A uniqueness theorem for holomorphic mappings in the disk sharing totally geodesic hypersurfaces
Jiaxing HUANG(黃家興)+
College of Mathematics and Statistics,Shenzhen University,Shenzhen 518060,China E-mail : hjamath @szu.edu.cn
Tuen Wai NG(吳端偉)
Department of Mathematics,The University of Hong Kong,Pokfulam,Hong Kong E-mail: ntw@maths.hku.hk
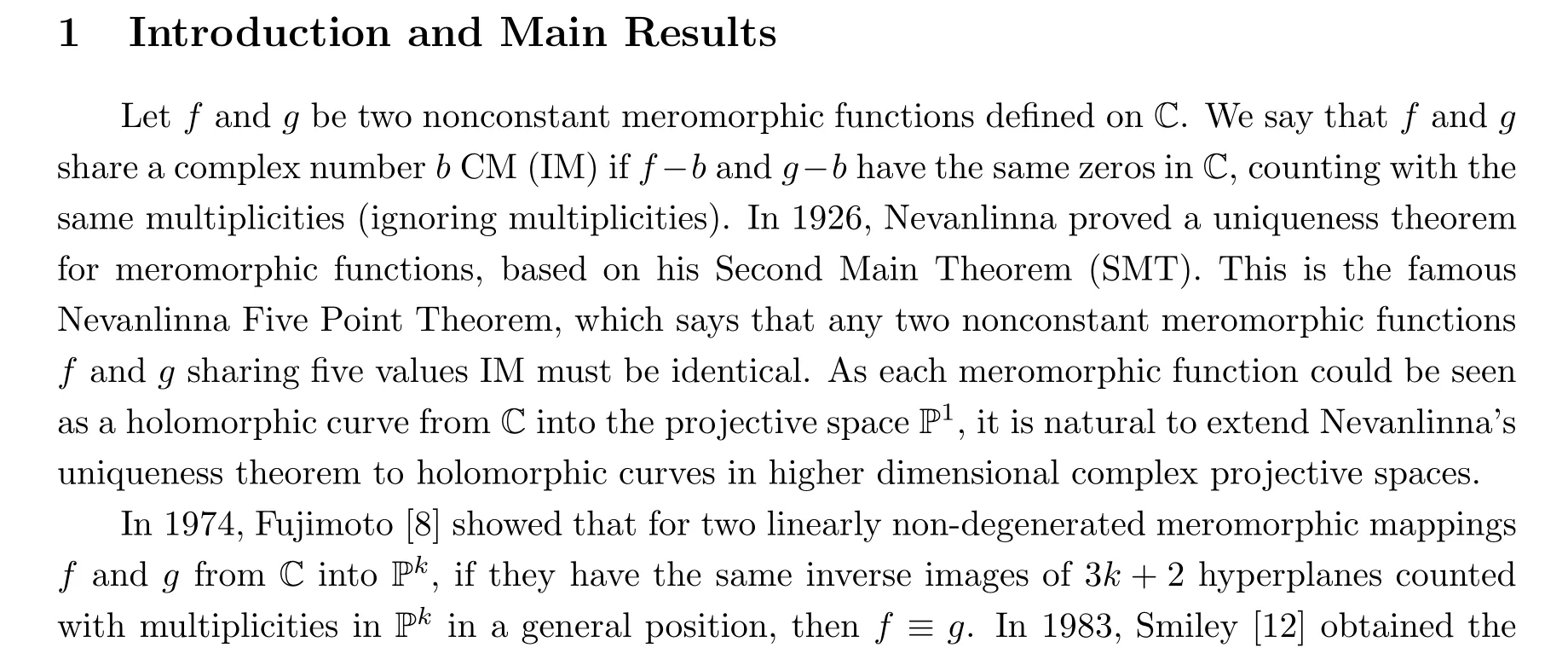


The proof of Theorem 1.1 is based on a Second Main Theorem of An and Phuong [2], and also the following lemma of Dulock and Ru [7]:
Lemma 1.2 ([7]) Let H be a hyperplane line bundle on Pk. For m = 1,2, we let πm: Pk×Pk→Pkbe the canonical projection mappings. Letting f ×g : C →Pk×Pkbe a holomorphic map such that f /≡g, there exists a section s of H′:= π*1H ?π*2H so that the diagonal Δ of Pk×Pkis contained in Supp(s), but the image (f ×g)(C) is not contained in Supp(s).
We notice that the number of sharing hypersurfaces in Dulock-Ru’s result is of order k2k,which is much bigger than 3k + 2 or 2k + 3 in the hyperplane case. As an improvement of the truncated version of Ru’s Second Main Theorem [9], an expected smaller number of hypersurfaces can be found in Theorem 1.4(below)of Quang and An[1]. However,this number is still much bigger than 3k+2 or 2k+3. Therefore, it would be interesting to try to get a uniqueness theorem for holomorphic curves sharing fewer hypersurfaces.
Let V be a complex projective subvariety of Pkof dimension m(≤k). Let d be a positive integer. We denote by I(V) the ideal of homogeneous polynomials in C[X0,...,Xk] defining V, and by Hdthe C-vector space of all homogeneous polynomials in C[X0,...,Xk] of degree d.Define

