急性胰腺炎患者NLR與凝血功能指標的變化及其臨床意義
方曉君 魏天南
[摘要] 目的 探討急性胰腺炎患者中性粒細胞/淋巴細胞比值(NLR)與凝血功能的變化及其臨床意義。 方法 選取2018年1月~2019年12月于我院急診內科與急診ICU治療的急性胰腺炎患者72例,按疾病嚴重程度分為輕癥急性胰腺炎組(MAP組,50例)與重癥急性胰腺炎組(SAP組,22例),并收集同期健康體檢對照組(60例),比較各組NLR和凝血指標變化,并分析其與急性生理與慢性健康評分Ⅱ(APACHE Ⅱ)的相關性。 結果 SAP組、MAP組與對照組相比,NLR、凝血酶原時間(PT)、活化部分凝血活酶時間(APTT)、D二聚體(D-Di)均顯著提高(P<0.05),而上述指標在MAP組與對照組之間差異無統計學意義(P>0.05)。SAP組內預后良好與預后不良的患者之間比較分析,上述指標差異有統計學意義(P<0.05)。Pearson相關分析顯示,NLR、PT、APTT、D-Di在SAP組患者中與APACHE Ⅱ評分呈正相關(P<0.05),在MAP組患者中則不相關(P>0.05)。 結論 NLR與凝血功能指標與急性胰腺炎患者病情嚴重程度有關,且上述指標的變化可以用來評估疾病的預后和轉歸。
[關鍵詞] 急性胰腺炎;NLR;凝血功能;預后
[中圖分類號] R657.5 ? ? ? ? ?[文獻標識碼] B ? ? ? ? ?[文章編號] 1673-9701(2020)23-0050-04
Changes and clinical significance of NLR and coagulation function indexes in patients with acute pancreatitis
FANG Xiaojun1 ? WEI Tian'nan2
1.Department of Emergency Medicine, Fujian Provincial Hospital, Fujian Provincial Emergency Center, Fuzhou ? 350001, China; 2.Department of Hematology, Fujian Provincial Hospital, Fuzhou ? 350001, China
[Abstract] Objective To explore the changes and clinical significance of neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and coagulation function in patients with acute pancreatitis. Methods Seventy-two cases of acute pancreatitis in the emergency medical and emergency ICU of our hospital from January 2018 to December 2019 selected and divided into mild acute pancreatitis group (MAP group, 50 cases) and severe acute pancreatitis group (SAP group, 22 cases) according to the severity of the disease. A healthy physical examination control group (60 cases) was collected during the same period. Changes of NLR and coagulation indexes in each group were compared and their correlation with acute physiology and chronic health score Ⅱ (APACHE Ⅱ) was analyzed. Results The NLR, prothrombin time (PT), activation partial thromboplastin time (APTT) and D-dimer (D-Di) in the SAP group were significantly higher than those of the MAP group and the control group(P<0.05). There were no statistically significant differences in the above indicators between the MAP group and the control group(P>0.05). There were statistically significant differences in the above indicators between the patients with good prognosis and the patients with poor prognosis within the SAP group(P<0.05). Pearson correlation analysis showed that NLR, PT, APTT and D-Di were positively correlated with APACHE Ⅱ score in SAP patients(P<0.05), but not in MAP patients(P>0.05). Conclusion ?NLR and coagulation functional indicators are related to the severity of acute pancreatitis, and the changes in these indicators can be used to assess the prognosis and outcome of the disease.
