基于CGA-BP神經網絡的好氧堆肥曝氣供氧量預測模型
丁國超,施雪玲,胡 軍
基于CGA-BP神經網絡的好氧堆肥曝氣供氧量預測模型
丁國超1,施雪玲1,胡 軍2※
(1. 黑龍江八一農墾大學信息與電氣工程學院,大慶 163319; 2. 黑龍江八一農墾大學工程學院,大慶 163319)
為提高好氧堆肥曝氣供氧量的曝氣效率以及預測精度,該研究利用遺傳算法(genetic algorithm, GA)對標準反向傳播(back propagation, BP)神經網絡的初始權值和閾值進行優化,再利用克隆選擇算法(clonal genetic algorithm, CGA)優化遺傳算法中的變異算子并復制算子,加快獲取最優參數的速度,構建基于CGA-BP神經網絡的曝氣供氧量預測模型。為驗證CGA-BP模型的有效性,與BP模型、GA-BP模型預測結果進行對比。試驗結果表明:克隆遺傳算法優化BP神經網絡能加快獲得最優解,效率相比BP模型和GA-BP模型分別提高了75.36%、51.30%;在曝氣供氧量預測模型中,CGA-BP模型具有更準確的預測效果,預測精度為99.65%,而BP模型與GA-BP模型預測精度分別為96.99%、99.26%;CGA-BP模型評價指標的均方誤差、平均絕對誤差、平均絕對百分誤差分別為0.003 4、0.038 9和0.350 6,均小于BP神經網絡和GA-BP神經網絡模型評價指標的誤差;利用CGA-BP好氧堆肥曝氣供氧量預測模型對好氧堆肥發酵過程進行精準曝氣,提高了3.22%的曝氣控制效率。由此可知CGA-BP神經網絡模型有更好的預測效果,可滿足好氧堆肥在發酵過程中曝氣供氧量的需求,提高曝氣效率,為精準控制曝氣提供更直接有效的方法。
模型;試驗;遺傳算法;好氧堆肥;曝氣供氧;BP神經網絡;CGA-BP神經網絡
0 引 言
中國年產各類有機廢棄物大約有45~50億t,其中農業廢棄物9.8億t、林業廢棄物1.6億t、有機生活垃圾1.5億t、畜禽糞污19億t左右[1-2]。隨意棄置未被處理的有機廢棄物不僅浪費大量資源,而且造成環境污染。好氧堆肥是對農業有機廢棄物無害化處理和資源化利用的有效方式之一[3-5]。好氧堆肥發酵過程中,堆肥中存在的微生物起著重要的作用,能促進堆肥反應的正常進行并充分反應并腐熟的堆肥才可作為有機肥產品用于農業施肥,提高作物產量而曝氣影響好氧堆肥中微生物的活性,能促進對有機物的氧化分解,曝氣裝置以及曝氣量在一定程度上決定著好氧堆肥發酵中有機物分解的效率和腐熟程度。因此,曝氣量在好氧堆肥發酵過程中起著至關重要的作用[6]。
