Quantum correlation and entropic uncertainty in a quantum-dot system
Ying-Yue Yang(楊穎玥), Li-Juan Li(李麗娟), Liu Ye(葉柳), and Dong Wang(王棟)
School of Physics and Optoelectronic Engineering,Anhui University,Hefei 230601,China
Keywords: entropic uncertainty relation,quantum correlation,quantum dot
1. Introduction
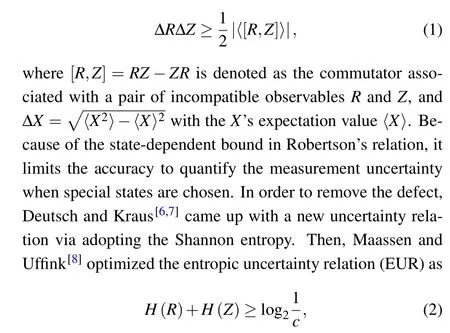
The uncertainty principle proposed by Heisenberg[1]is famous because it is one of fundamental characteristics in quantum mechanics, which differs from those in classical counterpart. It reveals that there exists inevitable uncertainty in measurement of any two non-commutative mechanical quantities within a quantum system. Inspired by this, a universal inequality with standard deviation form is presented by Kennard and Robertson,[2,3]which can be expressed as[4,5]
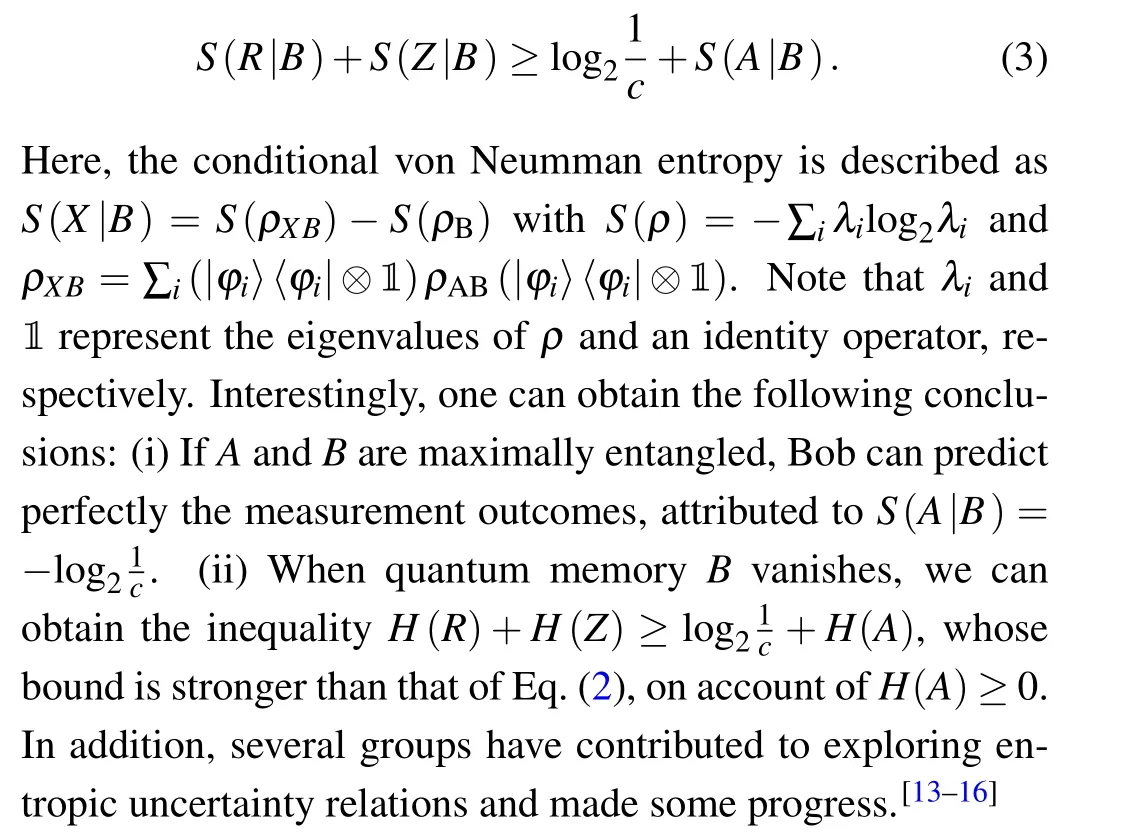
Later, a quantum-memory-assisted entropic uncertainty relation(QMA-EUR),which has been put forward by Refs.[9,10] and experimentally demonstrated by Refs. [11,12], modifies the outcomes of the measurement uncertainty. Remarkably, the relation can be illustrated by a well-known uncertainty game. In the game, we assume that there are two legitimate participants,Alice and Bob. First,Bob prepares two entangled particlesAandB.Ais subsequently sent to Alice while particleBis serving as a memory. Then,Alice chooses one of two measurementsRandZ,and it is agreed in advance to measure her particle and send her choice to Bob. According to Alice’s measurement choice,Bob can predict the outcomes measured by Alice as accurate as possible. The uncertainty can be mathematically expressed as[10]

