Spectroscopic Investigations for the Six New Synthesized Complexes of Fluoroquinolones and Quinolones Drugs With Nickel(Ⅱ) Metal Ion: Infrared and Electronic Spectroscopy
Samar O. Aljazzar
Department of Chemistry, College of Science, Princess Nourah Bint Abdulrahman University, Riyadh 11671, Saudi Arabia
Abstract Quinolone has a broad spectrum of synthetic antibiotics with a strong therapeutic effect and quinolone is a term used for chemical treatments used to treat a powerful bacteria. Quinolones are divided into 4 generations according to the bacterial spectrum, the majority of quinolones used clinically belong to the sub fluoroquinolones group, which has a fluorine atom linked to the central ring system, usually on its carbon atom 6 or 7. Herein in this article, six new nickel(Ⅱ) complexes (Ⅰ—Ⅵ) have been synthesized in aqueous alkaline media at pH ranged 8-9, the chemical reactions take place between levofloxacin (HLEV), lomefloxacin (HLOM), nalidixic acid (HNLA), oxolonic acid (HOXO), pipemidic acid (HPIP), and pefloxacin mesylate (HPEF) with nickel(Ⅱ) nitrate hexahydrate. The microanalytical (percentage of carbon, hydrogen and nitrogen), molar conductance (Λm), Infrared (FTIR) spectra, electronic (UV-Vis) spectra, and effective magnetic moment instrumentals were used to identify the suggested structures and their surface morphology. According the analytical and spectroscopic analyses, the stoichiometry between nickel(Ⅱ) metal ion and drug ligands was found to be 1∶2 with general formula as [Ni(L)2(H2O)2]·xH2O (L=LEV (Ⅰ), LOM (Ⅱ), NAL (Ⅲ), OXO (Ⅳ), PIP (V), and PEF (Ⅵ); x=2 or 4). By the comparison between FTIR spectra of quinolone drugs and their complexes, it can be deduced that all the drug ligands act as a bidentate chelates through oxygen atoms of pyridine ring and carboxylate group. The electronic configuration of all synthesized nickel(Ⅱ) complexes were octahedral geometry which confirmed based on the values of magnetic susceptibility and the electronic transition bands.
Keywords Quinolone; Fluoroquinolone; Nickel; FTIR; Chelates; UV-Vis; Octahedral geometry
Introduction
Quinolones are an important antibacterial drug family, because of their wide medicinal applications[1]against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. The essential structure of quinolone drug consists of bicyclic ring fitted with five essential substituted places at N-1,carboxylic group at C-3, carbonyl group at C-4, fluorine atom at C-6 and piperazinyl or methyl piperazinyl groups at C-7. The presence of a different functional group at sites C-7 or N-1 affects on microbiological and pharmacokinetic properties[2]. The quinolone drugs have a good ability to form complexity towards different metal ions that act as a unidentate, bidentate and bridging bidentate chelate[3-26]. Quinolone and fluoroquinolones drugs are binding as a bidentate fashion via oxygen atoms of carboxylic group and pyridin-4-one ring, uni-dentate chelate via nitrogen atom of piperazinyl ring, and in some rare cases the quinolones drugs are coordinated as a bidentate toward metal ions through the two oxygen atoms of carboxylic group or through two nitrogen atoms of piperazinyl ring[3]. There are number of quinolone (HNAL, HOXO and HPIP) and fluoroquinolones (HLEV, HLOM and HPEF) metal complexes have been synthesized and characterized in literature survey in order to recognized the speculated structures[3-28]. These can be summarized as follows regarding the six quinolone drugs which were studied in this article (Table 1).
