白介素-6和降鈣素原在低出生體重新生兒細菌感染性疾病中的預測價值
周煒 俞君 曾雪琪 季翠紅
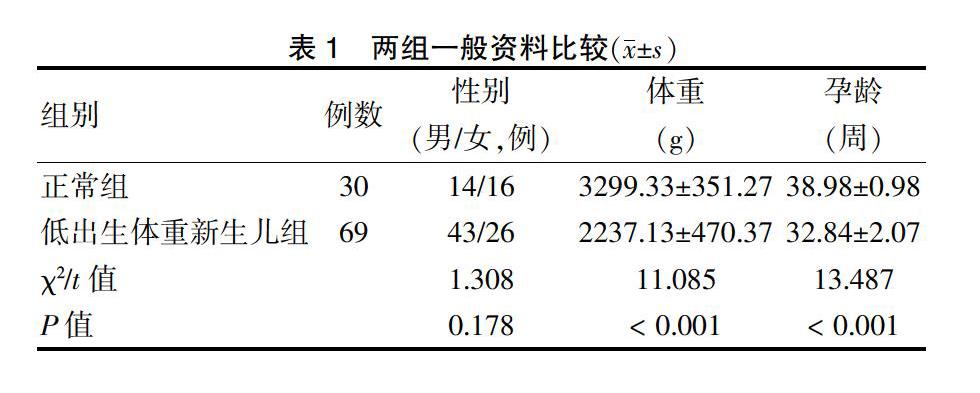
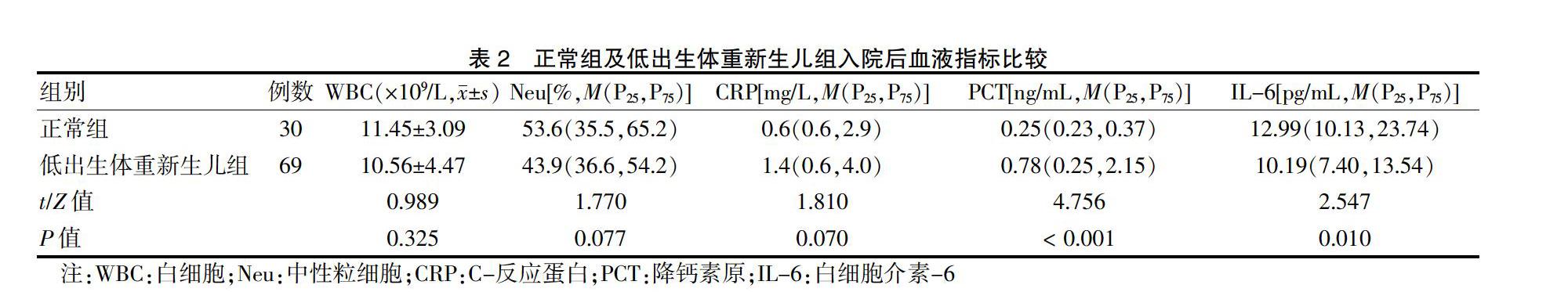
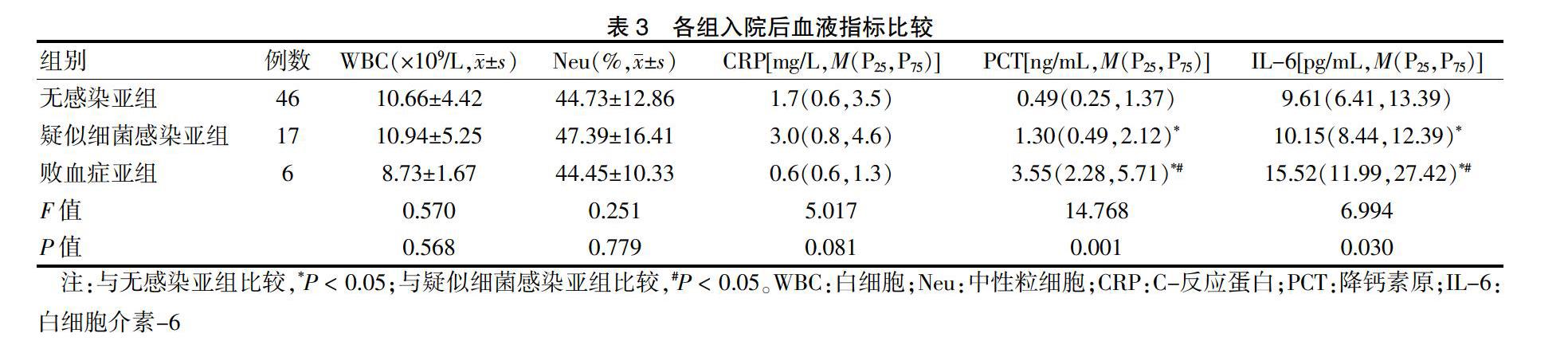
[摘要] 目的 探討白介素-6(IL-6)和降鈣素原(PCT)在預測低體重新生兒細菌感染性疾病中的價值,為預防和及時治療新生兒感染提供依據。 方法 選取2015年3月—2017年3月上海市奉賢區中心醫院兒科69例低出生體重新生兒為低出生體重新生兒組,選取同期產房分娩的正常新生兒30名為正常組。根據臨床癥狀將低出生體重新生兒組分為疑似細菌感染亞組(17例)、敗血癥亞組(6例)及無感染亞組(46例)。檢測正常組及低出生體重新生兒組入院后4 h內(入院后)白細胞(WBC)、中性粒細胞(Neu)、C反應蛋白(CRP)、PCT和IL-6水平;檢測不同亞組間入院后WBC、Neu、CRP、PCT和IL-6水平及治愈后4 h內(治愈后)PCT和IL-6水平。ROC曲線檢測低出生體重新生兒敗血癥的預測價值。 結果 低出生體重新生兒組入院后PCT水平高于正常組,IL-6水平低于正常組,差異均有統計學意義(均P < 0.05),兩組WBC、Neu、CRP水平比較,差異無統計學意義(P > 0.05)。入院后,三亞組間PCT和IL-6水平比較,差異均有統計學意義(均P < 0.05);但三亞組間WBC、Neu、CRP水平比較,差異無統計學意義(P > 0.05)。治愈后,三亞組間PCT和IL-6水平比較,差異無統計學意義(P > 0.05)。ROC曲線顯示,PCT和IL-6預測低出生體重新生兒敗血癥的最佳臨界值分別為2.15 ng/L和12.34 pg/mL時,敏感度均為83.3%,特異性分別為81.0%和71.4%;聯合檢測敏感度為87.3%,特異性為83.3%。 結論 PCT和IL-6檢測及二者聯合檢測對低出生體重新生兒敗血癥預測均有一定準確性,其中聯合檢測價值最優。
[關鍵詞] 白介素-6;降鈣素原;低出生體重;新生兒;敗血癥
[中圖分類號] R725.1? ? ? ? ? [文獻標識碼] A? ? ? ? ? [文章編號] 1673-7210(2020)07(c)-0109-04
The value of interleukin-6 and procalcitonin to predict bacterial infection in low birth weight neonates
ZHOU Wei? ?YU Jun? ?ZENG Xueqi? ?JI Cuihong
Department of Pediatrics, South Hospital of Shanghai Sixth People′s Hospital? Fengxian District Central Hospital, Shanghai? ?201499, China
[Abstract] Objective To explore the value of interleukin-6 (IL-6) and procalcitonin (PCT) to predict bacterial infection in low birth weight neonates, and provide reference to prevent and timely treatment of neonatal infection. Methods From March 2015 to March 2017, 69 neonates with low birth weight in Department of Pediatrics, Fengxian District Central Hospital of Shanghai were selected as the low birth weight neonate group, and 30 normal neonates delivered in the delivery room during the same period were selected as the normal group. According to clinical symptoms, the low birth weight