Wave–activity relation containing wave–basic flow interaction based on decomposition of general potential vorticity?
Na Li(李娜), Ling-Kun Ran(冉令坤),3,?, and Bao-Feng Jiao(焦寶峰),2
1Key Laboratory of Cloud-Precipitation Physics and Severe Storms(LACS),Institute of Atmospheric Physics,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Beijing 100029,China
2Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology,Nanjing 210044,China
3University of the Chinese Academy of Sciences,Beijing 100049,China
Keywords: wave–activity density,basic state–wave interaction,wave–activity relation
1. Introduction
The wave–activity relation is a useful tool for illustrating disturbance developments and evaluating the interaction between waves and basic flow.[1,2]Generally, the relation takes the following flux form:

Ran and Gao[13]derived a three-dimensional(3D)wave–activity relation for the pseudomomentum in Cartesian coordinates by the momentum–Casimir method. Because the relation was constructed in an ageostrophic and nonhydrostatic dynamic framework, it is applicable to mesoscale phenomena. Nevertheless,the wave–activity relation constructed by the Casimir method requires the basic-state velocity and basic-state Casimir function to satisfy a restriction relation,which greatly limits its applications. Realizing this, Gao and Ran[14]constructed the general wave–activity relations associated with vertical velocity perturbation on the basis of potential vorticity (PV) theorem.[15]These wave–activity relations are easy to calculate and flexible to use. An application of them to a heavy-rainfall event demonstrated that the general wave–activity densities were consistent with the rain rate simulated by numerical models.
However,the wave–basic flow interaction essentially contains two dynamic processes: the forcing of the basic states to waves and the feedback of waves to basic states. The former is represented by the“wave–activity(conservation)relation”,while the latter is generally described by the “Eliassen–Palm(E–P)flux theory”. A common problem in the previous investigations of wave–activity relations(also seen in Eq.(1))is that the two processes were separated. When the wave–activity relation was mainly considered,the feedback of waves to basic states was not taken into account.
In this paper, we derive a new wave–activity relation, in which the wave–activity density is the general PV(GPV)perturbation quadratic in disturbance amplitude. The GPV perturbation is defined as the scalar product of the curl of the horizontal velocity perturbation and the spatial gradient of an arbitrary scalar perturbation based on the work of Haynes and McIntyre[15]and Gao and Ran.[15]An important feature of this new wave–activity relation that differs from previous wave–activity relation is that it shares an exchange term with the basic-state GPV equation.Thus,the two equations connect the two processes in the wave–basic flow interaction. The theory is initially applied to a landfalling typhoon. The characteristics of the interaction between the wave–activity density and basic-state GPV during the event and their relations to heavy rainfall in the typhoon are examined.
The rest of this paper is arranged as follows. The theory is detailed in Section 2. The application of the newlyderived wave–activity relation to a landfall-typhoon heavyrainfall event is discussed and analyzed in Section 3. Concluding remarks are presented in Section 4.
2. Formulae
The general form of potential vorticity (GPV)[15]is defined as
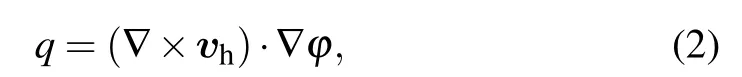
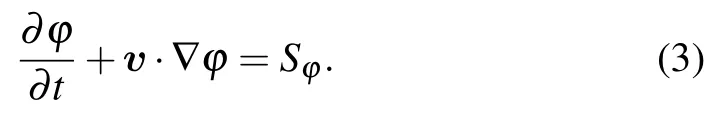
Note that ? can be any scalar, e.g., potential temperature,moist potential temperature or even potential vorticity,as long as it satisfies Eq.(3). S?is the source or sink of ?.
