X-ray phase-sensitive microscope imaging with a grating interferometer: Theory and simulation
Jiecheng Yang(楊杰成) Peiping Zhu(朱佩平) Dong Liang(梁棟)Hairong Zheng(鄭海榮) and Yongshuai Ge(葛永帥)
1Research Center for Medical Artificial Intelligence,Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Shenzhen 518055,China
2Platform of Advanced Photon Source Technology R&D,Laboratory of X-ray Optics and Technology,Beijing Synchrotron Radiation Facility,Institute of High Energy Physics,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Beijing,100049,China
3Beijing Advanced Innovation Center for Imaging Theory and Technology,Capital Normal University,Beijing 100048,China
4Paul C Lauterbur Research Center for Biomedical Imaging,Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Shenzhen 518055,China
Keywords: x-ray phase contrast imaging,x-ray microscope,grating interferometer
1. Introduction
The development of phase-sensitive x-ray imaging techniques over the last decades allows the measurement of the inner structure of weakly absorbing objects(e.g.,soft tissue,and carbon materials)with high sensitivity,and dramatically complements the conventional absorption imaging. Among the various promising x-ray phase contrast imaging methods,[1-4]the grating-based x-ray Talbot and Talbot-Lau interferometers have been subject to increasing attention due to its compatibility with x-ray tube imaging systems. Many efforts[5-10]have been taken by integrating the Talbot(-Lau)interferometry with the full-field transmission x-ray microscope. One exciting progress is demonstrated by Takanoet al.[10,11]on such a system to obtain superior phase information in comparison with the Zernike phase-contrast imaging approach. However,instead of generating the DPI images, such a combined x-ray microscope system produces the PDI images, which need to be post-processed via the iterative deconvolution method[12]or the maximum likelihood reconstruction method[13]to recover the phase information. Yashiroet al.[6,7]have provided pioneering theoretical explanations for such PDI phenomenon by exploiting the Talbot self-imaging effect.
In this work,a complete theoretical analysis for the imaging procedure of an x-ray microscope equipped with a grating interferometer is investigated. The theory has the capability to deal with various shaped source, and thus permits the explanations to other alternative interferometer designs, e.g., Lau typed interferometer. Additionally, the conversion condition from the PDI to the DPI, or vise versa, is quantitatively investigated with respect to the resolution limit of the imaging system. Finally, numerical simulations are performed to verify the consistency between the theoretical predictions and the previous experimental observations.[11]
2. Theoretical framework

In this study, the x-ray propagation is governed by Fresnel diffraction, which is a near-field approximation of the Kirchhoff-Fresnel diffraction for scalar waves. To simplify the derivations, the following analysis will be conducted in a one-dimensional (1D) case (along thexaxis). The twodimensional (2D) results can be easily obtained upon this basis. With the paraxial approximation, the diffracted fieldUout(x')at any distancedfrom the initial wave fieldUin(x)can be expressed as


whereλis the x-ray wavelength,andk(=2π/λ)is the wave number. Such propagation of the initial wave field can be formally denoted by an action of the operatorP.

Fig.1. Illustration of the x-ray phase contrast microscope system with an arrayed source and a π/2 phase grating.
By using Eq.(1), the scalar wave fieldU1(x1)of a point sourceδ(x0-η)(ηdenotes the off-axis distance)after propagating freely over a distanced1(before the sample) can be calculated as

The analysis dealing with a point source can be easily extended to study the signal formation process of an arrayed source by performing an integration of the final intensity according to the source shape.
Assuming that the thickness of the sample along the optical axis is negligible compared to the focal length of the zone plate,the modulation of the x-ray wavefront after penetrating the sample with a refractive indexn=1-δ+iβis approximated by

wherem=±1,±3,..., andfcorresponds to the first order(m=+1) focal length of the zone plate. Note that the zeroorder term corresponding to the transmission of the incident radiation in the forward direction is not included here. The reason is that such term would interfere with the imaging process involving the amplification by zone plate and is usually removed during experiments by a carefully designed imaging system.[10,14]TheV(x2),closely related to the size of the zone plate,stands for the correction factor of its amplitude transmission function.[7]With an ideal zone plate having an infinitely large area,V(x2)becomes a constant(V(x2)=1 is assumed)and the associated spatial resolution becomes infinitesimal.