國內外學者在精準控制曝氣方面已進行了一些研究,既往大多利用曝氣控制系統對曝氣量進行控制。李升等[7]分析自動曝氣系統運行情況,表明供氧量的控制精度穩定在1%左右,水中溶解氧的穩定程度超過0.9。沈軍等[8]利用精確曝氣系統研究污水池中的含氧量,通過參數控制,曝氣池內的含氧量變化不超過±0.5 mg/L,水質達標率提升5%左右。唐維等[9]利用污水進出水的指標建立遺傳算法優化BP神經網絡模型,預測生化池的曝氣量,測試樣本數據預測誤差在5%之內的比例達到98.67%。CHEN等[10]提出多變量最優控制模型,以曝氣過程中的最小耗能作為目標函數,保證系統正常供氧量時實現最優控制,能耗降低20%左右。上述研究均是對污水進行曝氣,與對好氧堆肥進行曝氣的原料、方式有差異,好氧堆肥曝氣量的研究大多是基于經驗對堆肥定量定時進行曝氣,按照一定通風速率間歇通氣[11-12],曝氣效率低。綜上,曝氣量作為影響堆肥發酵的重要因素,利用堆肥發酵過程中的多項指標與曝氣量之間的關系建立曝氣量預測模型,為能夠有效指導堆肥順利進行、提高曝氣控制效率奠定基礎。
本文從提高曝氣效率出發,利用克隆選擇算法(clonal genetic algorithm, CGA)的并行性、自適應性等優點,保持群體的多樣性,搜索最優解的速度較快,并結合遺傳算法優化BP(back propagation)神經網絡初始權值和閾值[13-16],建立CGA-BP神經網絡的曝氣供氧量預測模型,以預測好氧堆肥發酵所需的曝氣供氧量,縮短好氧堆肥發酵時間,為精準控制曝氣提供有力的技術支撐。
1 材料與方法
1.1 試驗裝置
好氧堆肥試驗以牛糞、牛糞沼渣、雞糞和玉米秸稈為好氧堆肥原料,由北京市密云區海華沼氣廠提供。其試驗設備放置于北京市農林科學院科技成果展示示范溫室,各原料初始理化參數如表1所示。
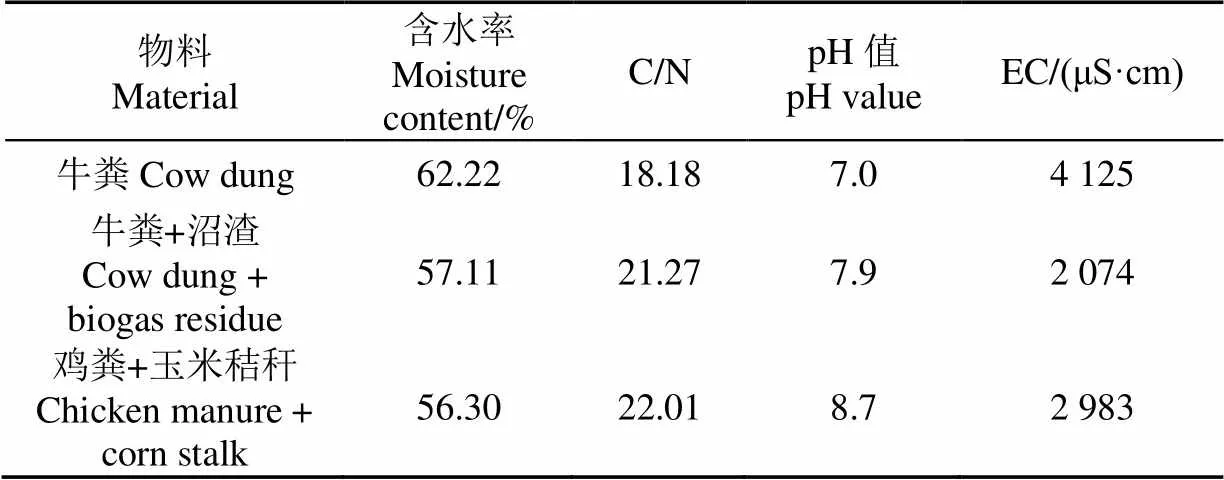
表1 堆肥原料初始理化參數
影響好氧堆肥發酵的因素主要包括堆體的溫度、有機質含量、含水率、pH值、發氧濃度以及碳氮比等[17-19]。本文試驗利用影響堆肥發酵的6個指標(溫度、濕度、氧氣濃度、室溫、pH值和EC(electrical conductivity)值與曝氣量的關系建立曝氣量預測模型。各指標參數數據信息通過發酵罐內的不同類型傳感器采集,好氧堆肥試驗裝置如圖1所示,利用自主研發的控制器獲取、傳輸并存儲傳感器數據。主要的傳感器參數如表2所示,其中EP-200傳感器是北京農林科學院根據DS18B20溫度傳感器與ECH2O土壤水分傳感器自主研發的無線溫濕度傳感器。
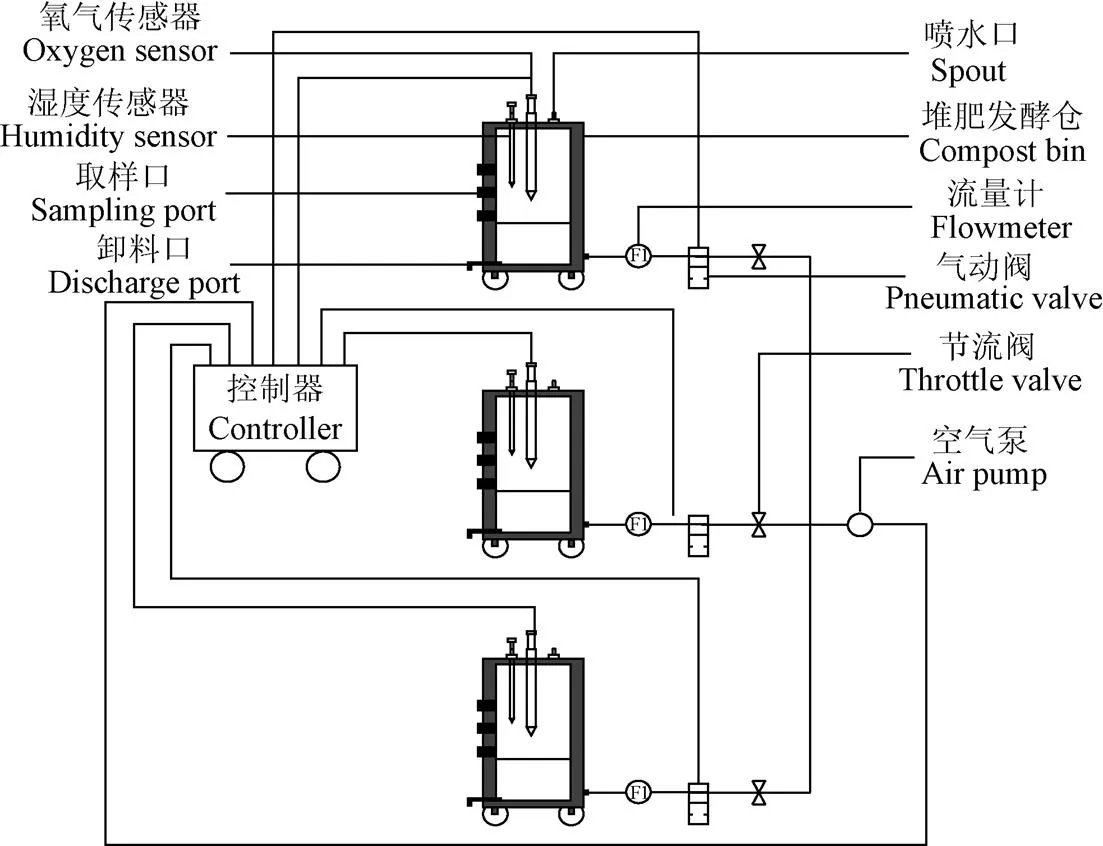
圖1 好氧堆肥試驗裝置結構簡圖
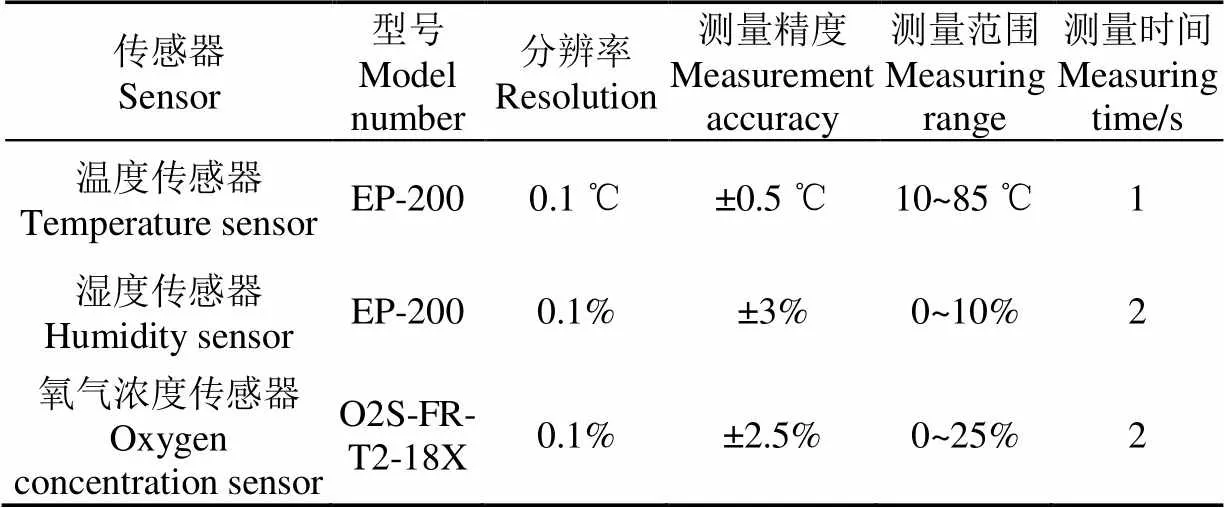
表2 溫濕度、氧氣濃度性能參數
1.2 數據來源及處理
1.2.1 數據來源及測定
試驗選取的數據來源于2019年1月4日-22日的1號反應器數據。從堆肥發酵開始,每間隔2 h利用EP-200溫濕度傳感器以及O2S-FR-T2-18X氧氣傳感器分別采集一次數據,并在3個不同高度的取樣口進行取樣,均勻混合后取出等量樣品180 g進行實驗室化驗分析,pH值與EC值分別采用按照國標土壤pH的測定(NY/T 1377-2007)和電導法測定。
1.2.2 數據預處理