All the variables in the primitive equations of atmosphere[16]and Eq. (3), e.g., u, v, ?, are assumed to be able to be decomposed into a basic state and a perturbation,

Substituting decompositions of the variables (such as Eq.(4))into Eq.(2),GPV can be decomposed into,

where

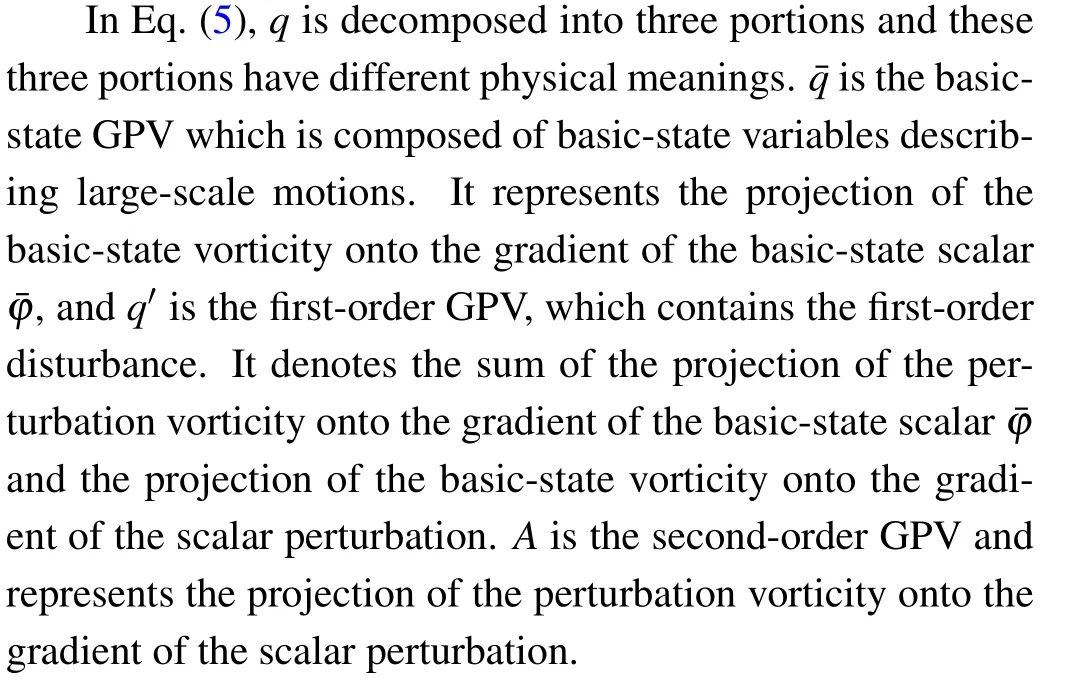
Since A is quadratic in perturbation fields,it is in essence a type of wave energy and is capable of representing mesoscale perturbation imposed on a basic flow. Therefore, A is the socalled wave–activity density in this paper. What kind of physical information is contained in the wave–activity density A is determined by the decomposition of the basic state and the perturbation.Here,the Reynolds average is used to yield the basic state and to derive the wave–activity relation for A. It will be found that through the Reynolds average,the basic state–wave interaction is contained in the wave–activity relation.
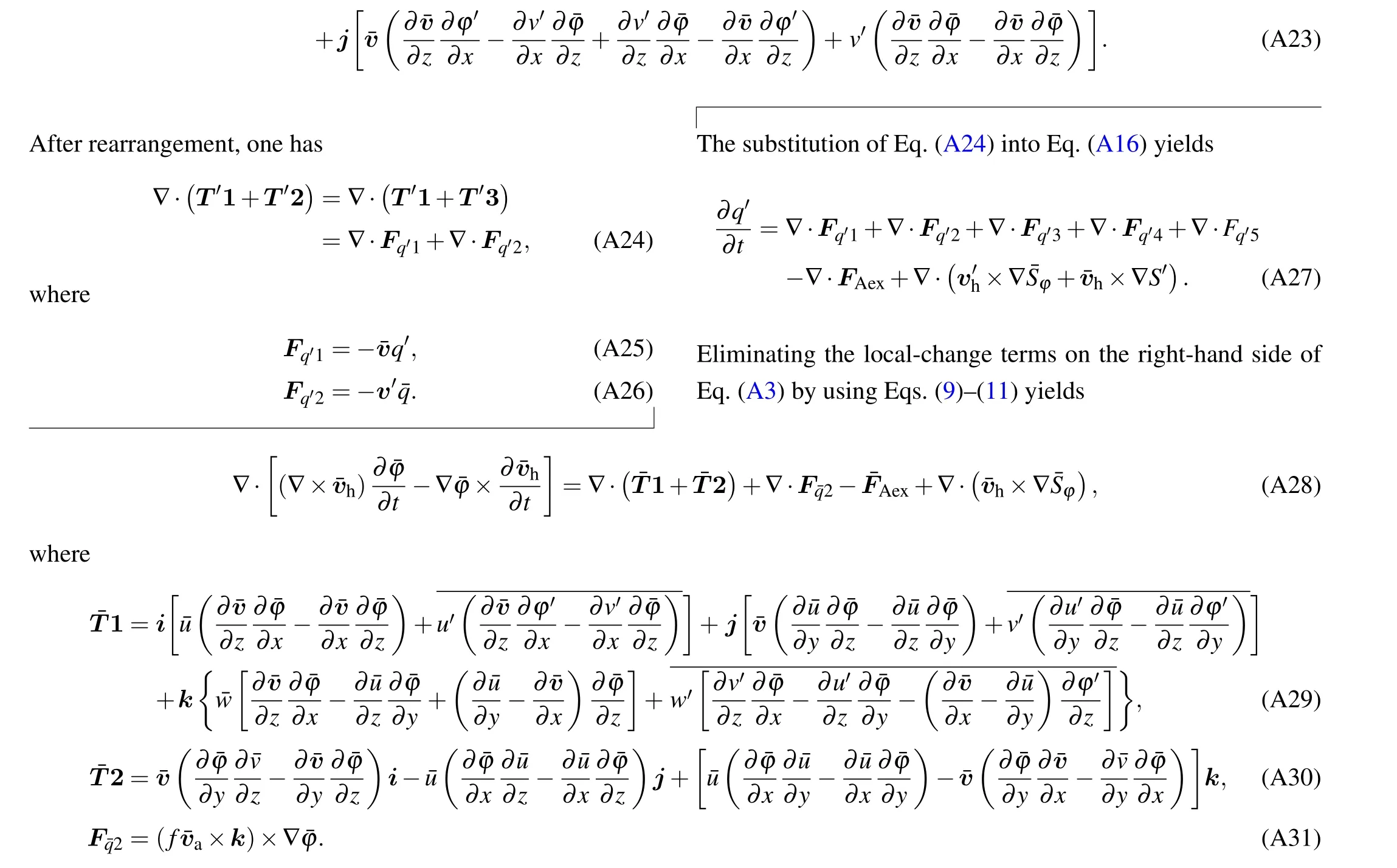
Substituting the decompositions like Eq. (4) into the primitive equations[16]and Eq.(3)and applying the Reynolds average, one can obtain the basic-state tendency equations as follows:


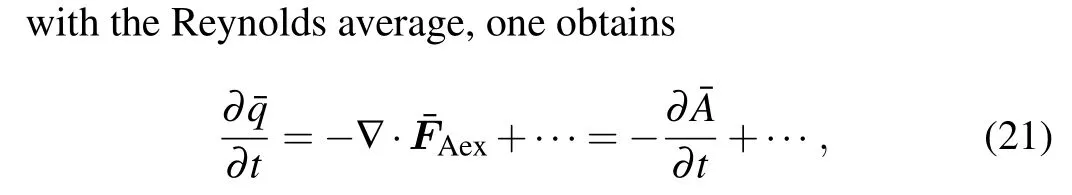
which states the interaction between the wave–activity density and basic-state GPV,and thus may be used to study the wave–mean flow interaction in mesoscale process.
