Development of a High-Resolution Melting Curve Analysis to Differentiate Candida parapsilosis Complex Species
SHAO Ya Kun , XU Juan , GONG Jie , and CHANG Jian Min,#
Owing to their ability to adhere to vascular catheters,prosthetic devices,and the skin of health care workers,the members of theCandida parapsilosiscomplex are considered as some of the most important non-C.albicansagents commonly detected in invasive candidiasis worldwide[1].In addition to causing bloodstream infections,C.parapsilosiscomplex species may also cause septic arthritis,peritonitis,vaginitis,and nail and skin infections.Clinically,theC.parapsilosiscomplex species constitute important pathogens among emerging non-C. albicansspecies,and their significance and prevalence have markedly increased over the past two decades[2].
Invasive candidiasis presents non-specific clinical symptoms,which make early diagnosis challenging.The serologic and phenotypic methods used for the diagnosis of invasive fungal infections—the current gold standards—lack sensitivity and speed,resulting in delayed treatment and decreased survival of patients with candidiasis.In contrast,the sensitivity of molecular methods increases the likelihood of detecting infections at an early stage,when it is easier to treat them or even prevent clinical manifestations.In this sense,diagnosis based on molecular techniques has become increasingly important,particularly for research on nosocomial candidiasis in patients at increased risk and studies on the diversity and dynamics ofCandidaspecies.
TheC.parapsilosiscomplex has three genetically distinct but not easily phenotypically distinguishable cryptic species:C.parapsilosissensu stricto,C.orthopsilosis,andC.metapsilosis[3].Each species in the complex manifests a unique epidemiology,virulence,and antifungal susceptibility[4,5]. For example,a 5-year surveillance ofCandidaspp.from sixty-five tertiary hospitals from the National China Hospital Invasive Fungal Surveillance Net (NCHIFSN)reported that theC.parapsilosiscomplex species were the second most common causative agents and that the susceptibility ofC.parapsilosissensu stricto,C.orthopsilosis,andC.metapsilosisto fluconazole was 93.4%,68.6%,and 70.1%,respectively[6].In this context,it is critical to identify the exact species involved in the infections.
Owing to their stability and greater resolution in typing,genotypic methods have advantages in differentiating and characterizing the taxonomy of fungal isolates.To date,studies have investigated the identification theC.parapsilosiscomplex species using DNA-based techniques,such as randomly amplified polymorphic DNA analysis,restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of specific gene loci,and sequencing of the internal transcribed spacer (ITS)[7].However,these methods are time consuming and labor intensive.Real-time quantitative PCR (qPCR) followed by a highresolution melting (HRM) curve analysis is a newly established PCR-based technique that has been used to differentiate medically importantCandidaspp.[8,9].The qPCR-HRM curve analysis method utilizes a dsDNA-binding saturation dye to monitor the shedding of the dye during the heating process,which facilitates the detection of genetic variation at the resolution of single nucleotide polymorphisms in amplified DNA fragments without sequencing.The differences in length,GC content,and sequence of DNA fragments lead to different melting profiles,which facilitate the detection of micro-differences among target sequences.Unlike other PCR-based technologies,this method does not require post-processing,such as electrophoresis or enzymatic digestion;thus,it avoids external nucleic acid contamination.The key to success in HRM curve analysis is the design of specific primers that generate discernibly different melting profiles with appropriate amplification lengths.It has been reported that single nucleotide modifications in short amplicons can cause unique changes in the melting curve.Furthermore,this qPCR-HRM method can also be used to quantify the concentrations of nucleic acids in the original specimen.
It was previously reported that mitochondrial genomes are more useful than nuclear genomes in the characterization of close phylogenetic relationships in yeasts.The cytochrome oxidase subunit gene (Cox) in the mitochondrial genome is useful forCandidaspp.typing and clustering[10].TheCox3gene was recognized to be a valuable target for evaluating close phylogenetic relationships among species in theC.parapsilosiscomplex with a multilocus sequence typing method[3].To explore the potential region for species identification using the qPCR-HRM method,we first collected the published sequences ofCox3inC.parapsilosisin NCBI(http://ncbi.nlm.nih.gov),DDBJ (www.ddbj.nig.ac),and EMBL (http://www.embl.fr/) databases.Then,sequence comparisons were performed using Vector software.Multiple primer pairs for theCox3gene were designed using LaserGene software (version 7.1).Optimal specific primers were obtained by performing gradient PCR using reference strain template DNA (the annealing temperature ranged from 48 °C to 64 °C),and a pair of appropriate primers that could amplify the DNA from all three species was identified using agarose gel electrophoresis. Other factors such as primer concentrations and other thermocycling parameters of the qPCR-HRM assay were also optimized using the DNA of each reference strain and the negative controls (Table 1).