whereq=d3(f-m(d1+d2))+f(d1+d2). In particular,the aforementioned x-ray microscope equipped with a Talbot (-Lau)interferometer[5,10]works under this condition.

withτ=(d1+d2)(f-m(d3+d4))+(d3+d4)f.
Further, the ordermis set to +1 because the diffraction efficiencies of other odd orders decrease rapidly by a factor of 1/m2. Similarly, the diffraction ordernof the grating is limited to 0 and±1.[16]By the first-order approximation, the detected beam intensity,i.e.,|U4(x4,η)|2,is proportional to



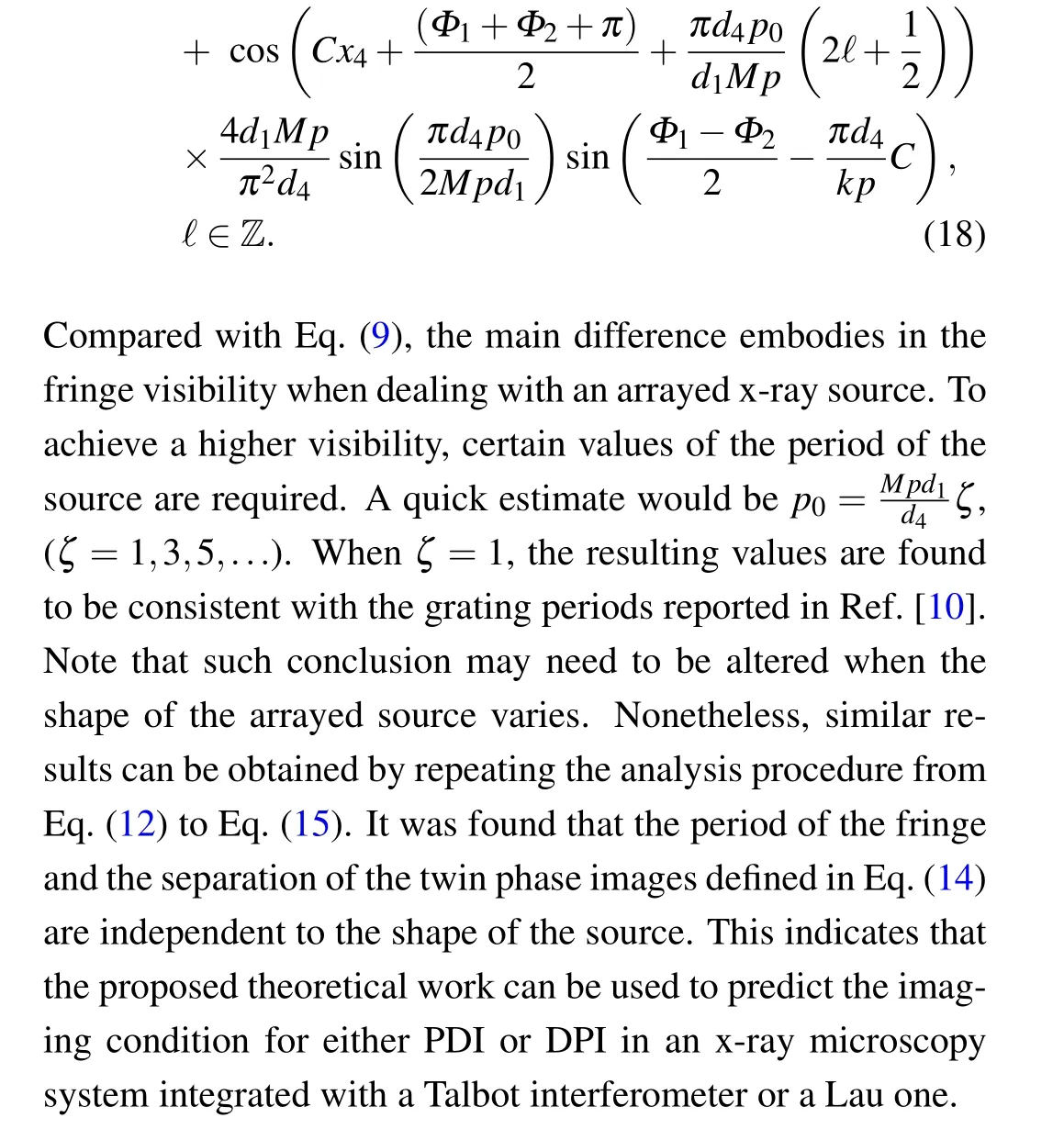
3. Numerical simulation
A series of 2D numerical simulations regarding the x-ray microscopic system shown in Fig. 1 are conducted. There comes with two main objectives. One is to verify the above theoretical derivations in comparison with the experimental measurements.[10,11]The other is to investigate the conversion condition and relationship between PDI and DPI.As discussed above,since the shape of the source only affects the fringe visibility, a point source is always considered in the subsequent numerical calculations for simplicity.
The subsequent simulation work is based on the previous theoretical derivation. Specifically,the Fresnel diffraction integral was calculated based on the discrete fast Fourier transform (DFFT) in Python. The transmission of x-rays through the optical components and the sample is imitated with the projection approximation. It is also assumed that the x-ray source is perfectly coherent and the detector has an ideal response without any crosstalk and photon shot noise. Besides,the resolution of the detector is determined by the discretization of the imaging field of view.To facilitate comparisons,the same imaging geometry and beam energy as listed in Ref.[10]were taken into account. In all simulations, the x-ray energy was fixed at 8.04 keV,and the imaging system ran in the large field of view(LFOV)mode with a 10-fold sample magnification. The simulated imaging field of view is 120μm×120μm with a zone plate having a resolution of 97.7 nm and a detector possessing a pixel dimension of 76.9 nm. Other key parameters to perform the calculations are shown in Table 1.