As a matter of fact, the QMA-EUR can be applied to achieve many kinds of quantum tasks in the realm of quantum information and computation, such as quantum cryptography,[17,18]quantum teleportation,[19]quantum key distribution,[20–23]quantum metrology[24–26]and entanglement witness.[11,12,27]Moreover, the relation has been experimentally demonstrated based on all-optics platforms,promoting its applications in real-life quantum information processing.[28–33]
Recently, the quantum coherence in a vertical quantumdot system(QDS)was investigated in Ref.[34],which demonstrated the coherence for electrons in the structure of a solid states. Remarkably, these investigations make for a further understanding of the coherent control of spins in diamond and manipulations electron spin qubits in QDSs. Nevertheless,the measurement uncertainty has never been revealed in any QDS,which play a fundamental and nontrivial role in quantum information processing. With this in mind,the aim of the paper is to address this issue.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows. We first review the Hamiltonian of the quantum systems in Section 2. In Section 3, we focus on the dynamical behavior of the QMA-EUR.Meanwhile,we analyze the physical interpretation of the measurement uncertainty in terms of the quantum correlation.Next,several improved bounds in QDSs are investigated in Section 4. Finally,a concise conclusion is rendered in Section 5.
2. Physical mode
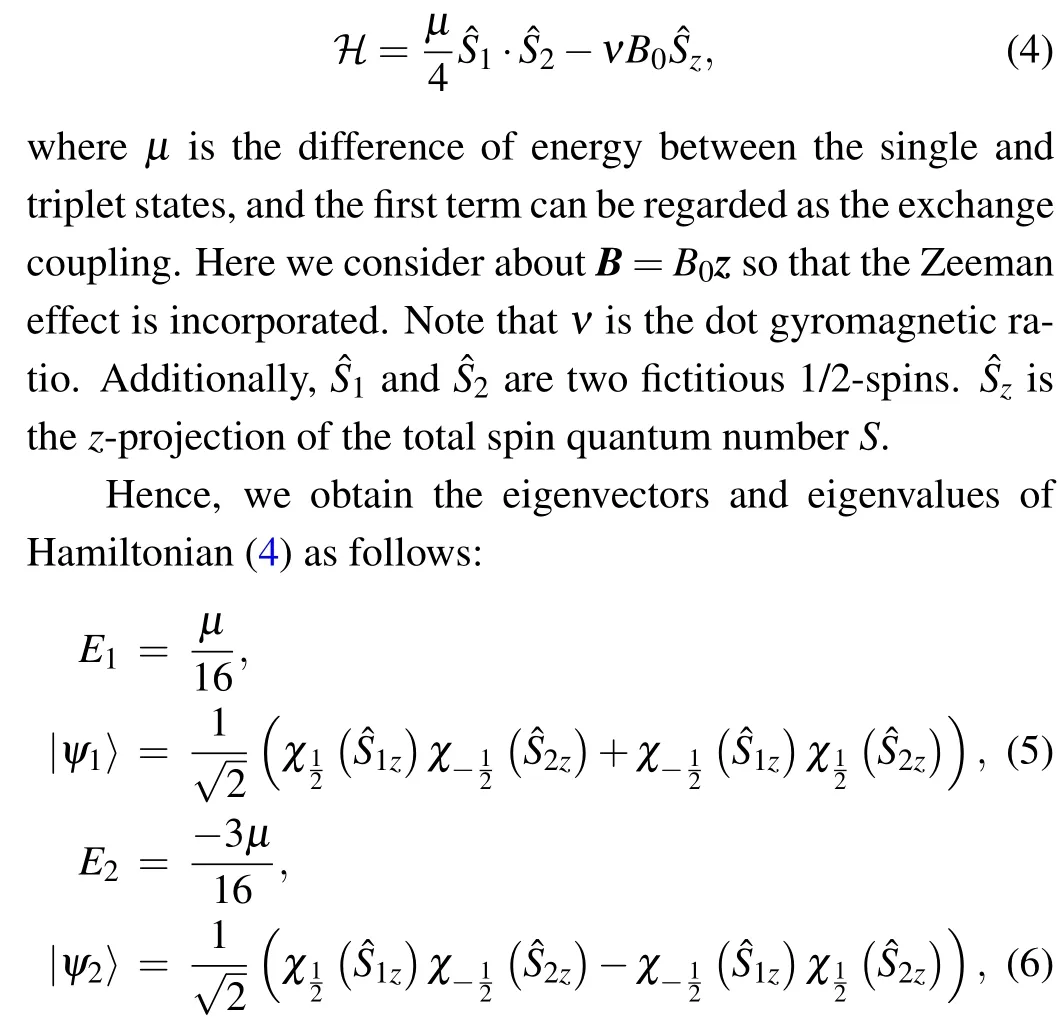
In quantum mechanics, optical and electronic properties of quantum dots differ highly from those in larger-scale particles, which can stimulate more and more interests to explore deeper phenomena and mechanics in quantum information theory.[35,36]Typically,Hamiltonian of a quantum-dot system can be written as[34,37]

3. The entropic uncertainty relation in quantum-dot system
