Quasi-synchronization of fractional-order complex networks with random coupling via quantized control
Hongwei Zhang(張紅偉), Ran Cheng(程然), and Dawei Ding(丁大為)
School of Electronics and Information Engineering,Anhui University,Hefei 230601,China
Keywords: complex network, fractional-order, random coupling, time-varying delay, quasi-synchronization,quantized control
1.Introduction
As critical dynamic systems composed of a large collection of interactive dynamical nodes,[1]complex networks (CNs) have received considerable attention in the past decade because of their potential applications in biological networks,[2]social networks,[3]neural networks,[4]and other fields.[5,6]Therefore, certain characteristics of CNs,such as stability,[7]coordination,[8]optimization,[9]and synchronization[10]have achieved good research results in these fields with increasing efforts.
Synchronization is a significant dynamic property of CNs and is the focus of this study.In many studies, researchers have focused on setting the controller to make the error of the complex network system approach zero with the advancement of time.[11–14]However, because of the existence of system disturbance in practical applications and because this disturbance is difficult to eliminate completely,sometimes the synchronization error cannot fully converge to zero.[15]Therefore,based on the above considerations,it is particularly necessary to study how to control the upper limit of the synchronization error by setting a controller to achieve quasisynchronization.Recent research on quasi-synchronization has also made progress.[16,17]In Ref.[16], Xuet al.studied a fractional-order CN model with delay and obtained global quasi-synchronization results by setting an appropriate intermittent controller.In Ref.[17], the network model was extended from a real number domain to a complex number domain, and the quasi-synchronization problem of fractionalorder neural networks in complex-valued systems was solved by separating the systems.
The concepts of fractional calculus and integer-order calculus were proposed simultaneously.[18]As a favorable mathematical tool,fractional calculus has the advantage that integerorder calculi such as genetics and memory can describe the system.[19,20]In recent years, they have been widely used by researchers to process physical systems.[21–24]Therefore,it is necessary to use fractional calculus to describe CNs in the study of synchronization phenomena.For example, in Ref.[25], Baoet al.studied adaptive synchronization for a class of fractional-order coupled neural networks (FCNNs)with output coupling.In Ref.[26],the authors investigated the stability and synchronization problems of fractional-order delayed multilink complex networks with nonlinear hybrid coupling.
For CNs, the coupling interference and latency between systems are inevitable due to channel crosstalk and transmission rate limitations.Undoubtedly,these two factors will impact the stability of the system.[27–29]Therefore, it is important to consider random coupling disturbances and time delays in the synchronization of complex networks.For example,in Refs.[30,31]and in the above-mentioned literature,only time delay is often considered to be constant, but in an actual system, with the evolution of network dynamics characteristics,the time delay often changes with time rather than being immutable,and may break the stability of the complex networks dynamics system.Therefore, it is more practical to consider time-varying delays in a network-dynamics system.
In recent years,researchers have proposed numerous synchronization control methods,such as adaptive control,[32]periodic intermittent control,[33]and pinning control.[34]In these control methods,researchers typically regarded a control signal as a continuous distortion-free signal without preprocessing it.However, in real life, when a signal is transmitted in a channel,signal attenuation distortion is often caused by the influence of the channel bandwidth or the channel itself.[35,36]To solve this problem,we quantify the signal before transmission such that the processed signal has good stability and antiinterference during the transmission process.This method,adopted for the control of CNs, is generally referred to as quantized control.In Ref.[37], Shiet al., through the quantized control method, studied the finite- and fixed-time synchronization problems of complex networks using the theory of linear matrix inequality.In Ref.[38],Fanet al.studied the synchronization of delayed neural networks using the quantized control theory.
Based on the above considerations,quasi-synchronization of FCNs via quantized control was the main focus of this study.The main contributions of this study are as follows:
1.Our research is centered around addressing the issue of quasi-synchronization in CNs by incorporating fractional calculus techniques.
2.Through logarithmic quantizer, the appropriate quantization controller is designed to make the complex network achieve quasi-synchronization.Simultaneously,this study considers the quasi-synchronization state of the complex network without delay and time-varying delay and designs different quantization controllers.Compared with Ref.[16], it undoubtedly expands the practicability of the results of the study.
