Direct measurement of nonlocal quantum states without approximation
Gang Yang(楊岡), Ran Yang(楊然), Yan-Xiao Gong(龔彥曉), and Shi-Ning Zhu(祝世寧)
National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructure,School of Physics and Collaborative Innovation Center of Advanced Microstructures,Nanjing University,Nanjing 210093,China
Keywords: direct measurement,quantum tomography,nonlocal quantum state
1.Introduction
Quantum states are the cornerstone of quantum information.An efficient method for characterizing quantum states is of importance for quantum information applications as well as quantum fundamentals.Quantum state tomography(QST)[1–12]is a conventional method for reconstructing the density matrix of a state,which typically involves a large number of projection measurements on several basis states, followed by a complex reconstruction algorithm.[13]
Alternatively,Lundeenet al.[14]proposed an efficient direct measurement scheme to determine a quantum wavefunction through weak measurements.This approach eliminates the complex reconstruction algorithm in previous methods,allowing for direct measurement of the wavefunction.Subsequently, this technique aroused great interest[25,26]and was developed to mixed states,[15–19]discrete two-dimensional[20]and higher-dimensional quantum systems.[21–24]Moreover,these schemes can be extended to arbitrary coupling strength,even to strong measurements.[27–31]
Recently, the direct measurement of wavefunctions with nonlocal entanglement was demonstrated in Ref.[32].This scheme utilizes the modular values[34]to obtain the weak value of the observable product,which allows for direct measurement of nonlocal states.Afterward,this approach was further extended to the nonlocal density matrix.[35]Despite the advantages of these schemes, such methods can only obtain the approximated values rather than precise ideal ones.
In this paper,we propose a new scheme to directly measure arbitrary two-party nonlocal quantum states.We consider the scenario that the two parties are spatially separated over a long distance.And the interaction of the two parties is physically forbidden.We use a specialized interaction between the system and a meter to avoid the influence of redundant terms on the measurement of the density matrix elements.It enables the direct measurement of the ideal values of the matrix elements without any approximations.Our approach overcomes the low precision problem in weak-coupling schemes,thus enabling a more accurate characterization of nonlocal systems.
The paper is arranged as follows.In Section 2 we give an introduction to the direct measurement using weak values and modular values.Then in Section 3 we present our scheme and analyze the precision numerically.Discussions and conclusions are made in Section 4.
2.Direct measurement using weak values and modular values

However, implementing this method on nonlocal quantum systems is not straightforward.Consider a nonlocal state composed of two space-like separated subsystemsAandB,with a basis given by the tensor product of local bases of the two subsystems,denoted as|n〉=|j,l〉=|j〉A|l〉B(|j〉A ∈HA,|l〉B ∈HB).In this case,the direct weak measurement scheme needs to introduce a nonlocal Hamiltonian ?H∝?PA?PB.Such a Hamiltonian implies an instantaneous interaction between the two distant subsystems, which is contradictory to the principle of causality in relativity.In fact, under certain coupling strengths,weak values of observable products can also be obtained by measuring local modular values.[34]In analogy to the measurement of weak values, the modular value of ?Acan be defined as〈A〉m=〈ψfin|e-ig?A|ψin〉/〈ψfin|ψin〉.When the relevant observable is a projection,it satisfies the corresponding relationship with weak values as

