基于腳本解釋器的區塊鏈交易合約原理與實踐
郭倩 王中豪 王晟典 林映春
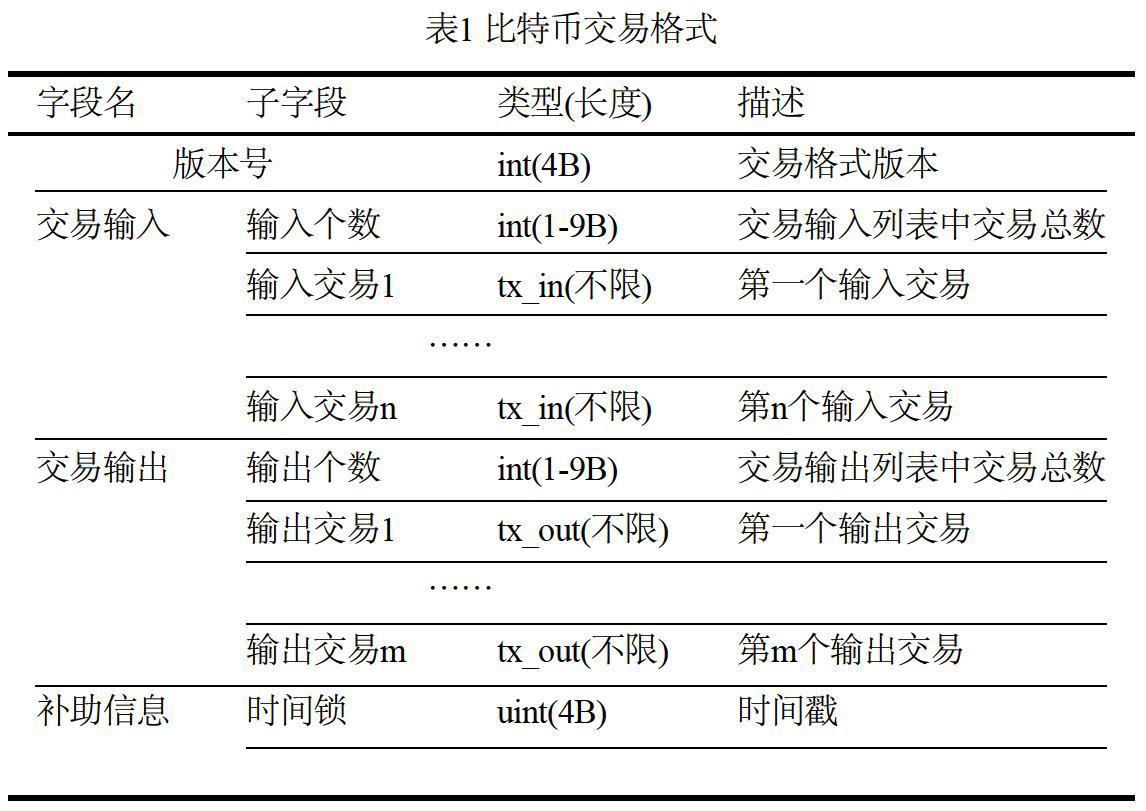
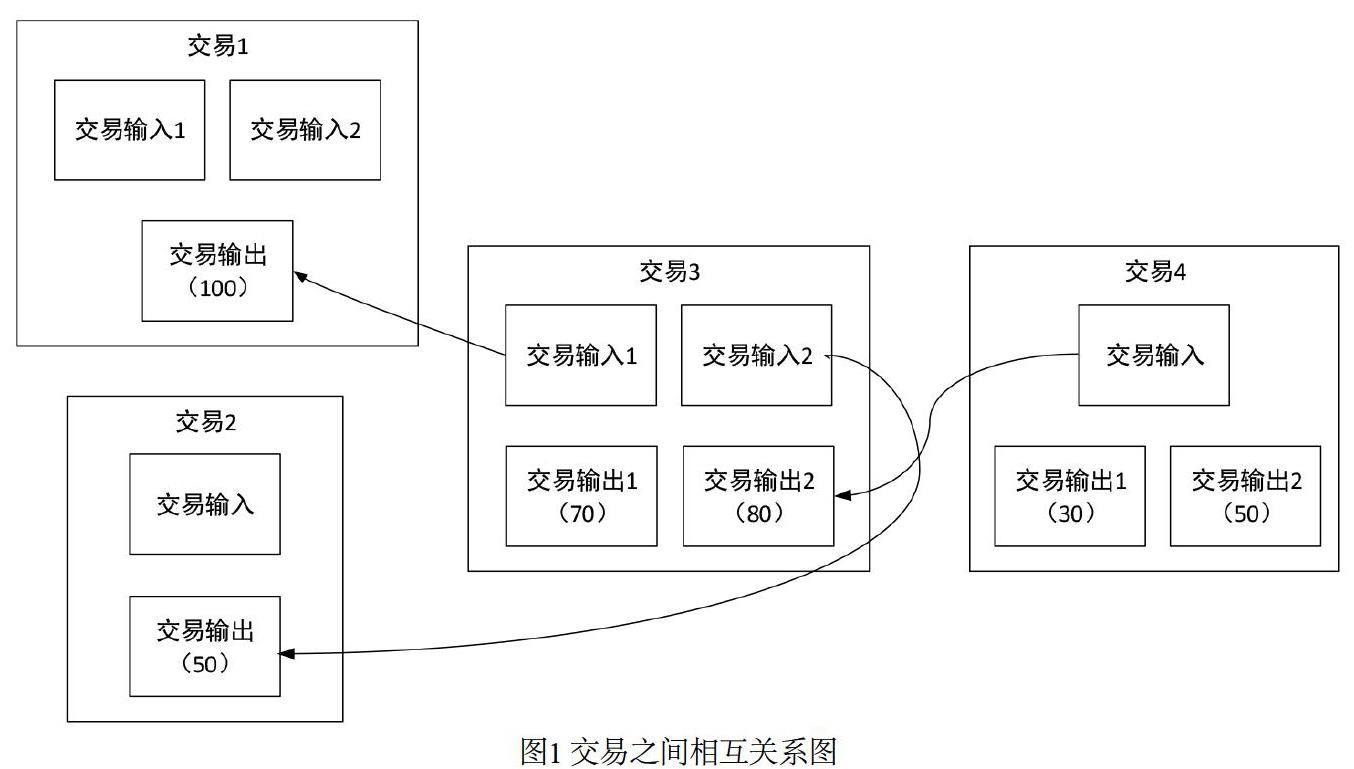
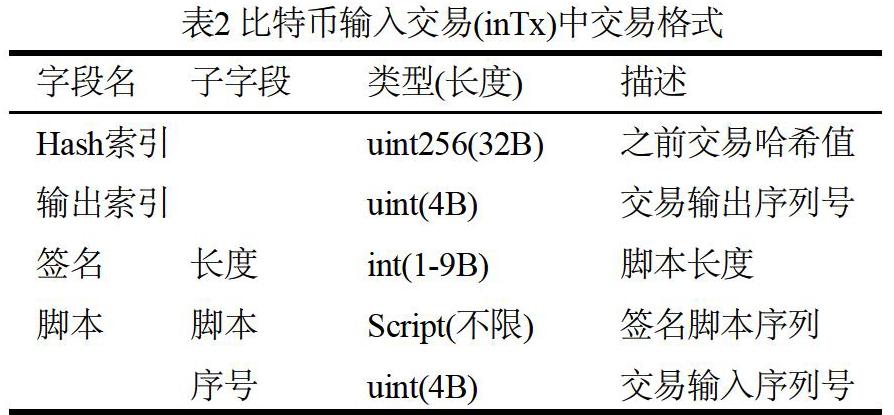
摘 ? 要:基于腳本解釋器的區塊鏈交易合約架構是目前最簡潔且高效的智能合約設計之一,它具有去中心化、總量固定、可自由兌換、匿名性等特點,也有利于密碼技術在區塊鏈中的靈活應用與實現。文章在整體介紹比特幣腳本系統交易結構的基礎上,闡述了面向未花費交易(UTXO)的輸入交易、輸出交易的結構,并詳細地給出了比特幣腳本指令系統及其執行過程和驗證機制,從而實現了區塊鏈交易合約中基于腳本解釋器的公鑰支付方案。
關鍵詞:智能合約;比特幣;運行機制
中圖分類號: TP312 ? ? ? ? ?文獻標識碼:A
Abstract: The blockchain transaction contract architecture based on the script interpreter is one of the most concise and efficient smart contract designs at present. It has the characteristics of decentralization, fixed total amount, free exchange, and anonymity. It is also conducive to the flexible application and implementation of cryptography in the blockchain. Based on the overall introduction of the transaction structure of the Bitcoin script system, this