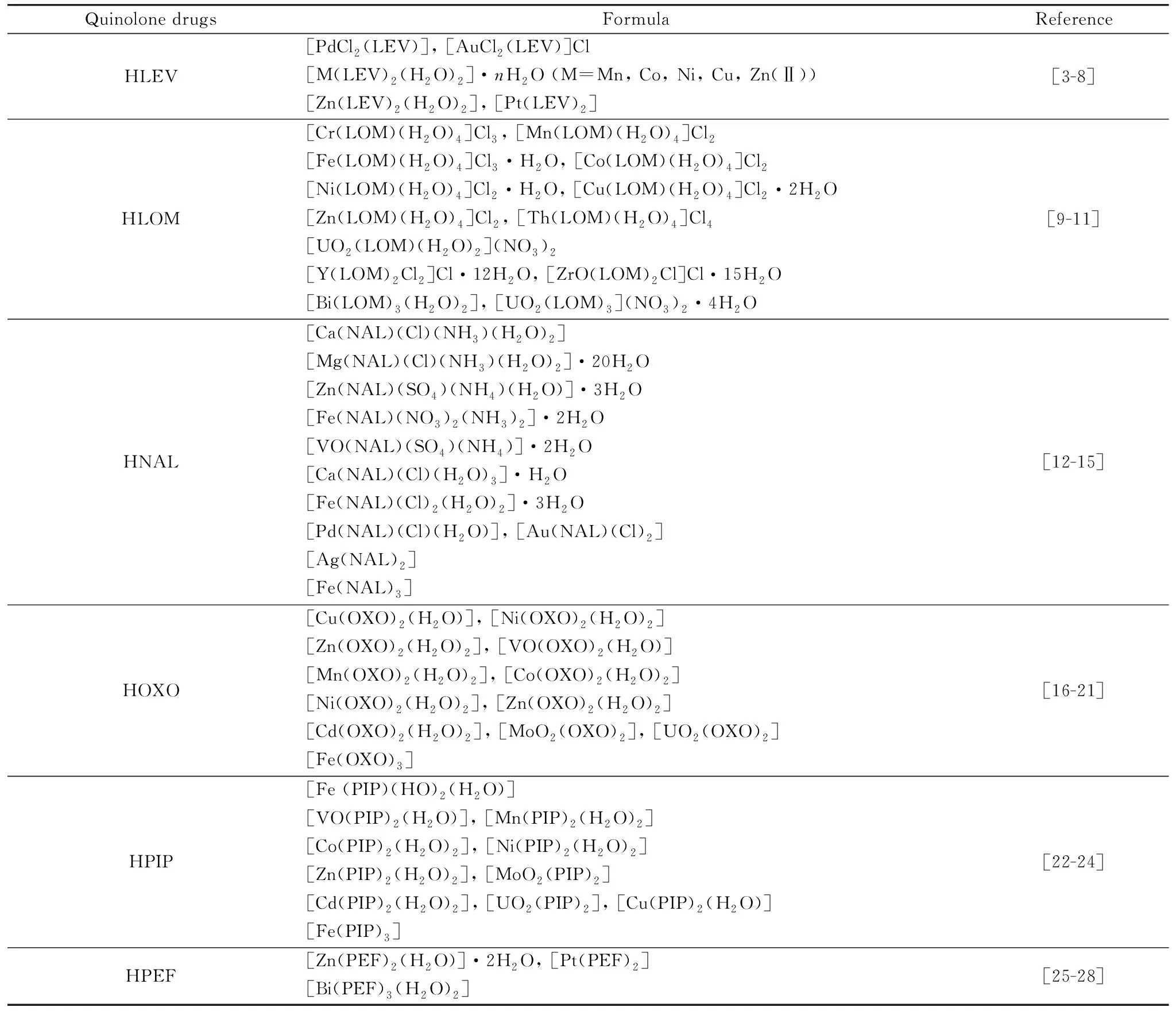
Table 1 Literature survey of HLEV, HLOM, HNAL, HOXO, HPIP, and HPEF metal complexes
This article aimed to synthesis and spectroscopic characterizations for the six new complexes associated from the chemical interaction between HLEV, HLOM, HNAL, HOXO, HPIP, and HPEF drug chelates with Ni(NO3)2·6H2O by 1∶2 (M∶L) ratio in alkaline media. The chelation behavior and structural elucidation of the nickel(Ⅱ) complexes have been built up according to elemental analysis, molar conductance, magnetic, FTIR, and electronic UV(Vis spectroscopic analyses.
