Nonreciprocal coupling induced entanglement enhancement in a double-cavity optomechanical system
Yuan-Yuan Liu(劉元元) Zhi-Ming Zhang(張智明) Jun-Hao Liu(劉軍浩)Jin-Dong Wang(王金東) and Ya-Fei Yu(於亞飛)
1Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Nanophotonic Functional Materials and Devices(School of Information and Optoelectronic Science and Engineering),South China Normal University,Guangzhou 510006,China
2Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Quantum Engineering and Quantum Materials,South China Normal University,Guangzhou 510006,China
Keywords: quantum entanglement,double-cavity optomechanical system,nonreciprocal coupling
1. Introduction
Cavity optomechanics[1,2]is the study of the radiation pressure interaction between the optical cavity field and the mechanical motion. In general, a cavity optomechanical system (COMS) consists of a Fabry-Perot cavity with one movable mirror, where the cavity mode couples with the mechanical mode via radiation pressure. COMS has attracted increasing attention due to its prominent applications in gravitational-wave detection,[3]photonic network,[4]metrology,[5]etc. With the rapid development of nanotechnology, COMS also provides a substantial platform for exploring quantum effects in an exceedingly wide range from microscale to macroscale, for instance, entanglement,[6-9]squeezing,[10-13]photon blockade,[14-18]transmission,[19]etc.As is known, entanglement is an enigmatic phenomenon in quantum mechanics and its detailed study would be beneficial.Firstly,it can help us identify the boundary between the classical and quantum worlds.[20]Secondly,it has numerous potential applications in quantum technology and science, such as quantum computation,[21]quantum communication,[22]quantum metrology,[23]etc.
In recent years, great efforts have been made to explore quantum entanglement in various hybrid COMSs. In 2007,Vitaliet al. investigated the steady-state entanglement between the cavity mode and the movable mirror in a standard COMS.[24]In 2012,three photomechanical cavity arrays coupled reversibly or irreversibly to each other were studied,and it was found that this composite system exhibits photon-phonon entanglement between cavities.[25]Then,Liaoet al. proposed a scheme to generate quantum entanglement between two mechanical resonators in a two-cavity optomechanical system in 2014.[26]Later, Liuet al. proposed a scheme to generate the entanglement between two COMS via a flying two-level atom in 2017,[27]and Xuet al.explored a scheme to generate single entangled photon-phonon pair in a hybrid COMS via atomphoton-phonon interaction in 2019.[28]Recently, Jiaoet al.showed how to achieve the nonreciprocal entanglement in a COMS.[29]
At present, the non-Hermitian systems have drawn extensive interest because of its novel properties.[30,31]There are two kinds of implementation schemes, i.e., the gain systems[32,33]and the nonreciprocally coupled systems.[34-36]Here, the objective is to study the quantum entanglement in a nonreciprocally coupled system. Therefore, we propose a double-cavity optomechanical system, which is composed of an optomechanical cavity and an auxiliary cavity. In this system, the optomechanical cavity mode couples with the mechanical mode via radiation-pressure interaction,and couples with the auxiliary cavity mode via nonreciprocal coupling.[37]Such a kind of nonreciprocal coupling can be achieved by using an imaginary gauge field,[38,39]impurity,[40]or auxiliary nonreciprocal transition device.[41,42]We adopt the logarithmic negativityE(1)n(E(2)n)to quantify the entanglement degree between the mechanical mode and the optomechanical cavity mode(the auxiliary cavity mode). We find that bothE(1)nandE(2)nhave maximum values in the case of reciprocal coupling.By using the nonreciprocal coupling,E(1)nandE(2)ncan exceed those maximum values,and a wider detuning region where the entanglement exists can be obtained. Moreover,the entanglement robustness with respect to the environment temperature can be effectively enhanced.
This paper is organized as follows. In Section 2,we present the Hamiltonian of the system and derive the Heisenberg-Langevin equations. Furthermore, we introduce the logarithmic negativity to quantify the entanglement degree between the mechanical mode and the optical cavity modes.In Section 3,we demonstrate the nonreciprocal coupling induced enhancement of the entanglement degree and entanglement robustness. Finally,a brief summary is given in Section 4.
2. Model and analytical expressions
As shown in Fig.1,we consider a cavity optomechanical system where the cavity mode(?a1)couples with the mechanical mode(?p, ?q)via radiation pressure,and an auxiliary cavity mode(?a2)couples with the optomechanical cavity mode(?a1)via nonreciprocal interaction. In a frame rotating at the frequencyωlof the driving field, the total Hamiltonian of the non-Hermitian system can be expressed as follows:

