一種求解時間分數階非線性拋物型方程的等階混合有限元



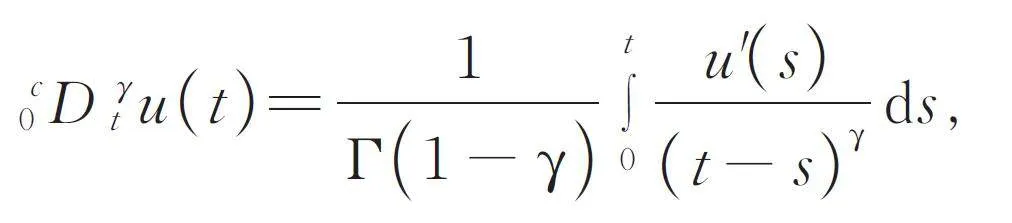




摘 要: 為數值求解時間分數階非線性拋物型方程,本文提出了一種k 次等階混合有限元.為獲得有限元的完全離散格式,本文在時間方向上考慮經典L1 格式、在空間方向上使用基于局部投影的穩定混合有限元. 本文定義了混合投影并得到了有限元的誤差估計. 數值算例驗證了理論結果.
關鍵詞: 混合有限元; 時間分數階非線性拋物型方程; 逼近
中圖分類號: O241. 82 文獻標志碼: DOI: 10. 19907/j. 0490-6756. 2024. 041004
Abstract: In this paper, we propose a k-th equal-order mixed finite element for the numerical solutions of thetime fractional nonlinear parabolic equations. To obtain the fully discrete scheme of finite element, the classicalL1 scheme is used in the time direction and the stabilized mixed finite element method based on local projectionis used in the spatial direction. We define the mixed projection and give the error estimate for the finiteelement. Numerical examples verify the theoretical results.
Keywords: Mixed finite element; Time fractional nonlinear parabolic equation; Approximation
1 Introduction
Parabolic equations are extensively employedto describe the unsteady physical phenomena suchas the diffusion of molecules in porous medium(air, water, etc). Many problems in science and engineeringcan be described by linear or nonlinearparabolic equations. In particular, time fractionalparabolic equations arise in the cases where thereare spatial or temporal constraints[1]. Unfortunately,only very special cases of these equations can besolved analytically. Therefore, the stable numericalschemes for these equations have long been a hot researchtopic[2-5], in which the mixed finite element isone of the promising methods.
Generally, a mixed finite element method hastwo variational forms, one is the dual mixed finiteelement method, the other is the primal mixedvariational form, which is based on the function spaces H (div;Ω)×L2 ( Ω) and (L2 ( Ω))2 ×H 1 ( Ω),respectively. Note that the velocity element neednot be imposed such high regularity and only needto be square integrable. Based on the primal mixedvariational form, Chen et al. [2] developed a P 20 ?P1mixed finite element method to solve some ellipticproblems. Weng et al. [3] considered the Crank-Nicolson P 20 ?P1 mixed finite element approximationsfor the linear parabolic problems. Shi et al.[4,5]applied a P 20 ?P1 mixed finite element method tosolve the nonlinear parabolic equations and nonlinearSchr?dinger equations. However, the abovementionedfinite element function spaces are so specialthat the inf-sup condition must be strictly satisfied.In this sense, some known and widely used finiteelement spaces are thereby excluded. Meanwhile,it is not easy to construct such mixed finiteelement function spaces in high-dimensional problems.
To overcome these difficulties, some stabilizationmethods have been proposed. The classical stabilizationmethods are Petrov-Galerkin type[6], somesymmetric stabilization methods are proposed[7,8].Subsequently, due to the computationally convenientof equal orders, especially the lowest equal orderpair in parallel processing and multigrid context,a stabilized finite element method based on local projectionis proposed for the Navier-Stokes equations[9]. However, most of these stabilization methodscan be applied only to steady or integral differentialequations rather than fractional differential equations.
