lactobacillus acidophilus+Saccharomyces cerevisiae+Bacillus subtilis results in the highest elasticity of the corn dough. The fine structure of its starch is analyzed, and the results show that the particle size and crystallinity of starch significantly decrease after fermentation (Plt;0.05). The Mw and
Mn of starch ""by single strain fermentation increase, while Mw and Mn of starch by combined fermentation decrease. After fermentation, starch A and B1"chains are widely distributed. The combined fermentation of strains has a great effect on the processing characteristics and starch structure of corn flour, which has provided references for the deep processing of corn flour.
Key words: fermentation; fine structure; corn flour; processing characteristics; Lactobacillus acidophilus; Saccharomyces cerevisiae; Bacillus subtilis
玉米(Zea mays)是世界上最重要的谷物之一,其籽粒含有豐富的營(yíng)養(yǎng)物質(zhì),是供能的良好來源[1],但玉米的食用品質(zhì)較差,其硬度高、黏性低,玉米粉在增稠性方面的發(fā)展遠(yuǎn)不如其他谷物,且玉米粉與水混合形成的面團(tuán)黏彈性差,不易加工[2],這些缺陷在很大程度上限制了玉米在食品加工中的應(yīng)用,因此,改善玉米加工特性、擴(kuò)展玉米加工方式對(duì)玉米在食品行業(yè)的應(yīng)用具有重要意義。……