neonate group were divided into suspected bacterial infection subgroup (17 cases), sepsis subgroup (6 cases) and non-infection subgroup (46 cases). White blood cell (WBC), neutrophil (Neu), C-reactive protein (CRP), PCT and IL-6 levels were measured in the normal group and the low birth weight neonate group within 4 h after admission (after admission); WBC, Neu, CRP, PCT and IL-6 levels after admission and PCT and IL-6 levels within 4 h after treatment (after treatment) were measured between different subgroups. The predictive value of ROC curve in detecting low birth weight neonates sepsis. Results The levels of PCT and IL-6 in the low birth weight neonate group after admission were higher than those in the normal group, and the differences were statistically significant (all P < 0.05). WBC, Neu and CRP levels of the two groups were not statistically significant (P > 0.05). After admission, PCT and IL-6 levels were compared among three subgroups, and the differences were statistically significant (all P < 0.05); while there were no significant differences in WBC, Neu and CRP levels among three subgroups (P > 0.05). After treatment, there were no significant differences in PCT and IL-6 levels among three subgroups (P > 0.05). ROC curve showed that the optimal critical values of PCT and IL-6 for predicting in low birth weight neonate sepsis were 2.15 ng/L and 12.34 pg/mL, sensitivity was all 83.3%, specificity were 81.0% and 71.4% respectively, and the sensitivity and specificity of the combined test were 87.3% and 83.3% respectively. Conclusion Both PCT and IL-6 test and their combined test have certain accuracy in predicting low birth weight neonate sepsis, among which combined test has the best value.
[Key words] Interleukin-6; Procalcitonin; Low birth weight; Neonate; Sepsis
新生兒免疫系統功能低下,出生后容易發生細菌感染性疾病,在院內和院外的發病率均較高[1]。新生兒病情進展迅速[2],如未及時診斷治療,易繼發敗血癥,多器官功能受累[3],病死率高。低出……