3.In FCNs, both random coupling and external disturbance are simultaneously considered.In the absence of delay and time-varying delay, we have successfully achieved quasi-synchronization,ensuring system stability under the influence of these two types of disturbances.Furthermore,we are able to accurately calculate the maximum upper bound of quasi-synchronization error,and by adjusting the parameters of the controller,we can control the upper limit of synchronization error.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows: In Section 2, we present the concepts necessary for the discussion, lemmas, and the FCNs model.Based on the fractional Lyapunov stability theory, we present the results of quasisynchronization in both non-delay and time-delay scenarios in Section 3.Section 4 presents the correctness of the theoretical results obtained from numerical simulations.Finally,Section 5 summarizes this study.
NotionsLet R and Rnbe real number set andndimensional Euclidean space,respectively.Inand||·||denote the unit matrix and Euclidean norm, respectively; and||·||∞r(nóng)epresents the infinity norm,||·||1represents the 1-norm;?denotes the Kronecker product, andn×nset of matrices is represented by Rn×n.LetHbe a square matrix of ordern, if for any nonzero column vectorx,there isxTHx>0,wherexTdenotes the transpose ofx,thenHis called a positive definite matrix, otherwise,His called a negative definite matrix, andλmax(H)is the maximum eigenvalue of matrixH.
2.Preliminaries