好氧堆肥測定的指標數據單位均不同,為加快程序運行的收斂速度,對樣本數據做歸一化處理,本文采用mapminmax函數使數據均勻分布在[0,1]之間,其計算式為
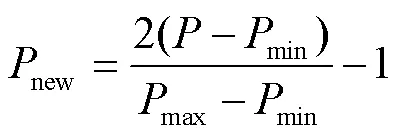
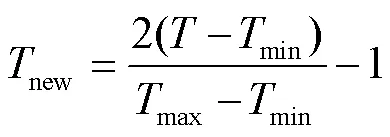
式中表示輸入數據,表示輸出數據;min和max分別表示的最小值和最大值;min和max分別為的最小值和最大值;new和new分別為歸一化后的輸入和輸出數據。
試驗修復樣本數據、剔除異常值后,選取數據樣本共268組,隨機選擇其中的218組數據作為測試集,余下的50組數據作為檢驗集。通過MATLAB分別建立BP、GA-BP、CGA-BP神經網絡曝氣供氧量預測模型,并計算模型誤差,分析模型預測精度、平均絕對誤差、平均絕對百分誤差、均方根誤差。
1.3 曝氣供氧量預測模型的建立
1.3.1 BP神經網絡
本次試驗的BP神經網絡的輸入層、輸出層的神經元個數分別設置為6和1。隱含層神經元個數會影響神經網絡的性能,本文采用經驗公式法來確定BP神經網絡隱含層的節點數,選取網絡誤差最小時對應的隱含層節點數。常用的經驗公式為
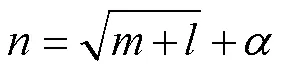
式中表示隱含層節點數目,為輸入層節點數目,為輸出層節點數目,為1~13之間的整數,根據式(3)確定隱含層神經元個數的范圍為3~15。
運行程序,在樣本集和訓練次數相同的情況下,計算得出不同隱含層節點數的均方誤差,如表3所示。從表3對比均方誤差可知,均方誤差最小,為0.000 447,對應的隱含層節點數為14。因此文中神經網絡模型隱含層節點數設為14。
通過上述分析,本次試驗建立的BP神經網絡好氧堆肥曝氣量的預測模型的輸入層、隱含層和輸出層的神經元個數分別為6、14、1,網絡結構如圖2所示。
1.3.2 GA-BP神經網絡
本文將遺傳算法與BP神經網絡相結合,建立基于遺傳算法優化BP神經網絡的曝氣供氧量預測模型,記作GA-BP神經網絡模型[20]。遺傳算法從任一初始種群出發,通過隨機選擇、交叉和變異操作獲取的最優參數對BP神經網絡的權值和閾值進行賦值和訓練[21],計算種群適應度值,最終找出基于GA-BP神經網絡的曝氣供氧量預測模型的最優個體。
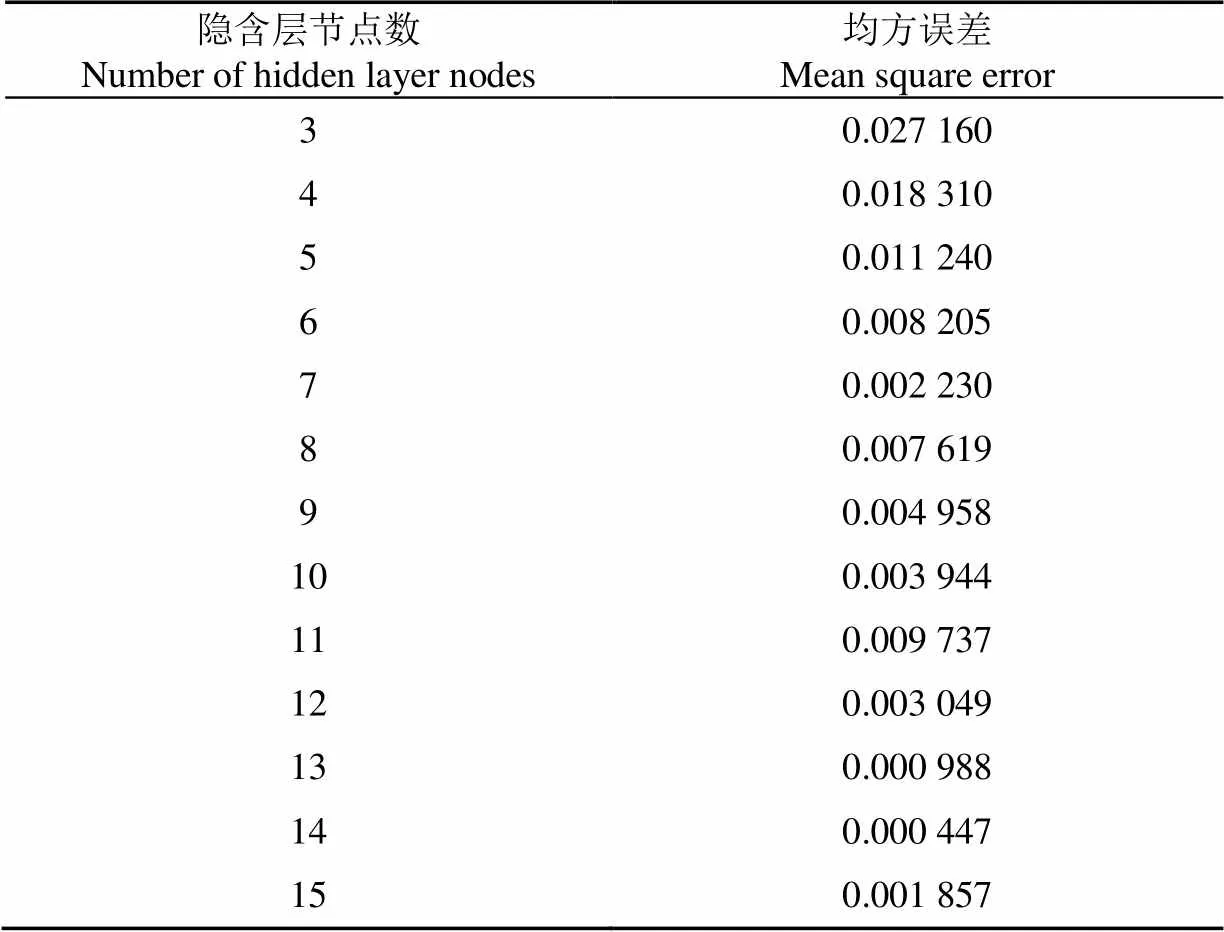
表3 不同隱含層節點數對應的均方誤差
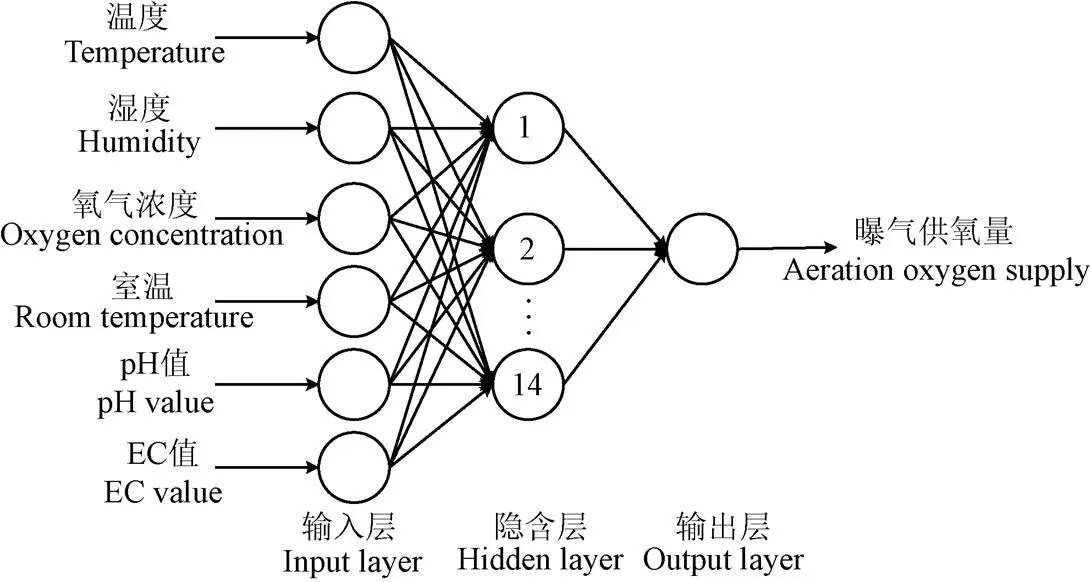
圖2 BP神經網絡模型結構圖
GA優化BP神經網絡算法參數主要有適應度函數、種群規模、迭代次數、交叉概率和變異概率,下面對主要參數設置進行確定:
1)適應度函數
用來度量種群中個體適應性的函數為適應度函數[22],試驗中的適應度函數為:預測輸出和期望之間的誤差平方和的倒數。
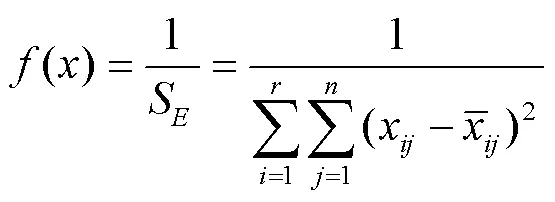
2)種群規模