3. Application
As a first application, the above newly-derived wave–activity density and wave–activity relation are calculated and analyzed in a landfalling typhoon in China–Mujigae (2015).The purpose is to preliminarily see the characteristics of the interactions between waves and basic states diagnosed from Eq.(23),and also the relation of the interaction to strong precipitation.
3.1. Determination of ?
Before application, an important task is to determine the arbitrary scalar ?. Here, considering the characteristics of the rainfall atmosphere, a moist potential temperature called generalized potential temperature (θ?, GPT) is used, namely,? =θ?. The GPT proposed by Gao et al.[17]is used to describe a non-uniformly saturated characteristic of the precipitation atmosphere. It is defined as
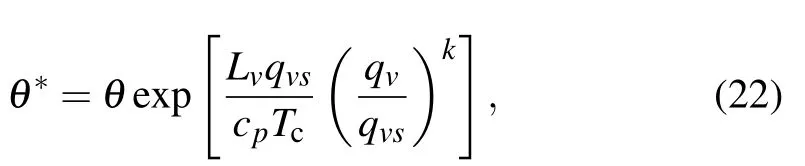
where Lvis he latent heat, qvis the specific humidity, qvsis the saturated specific humidity, Tcis the temperature at the condensation lift level, and k is a constant, θ?decreases to θ for dry air,and is equal to the equivalent potential temperature θse=θ exp(Lvqvs/cpTc)for a saturated moist atmosphere.The GPT may describe the thermodynamical situation of a moist atmosphere more realistically than θ and θse.