A 115 bp amplified fragment was obtained as thetarget (Figure 1),which only contained 6 bp differences among the threeCandidaspecies.The sequences of the primers were as follows:forward(F):5′-ACTGGTTTACATGGWTTACA-3′ and reverse (R):5’-TAGTTGTTTCAGCACCAAC-3’.A BLASTn search in NCBI (http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi) was performed to verify the specificity of the primers to each species.The optimized qPCR was performed using the ABI QuantStudio 6 Flex real-time PCR system (Thermo Fisher Scientific,USA) in a 30 μL reaction mixture containing 15 μL TaqMan qPCR Mix(2×;TaKaRa),0.9 μL each of forward and reverse primers,0.3 μL Rox Reference Dye II (100×),1.5 μL EvaGreen (20× dilution in water),2 μL DNA template,and 9.4 μL ultrapure water.The PCR conditions were as follows:95 °C for 10 min,followed by 40 cycles of 95 °C for 12 s,60 °C for 20 s,and 70 °C for 20 s.The heating and cooling rate was 1.6 °C/s,and HRM ramping was performed from 60 °C to 95 °C;then,the fluorescence signals were collected during a temperature increase of 0.025 °C/s to generate a melting curve.All data were entered into Excel 2007,and the means and standard deviation (SD) of melting temperature (Tm) were calculated.

Figure 1. Aligned sequences of the amplified Cox3 region in three reference strains.Conserved bases are represented in yellow,whereas variable sites are indicated in blue and white.The primer regions are underlined in red.
The assay was performed with the reference strains and the negative controls.The results showed that the negative control DNA was not amplified,indicating the high specificity of the method.The reference strains showed three specific melting profiles (Figure 2A). Taking the first derivative of the fluorescence signal,we obtained three reproducible melting peaks (Figure 2B).The melting curves of the three species were unimodal,and their corresponding Tmvalues differed.The Tm(mean ± 3SD) values ofC.parapsilosis sensu stricto,C.orthopsilosis,andC.metapsilosiswere 76.015 ±0.035 °C,75.389 ± 0.031 °C,and 75.713 ± 0.020 °C,respectively.
The sensitivity and detection limit were analyzed using the synthesized plasmids for each species.The quantified plasmids were synthesized in Sangon Biotech (Shanghai) Co.,Ltd.,using the cloned sequences of the amplified fragment in each species.The concentrations of the plasmids were measured by Qubit,and their unit was converted to copies per microliter with the following formula:number of copies/μL=(6.02 × 1023) × (ng/μL × 10-9)/ (DNA length × 660).Using a gradient dilution of the plasmids with ultrapure water (1 × 107-1 × 101copies/μL),the qPCR-HRM analysis was performed again to examine the minimum detection limits of the method.The HRM profiles were then analyzed using ABI QuantStudio 6 Flex HRM analysis software;the highly dense measurement points recorded during the high-resolution melting stage were used to generate the species-specific HRM curves.The above procedure was repeated three times,and different ranges of Tmvalues were assessed.The mean Tm± 3 SD range was selected to overcome intra-assay variability and achieve maximum sensitivity and reproducibility.In the qPCR-HRM assay performed on plasmids with gradient dilution,the amplification curves exhibited a typical "S" shape within the concentration range of 1 × 107-1 × 101copies/μL (Figure 2C).The standard curve based on the dilutions of the plasmid DNA showed a linear relationship between the logarithmic value of the copy number and the threshold cycle number (Ct;Figure 2D).Species-specific copy numbers were obtained by the following equation using the standard curve:Y(Ct)=-3.3735X(log [copy number])+38.913 (R2=0.9987).The maximum Ct value (Ct=35) in the linear range corresponded to the concentration of 1 × 101copies/μL for each species.Therefore,the minimum detection limit was approximately 1 × 101copies/μL.However,the distinguishable melting curve for each species were obtained only after the concentration ≥ 1 × 102copies/μL;thus,the minimum detection limit of this assay was decided as 1 × 102copies/μL.