初始解的個數即為種群規模,與個體基因的復雜程度有關。取值越大越利于找尋全局最優解,但運行時間過長。為了讓初始解在解空間分布均勻,考慮時間及效率成本取種群規模為10~80[23],本文的種群規模由優化精度比較確定,結果如表4所示。
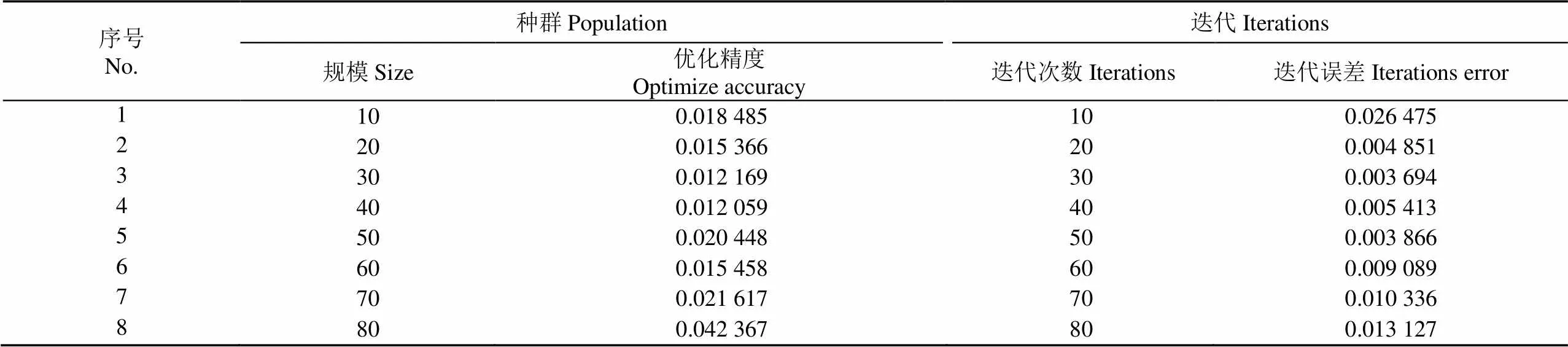
表4 不同種群規模、迭代次數算法誤差比較
根據表4中的種群規模的優化精度算法對比,種群規模為40時,試驗優化精度值最高。
3)迭代次數
遺傳算法收斂時達到的精度和系統的性能會受到迭代次數的影響,需要平衡算法的精度和執行效率。利用適應度函數控制迭代次數,當迭代次數達到30時,算法已收斂(表4)。由表4中不同迭代次數的算法誤差比較可知,設置迭代次數為30,此時算法誤差最小為0.003 694。
4)交叉概率
通過交叉操作產生新的個體,可提高遺傳算法的全局搜索能力[24]。交叉概率的大小要求盡可能不破壞個體結構和群體中優良的模式,但要有效產生較好的新個體模式。因此,交叉概率一般設置在0.40~0.99之間[23]。在此范圍內,不同的交叉概率所對應算法誤差比較如表5所示。

表5 不同交叉概率的算法誤差比較
根據表5對比不同交叉概率所得算法誤差可得,當交叉概率為0.8時,算法誤差較小,為0.013 289。
5)變異概率
遺傳算法的局部搜索能力會因設置變異概率的大小而變化。變異概率較大時,能夠產生較多的新個體,但也可能改變較好的模式結構導致近似于隨即搜索算法的性能[15];若變異概率取值太小,會抑制產生新的個體和抑制早熟現象的能力。一般限定在0.000 1~0.1之間以有效維持群體的多樣性[23],試驗中需要產生較多新個體搜索最優解,變異概率設置值最大時的算法模式結構并未被破壞,因此,試驗的變異概率設置為0.1。
1.3.3 CGA-BP神經網絡好氧堆肥的曝氣供氧量預測模型的建立
為提高GA-BP算法運行效率,縮短GA-BP模型訓練時間,本文利用克隆免疫算法優化GA-BP模型,該算法是2002年DE等通過仿生免疫反應中的親和度的成熟過程提出的。克隆選擇算法作為克隆免疫算法中的一種,具有自學習、記憶機制和并行性等優點,并成功應用于多模態函數優化、組合優化等方面[25]。BP神經網絡經過克隆遺傳算法優化后,記作CGA-BP神經網絡模型。相比GA-BP神經網絡模型、BP神經網絡模型,CGA-BP神經網絡模型加快了搜索最優解的速度,提升算法的運算效率。
克隆遺傳算法以遺傳算法為主,當進行遺傳交叉和變異之后,利用克隆、高頻變異保持群體的多樣性,不斷迭代得到最優個體[26]。本文建立的CGA-BP神經網絡預測曝氣供氧量模型的流程圖,如圖3所示。通過克隆選擇算法對BP神經網絡和GA的參數進行優化,采用比例復制算子和比例變異算子保持群體的多樣性,同時利用記憶單元平衡全局與局部搜索的能力[27]。通過上述克隆遺傳算法優化BP神經網絡,CGA-BP神經網絡預測曝氣供氧量模型的參數設置如表6。
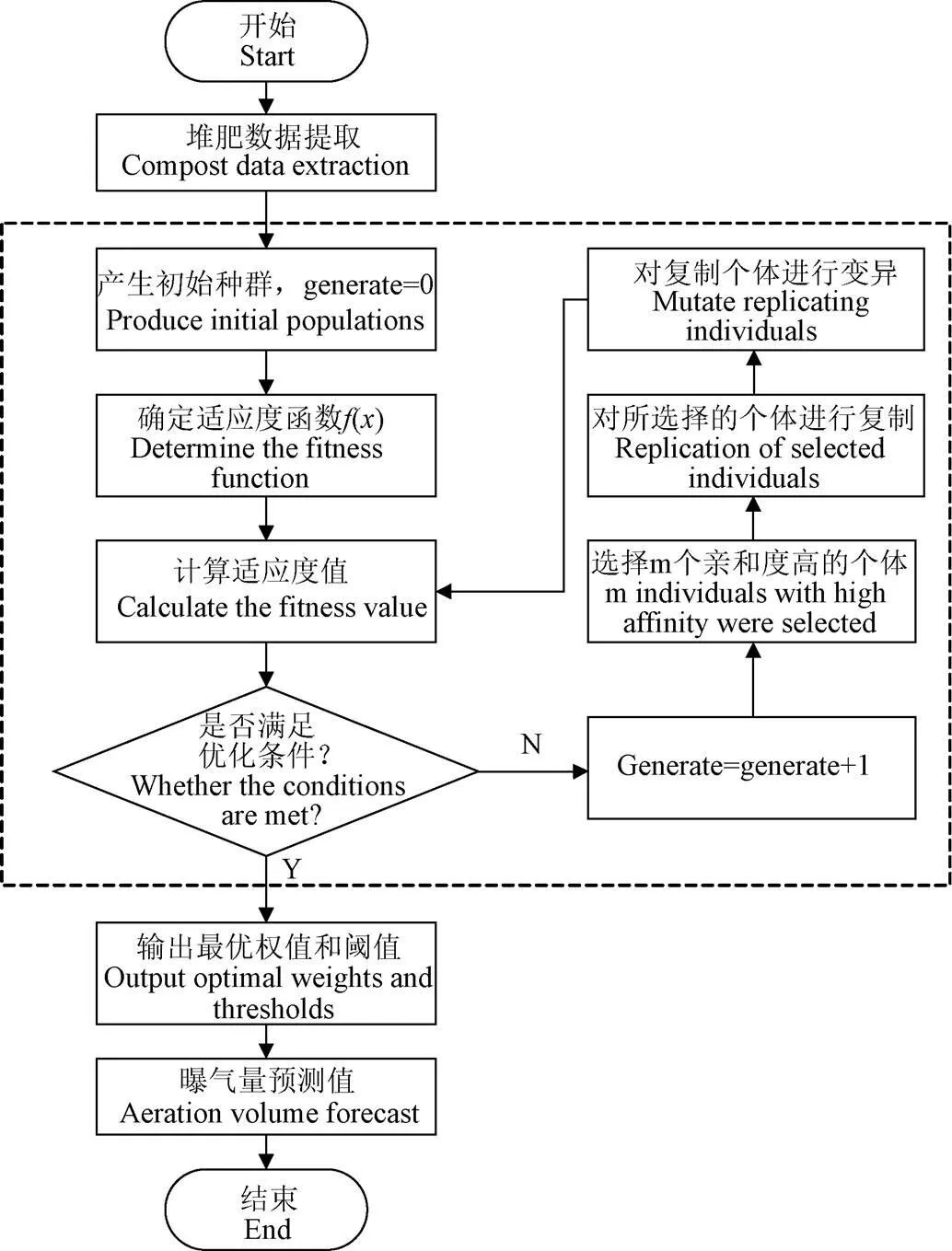