Table 1. Simulation parameters of the phase grating, zone plate and layout of the interferometer.


Fig.2. Numerical simulation results: (a)the fringe distribution,(b)the phase difference imaging results to evaluate the spatial resolution,(c)the phase difference imaging results,and(d)the differential phase imaging results. The white and black scale bars denote 1μm and 10μm,respectively.


Fig.3. Conversion conditions between PDI(gray area)and DPI(colored area)for the settings in Ref.[10]: (a)with varied spatial resolutions and grating periods;(b)with varied spatial resolutions and the geometrical factor d4/M. The color bar denotes the sensitivity of the DPI.The inverted triangle corresponds to the LFOV mode.
4. Discussion and conclusion
As demonstrated in the theoretical analysis,both the PDI and the DPI can be explained by the same imaging theory,upon which the PDI and DPI are unified. Meanwhile,certain phase signals,either PDI or DPI ones,can be retrieved under specific imaging conditions. By adjusting the imaging condition appropriately, the PDI can be converted to the DPI, or vise versa. For instance, increasing the grating period while maintaining other system settings would transform the x-ray microscope from the PDI mode to the DPI mode. However,our theoretical analysis also reveals that the sensitivity of DPI may be limited when pursuing a high image resolution.To this end,the parameters of an x-ray microscope system integrated with a grating interferometer need to be carefully optimized to meet the desired imaging applications.
In conclusion, we have developed a comprehensive theoretical framework based on the diffraction theory to explain the formation of the phase information in a grating-based x-ray microscope. Analysis demonstrates that the phase difference imaging and the differential phase imaging originate from a unified phase imaging theory and can be converted by changing certain conditions. Additionally, the impact of different optical components including the x-ray source can be analyzed by this imaging theory. In future, optimizations such as exploiting different shaped and polychromatic x-ray sources and varied grating types would be investigated for given x-ray microscope imaging tasks.
Acknowledgements
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 12027812 and 11804356) and the Youth Innovation Promotion Association of the Chinese Academy of Sciences(Grant No.2021362).
- Chinese Physics B的其它文章
- Erratum to“Accurate determination of film thickness by low-angle x-ray reflection”
- Anionic redox reaction mechanism in Na-ion batteries
- Regulation of the intermittent release of giant unilamellar vesicles under osmotic pressure
- Bioinspired tactile perception platform with information encryption function
- Quantum oscillations in a hexagonal boron nitride-supported single crystalline InSb nanosheet
- Temporal response of laminated graded-bandgap GaAs-based photocathode with distributed Bragg reflection structure:Model and simulation