1 Experimental
1.1 Chemical reagents
The chemical reagents (Ni(NO3)2·6H2O, dimethylsulfoxide, levofloxacin, lomefloxacin, nalidixic acid, oxolonic acid, pipemidic acid, and pefloxacin mesylate) received in this study were of analytical grade and used without further purifications. These chemicals were purchased from Aldrich-Sigma chemical company.
1.2 Instrumental analysis
The microanalytical and spectroscopic analysis that used to discussed the chemical formula of nickel(Ⅱ) quinolone complexes can be summarized in Table 2.
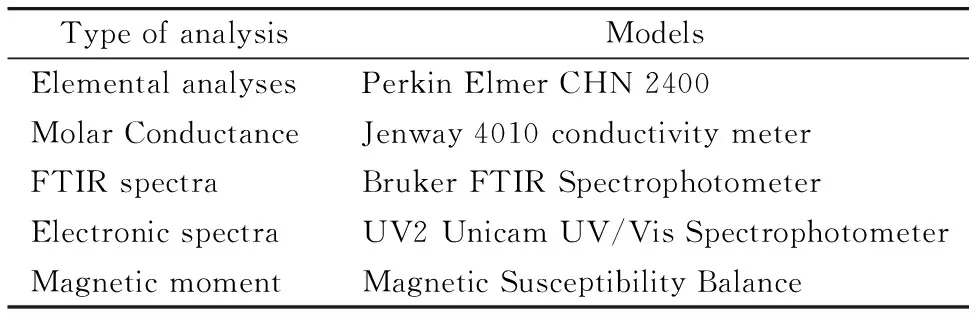
Table 2 The type of analysis and the model of instrument
1.3 Synthesis of Ni(Ⅱ) quinolones complexes
The six solid nickel(Ⅱ) quinolone complexes were synthesized by mixing 2.0 mmol HLEV, HLOM, HNAL, HOXO, HPIP or HPEF drugs in 50 mL of methanol solvent with 1.0 mmol of Ni(NO3)2·6H2O in 20 mL of distilled water. The reaction mixtures were adjust the pH value between 8~9 using ammonia solution (5%), then the mixtures were refluxed on the hotplate for three hours till the precipitate appeared. After cooling to room temperature, the green solid complexes were filtered off and washed with a hot methanol and little amount of distilled water in order to remove the un-reacted chemicals. The clean precipitates were dried and stored in a glass desiccators over anhydrous CaCl2. The yield of the isolated products was ranged between 77%~74%. The melting points of synthesized nickel(Ⅱ) complexes have a higher m.p over >250 ℃.
2 Results and discussion
The green solid nickel(Ⅱ) quinolone complexes were well characterized using elemental analysis, magnetic measurements, molar conductance, FTIR, and electronic spectroscopy. Because of these complexes have an amorphous status, so the X-ray crystal structure didn’t performed.
2.1 Microanalytical and conductance measurements
The elemental analysis (calculated/Found) and physical values of the six new nickel(Ⅱ) quinolone complexes are listed in Table 3. The experimental percentage (%) of each elements C, H, N and nickel metal in situ synthesized complexes were matched with the theoretical values, which confirmed the speculated structures of the six nickel(Ⅱ) complexes (Fig.1). The synthesized Ni(Ⅱ) complexes were stable in air and insoluble in most organic solvent but soluble in dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) and dimethylformamide (DMF) with warming. The molar conductivities (Λm) values are located within 9~12 ohm-1·cm2·mol-1, which were considered as non-electrolytes nature[29].