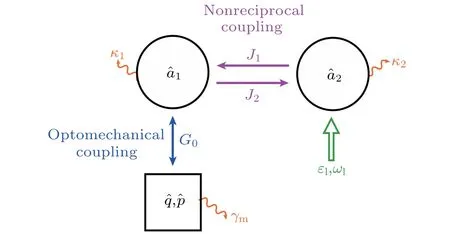
Fig.1. Schematic diagram of the double cavity optomechanical system with nonreciprocal coupling. G0 denotes the single photon optomechanical coupling strength, J1 (J2)represents the tunneling strength of photon jumping into cavity ?a1(?a2). εl (ωl)is the amplitude(frequency)of the pump field. κ1 (κ2)is the decay rate of the cavity mode ?a1 (?a2),and γm is the mechanical damping rate.
By using the Hamiltonian and introducing the dissipation and fluctuation terms,the Heisenberg-Langevin equations can be written as

whilenm=[exp(ˉhωm/kBT)-1]-1denotes the thermal photon number,kBis the Boltzmann constant andTis the temperature of the mechanical oscillator. Their mean values〈?aj,in(t)〉=〈?ξ(t)〉=0.
Under the condition of strong optical driving, the nonlinear Eq. (2) can be linearized by rewriting each operator as a sum of its steady-state mean value plus a small fluctuation around it,i.e.,

By substituting the above ansatz Eq.(4)into Eq.(2),the equations will be decoupled into a set of nonlinear algebraic equations for the steady-state mean values and a set of quantum Heisenberg-Langevin equations for the fluctuation operators.The steady-state mean values can be obtained by setting the time derivatives to zero,as follows:



the entanglement will emerge in the corresponding subsystem if and only ifV <1/2.
In the following numerical simulations, to ensure the stability of the system, we use the experimentally feasible parameters[46-48]L=1 mm,λl=810 nm,P=35 mW, andωm/2π=10 MHz. We also assume that the two cavities have the same decay rate, i.e.,κ1/2π=κ2/2π=κ/2π=5 MHz,andm=5 ng,γm/2π=100 Hz. Moreover, we assume thatΔ2=-Δ'1=Δ.[49]
3. Numerical simulations
3.1. Nonreciprocal coupling induced entanglement enhancement
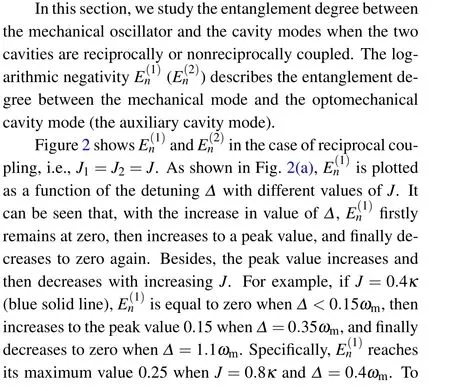
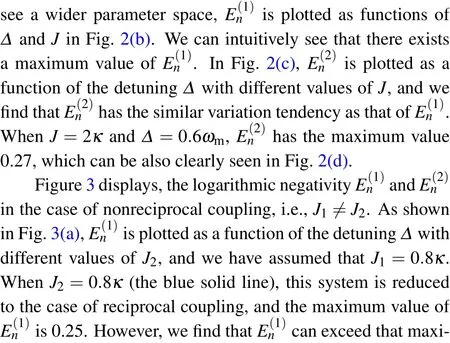