Nowadays, many numerical methods havebeen proposed for time fractional equations. In Ref.[10], Gao and Sun constructed a compact differencemethod to solve the fractional sub-diffusionproblems. In this method the L1 scheme is appliedfor the time-fractional derivative and the fourthorderaccuracy compact approximation for the spatialdirection, then the stability and convergence ofthe finite difference scheme in maximum norm areobtained by using the energy method. Jin et al. [11]proposed a finite element method to solve the time fractional diffusion equation with non-smooth initialdata and established optimal with respect to theregularity of the solution error estimates. In Ref.[12], the semi-linear time fractional reaction diffusionequation was considered by using the mixed finiteelement method.
In this paper, we propose a k-th equal-ordermixed finite element for the following time fractionalnonlinear parabolic equation (0 lt; γ lt; 1):
c0 D γt u - Δu + f (u) = g, in Ω × (0,T ]
with the boundary condition u ( x,t ) = 0,on ?Ω ×(0,T ] and initial value u ( x,0) = u0 ( x) in Ω ×{ 0 },where g is a given function, c0 D γt u is the Caputo derivativein time,say,
and Γ ( ? ) is the gamma function. Assume that Ω is abounded domain in R2 with boundary ?Ω. For the reactionterm f (u), we assume that there exists a constantL gt; 0 such that | f '(u) |≤ L,u'≤ L. We proposea (P disk - 1 ) 2 ?P ck mixed finite element approximationand a new (P ck ) 2 ?P ck stabilized mixed finiteelementmethod to solve the equation. We introducea mixed projection and give the error estimates.Moreover, we give some numerical examples toverify the theoretical results.
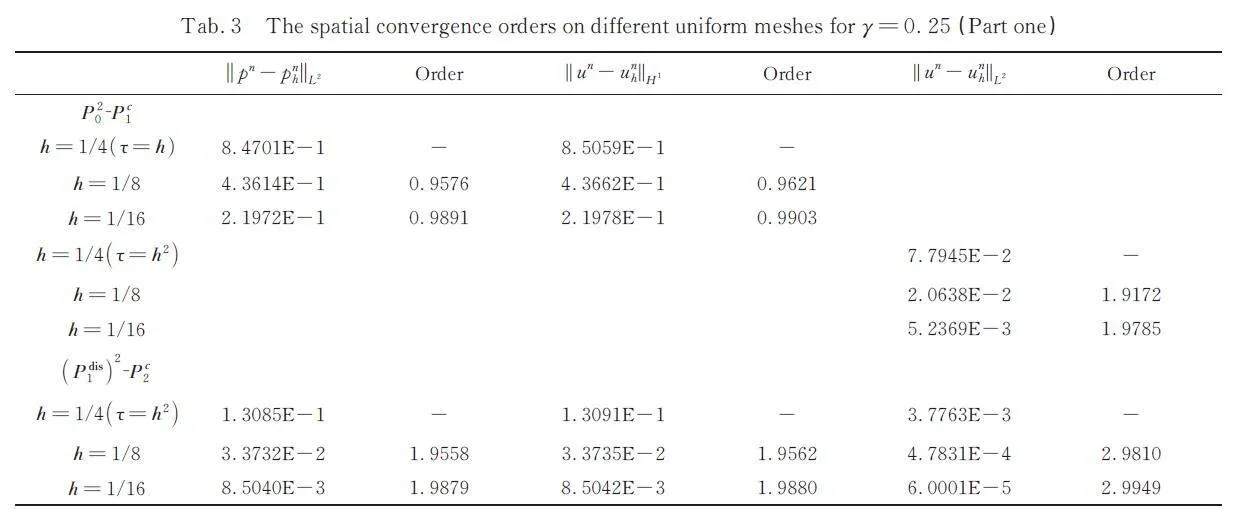
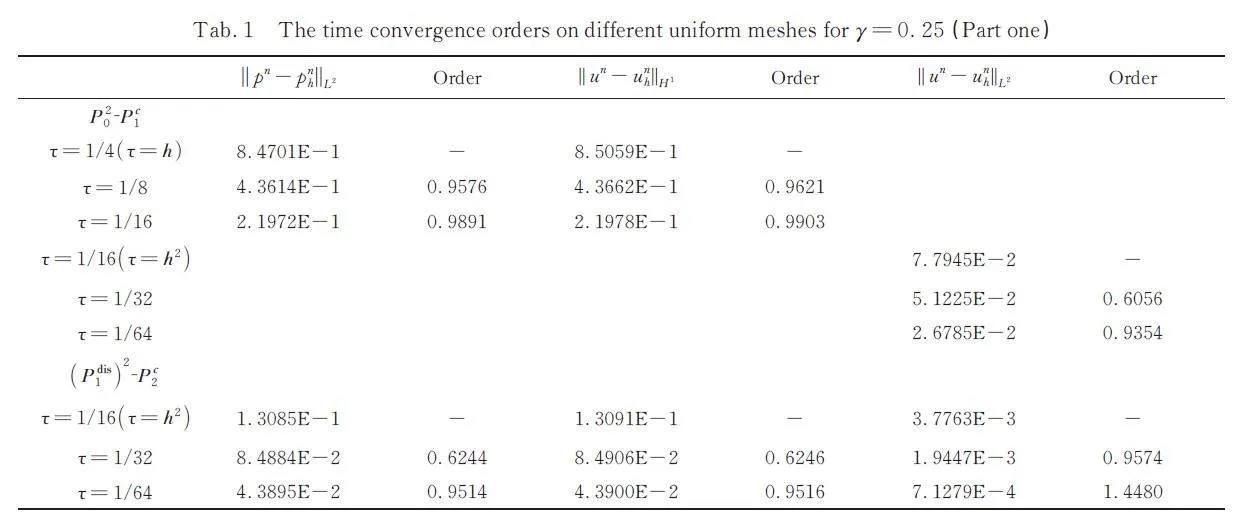
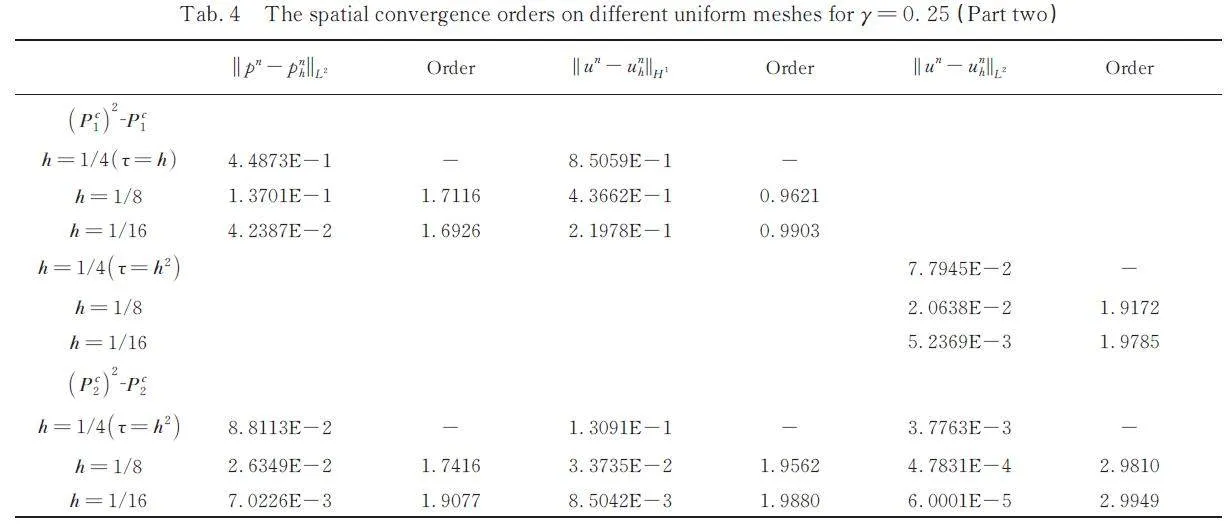
The rest of this paper is organized as follows.Noting that the velocity p = ?u only needs to besquare integrable, we give a primal mixed formulationin Section 2. In Section 3, we address thestable conforming finite element approximation forthe (P disk - 1 ) 2 ?P ck pair and we give a stabilized finite elementapproximation for the (P ck ) 2 ?P ck pairs, thenwe analyze the error results. In Section 4, numericalexamples are given. In Section 5 we symmarize theobtained results.