In this section, for preferably setting the problem, some essential definitions of the logarithmic quantizer and Caputo fractional calculus are reviewed, helpful lemmas are presented,and a mathematical model of FCNs is developed.
Definition 1[38]In the fractional derivative of orderαfor a given functionf(t), its fractional derivative of orderαis defined as

Specifically,E1,1(r)= er.
2.1.Model description
Considering FCNs withNnodes, the dynamic formulas for each node can be expressed as follows:
whereα ∈(0,1),xi(t)=(xi1(t),xi2(t),...,xin(t))T∈Rn,i=1,2...,N, represents the state vector ofi-th node,f(xi(t)):Rn →Rnare continuous functions.If a connection betweenj-th node toi-th node (i/=j) exists, thenli j ≥0; otherwise,li j= 0 and the diagonal elementslii=-∑Nj=1,j/=i lij,(i=1,2,...,N).G=diag(g1,g2,...,gm)∈Rndenotes the internal coupling strength matrix, which refers to the coupling relationship between different dimensional parameters in the network nodes.Here,c(t) denotes the random coupling strength representing the variation of the external coupling strength between nodes in a complex network over time;ωi(t)denotes an external disturbance,andui(t)represents the quantized controller.
The dynamic formula for an isolated node is as follows:
whereL>0,x(t),y(t)∈Rn.
Lemma 1[14]Givenx,y ∈Rn, there existsε ∈(0,+∞)and anyn×nreal matrixQ ∈(0,+∞)such that the following formula holds:

3.Main result
In this section, we design the corresponding quantized controller such that the network system in different states can achieve quasi-synchronization,and the quasi-synchronization criteria of FCNs with random coupling are obtained under non-delay and time-varying delays.