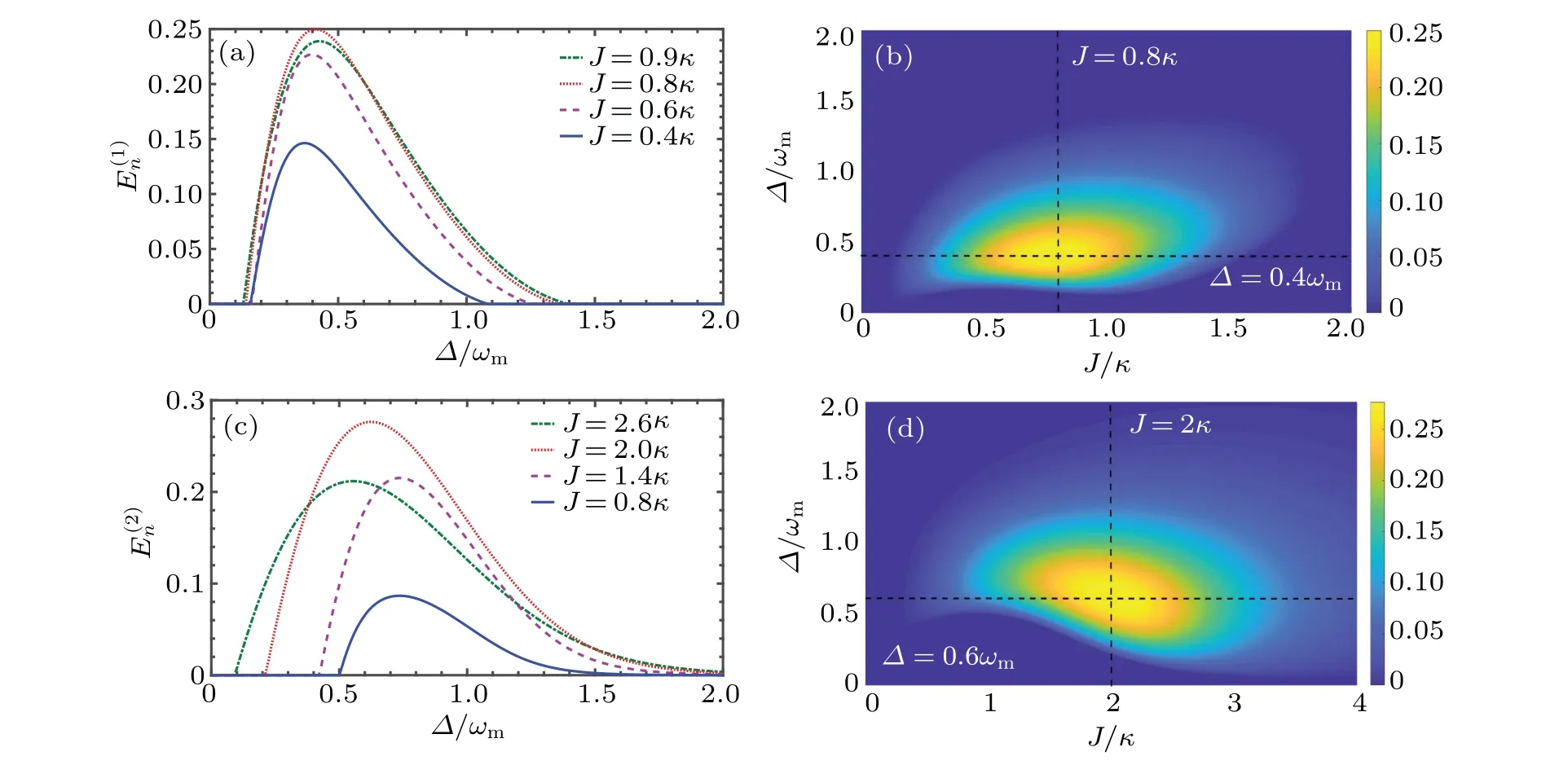
Fig.2. (a),(c)The logarithmic negativity E(1)n and E(2)n as a function of the detuning Δ with different values of reciprocal coupling strength J.(b),(d)E(1)n and E(2)n as functions of Δ and J. The detailed parameters can be found in the text.

