2型糖尿病統一標準化延續性管理模式的應用效果觀察
趙玲 繆園園 柯亭羽 周湘明
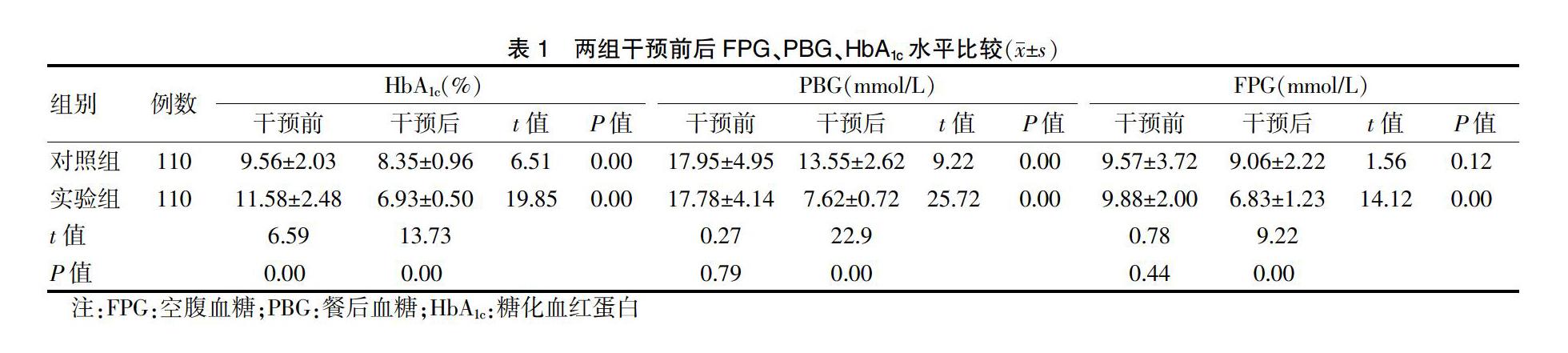
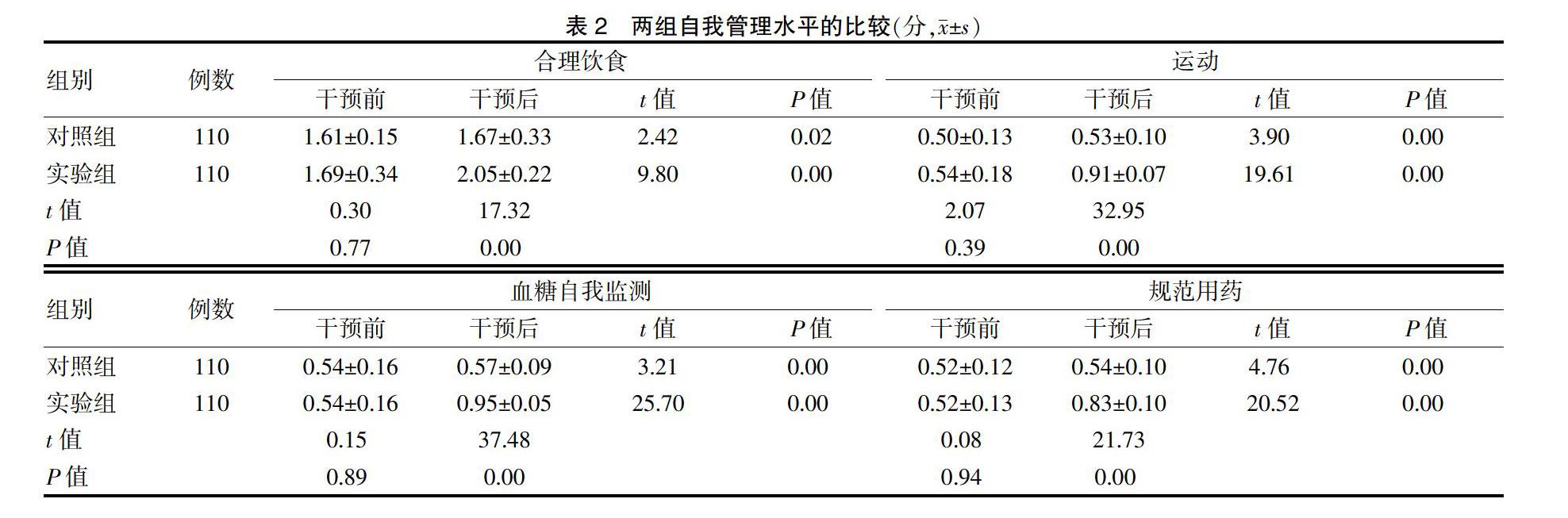
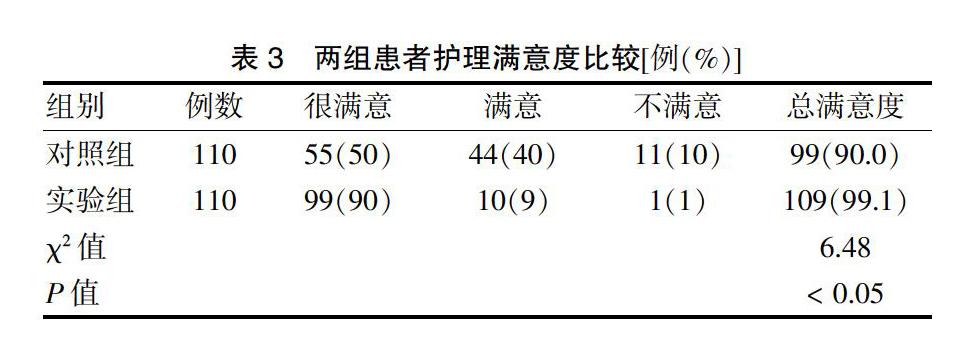
[摘要] 目的 分析統一標準化延續性管理模式對2型糖尿病(T2DM)患者行為改變、血糖控制效果的影響。 方法 選擇2017年11月—2018年11月在昆明醫科大學第二附屬醫院國家標準化代謝性疾病管理(MMC)中心就診的220例T2DM患者,根據隨機數字表法分為對照組和實驗組,每組110例。對照組實施常規管理模式,實驗組采用統一標準化延續性管理(即MMC管理模式)。對兩組管理前后血糖變化、自我管理水平及護理滿意度進行比較。結果 干預后,兩組糖化血紅蛋白(HbA1c)、空腹血糖(PBG)水平均低于干預前,實驗組餐后血糖(FPG)低于干預前,且實驗組FPG、PBG、HbA1c低于對照組,差異均有高度統計學意義(均P < 0.01)。兩組合理飲食、運動、血糖自我檢測、規范用藥評分高于干預前,且實驗組合理飲食、運動、血糖自我檢測、規范用藥評分均高于對照組,差異均有統計學意義(均P < 0.05)。實驗組護理滿意度高于對照組,差異有統計學意義(P < 0.05)。 結論 MMC管理模式有助于提高T2DM患者FPG、PBG、HbA1c的達標率,能有效地改善T2DM患者的自我管理行為,提高患者滿意度,具有臨床推廣應用價值。
[關鍵詞] 國家標準化代謝性疾病管理中心;統一標準化延續性護理管理模式;2型糖尿病;血糖達標;行為改變
[中圖分類號] R587.1? ? ? ? ? [文獻標識碼] A? ? ? ? ? [文章編號] 1673-7210(2020)07(c)-0070-04
Observation on the application effect of unified standardization continuity management mode for type 2 diabetes
ZHAO Ling? ?MIAO Yuanyuan▲? ?KE Tingyu? ?ZHOU Xiangming
Department of Endocrinology, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Yunnan Province, Kunming? ?650101, China
[Abstract] Objective To analyze the impact of unified and standardized continuity management mode on behavior change and blood glucose control effect of patients with type 2 diabetes (T2DM). Methods From November 2017 to November 2018, 220 patients with T2DM who were treated at the National Metabolic Management Center (MMC) of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University were selected. According to the random number table method, they were randomly divided into control group and experimental group, with 110 cases in each group. The control group implemented a routine management model, and the experimental group performed unified and standardized continuous management (MMC management