3.1.Quasi-synchronization of FCNs
Theorem 1Assume that Assumptions 1 and 2 hold, if there exists a constantε1>0,we can gaink*>such that

According to Assumptions 1 and 2 and Lemma 1,we can obtain the fractional derivative ofV(t):
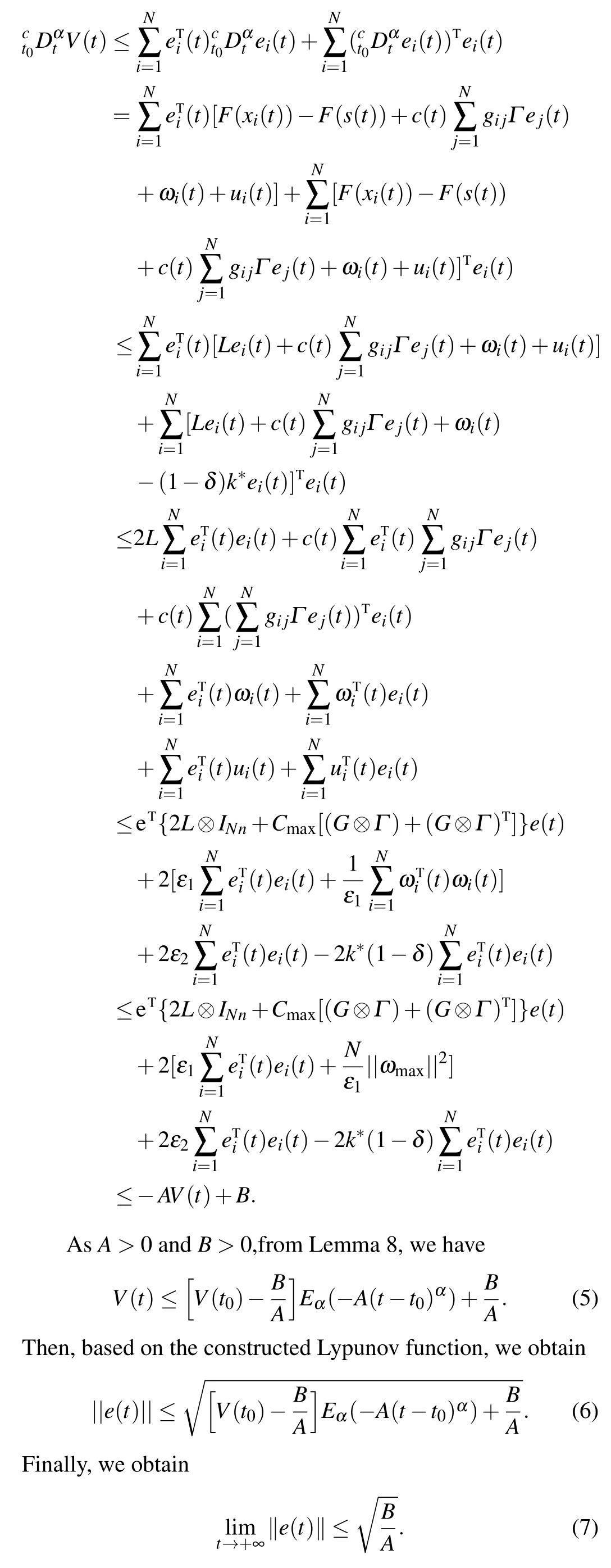
The proof is completed.
3.2.Quasi-synchronization of FCNs with time-varying delays
Consider the following FCNs composed ofNidentical nodes with time-varying delays,described by

From Assumptions 1 and 2 and Lemma 2,we can calculate the fractional derivative ofV(t)as

Then,according to condition(19),we obtainV1≤0.
ForV2(t),we can obtain:
wheni/=j
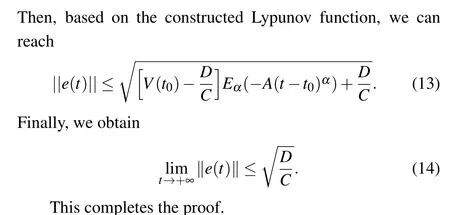
Remark 1 The result of Theorem 2 is based on the FCNs system with time-varying delay.If we changeτ(t)toτ,that is,the type of time delay in system(8)is a fixed time delay, the results of Theorem 2 will be applicable.Thus, the results of Theorem 2 include the consideration of the FCNs system with fixed time delay.
4.Numerical simulations
In this section,we mainly conduct numerical simulations on the two theorems presented in Section 3.By observing the dynamic behavior of the nodes in the given FCNs, we have verified the correctness of Theorems 1 and 2.
Example 1 The FCNs dynamics formula of threedimensional Lorenz system is given,and the number of nodes is four.We have
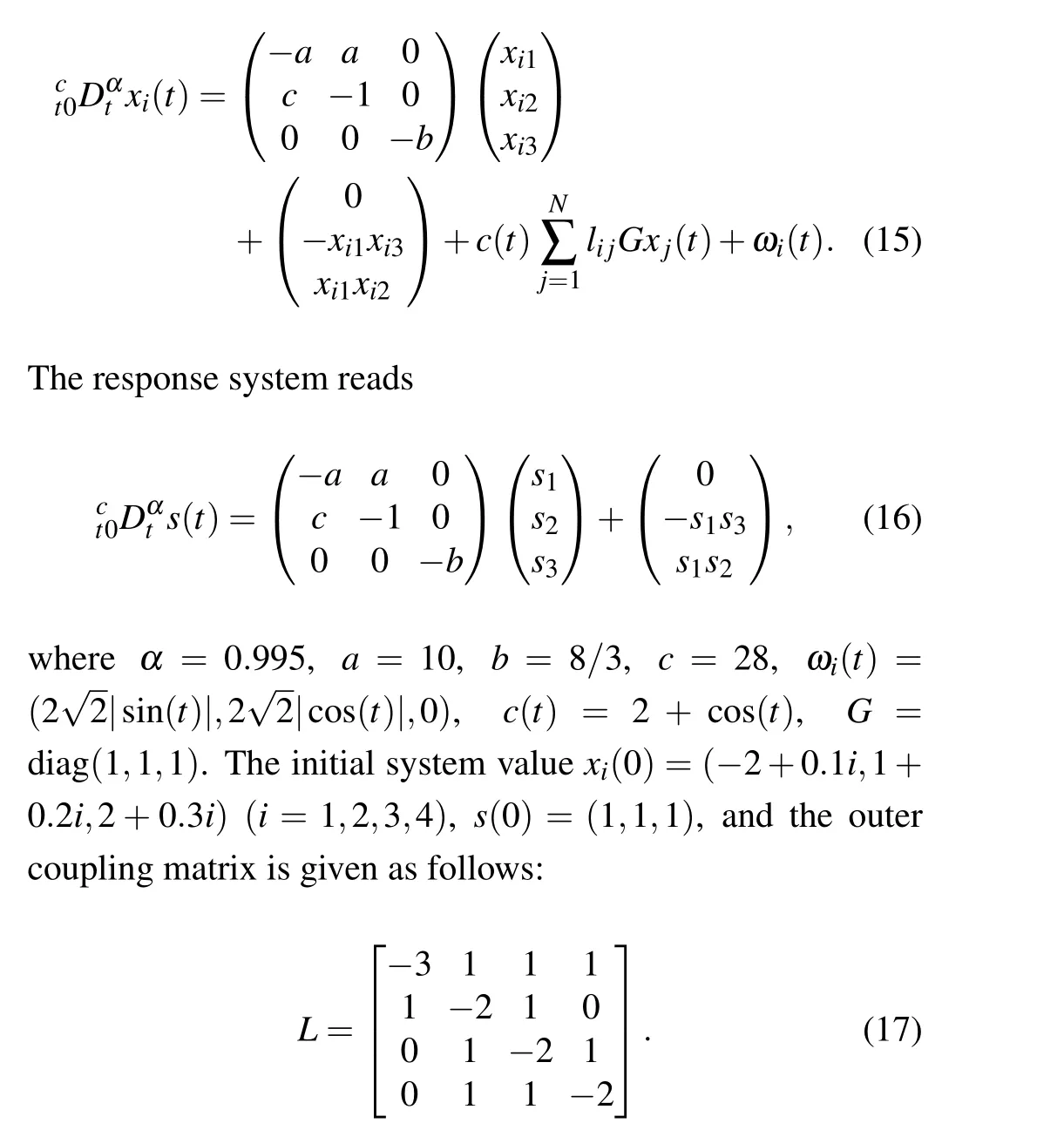
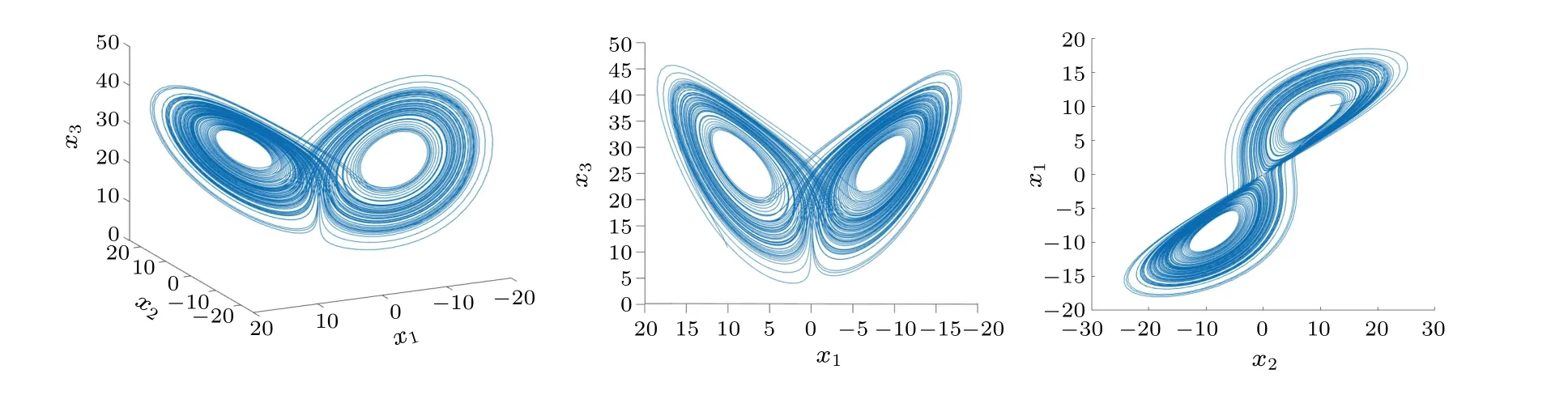
Fig.1.Phase plot of the Lorenze system(α=0.995).