圖3 基于CGA-BP神經網絡的流程圖

表6 CGA-BP神經網絡模型參數設置
1.4 模型評價指標
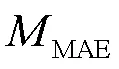
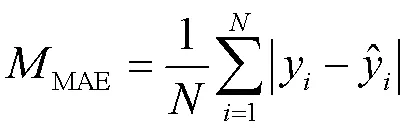
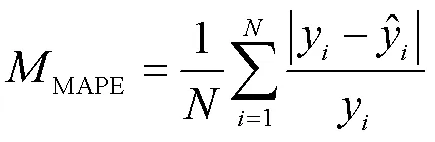
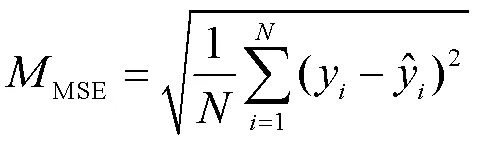

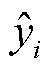
2 結果與分析
2.1 模型預測結果
為檢驗克隆遺傳算法優化BP神經網絡的效果,本文利用測試集對訓練好的BP模型、GA-BP模型和CGA-BP模型的好氧堆肥曝氣供氧量預測效果進行對比分析,并分別將3種模型的預測值與真實值進行對比,結果如圖4所示。
CGA-BP模型與真實值的擬合程度最好,預測精度達到99.65%,比BP模型、GA-BP模型的預測精度96.99%、99.26%分別提高2.66個百分點、0.39個百分點。CGA-BP神經網絡算法、GA-BP神經網絡算法和BP算法的曝氣供氧量變化趨勢與真實值變化趨勢整體是一致的。但是本文提出的CGA-BP模型的預測精度相比其他2種模型都有一定提升。
本文通過影響堆肥發酵的多指標與曝氣量的關系直接建立BP曝氣供氧量模型、GA-BP曝氣供氧量模型和CGA-BP曝氣供氧量預測模型,3種模型中,CGA-BP模型預測精度最高。試驗結果表明,CGA-BP模型預測曝氣量能夠更準確預測好氧堆肥發酵過程中堆肥實際需要的曝氣量,提高堆肥曝氣控制效率。
2.2 模型誤差對比
BP神經網絡算法、GA-BP神經網絡和CGA-BP神經網絡3種算法的曝氣供氧量的絕對誤差值比較,如圖5所示。從圖5中3個模型的絕對誤差值可知,BP神經網絡與GA-BP神經網絡的誤差波動范圍較大,BP神經網絡模型誤差波動在±0.5,GA-BP神經網絡模型誤差波動在±0.4,而CGA-BP神經網絡模型的誤差穩定在±0.1之間,相比其他2個模型,絕對誤差波動范圍更小,預測結果更準確。
此外,將3種好氧堆肥的曝氣供氧量預測模型的評價指標進行對比,結果見表7。CGA-BP模型的MAE值、MAPE值和MSE值分別為0.038 9、0.350 6、0.003 4,相比其他2個模型的性能指標也都有很大提升。GA-BP神經網絡模型的MAE值、MAPE值和MSE值與BP模型相比,分別提高了29.49%、30.16%和53.25%,CGA-BP模型的MAE值、MAPE值和MSE值比GA-BP模型分別提高了53.16%、52.56%和74.43%。在搜索最優解的速度上,CGA-BP模型的效率也更高,比BP模型和GA-BP模型分別提高了75.36%、51.30%。
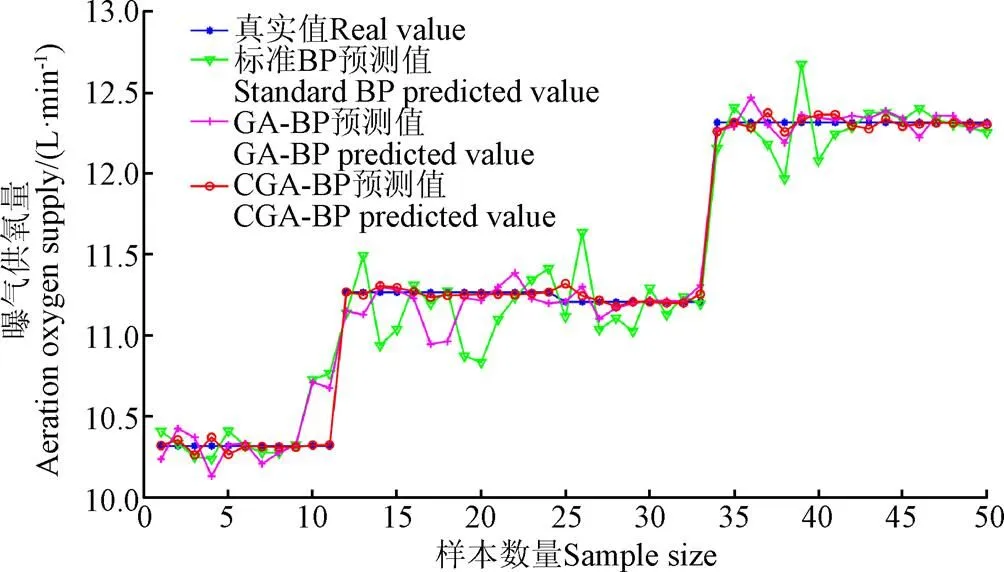
圖4 BP、GA-BP和CGA-BP模型預測值和真實值比較