[Key words] Acute pancreatitis; NLR; Cagulation function; Prognosis
急性胰腺炎(Acute Pancreatitis,AP)是臨床常見的急危重癥,也是急診、消化與重癥醫學科醫師關注的臨床焦點。隨著人民生活條件的改善與生活習慣的改變,急性胰腺炎的發病率逐年上升[1];其中重型急性胰腺炎(Severe acute pancreatitis,SAP)病情兇險,具有發病急、進展快、預后差等特點,且治療難度大、時間長、費用高。因此,在發病時準確預判疾病的嚴重程度顯得十分重要。目前,根據重型急性胰腺炎的診斷標準,有急性生理與慢性健康評分(Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation Ⅱ Score,APACHEⅡ評分)[2]等方法預估病情嚴重程度,但存在評分標準復雜、涉及指標繁瑣以及重復性不理想等問題。因此,在臨床中,尤其在廣大基層醫院,篩選出簡便易行又準確可靠的預后與嚴重性評估指標十分重要。本研究探討急性胰腺炎患者中性粒細胞/淋巴細胞比值(Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio,NLR)與凝血功能指標在疾病過程中的水平與演變,探討上述指標是否可以用來判斷急性胰腺炎患者的病情嚴重程度、預后以及臨床療效。
1 資料與方法
1.1一般資料
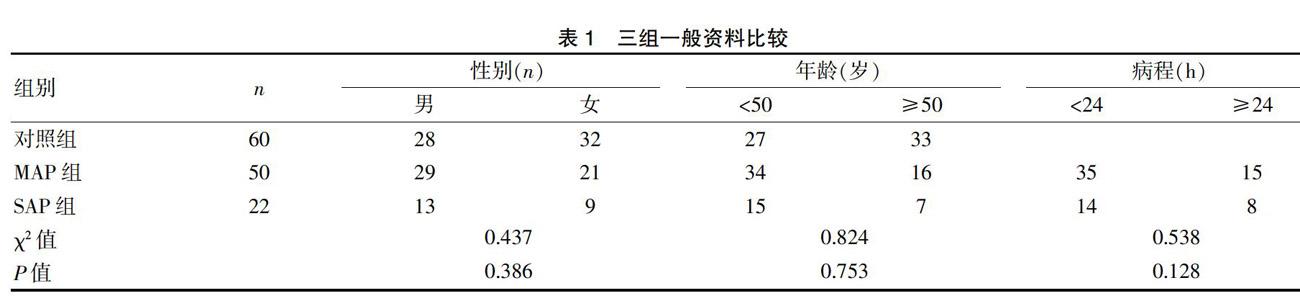
選取2018年1月~2019年12月于我院急診內科與急診ICU治療的急性胰腺炎患者72例,按疾病嚴重程度分為輕癥急性胰腺炎組(Mild acute pancreatitis,MAP組,50例)與重癥急性胰腺炎組(Severe acute pancreatitis,SAP組,22例),并收集同期健康體檢對照組60例。納入標準[3]:(1)所有患者的診斷和分型均符合《中國急性胰腺炎診治指南》;(2)發病時間<48 h,住院時間超過120 h;(3)患者入院時神志清楚,配合治療,自愿簽署知情同意書。排除標準[4-6]:(1)入院時合并嚴重的肝腎功能損害;(2)入院時合并其他原因導致的凝血功能異常如彌散性血管內凝血(DIC)等;(3)合并晚期惡性腫瘤;(4)合并慢性胰腺炎或肝膽胰腺腫瘤;(5)長期口服抗凝藥。本研究經醫院倫理委員會批準。各組患者一般資料比較差異均無統計學意義(P>0.05)。見表1。
1.2 方法
收集所有患者確診時與出院/死亡時的下列指標:患者入院24 h內,于清晨抽取空腹靜脈血3 mL,采用全自動血液分析儀,分別檢測血常規與凝血功能常規,包括凝血酶原時間(Prothrombin time,PT),活化部分凝血活酶時間(Activated partial thromboplastin time,APTT)與D二聚體(D-Dimer,D-Di)等臨床指標,并計算中性粒細胞與淋巴細胞比值(NLR)。分別比較對照組與MAP組、對照組與SAP組、MAP組與SAP組的上述指標。所有急性胰腺炎患者在出院當天重復檢測:于清晨抽取空腹靜脈血3 mL,采用全自動血液分析儀,按相同方法分別檢測上述指標,并比較MAP組與SAP組患者治療前與治療后上述指標的變化。根據生命體征、血常規、動脈血氣分析、電解質、紅細胞壓積等臨床指標計算急性生理學評分,并與年齡積分、慢性健康狀況評分相加,計算每例急性胰腺炎患者的APACHEⅡ評分[7],并將上述指標與所有患者APACHEⅡ評分進行相關性分析。