3.2. Data
The data for the analysis come from a high-resolution simulation of Mujigae with the weather research and forecasting model(WRF)[18]performed by Jiao et al.[19,20]The simulation began at 1200 UTC 3 October 2015 and ran for 30 h with a horizontal grid spacing of 2 km.Specific configurations of the experiment and also verifications of the simulation can be found in Jiao et al.[19]Therefore, here we directly use the model output to perform the analyses. The data, which have 1-h time interval,are interpolated into a local z coordinate for calculation in this paper.In the vertical includes 40 layers with a fixed vertical grid spacing of 500 m.
As indicated above, the whole theory described in Section 2 needs the data to be decomposed into basic-state fields and perturbations (or waves) deviated from the basic states through the Reynolds average, to keep the interactive term.However, Reynolds average conditions are difficult to satisfy only if the zonal average is used. In that case, meso- or smaller-scale process that are related to heavy precipitation in typhoon will not be separated from the basic states. Therefore,in this paper,we use the Barnes filter technique to replace the zonal average, which is seen to approximately satisfy the Reynolds average conditions here. The Barnes filter technique is conducted with a horizontal scan radius of approximated 20 km. The response function larger than 0.8 corresponds to the theoretical wave length approximately larger than 250 km,which referred to as the basic state. The fields deviated from the basic state are explained as the perturbation field with most of wave lengths being less than 250 km.
3.3. Results
3.3.1. Wave activities and precipitation in typhoon
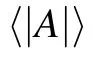
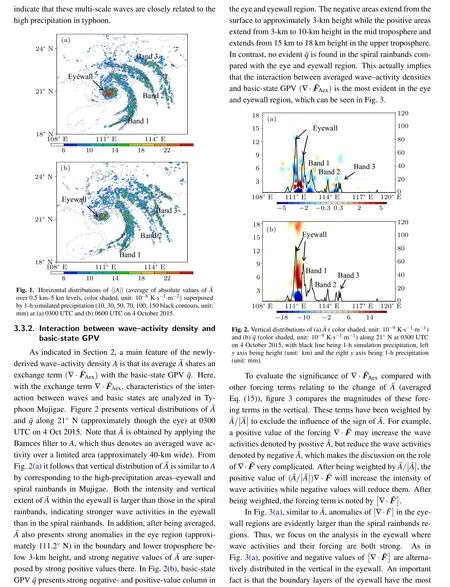
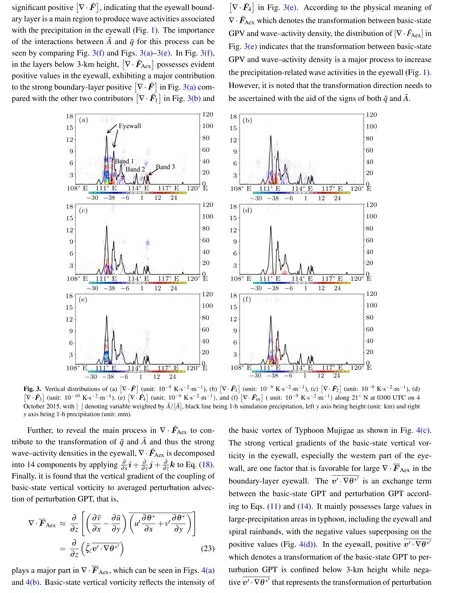
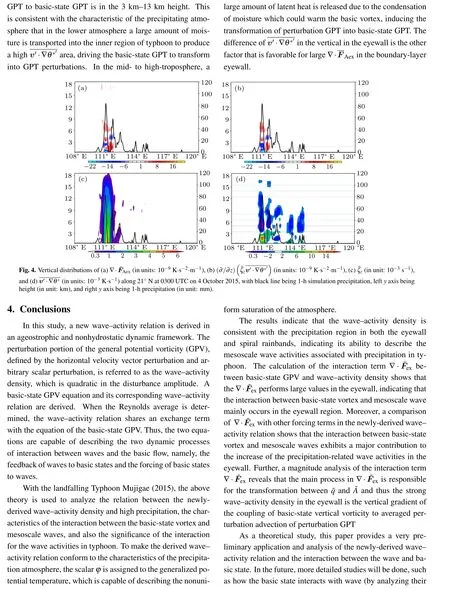

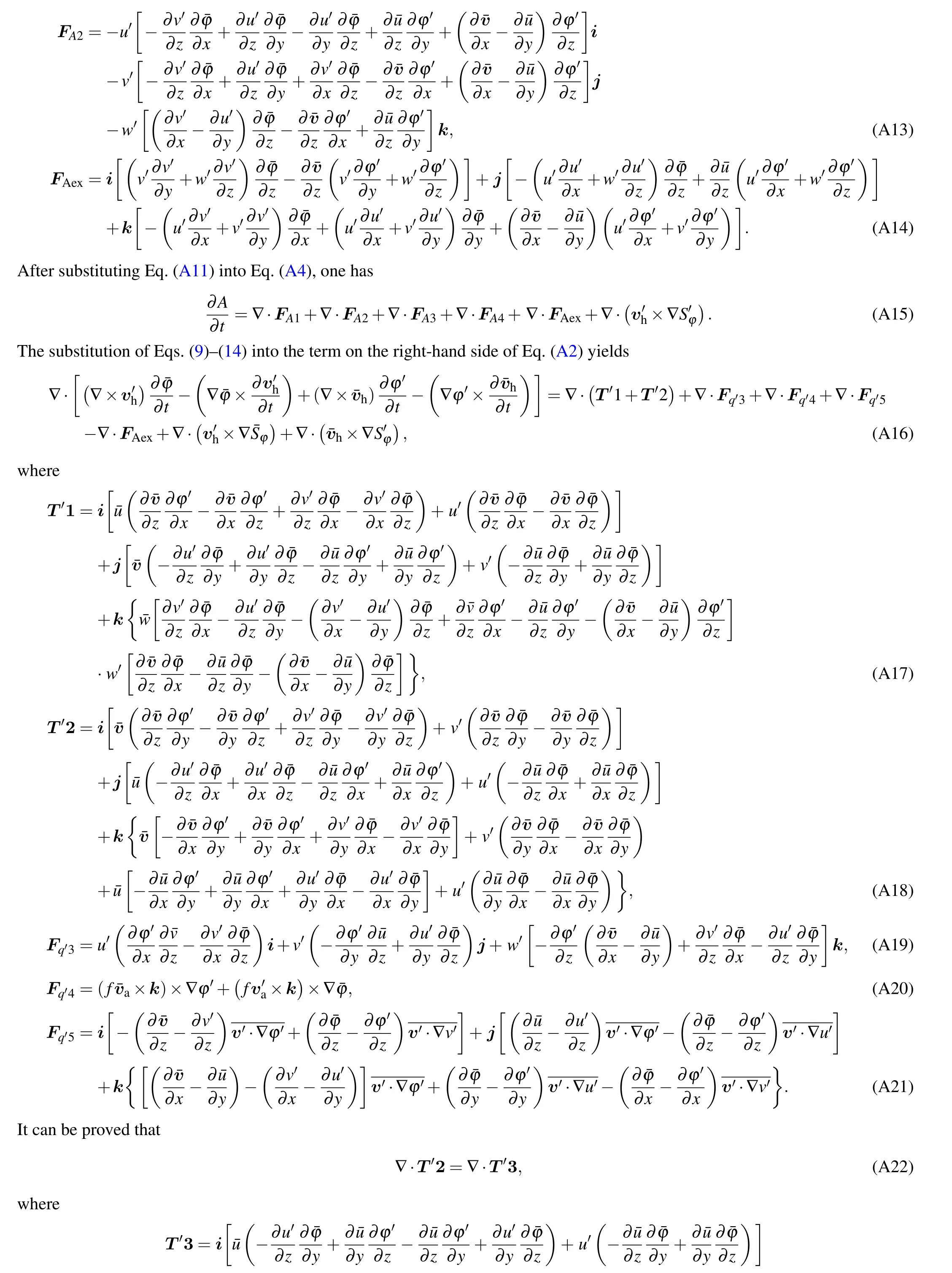

- Chinese Physics B的其它文章
- Quantum annealing for semi-supervised learning
- Taking tomographic measurements for photonic qubits 88 ns before they are created*
- First principles study of behavior of helium at Fe(110)–graphene interface?
- Instability of single-walled carbon nanotubes conveying Jeffrey fluid?
- Relationship between manifold smoothness and adversarial vulnerability in deep learning with local errors?
- Weak-focused acoustic vortex generated by a focused ring array of planar transducers and its application in large-scale rotational object manipulation?