First of all, we will focus on exploiting the dynamical evolution of the measurement uncertainty in the quantum-dot systems. Herein, we take two Pauli observables, ?σxand ?σz,as the incompatibility. Therefore,the post-measurement states can be written as

To reveal the nature of the measurement uncertainty of interest in quantum-dot systems,we depict the entropy uncertainty and the lower bound of entropy uncertainty as a function of temperatureTin Fig.1. From Fig.1,it is clear that the uncertainty increases with the growth of temperature.Intuitively,the higher the temperature is,the more disordered the system is,and hence the weaker the systemic quantum correlation will be,which results in the inaccuracy of the prediction to the outcomes of Alice’s measurement. In addition, one can see that the lower bound also increases with the growth ofTand it always satisfiesUL≥UR.When the temperature is enough high,it is easy to find that the measurement uncertainty shrinks to a fixed value andUR→UL.
In the following,we focus on the effect of the parametersμandβon the entropic uncertainty in Fig.2.Interestingly,the behaviors of the measurement uncertainty are divided into two regions,i.e.,T=0.1 region andT=1 region. The evolutions in the two regions are different. The entropic uncertainty will firstly increase and subsequently decrease with the growth ofμandβwhen temperatureT=0.1, and the entropic uncertainty has a maximum value in the whole evolution. On the other hand, the uncertainty always decreases with increasingμandβin theT=1 regime, which is contrast to the nonmonotonic variation of entropic uncertainty with increasingμandβin theT=0.1 region.
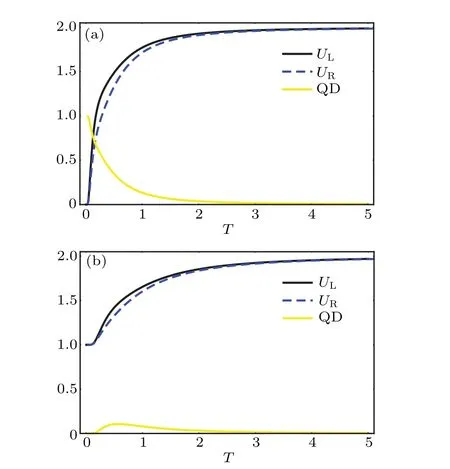
Fig.1. Measurement uncertainty and the quantum discord depicted as functions of temperature T for different values of μ and β: (a) μ =5,β =1,(b)μ =5,β =2.