Definition 1.3 Let f : C →V be a holomorphic mapping of C into V. Then f is said to be degenerated over Id(V) if there exists a non-zero [Q] ∈Id(V) such that Q(f) ≡0.Otherwise, we say that f is non-degenerated over Id(V). One can see that if f is algebraically non-degenerated, then f is non-degenerated over Id(V) for d ≥1.
In 2017, Quang and An first established a truncated version of the Second Main Theorem involving HV(d) and as an application of this, they improved Dulock-Ru’s result (Theorem 1.1) and obtained the following uniqueness theorem for holomorphic curves sharing a possibly

Remark 1.5 Part (b) of Theorem 1.4 implies Chen-Yan’s result [3] (see Corollary 1 in[1]).
Although the number of sharing hypersurfaces in Theorem 1.4 is much smaller than the one in Dulock-Ru’s result (Theorem 1.1), the number HV(d) is not easy to explicitly estimate and is bounded by O(kd) depending on the degree d of the hypersurfaces. In this paper, we would like to give an explicit estimation (around O(k3) and independent over the degree d) of the number of shared special hypersurfaces.
So far, the tools to solve the unicity problem of holomorphic curves have been various versions of the Second Main Theorem. In 2012, Tiba [13] made use of Demailly’s [4] meromorphic partial projective connection (see Definition 1.6)to prove a Second Main Theorem for a holomorphic curve in Pkcrossing totally geodesic hypersurfaces (see Definition 1.8). As a consequence, one can obtain a uniqueness theorem of holomorphic curves intersecting totally geodesic hypersurfaces;the required number of hypersurfaces is smaller than the one in Dulock-Ru’s result(Theorem 1.1), and more precise than the one in Quang-An’s result(Theorem 1.4).
To formulate our result, we have to introduce the definition of meromorphic partial projective connections first provided by Siu [11], and that of totally geodesic hypersurfaces on a complex projective algebraic manifold X. One can refer to Demaily[4],Section 11 or Tiba[13],Section 3 for the details.
Let {Uj}1≤j≤Nbe an affine open covering of X.
Definition 1.6 (Meromorphic partial projective connection) A meromorphic partial projective connection Λ, relative to an affine open covering {Uj}1≤j≤Nof X, is a collection of meromorphic connections Λjon Ujsatisfying

Let D be a reduced effective divisor of a k-dimensional complex projective algebraic manifold X, and let Λ be a meromorphic connection. Consider the holomorphic function s on an open set U ?X such that D|U= (s), and fix a local coordinate system (z1,...,zn) on U. In particular, if X = Pk, one can always construct a meromorphic partial projective connection from some given homogenous polynomials (see Demailly [4] or Tiba [13]).
Let S0,...,Skbe homogenous polynomials of degree d in C[X0,...,Xk] such that


As H1,...,Hqare in a general position, for any k+1 hyperplanes {Hi0,...,Hik},the determinant of (Hi0,...,Hik) is nonzero, hence fi=mgi, and therefore f ≡g.
Recently, Ru and Sibony [10] defined a growth index of a holomorphic map f from a disc DRcentred at zero with radius R to a complex manifold and generalized the classical value distribution theory for holomorphic curves on the whole complex plane.
Definition 1.11 Let M be a complex manifold with a positive (1, 1) form ω of finite volume. Let 0 <R ≤∞and let f : DR→M be a holomorphic map. The growth index of f with respect to ω is defined as

Assume that σj,1 ≤j ≤q are elements of the linear system Yα={α0S0+α1S1+···+αkSk=0}such that the hypersurfaces Yj= (σj),1 ≤j ≤q are smooth and in a general position. Let f and g be two holomorphic maps from DRinto Pkwith cf<∞and cg<∞such that their images are neither contained in the support of an element of the linear system Yαnor contained in the polar locus of Λ. Suppose that f(z)=g(z) for all z ∈S, where


2 Notations and Prelimiraries


3 Proofs of Theorems 1.13 and 1.14




3.2 Proof of Theorem 1.14
Let [X0: ···: Xk] be a homogeneous coordinate system of Pk. Then by the same method used in Section 3 of Tiba[13], one can construct the meromorphic partial projective connection Λ={(Λj,Uj)}0≤j≤kon Pk, where Uj={[X0:···:Xk]∈Pk|Xj/=0}. By Crammer’s rule,the solutions are of the form

4 Proof of Theorem 1.12
To prove Theorem 1.12, we need the following important proposition from [6]:
Proposition 4.1 ([6]) Let σj,1 ≤j ≤q be the smooth hypersurfaces defined in Theorem 1.12. Let f and g be two holomorphic maps from DRinto Pkwith cf<∞and cg<∞.Suppose that f(z)=g(z) for all z ∈S, where


4.1 Proof of Theorem 1.12(i)

4.2 Proof of Theorem 1.12(ii)
We follow the method of Chen and Yan [3]. Suppose that the assertion does not hold. By changing indices if necessary, we may assume that



 Acta Mathematica Scientia(English Series)2022年4期
Acta Mathematica Scientia(English Series)2022年4期
- Acta Mathematica Scientia(English Series)的其它文章
- ITERATIVE ALGORITHMS FOR SYSTEM OF VARIATIONAL INCLUSIONS IN HADAMARD MANIFOLDS*
- Time analyticity for the heat equation on gradient shrinking Ricci solitons
- The metric generalized inverse and its single-value selection in the pricing of contingent claims in an incomplete financial market
- The global combined quasi-neutral and zero-electron-mass limit of non-isentropic Euler-Poisson systems
- Some further results for holomorphic maps on parabolic Riemann surfaces
- Global well-posedness of the 2D Boussinesq equations with partial dissipation