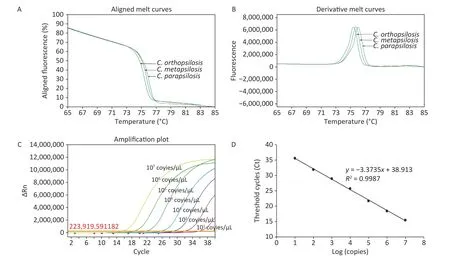
Figure 2. Melting curves,peak diagrams,and standard curves based on plasmid DNA for three species in the Candida parapsilosis complex obtained using the quantitative PCR high-resolution melting (qPCRHRM) curve analysis.In the period during which the fluorescence signal decline accelerated,three mutually distinct curves were observed,which were used for species identification (A).The melting curves of the three species are unimodal,and the mean melting temperature (Tm) of C.parapsilosis sensu stricto,C.orthopsilosis and C.metapsilosis was 76.015 ± 0.035 °C,75.389 ± 0.031 °C,and 75.713 ± 0.020 °C,respectively (B).The qPCR amplification curves exhibited a typical "S" shape between plasmid DNA concentrations of 1 × 107 to 1 × 101 copies/μL (C).The standard curve based on gradient dilution of plasmid DNA showed a linear relationship between the logarithmic value of the copy number and threshold cycle number.Species-specific copy numbers could be obtained by the following equation using the standard curve:Y (Ct)=-3.3735X (log [copy number])+38.913 (R2=0.9987;D).
The above results indicated that this qPCR-HRM assay is effective for yeast culture identification.Its applicability to clinical practice is also crucial.However,the patients infected withC.parapsilosiscomplex present variable clinical symptoms;collecting clinical specimens in a short time from patients in one department even at one hospital is challenging.Sample spiked with the target species is one useful method to mimic fungal-contaminated clinical specimens.To assess the applicability of the assay for species detection directly obtained from clinical specimens,twenty EDTA-whole blood samples stocked in the laboratory,which were previously obtained from anonymous healthy donors,were screened for non-Candidacontamination using both culture and traditional PCR methods.Each sample was spiked with 101to 106CFU/mLC.parapsilosiscomplex species.DNA was extracted using QIAamp DNA Blood Mini Kit (Qiagen,51304),and the qPCR-HRM curve assay was performed as described above. qPCR analysis showed that all original samples were negative for each species in theC.parapsilosiscomplex.The limit of detection reached up to 103CFU/mL for each species in the spiked samples (Ct ≤ 35,and the melting curves were distinguishable).Although the clinical applicability of this assay was demonstrated in the present study using spiked samples,its applicability to direct clinical specimens remains to be verified.A collaborative study between multiple departments and hospitals will be considered in the future.
In conclusion,the assay described in this work can be used for the rapid and accurate detection and differentiation of theC. parapsilosiscomplex species.It would be useful both in clinical diagnosis and epidemiological investigation.
The authors declare no competing financial interest.SHAO Ya Kun performed the experiments,analyzed the data,and wrote the manuscript.XU Juan cultured the fungal strains and prepared the figures.GONG Jie provided the reference strains.CHANG Jian Min contributed to manuscript revision.
 Biomedical and Environmental Sciences2021年6期
Biomedical and Environmental Sciences2021年6期
- Biomedical and Environmental Sciences的其它文章
- Collaborative Efforts of Families,Schools,Health Care Providers,and the Government to Control Childhood Obesity in China
- The Improved Lipid Accumulation Product is an Accurate Index for Predicting Metabolic Syndrome in the Xinjiang Population
- Benzodiazepines and Amphetamines Use among Methadone Maintenance Participants and Their Associations with Treatment Adherence
- Quantitative Microbial Risk Assessment of Cryptosporidium and Giardia in Public Drinking Water in China*
- Campylobacter Outbreak Associated with Duck Blood Curd in 2019 in Shunyi District,Beijing,China
- Phylogenetic Analysis of Legionella Strains and ldentification of Serogroups by Lipopolysaccharide-and O-antigen-based PCR Assay*