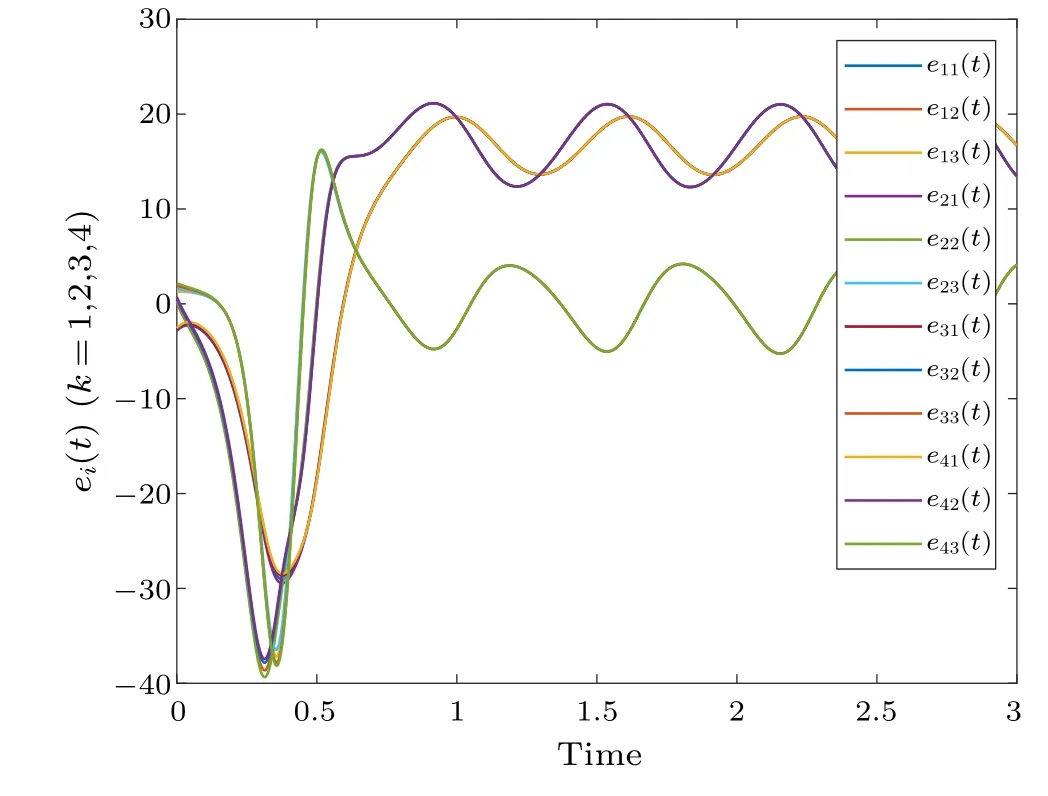
Fig.2.Profiles of ei(t)of the error system without control.


Figure 2 shows the synchronization errorei(t) fluctuations under uncontrolled conditions.Figure 3 shows the synchronization quantized errorq(ei(t)) fluctuations under uncontrolled conditions.Figure 4 shows that the synchronization errorsei(t) fluctuate within an interval.Figure 5 shows that the synchronization quantized errorsq(ei(t)) fluctuate within an interval.Figure 6 displays the quasi-synchronization error||e|| under uncontrolled conditions.Figure 7 shows the quasi-synchronization error||e||, which indicates that quasisynchronization is realized.Through a simulation comparison,we observe that the results of Theorem 1 are correct.