Fig.3. (a)The logarithmic negativity E(1)n as a function of the detuning Δ with different values of nonreciprocal coupling strength J2. (b)E(1)n as functions of Δ and J2. (c)The logarithmic negativity E(2)n as a function of the detuning Δ with different values of nonreciprocal coupling strength J1. (d)E(2)n as functions of Δ and J1. (a),(b)J1=0.8κ,(c),(d)J2=2κ,and the other parameters are shown in the text.
3.2. Nonreciprocal coupling induced robustness enhancement
In this section, we show that the nonreciprocal coupling results in an enhancement of the entanglement robustness with respect to the environment temperature. Using similar methodology, we compare the influence of environment temperatureTon the logarithmic negativityE(1)nandE(2)nin the case of reciprocal and nonreciprocal coupling.
As shown in Fig. 4(a), the logarithmic negativityE(1)nis plotted as a function of the environment temperatureTwith different values of reciprocal coupling strengthJ. It can be seen thatE(1)nfirstly decreases and eventually vanishes with the rise ofT. With the increase in value ofJ,the critical value of temperatureTc(Tcis defined asT ≥Tc,En=0)firstly increases and then decreases. WhenJ=1.2κ(the red dotted line),Tcreaches the maximum value of 1.6 K. For comparison,E(1)nis plotted as a function ofTwith different values of nonreciprocal coupling strengthJ2, and we have assumed thatJ1=1.2κ. We find thatE(1)nalso gradually decreases to zero with the increase in value ofT. However, the critical value of temperatureTccontinuously increases withJ2. WhenJ2=3.6κ(the purple dotted-dashed line),Tccan reach 45 K,which is several orders of magnitude larger than the ground state temperature of the mechanical oscillator and is higher than that in Refs. [50,51]. Furthermore,Tccan rise further ifJ2increases further.
The logarithmic negativityE(2)nis plotted as a function of the environment temperatureTwith different values of reciprocal coupling strengthJin Fig.4(c). We find a similar result that,Tcfirstly increases and then decreases with the increase in value ofJ. WhenJ=2κ(the red dashed line),Tcreaches the maximum value of 22 K.Furthermore,E(2)nis plotted as a function ofTwith different values of nonreciprocal coupling strengthJ1, andJ2=2κin Fig. 4(d). It is also found thatE(2)ngradually decreases to zero with the increase inT,andTccontinuously increases withJ1. WhenJ1=2.6κ(the purple dotted-dashed line),Tccan reach 78 K.

Fig. 4. (a), (c) The logarithmic negativity E(1)n and E(2)n as a function of the environment temperature T with different values of reciprocal coupling strength J. (b),(d)E(1)n and E(2)n as a function of T with different values of nonreciprocal coupling strength J2 and J1. (b)J1=1.2κ,(d)J2=2κ,and the other parameters can be found in the text.
4. Conclusion


Acknowledgement
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China(Grant Nos. 12047520,61941501,61775062,11574092,61378012,91121023,62071186 and 61771205).
- Chinese Physics B的其它文章
- Erratum to“Accurate determination of film thickness by low-angle x-ray reflection”
- Anionic redox reaction mechanism in Na-ion batteries
- X-ray phase-sensitive microscope imaging with a grating interferometer: Theory and simulation
- Regulation of the intermittent release of giant unilamellar vesicles under osmotic pressure
- Bioinspired tactile perception platform with information encryption function
- Quantum oscillations in a hexagonal boron nitride-supported single crystalline InSb nanosheet