mode). Blood glucose, self-management level and nursing satisfaction were compared before and after management. Results After intervention, the levels of glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) and postprandial blood glucose (PBG) in the two groups were lower than those before intervention, fasting glucose (FPG) in the experimental group was lower than those before intervention, and FPG, PBG and HbA1c in the experimental group were lower than those in the control group, with highly statistically significant differences (all P < 0.01). Scores of rational diet, exercise, blood glucose self-test and standardized drug use in the two groups were higher than those before intervention, and scores of rational diet, exercise, blood glucose self-test and standardized drug use in the experimental group were higher than those in the control group, with statistically significant differences (all P < 0.05). The nursing satisfaction of the experimental group was higher than that of the control group, and the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). Conclusion The MMC management mode helps to improve the compliance rate of FPG, PBG, and HbA1c in T2DM patients, it can effectively improve the self-management behavior, increase patients′ satisfaction, and has clinical application value.
[Key words] National Standardized Metabolic Disease Management Center; Unified and standardized continuous care management model; Type 2 diabetes; Blood glucose compliance; Behavioral changes
隨著物質生活水平提升、生活習慣改變,加上人口老齡化等因素,我國糖尿病患病率呈快速上升趨勢,已成為繼心血管疾病、腫瘤之后的另一個嚴重危害人們健康的重要慢性非傳染性疾病[1-2]。我國1980年開展30萬人口糖尿病流行病學調查發現患病率為0.67%[3]。上海瑞金醫院寧光院士科研團隊研究新成果揭示:我國18歲以上的人群中糖尿病和糖尿病前期的患病率分別達到了11.6%和50.1%[4]。流行病學調查數據都充分說明我國糖尿病患病率正在節節攀升。飲食、運動、血糖的自我監測、健康教育、心理治療和藥物治療都是缺一不可的。糖尿病患者常常需要花費大量時間往返于就診與復診的過程中。……