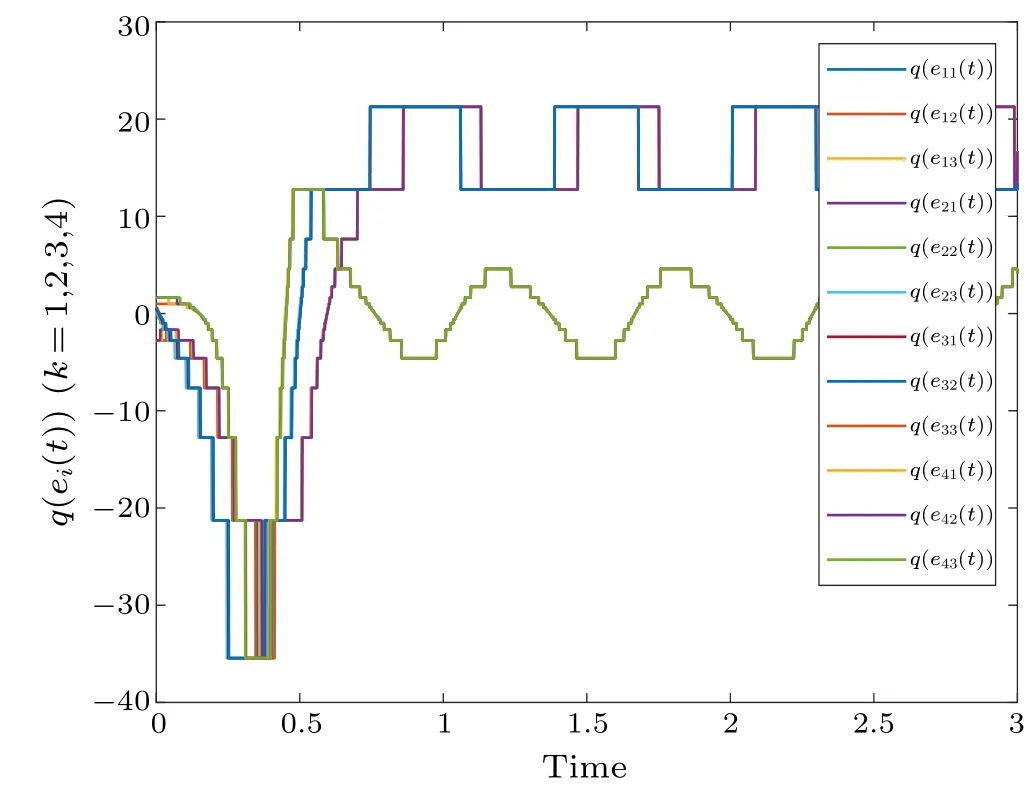
Fig.3.Profiles of q(ei(t))of the error system without control.
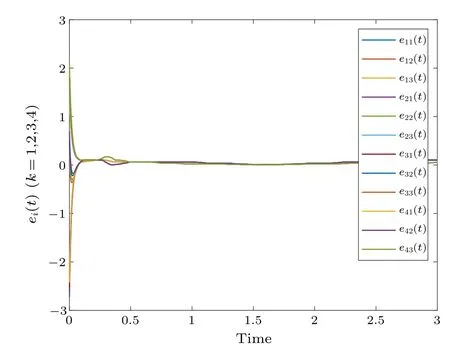
Fig.4.Profiles of ei(t)of the error system.

Fig.5.Profiles of q(ei(t))of the error system.
Example 2 Considering the three-dimensional FCNs composed of 4 nodes with time-varying delay, the node dynamics system is the same as Example 1:
wherea=10,b=8/3,c=28,ωi(t)=(0,2-e-t,0)T,c(t)=|cos(t)|,τ(t)=|sin(t)|.The system initial value isxi(0)=(4+0.1i,1+0.1i,4-0.1i)(i=1,2,3,4),s(0)=(1,2,1).The settings for the logarithmic quantizers are the same as those in Example 1.
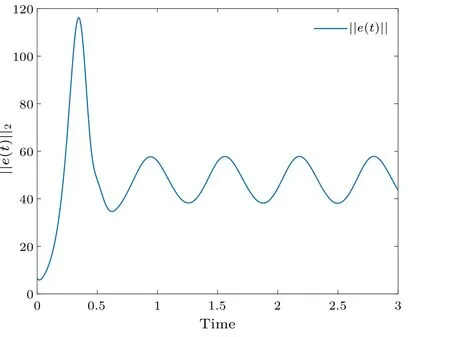
Fig.6.Profiles of||e(t)||of the error system without control.

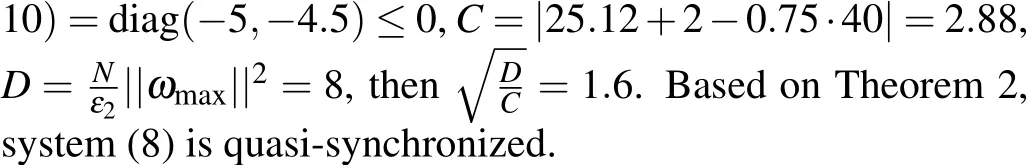
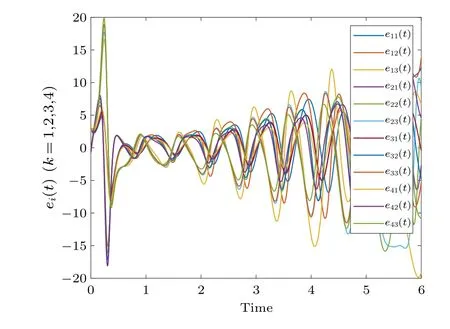
Fig.8.Profiles of ei(t)of the time-varying delay error system without control.