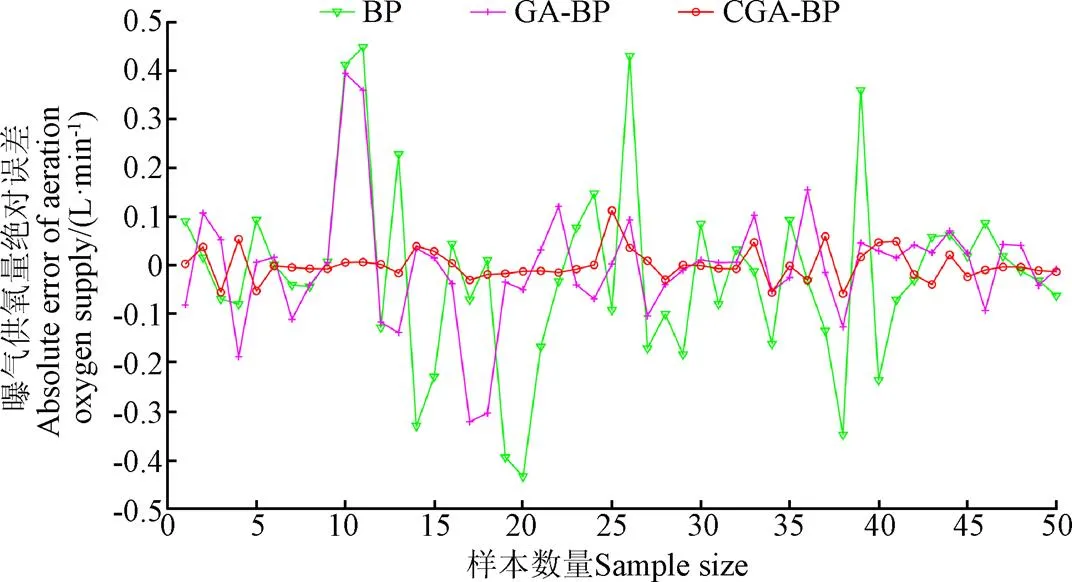
圖5 BP、GA-BP和CGA-BP神經網絡預測模型誤差
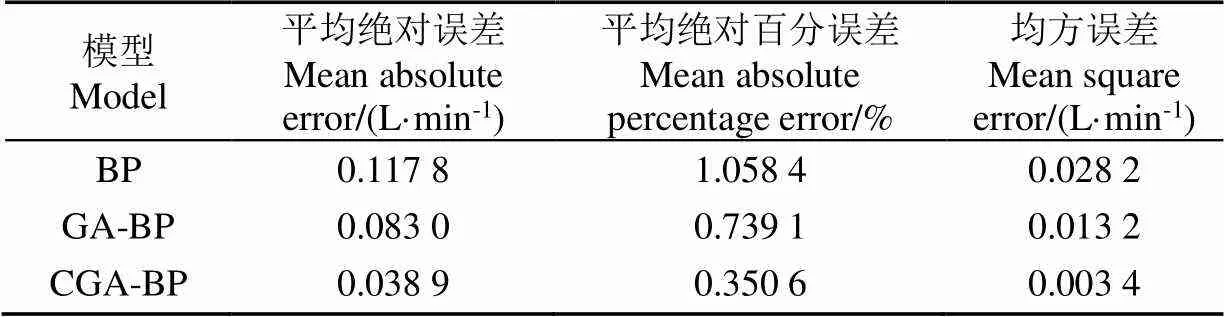
表7 BP、GA-BP和CGA-BP模型評價指標對比
基于上述分析得出,克隆遺傳算法起到了優化作用,CGA-BP好氧堆肥曝氣供氧量預測模型優于GA-BP神經網絡模型和BP神經網絡模型,能夠更好地預測曝氣供氧量。
另一方面,CGA-BP模型是利用好氧堆肥實驗裝置控制傳感器采集到的數據進行預測堆肥所需的曝氣量,數據異常會影響曝氣量預測結果的準確性,需要及時對各傳感器進行定期維護和堆肥發酵過程中異常值的監測,保證預測結果的準確性,減少誤差。
2.3 試驗驗證
選取北京市密云區海華沼氣廠2019年2月2組堆肥數據進行分析。在整個好氧堆肥發酵過程中,一組數據根據CGA-BP模型預測的曝氣量進行控制曝氣,另一組數據直接利用實際值曝氣作為對照組,并將CGA-BP模型預測曝氣量和實際曝氣量進行對比分析。兩組好氧堆肥反應均完成后,對照組曝氣量總共為3 366.67 m3/h,預測模型曝氣量為3 257.82 m3/h,利用CGA-BP模型預測曝氣量提高了約3.22%的曝氣控制效率,并且根據CGA-BP模型預測曝氣供氧量對堆肥進行精準曝氣試驗,比對照組提前6 h結束發酵過程,縮短了好氧堆肥發酵的時間,達到了節能減排的效果。
基于上述分析,通過建模方法的CGA-BP神經網絡的好氧堆肥曝氣供氧量預測模型能夠實現精準曝氣的效果并提高堆肥發酵效率。
3 結 論
本研究針對好氧堆肥曝氣量的預測精度,利用樣本數據訓練神經網絡,根據程序運行結果調整模型的參數,最終建立3種好氧堆肥曝氣供氧量預測模型,對3種模型進行對比分析,結論如下:
1)克隆遺傳算法對BP神經網絡起到了優化作用,加快獲得最優解,效率相比BP模型和GA-BP模型分別提高了75.36%、51.30%。
2)在好氧堆肥曝氣供氧量預測模型中,CGA-BP模型的預測結果更佳,預測精度達到99.65%,比BP模型、GA-BP模型的預測精度分別提高2.66、0.39個百分點。CGA-BP模型的均方誤差、平均絕對誤差、平均絕對百分誤差分別為0.003 4、0.038 9和0.350 6,均小于BP神經網絡和GA-BP神經網絡模型評價指標的誤差。
3)CGA-BP好氧堆肥曝氣供氧量預測模型的預測精度較高,能對好氧堆肥發酵過程實現精準曝氣,提高了3.22%的曝氣控制效率,并縮短了堆肥發酵時間。
[1] TOKARSKI D, ?IME?KOVá J, KU?ERíK J, et al. Detectability of degradable organic matter in agricultural soils by thermogravimetry[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 2019, 182(5): 729-740.