Table 3 Microanalytical and physical data of Ni(Ⅱ) quinolone complexes
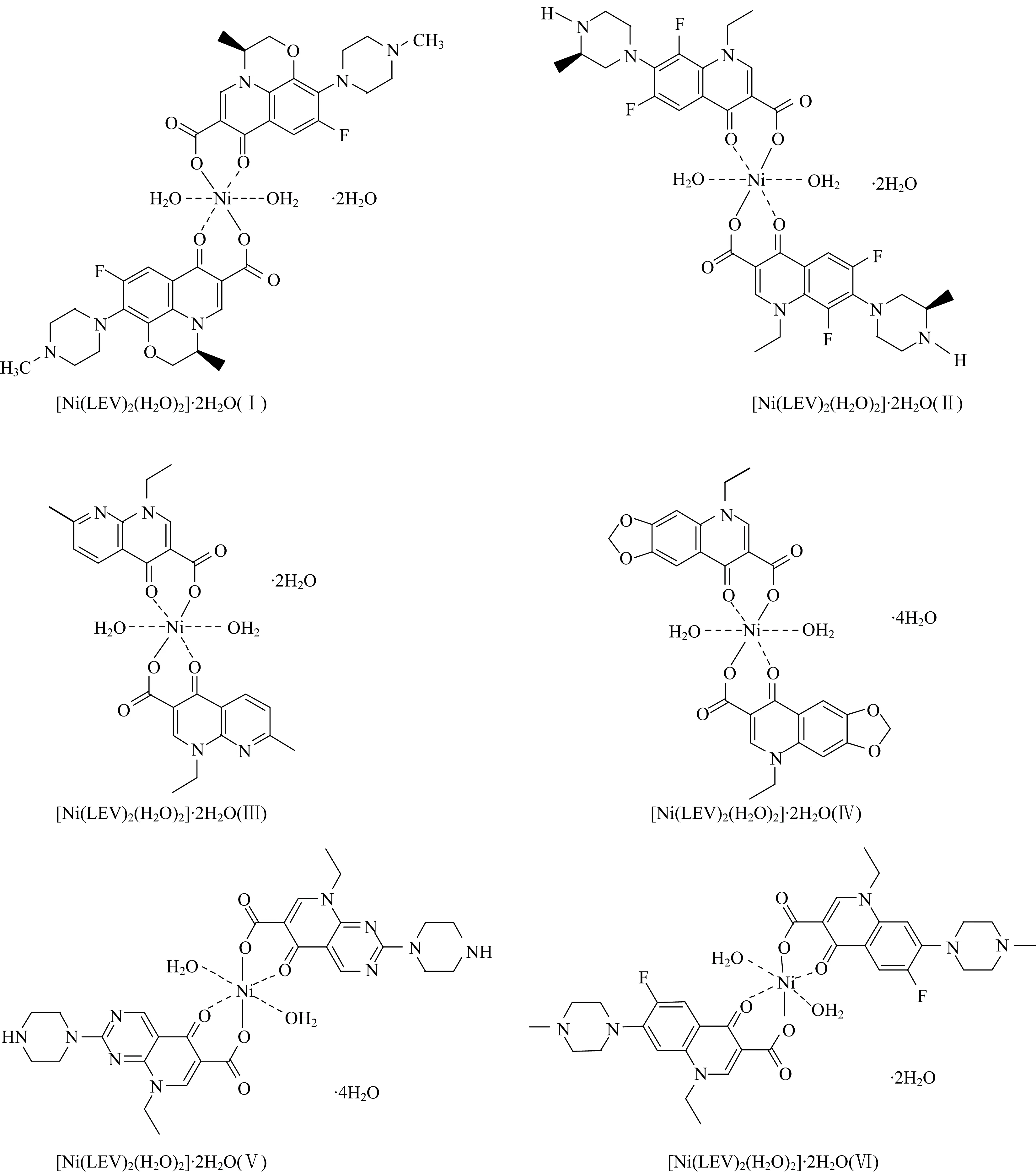
Fig.1 Speculated structures of Ni(Ⅱ) quinolone complexes
2.2 Infrared spectra

2.3 Electronic spectra
The electronic spectra of six nickel(Ⅱ) quinolone complexes contains three absortion bands exhibited at three regions as 13 333~14 388, 14 535~15 674, and 24 390~25 707 cm-1, these electronic transition bands are assigned to3A2g→3T2g(F), (ν1);3A2g→3T1g(F), (ν2) and3A2g→3T2g(P), (ν3) transitions, respectively. The divide data ofν2/ν1ratios concerning the synthesized nickel(Ⅱ) complexes are presence at 1.04~1.16, this results located within the range of an octahedral geometry for the Ni(Ⅱ) complexes (Table 5)[31]. The low values ofν2/ν1are due to the strong interaction between3T1g(P) and3T1g(F) states. The Racah inter-electronic repulsion (B), ligand field splitting energy (10 Dq), covalency factor (β) and ligand field stabilization energy (LFSE) as a physical spectroscopic parameters have been estimated according to the electronic spectra. The B parameter is low in comparison with free nickel(Ⅱ) ion (1 038 cm-1), this meaning that nickel(Ⅱ) complexes have a covalent character. The covalency factor (β) of the six nickel(Ⅱ) complexes has data within 0.04~0.17 region and the percentage lowering of energy in free gaseous ion (β°) has data within 82%~96% which their assigned to the covalency nature of complexes.