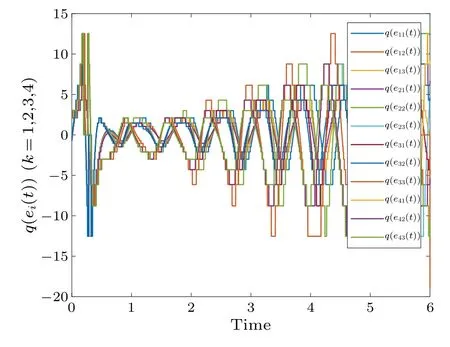
Fig.9.Profiles of q(ei(t))of the time-varying delay error system without control.
Fig.10.Profiles of ei(t)of the error system with time-varying delay.
With a time-varying delay, Fig.8 shows the synchronization errorei(t)fluctuations under uncontrolled conditions.Figure 9 shows the synchronization quantized errorq(ei(t))fluctuations under uncontrolled conditions.Figure 10 shows that the synchronization errorsei(t) fluctuate within an interval.Figure 11 shows that the synchronization quantized errorsq(ei(t)) fluctuate within an interval.Figure 12 shows the quasi-synchronization error||e|| under uncontrolled conditions.Figure 13 shows the quasi-synchronization error||e||,which indicates that quasi-synchronization is realized.
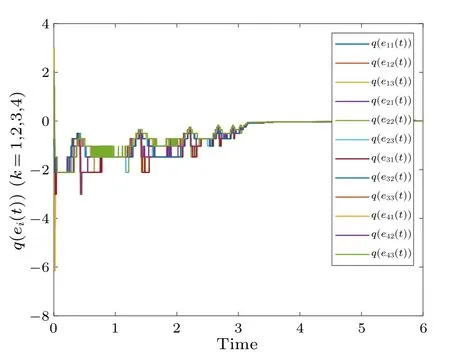
Fig.11.Profiles of q(ei(t))of the error system with time-varying delay.
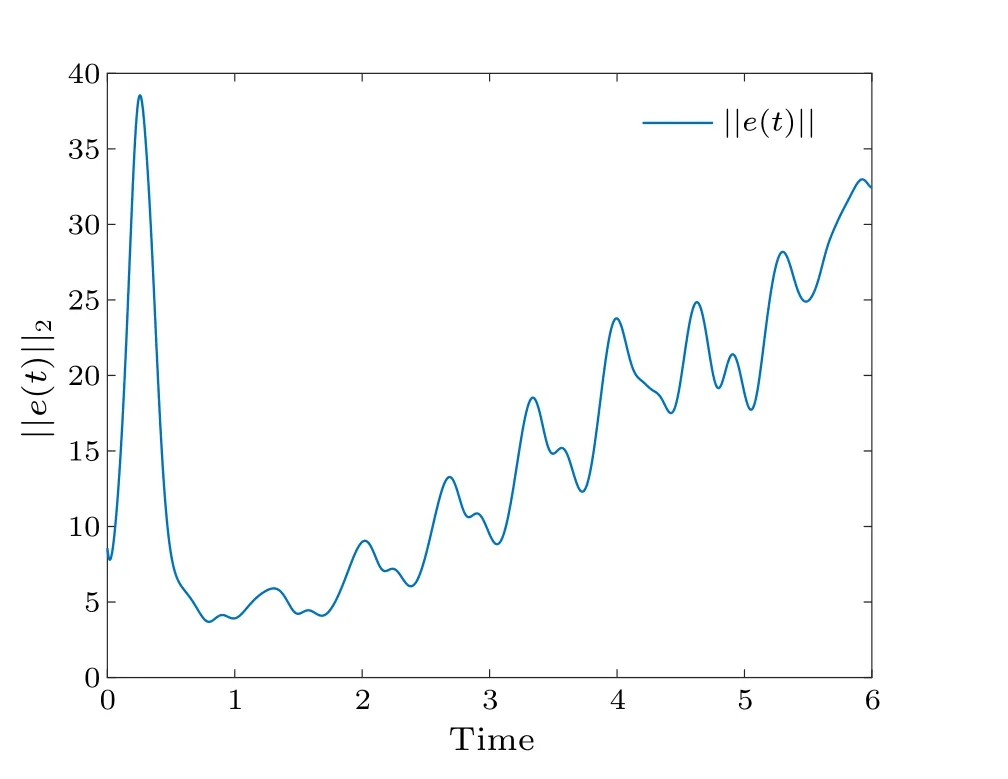
Fig.12.Profiles of||e(t)||of the error system without control.