2 Stable conforming finite elementfor the ( P disk - 1 ) 2 ?P ck pair
Let Q = (L2 ( Ω) )2 and V = H 10 ( Ω). Settingp = ?u, we get the following primal mixed formula?tion of( 1). It aims to find ( p,u) ∈ Q× V such that
In this paper, a new mixed finite elementmethod is proposed for the time fractional nonlinearparabolic equations, and the existence and uniquenessare obtained. We hav addressed the correspond?ing finite element for the (P disk - 1 ) 2 ?P ck and (P ck ) 2 ?P ck finiteelement pairs and given some numerical examplefor the (P disk - 1 ) 2 ?P ck, (P ck ) 2 ?P ck pairs (k = 1,2)pairs to verify the theoretical results. Obviously,this method can be expanded to the three dimensioncase easily.
References:
[1] Havlin S, Selinger R B, Schwartz M, et al. Randommultiplicative processes and transport in structureswith correlated spatial disorder [J]. Phys Rev Lett,1988, 61: 1438.
[2] Chen S C, Chen H R. New mixed element schemesfor second order elliptic problem [J]. Math NumerSin, 2010, 32: 213.
[3] Weng Z, Feng X, Huang P. A new mixed finite elementmethod based on the Crank-Nicolson schemefor the parabolic problems [J]. Appl Math Model,2012, 36: 5068.
[4] Shi D Y, Yan F N, Wang J J. Unconditional superconvergenceanalysis of a new mixed finite elementmethod for nonlinear Sobolev equation [J]. ApplMath Comput, 2016, 274: 182.
[5] Shi D Y, Yang H J. Unconditionally optimal error estimatesof a new mixed FEM for nonlinearSchr?dinger equations [J]. Adv Comput Math,2019, 45: 3173.
[6] Johnson C, Navert U, Pitkaranta J. Finite elementmethods for linear hyperbolic problems [J]. ComputMeth Appl M, 1984, 45: 285.
[7] Burman E, Hansbo P. Edge stabilization for Galerkinapproximations of convection-diffusion-reaction problems[ J]. Comput Meth Appl M, 2004, 193: 1437.
[8] Codina R. Stabilization of incompressibility and convectionthrough orthogonal sub-scales in finite elementmethods [J]. Comput Meth Appl M, 2000,190: 1579.
[9] Jian L, He Y, Chen Z. A new stabilized finite elementmethod for the transient Navier – Stokes equations[ J]. Comput Meth Appl M, 2007, 197: 22.
[10] Gao G H, Sun Z Z. A compact finite differencescheme for the fractional sub-diffusion equations [J].J Comput Phys, 2011, 230: 586.
[11] Jin B, Lazarov R, Zhou Z. Error estimates for asemi-discrete finite element method for fractional orderparabolic equations [J]. SIAM J Numer Anal,2013, 51: 445.
[12] Li Q, Chen Y, Huang Y, et al. Two-grid methodsfor semi-linear time fractional reaction diffusion equationsby expanded mixed finite element method [J].Appl Numer Math, 2020, 157: 38.
[13] Shi F, Yu J, Li K. A new stabilized mixed finiteelementmethod for Poisson equation based on two localGauss integrations for linear element pair [J]. IntJ Comput Math, 2011, 88: 2293.
[14] Lin Y, Xu C. Finite difference/spectral approximationsfor the time-fractional diffusion equation [J]. JComput Phys, 2007, 225: 1533.
[15] Li D, Liao H L, Sun W, et al. Analysis of L1-GalerkinFEMs for time-fractional nonlinear parabolic problems[ J]. Commun Comput Phys, 2018, 24: 86.
[16] He Y, Jian L. A stabilized finite element methodbased on local polynomial pressure projection for thestationary Navier – Stokes equations [J]. Appl NumerMath, 2008, 58: 1503.
[17] Layton W, Tobiska L. A two-level method withbacktracking for the Navier-Stokes equations [J].SIAM J Numer Anal, 1998, 35: 2035.
(責任編輯: 周興旺)
基金項目: 國家自然科學基金(11971337)