1.3統計學方法
采用SPSS18.0統計學軟件進行分析,計量資料用(x±s)表示,采用t檢驗和方差分析;計數資料用[n(%)]表示,采用χ2檢驗,P<0.05表示差異有統計學意義。相關性分析采用Pearson檢驗,以P<0.05表示結果有統計學意義。
2 結果
2.1 三組患者入院時NLR及凝血指標比較
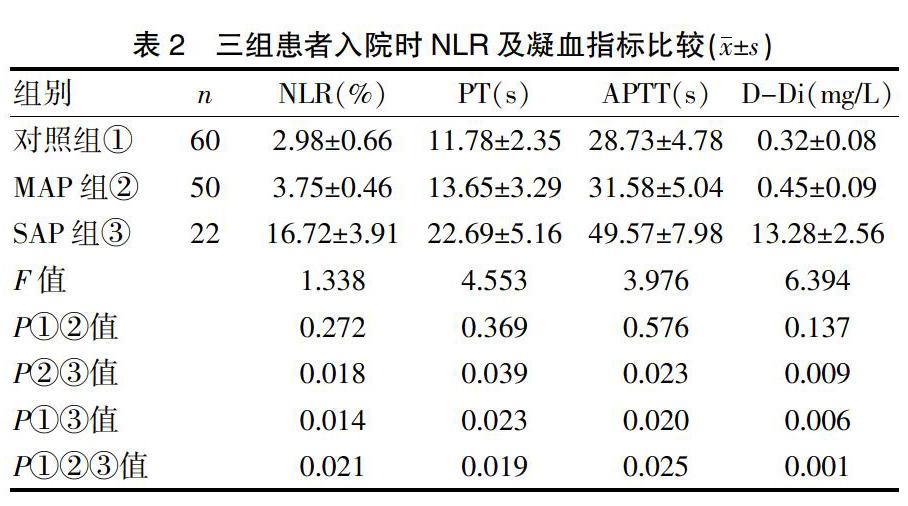
各組患者在入院時的NLR值及凝血指標見表2。其中MAP組與對照組的NLR值及凝血指標無顯著性差異(P>0.05),而SAP組與MAP組、SAP組與對照組的NLR值及凝血指標有統計學差異(P<0.05)。
2.2 急性胰腺炎患者治療前與治療后NLR及凝血指標比較
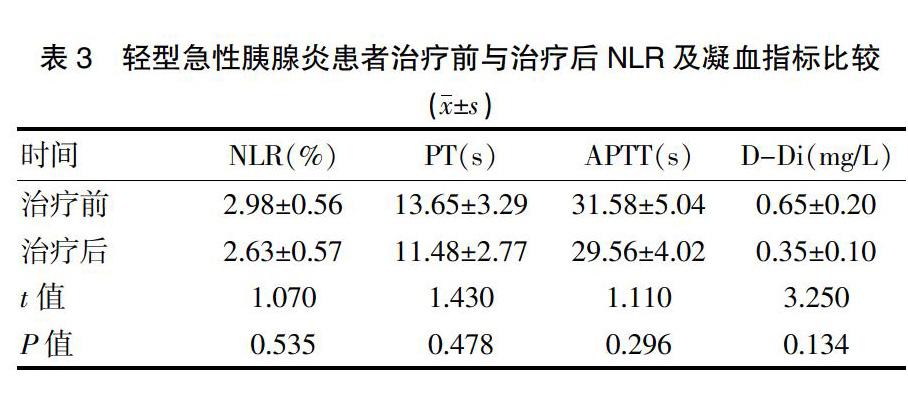
MAP組患者均好轉出院,而SAP組患者有19例好轉出院(預后好組),3例病情加重或死亡(預后差組)。分別比較MAP組治療前后、SAP組內的預后好組與預后差組在治療前后上述指標的變化。結果顯示,MAP組上述指標在治療前后無統計學差異(P>0.05)。而SAP組在治療前,預后好與預后差兩組之間的相關指標無明顯差異(P>0.05);治療后,兩組之間則存在統計學差異(P<0.05)。預后好組治療前后的組內比較,上述指標除APTT外均顯著改善(P<0.05);而預后差組治療前后的組內比較,治療后上述指標較治療前均進一步惡化(P<0.05)。見表3、4。
2.3急性胰腺炎患者NLR與凝血指標與APACHEⅡ評分相關性分析
Pearson相關分析顯示,MAP組患者的NLR、PT、APTT、D-Di與APACHEⅡ評分無相關性(P>0.05),而SAP組患者的NLR、PT、APTT、D-Di與APACHEⅡ評分呈正相關(r=0.513,0.575,0.623,0.356,P<0.05)。見表5。
3討論
急性胰腺炎是臨床常見的急危重癥,尤其在急診科、重癥醫學科、消化科、肝膽胰外科較為多見,是臨床研究的熱點與焦點,也是臨床醫師十分關注的話題。近年來隨著人民生活水平提高,急性胰腺炎發病率逐年上升,雖然通過臨床醫師認識與診療水平的提升和治療措施的及時性與多樣化改變,急性胰腺炎的死亡率不斷下降,但仍有一部分患者預后較差。急性胰腺炎分為輕癥急性胰腺炎(MAP)與重癥急性胰腺炎(SAP),其中SAP進展快、預后差、并發癥多、治療難度大[8]。因此,在疾病早期快速甄別出重型患者,并對病情的發展、轉歸進行合理預判就顯得尤為重要。目前,APACHEⅡ評分是常用的風險評估和嚴重程度預測工具,但仍然存在評分標準復雜、重復性與辨識率偏低的問題,亦無法預測器官衰竭、感染嚴重性等[9]。有研究顯示,紅細胞分布、肌酐、白蛋白、血鈣水平等可以作為死亡率的早期預測指標[8]。