[2] GUO H, GU J, WANG X, et al. Negative effects of oxytetracycline and copper on nitrogen metabolism in an aerobic fermentation system: Characteristics and mechanisms[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 403: 123890.
[3] CUI X, GUO L, LI C, et al. The total biomass nitrogen reservoir and its potential of replacing chemical fertilizers in China[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2021, 135: 110215.
[4] 沈玉君,張朋月,孟海波,等. 通風方式對豬糞堆肥主要臭氣物質控制的影響研究[J]. 農業工程學報,2019,35(7):203-209.
SHEN Yujun, ZHANG Pengyue, MENG Haibo, et al. Study on the influence of ventilation mode on the control of main odorous substances in pig manure compost[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2019, 35(7): 203-209. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 張秧, 艾為黨, 馮海艷,等. 小麥秸桿好氧堆肥過程中微生物多樣性與優勢菌群分析[J]. 農業工程學報, 2021, 37(11):206-212.
ZHANG Yang, AI Weidang, FENG Haiyan, et al. Analysis of microbial diversity and dominant microbiota during aerobic composting of wheat straw[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2021, 37(11): 206-212. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 王雅雅,陳高攀,孫浩,等. 基于EDEM的分倉立式好氧堆肥反應器設計與試驗[J]. 農業工程學報,2023,39(3):171-179.
WANG Yaya, CHEN Gaopan, SUN Hao, et al. Design and test of separate silo vertical aerobic composting reactor based on EDEM[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2023, 39(3): 171-179. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 李升,胡曉東,許飛飛,等. 馬頭崗污水廠精確曝氣系統的實施及應用[J]. 中國給水排水,2016,32(15):26-31.
LI Sheng, HU Xiaodong, XU Feifei, et al. Implementation and application of precision aeration system of Matougang sewage plant[J]. Water Supply and Drainage in China, 2016, 32(15): 26-31. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 沈軍. 精確曝氣系統(AVS)在 AAO 工藝中的運行分析[J]. 凈水技術,2016,35(5):73-78.
SHEN Jun. Operational analysis of precision aeration system (AVS) in AAO processes[J]. Water Purification Technology, 2016, 35(5): 73-78.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 唐維,陶鈺欣,郝啟文,等.基于遺傳算法優化BP神經網絡的曝氣量預測[J].控制工程,2022,29(7):1600-1605.
TANG Wei, TAO Yuxin, HAO Qiwen, et al. Optimization of aeration prediction of BP neural network based on genetic algorithm[J]. Control Engineering, 2022, 29(7):1600-1605.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] CHEN Y S, ZHANG H J, YIN Y F, et al. Smart energy savings for aeration control in wastewater treatment[J]. Energy Reports, 2022, 8: 1711-1721.
[11] 王麗麗,許雷,姚紀宇,等.堆肥廢氣余熱回用對寒區好氧堆肥的影響[J].農業工程學報,2022,38(7):237-244.
WANG Lili, XU Lei, YAO Jiyu, et al. Effect of waste heat reuse of compost waste gas on aerobic composting in cold areas[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering(Transactions of the CSAE), 2022, 38(7): 237-244. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 王友玲,邱慧珍,PHILIP Ghanney,等.通風方式對牛糞堆肥氨氣排放與氮素轉化的影響[J].農業機械學報,2020,51(11):313-320.
WANG Youling, QIU Huizhen, PHILIP Ghanney, et al. Effects of ventilation on ammonia emission and nitrogen conversion of cow manure compost[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2020, 51(11): 313-320. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 李成杰,王濤,李海漪,等. 基于BP神經網絡的堆肥物料抗剪強度預測模型[J]. 中國給水排水,2020,36(7):108-113.
LI Chengjie, WANG Tao, LI Haiyi, et al. Shear strength prediction model of compost materials based on BP neural network[J]. Water Supply and Drainage in China, 2020, 36(7): 108-113. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 聞新. 智能故障診斷技術:MATLAB應用[M]. 北京:北京航空航天大學出版社,2015.
[15] ZHANG X, LIAO Z, MA L, et al. Hierarchical multistrategy genetic algorithm for integrated process planning and scheduling[J]. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 2022, 33: 223-246.
[16] ZHENG Y C, XUE Y Y, YA L L, et al. Throughput optimization in cognitive wireless network based on clone selection algorithm[J]. Computers and Electrical Engineering, 2016, 52(5): 328-336.
[17] TRAN H T, LIN C, BUI X T, et al. Aerobic composting remediation of petroleum hydrocarbon-contaminated soil. Current and future perspectives[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 753: 142250.
[18] 劉娟,沈玉君,羅文海,等. 鹽含量對餐廚垃圾好氧堆肥腐殖化過程及微生物演變的影響[J].農業工程學報,2022,38(19):190-201.