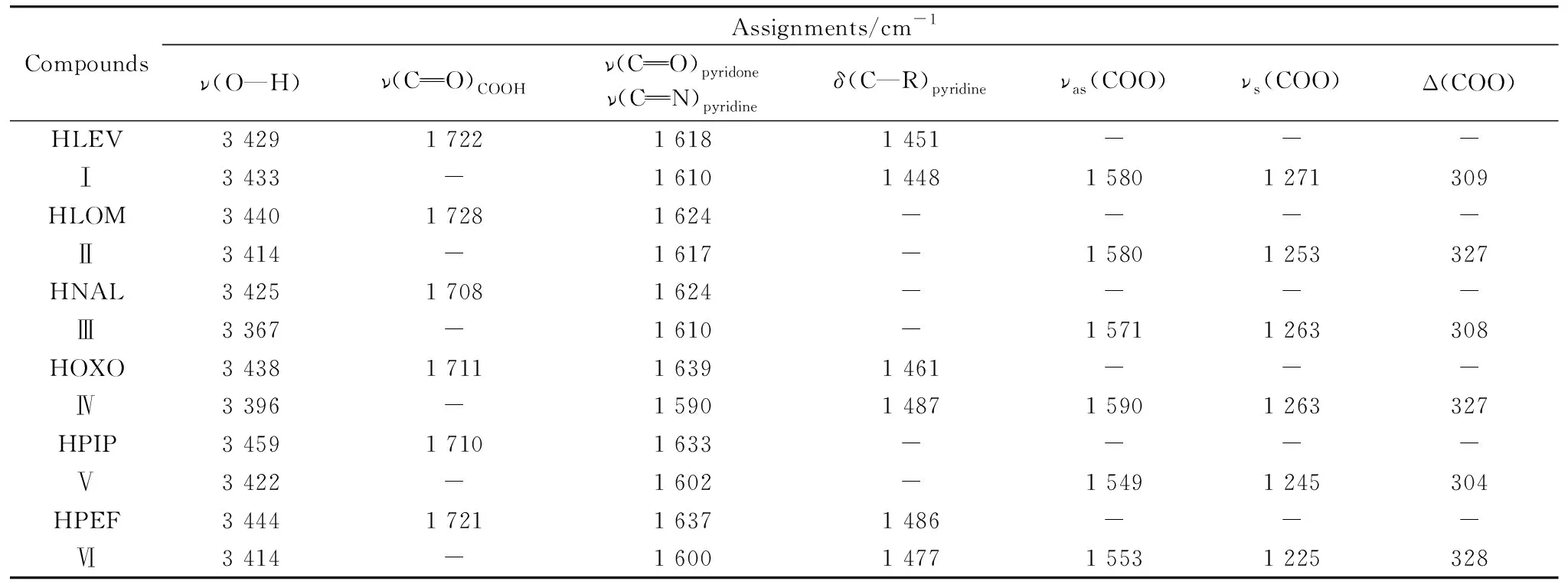
Table 4 FTIR assignments of Ni(Ⅱ) quinolone complexes (Ⅰ—Ⅵ)
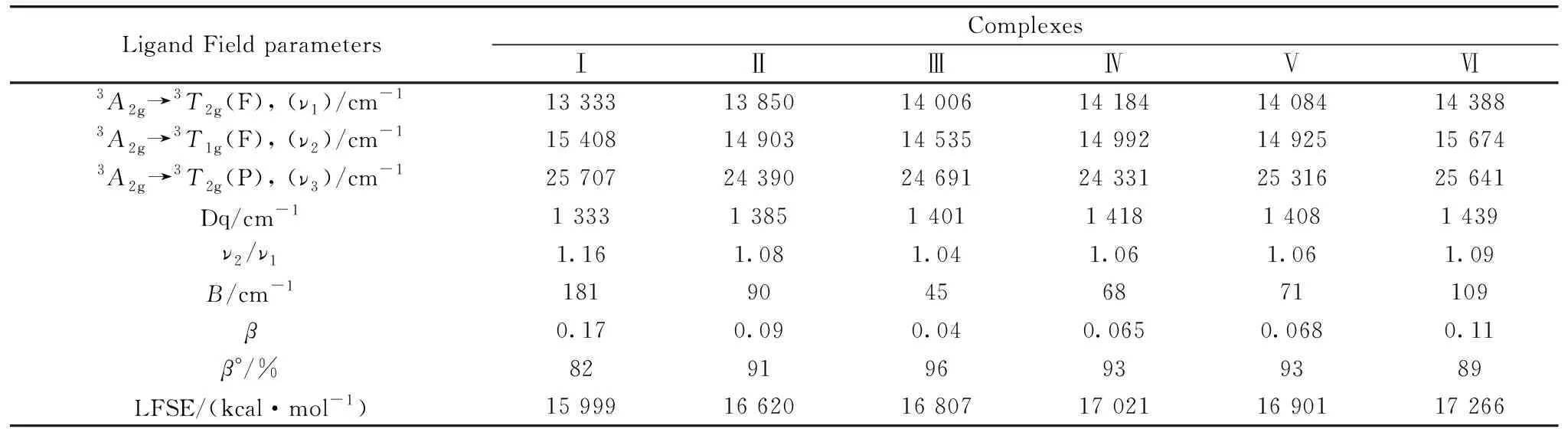
Table 5 Ligand field parameters of the Ni(Ⅱ) quinolone complexes (Ⅰ—Ⅵ)
2.4 Magnetic measurements
The experimental effective magnetic moment of the nickel(Ⅱ) quinoloe complexes (Ⅰ—Ⅵ) are presence within 3.12~347 BM that agreement with the high spin octahedral geometry (3.00~3.50 BM)[31-32]. The high spin values may be assigned to the quenched of3A2gground state regarding the Ni(Ⅱ) ion in an octahedral structure[31-32].
- 光譜學(xué)與光譜分析的其它文章
- Synthesis, Structural, Spectroscopic Characterization and Biological Properties of the Zn(Ⅱ), Cu(Ⅱ), Ni(Ⅱ), Co(Ⅱ), and Mn(Ⅱ) Complexes With the Widely Used Herbicide 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic Acid
- 激光誘導(dǎo)擊穿光譜在疾病診斷中的應(yīng)用前景
- 沸水浸提-電感耦合等離子體發(fā)射光譜法測(cè)定土壤中的有效硼
- 生成式對(duì)抗網(wǎng)絡(luò)的土壤有機(jī)質(zhì)高光譜估測(cè)模型
- Tb3+摻雜鋰鋁硅酸鹽玻璃的光致發(fā)光和輻照致發(fā)光
- 典型光譜吸收模型對(duì)靜止軌道毫米波輻射分析