However, the direct measurement schemes using weak values and modular values are both not theoretically exact in characterizing the system state.In these schemes,a small parameter is employed,and the first-order approximation on the parameter is implemented with all the higher-order terms discarded from the measurement of the final state of the meter.However, if we could avoid the contribution of the higherorder terms, we would directly extract the precise modular information.With such an idea,we propose a direct measurement scheme for nonlocal quantum states,which can directly read out the theoretical value of the density matrix elements without relying on approximations.
3.Direct measurement of nonlocal quantum states without approximation
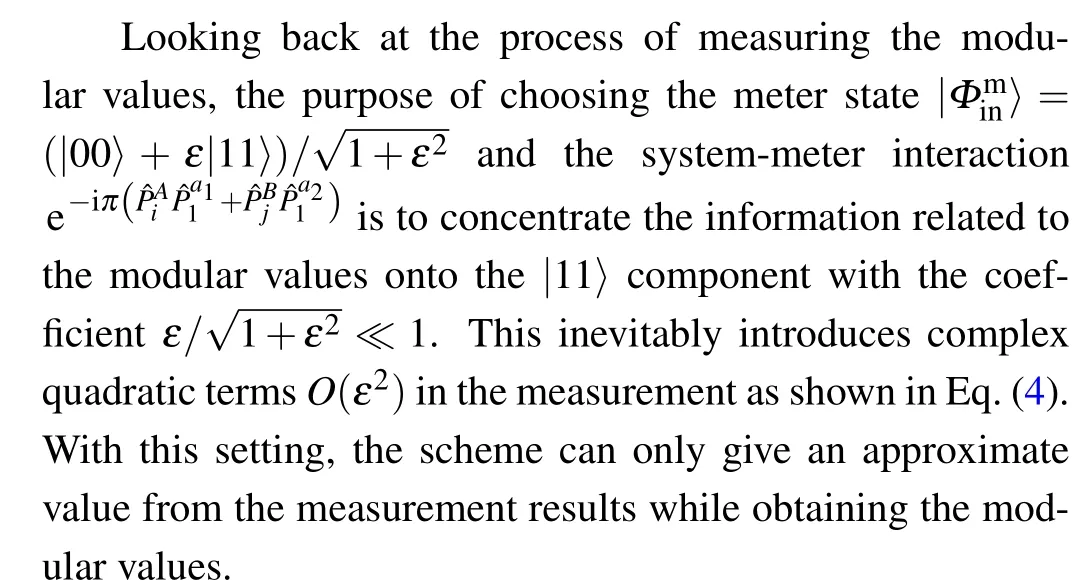

Fig.1.Direct measurement of nonlocal states.(a)The measurement of PAB in Section 3,or〈PiA +PBj m in Section 2.(b)The measurement of PA in Section 3 orPAim in Section 2.(c)The measurement of PB in Section 3 or〈PBjm in Section 2.The system and the meter interact via controlled-Z operations using the basis|i〉〈i|and|j〉〈j|(or|i〉〈i|/|j〉〈j|)as control bits for addressing,followed by post-selection on the system using|f〉〈f|,where|f〉=|f1〉A|f2〉B.




Therefore,traversing through all the basis{|n〉〈n|}allows us to obtain the complete distribution.

Fig.2.The average precision of direct characterization of arbitrary two-particle two-dimensional states using both our method and approximated modular value schemes.Our method shows better precision as N increases.
To evaluate the precision improvement of our scheme,we numerically analyze the fidelity between states measured using different methods and the ideal states.We define the precision of characterization schemes as average infidelity

4.Discussion and conclusions
We propose a new direct measurement scheme of nonlocal quantum state without any approximations.This scheme effectively avoids the impact of redundant terms on measuring the density matrix elements through a special system–meter coupling.Consequently,it enables the direct measurement of the ideal value of nonlocal density matrix element without taking approximations.Our numerical results show the advantage of higher precision compared to the approximation methods.Our approach overcomes the inherent low precision associated with weak coupling schemes, which facilitates a more accurate characterization of nonlocal systems and opens up new avenues for directly measuring nonlocal quantum states.Furthermore,it is possible to extend our method to direct characterization of multiparticle states by utilizing entangled ancillary states,such as GHZ state.The specific density matrix elements can be directly acquired from the measurement statistics with elaborate quantum circuits and post-selections.
Acknowledgements
Project supported by National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No.2019YFA0705000)and the National Natural Science Foundation of China(Grant No.11974178).
- Chinese Physics B的其它文章
- The application of quantum coherence as a resource
- Special breathing structures induced by bright solitons collision in a binary dipolar Bose–Einstein condensates
- Effect of short-term plasticity on working memory
- Directional-to-random transition of cell cluster migration
- Effect of mono-/divalent metal ions on the conductivity characteristics of DNA solutions transferring through a microfluidic channel
- Off-diagonal approach to the exact solution of quantum integrable systems