[9] 張苗,仲蕊,劉影,等.聯合檢測APOB/APOA1、PCT、FIB對重癥急性胰腺炎早期病情的評估[J].胃腸病學和肝病學雜志,2020,29(4):401-405.
[10] Fan W,Zhang Y,Wang Y,et al.Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratios as predictors of survival and metastasis for recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma after transarterial chemoembolization[J].PLo S One,2015,10(3):173-175.
[11] Guillermo G,Karina C,Enrique de-M.Towards evidence-based and personalised care of acute pancreatitis[J].United European Gastroenterol J,2020,8(4):403-409.
[12] Vilja K,Andrea T,Marianne U,et al.Diclofenac does not reduce the risk of acute pancreatitis in patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis after endoscopic retrograde cholangiography[J].United European Gastroenterol J,2020, 8(4):462-471.
[13] 李建洪.急性重癥胰腺炎的診斷與治療[J].中外醫療,2016,24(15):42-44.
[14] 金爽,許智利,陳建時.急性胰腺炎患者早期凝血功能及血管內皮功能檢測及臨床意義[J].中國中西醫結合消化雜志,2019,27(3):215-218.
[15] Penven M,Lalieu A,Boruchowicz A,et al.Bacteremia caused by elizabethkingia miricola in a patient with acute pancreatitis and peritoneal dialysis[J].Med Mal Infect,2020,50(4):379-381.
[16] Maan EH,Halim BD,Luma BO,et al.Characteristics and outcome of patients presenting with acute pancreatitis:A one-year descriptive study from a tertiary care center in Lebanon[J].Arab Journal of Gastroenterology,2020,29(2);556-559.
(收稿日期:2020-05-12)