paper explains the structure of input transactions and output transactions for unspent transactions (UTXO). In addition, this paper details the Bitcoin script instruction system and its execution process and verification mechanism, so as to implement the public key payment scheme based on the script interpreter in the blockchain transaction contract.
Key words: smart contracts; bitcoin; operating mechanism
1 引言
智能合約(Smart Contracts)在廣義上講是指任何符合多方之間約定的計算機協議,現多指運行在區塊鏈上的一個程序或者腳本,具有自動執行、不可篡改、可回溯等特性。Nick Szabo在1994年提出“智能合約”的概念[1],并將其定義為一個使用計算機處理執行合約條款的交易協議。其目的在于以最小化惡意或意外的異常情況,以及最大限度減少對第三方中介需求的前提下,簡化合約的執行和減少合約的執行成本來完成一些常見合約條件。但由于當時缺乏一個可信的第三方平臺,加上合約在社會生活中的重要性,智能合約未能真正成為主流合約指定方式。
2008年,學者Satoshi Nakamoto發表了題為《Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System》的研究報告[2],并在此基礎上設計并實現了比特幣這種新型數字貨幣。比特幣在對等網絡的基礎上使用了大量密碼學技術[3],并使用工作量證明作為一致性共識算法解決了數字貨幣面臨的“雙花”問題。……