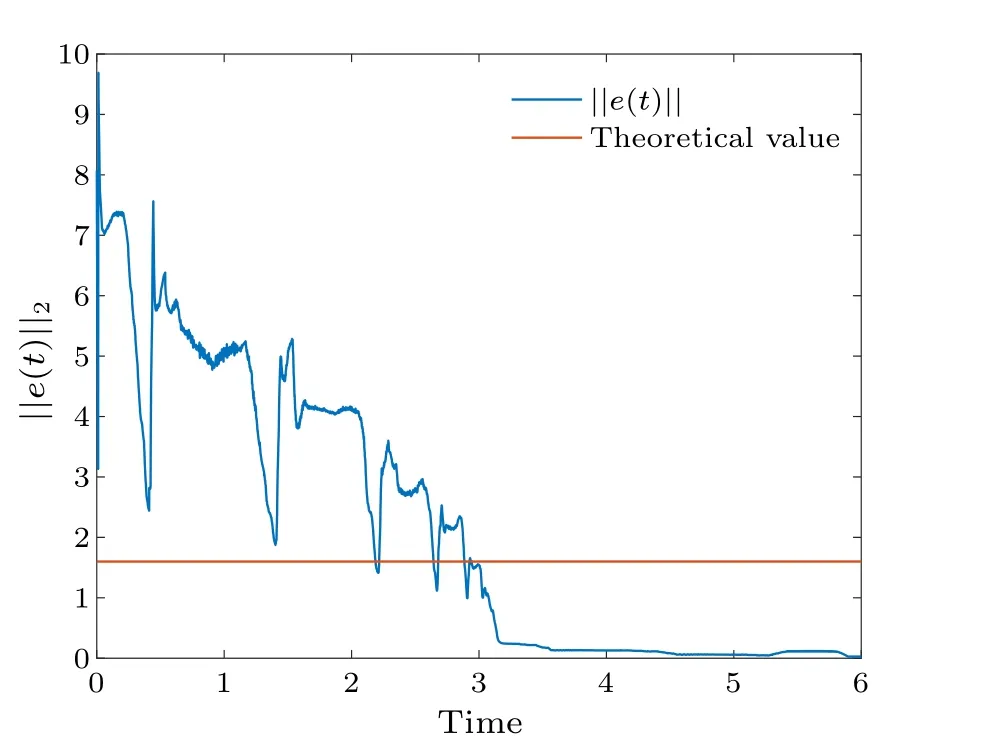
Fig.13.Profiles of||e(t)||of the error system with time-varying delay.
5.Conclusion
In summary, we have investigated quasi-synchronization of FCNs.Firstly, using the given logarithmic quantizer theory and the Lyapunov stability theory, we design a new quantitative feedback controller and obtain sufficient criteria such that FCNs with random coupling can achieve quasisynchronization.Secondly,we study an FCN model with random coupling and time-varying delays.Another quantized controller is designed to obtain the quasi-synchronization criterion in this model.Notably, the upper bound of quasisynchronization in both the cases can be adjusted by setting the relevant controller parameters.Finally,we prove the validity of our theory with two numerical examples.In the future,we will focus on the use of new control methods such that the time upper bound to achieve quasi-synchronization of FCNs can be controlled to achieve finite-time quasi-synchronization of FCNs.
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by the Anhui Provincial Development and Reform Commission New Energy Vehicles and Intelligent Connected Automobile Industry Technology Innovation Project.
- Chinese Physics B的其它文章
- The application of quantum coherence as a resource
- Special breathing structures induced by bright solitons collision in a binary dipolar Bose–Einstein condensates
- Effect of short-term plasticity on working memory
- Directional-to-random transition of cell cluster migration
- Effect of mono-/divalent metal ions on the conductivity characteristics of DNA solutions transferring through a microfluidic channel
- Off-diagonal approach to the exact solution of quantum integrable systems