Next,we turn to probe the systemic quantum correlation.Generally,the quantum discord(QD)is usually deemed as one of effective quantification of quantum correlation,[38–40]which is defined by
Furthermore, we plot the quantum discord as shown in Figs.1 and 2. In contrast to the dynamics of the entropic uncertainty, the QD decreases with increasingT. Based on this phenomenon, we here offer a physical explanation. By connecting Eqs.(3)and(24)–(26),the lower bound can be derived as

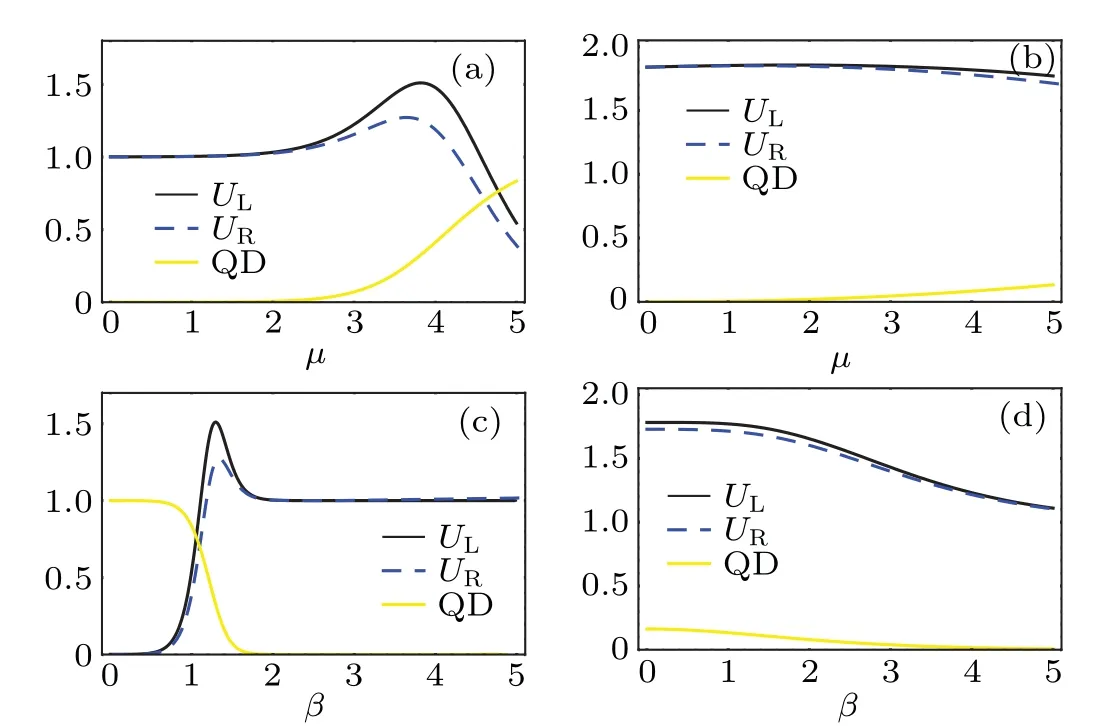
Fig.2. Measurement uncertainty and the quantum discord depicted as functions of μ and β in different regimes of temperature T:(a)T =0.1,β =1,(b)T =1,β =1,(c)μ =5,T =0.1,(d)μ =5,T =1.