LIU Juan, SHEN Yujun, LUO Wenhai, et al. Effects of salt content on aerobic compost humification process and microbial evolution of food waste[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering(Transactions of the CSAE), 2022, 38(19): 190-201. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 楊佳,王國英,唐若蘭,等. 生物炭和菌劑對羊糞微好氧堆肥腐熟度和溫室氣體排放的影響[J].農業工程學報,2022,38(10):224-231.
YANG Jia, WANG Guoying, TANG Ruolan, et al. Effects of biochar and fungicides on decay and greenhouse gas emissions of microaerobic compost of sheep manure[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering(Transactions of the CSAE), 2022, 38(10): 224-231. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] ZHAO L, HU Y M, ZHOU W, et al. Estimation methods for soil mercury content using hyperspectral remote sensing[J]. Sustainability, 2018, 10(7): 2474.
[21] 郭利進,喬志忠. 基于遺傳算法優化BP神經網絡的糧食溫度預測研究[J]. 糧食與油脂,2023,36(1):34-37,51.
GUO Lijin, QIAO Zhizhong. Research on grain temperature prediction based on BP neural network optimization based on genetic algorithm[J]. Grain and Fat, 2023, 36(1): 34-37, 51. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] ISMAIL F S, BAKAR N A. Adaptive mechanism for GA-NN to enhance prediction model[C] //Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Ubiquitous Information Management and Communication, New York, US: ACM, 2015: 1-5.
[23] 周明,孫樹棟. 遺傳算法原理及應用[M]. 北京:國防工業出版社,1999.
[24] LIU R, LIU L. Predicting housing price in China based on long short-term memory incorporating modified genetic algorithm[J]. Soft Computing, 2019, 23(22): 11829-11838.
[25] DE C L N, VON Z F J. Learning and optimization using the clonal selection principle[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2002, 6(3): 239-251.
[26] 李陽,周步祥,林楠,等.修正克隆遺傳算法在分布式電源規劃中的應用[J].電力系統及其自動化學報,2013,25(4):128-132.
LI Yang, ZHOU Buxiang, LIN Nan, et al. Correction of the application of cloning genetic algorithm in distributed power planning[J]. Proceedings of the Department of Power Systems and its Automation, 2013, 25(4): 128-132.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] 謝宏,李云峰,禹文科,等. 改進免疫克隆選擇算法的多目標軌跡優化[J]. 電子測量與儀器學報,2016,30(10):1534-1542.
XIE Hong, LI Yunfeng, YU Wenke, et al. Improved multi-objective trajectory optimization of immunocloning selection algorithm[J]. Journal of Electronic Measurement and Instrumentation, 2016, 30(10): 1534-1542. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] YAN J, XU Z, YU Y, et al. Application of a hybrid optimized BP network model to estimate water quality parameters of Beihai Lake in Beijing[J]. Applied Sciences, 2019, 9(9): 1863.
[29] 陳嘯,王紅英,孔丹丹,等.基于粒子群參數優化和BP神經網絡的顆粒飼料質量預測模型[J]. 農業工程學報,2016,32(14):306-314.
CHEN Xiao, WANG Hongying, KONG Dandan, et al. Quality prediction model of pellet feed basing on BP network using PSO parameters optimization method[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(14): 306-314. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Prediction model of the aeration oxygen supply for aerobic composting using CGA-BP neural network
DING Guochao1, SHI Xueling1, HU Jun2※
(1.,,163319,;2.,,163319,)
Aerobic compost has been commonly used to efficiently dispose of resources recycling and environmental protection in modern agriculture. Among them, aeration can be one of the most important environmental factors to affect composting fermentation. It is necessary for a feasible network model to accurately control the oxygen supply of aeration. This study aims to improve the aeration efficiency and prediction accuracy of aerobic composting aeration. In-depth learning was selected to train a network model, in order to predict the oxygen supply of aeration during aerobic composting fermentation in this experiment. Raw materials were taken as cow dung, cow dung biogas residue, chicken manure, and corn straw in the Haihua Biogas Plant in Miyun District, Beijing, China. The corn straw was crushed by 1-2 cm in grain size. The cow dung, cow dung biogas residue, and chicken manure were uniformly mixed with the crushed corn straw for composting and fermentation. The sensor was used in the composting fermentation tank to collect the parameter data during aerobic fermentation. 268 groups of data were selected as the sample data, 218 groups of data were randomly selected as the input data, and 50 groups of data were selected as the test data. Clonal genetic algorithm (CGA) was used to predict the standard back propagation (BP) neural network model for the aeration oxygen supply, whereas, the 6-14-1 three-layer network structure was used as the basic structure of the prediction model. The input parameters were the temperature, humidity, oxygen concentration, room temperature, pH value, and electrical conductivity (EC). The mean square error (MSE) of the number of hidden layer nodes was determined to be 14 after training and calculation. The output data was aeration. This article establishes BP neural network model for predicting aeration oxygen supply. Then the genetic algorithm (GA) and clonal selection algorithm were used to improve the prediction accuracy of the model. The experiment shows that the CGA-BP neural network model has the best prediction effect on aeration oxygen supply. 1) The CGA-BP neural network model accelerated the obtaining of the optimal solution, with an efficiency improvement of 75.36% and 51.30% compared to the BP model and GA-BP model, respectively. 2) In the prediction model of aeration oxygen supply, the CGA-BP model had a more accurate prediction effect, with a prediction accuracy of 99.65%. The prediction accuracy of aeration oxygen supply was 96.99% and the prediction accuracy of the GA-BP neural network model reached 99.26%. A comparison was made to evaluate the errors of BP, GA-BP and CGA-BP neural models. The model evaluation showed that the best performance was found in the CGA-BP neural network model with the smallest error, as shown by the mean absolute error (MAE), mean absolute percentage error (MAPE) and mean square error (MSE). 3) The improved CGA-BP neural network model can be predicted the aeration oxygen supply of aerobic composting, increasing the aeration control efficiency by 3.22%. The improved model can be expected to accurately predict the aeration oxygen supply of aerobic compost. The finding can provide a strong reference for accurate data for the next aeration.
model; trial; genetic algorithms; aerobic composting; aerated oxygen supply; BP neural networks; CGA-BP neural networks
2022-11-09
2023-02-06
國家重點研發計劃:農業廢棄物好氧發酵技術與智能控制設備研發(2016YFD0800600)
丁國超,博士,副教授,研究方向為生物信息處理。Email:dgcer@163.com
胡軍,博士,教授,研究方向為農業機械化工程。Email:gcxykj@126.com
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.202211088
TP183; TP389.1; S210.6
A
1002-6819(2023)-07-0211-07
丁國超,施雪玲,胡軍. 基于CGA-BP神經網絡的好氧堆肥曝氣供氧量預測模型[J]. 農業工程學報,2023,39(7):211-217. doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.202211088 http://www.tcsae.org
DING Guochao, SHI Xueling, HU Jun. Prediction model of the aeration oxygen supply for aerobic composting using CGA-BP neural network[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2023, 39(7): 211-217. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.202211088 http://www.tcsae.org