4. The improved bounds in quantum-dot system
The uncertainty principle is regarded as as an important tool to quantify the precision of the measurement outcomes concerning two incompatible observables, the uncertainty bound essentially plays a prominent role in quantum information theory.[41]Recently, more and more attention has been paid to optimizing the lower bounds. Typically, Patiet al.[42]proposed an improved bound via quantum correlation between the subsystems,which has the form of
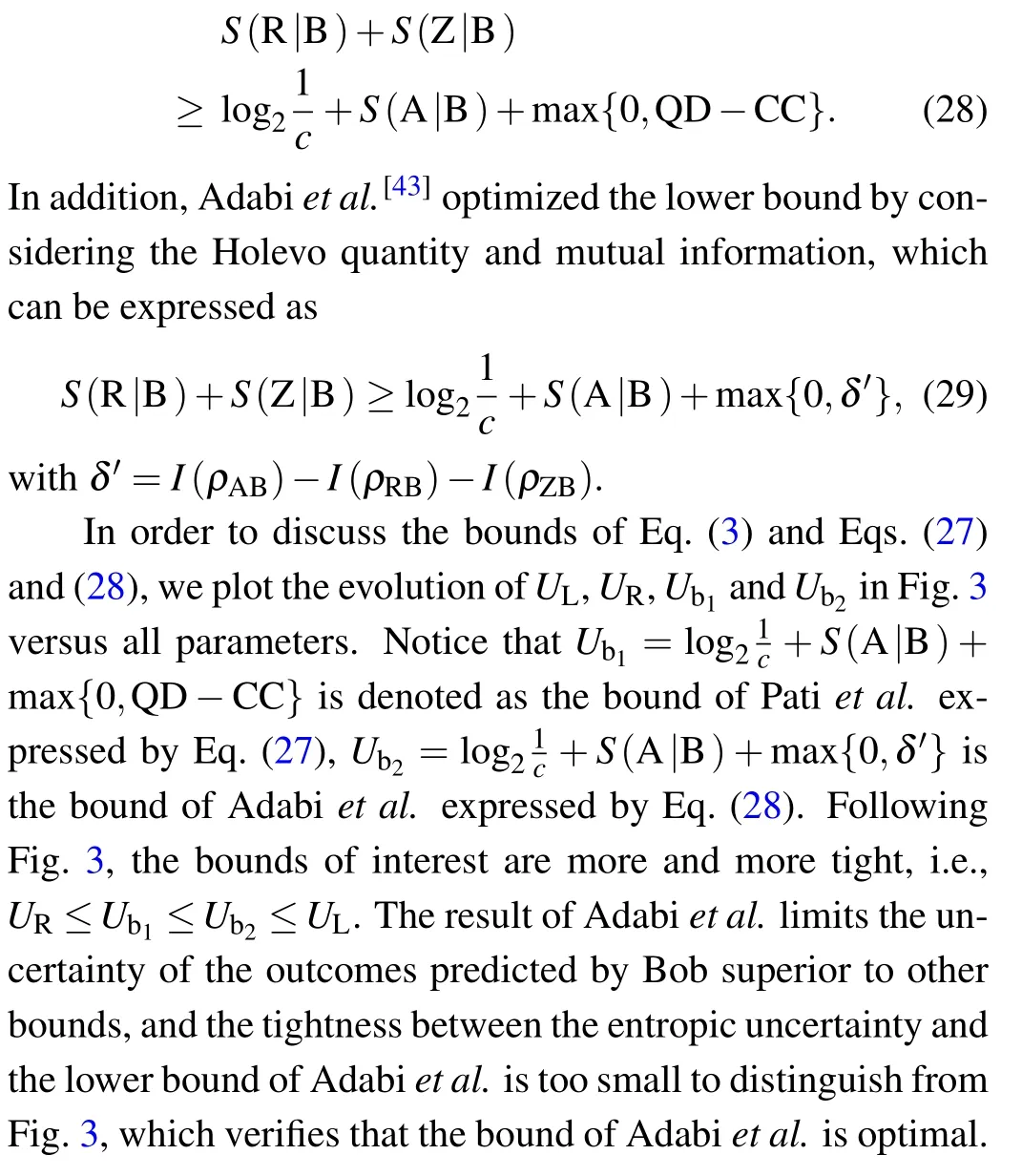
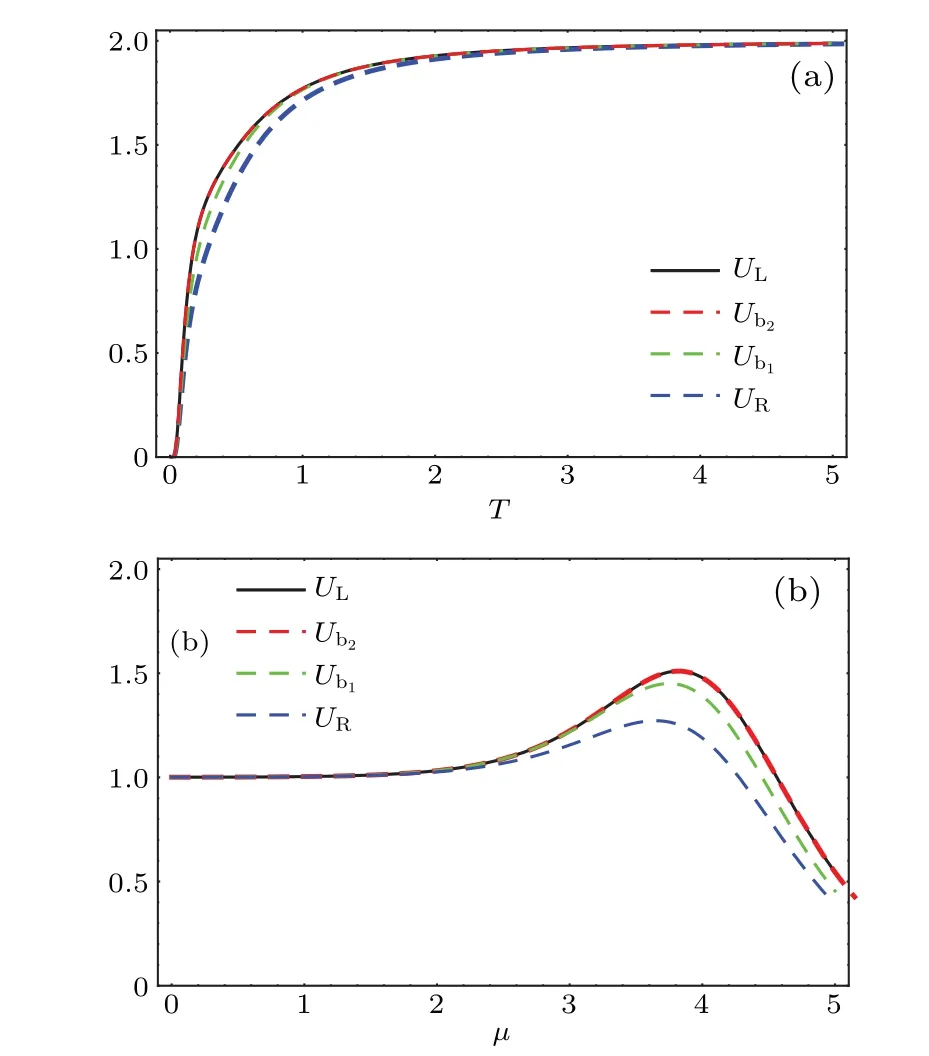
Fig. 3. Measurement uncertainty, the lower bound and two improved bound depicted as functions of T, μ and β: (a) μ = 5, β = 1, (b)T =0.1,β =1.
5. Conclusion


Acknowledgements
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 12075001, 61601002, and 12175001), the Anhui Provincial Key Research and Development Plan(Grant No.2022b13020004), the Anhui Provincial Natural Science Foundation(Grant No.1508085QF139),and the Fund of CAS Key Laboratory of Quantum Information(Grant No.KQI201701).
- Chinese Physics B的其它文章
- Design of vertical diamond Schottky barrier diode with junction terminal extension structure by using the n-Ga2O3/p-diamond heterojunction
- Multiple modes of perpendicular magnetization switching scheme in single spin–orbit torque device
- Evolution of the high-field-side radiation belts during the neon seeding plasma discharge in EAST tokamak
- Phase-matched second-harmonic generation in hybrid polymer-LN waveguides
- Circular dichroism spectra of α-lactose molecular measured by terahertz time-domain spectroscopy
- Recombination-induced voltage-dependent photocurrent collection loss in CdTe thin film solar cell