Thermal decomposition characteristicsof ammonium dinitramide andnano-Fe2O3 mixtures
LI Yajin,WANG Haiyang,HUANG Haitao,XIE Wuxi,ZHANG Wei
(Xi’an Modern Chemistry Research Institute,Xi’an 710065,China)
Abstract:Ammonium dinitramide(ADN)is one of the most promising new solid oxidizers for rocket propellants,since its oxygen balance and energy content are relatively high,and it does not contain halogens.In this paper,the effect of nano-Fe2O3 on the thermal behavior of ADN was investigated.The thermal behavior and activation energy associated with the decomposition of ADN/nano-Fe2O3 mixtures were analyzed by using differential scanning calorimetry(DSC)and thermal-gravimetry-differential thermal analysis(TG-DTA),and the activation energy was calculated by using the Friedman method.The composition of gas products and decomposition mechanisms of pure ADN and ADN/nano-Fe2O3 mixtures during simultaneous heating were investigated by using TG-DTA-MS and TG-DTA-IR.The results show that the nano-Fe2O3 reduces the initial decomposition temperature and the maximum decomposition temperature of ADN,and promotes the thermal decomposition of ADN.The mass of nano-Fe2O3 remaining following the reaction is equal to the amount originally added to the ADN.The nano-Fe2O3 does not change the reaction process.
Key words:ammonium dinitramide;nano-Fe2O3;solid propellant;thermal decomposition
0 Introduction
Ammonium dinitramide[NH4N(NO2)2,ADN]is considered as a possible replacement for ammonium perchlorate(AP)in nearly all kind of rocket propellants in the coming future[1-3],and its structure is shown in Fig.1.ADN possesses a high oxygen coefficient and contributes the energy to a high level,and it is also halogen-free and has lower toxicity potential than hydrazine.Recent researches have focused on the thermal decomposition of ADN[4-6].The information on thermal decomposition behavior is vital to understand the combustion behavior,predict the safe storage lifetimes and choose the appropriate stabilizers,and investigations under various conditions of heating rate,sample mass,atmosphere and additives are required[7-9].Many studies concerning the thermal decomposition mechanism for ADN have been conducted[10-12],and it has been reported that ADN decomposes into numerous products,including N2O,NO2,NO,NH4NO3,HNO3,N2,HONO,H2O,NH3,and so on.

Fig.1 Molecular structure of ADN
Metallic oxide is known to be particularly effective in modifying the thermal decomposition and combustion characteristics of many energetic materials[13-14].Fujisato[15-16]found that the micrometer-sized particles Fe2O3have no effective catalysis,it can't alter the onset temperature of pure ADN.However,the adsorption and acidity/alkalinity of iron oxide surface can play a catalytic role in the decomposition products of energetic materials,and the details of interaction on ADN/Fe2O3mixtures is still not clear.In addition,nano-oxidizer constituents with nano-scale dimensions,benefit greatly from the enhanced specific surface area of interaction between fuel and oxidizer.Reduced particle dimensions can improve the homogeneity of the mixture,and decrease the diffusion distance required for reactions.
In this work,we clarify the thermal decomposition of spherical ADN and spherical ADN/nano-Fe2O3mixtures.The thermal behavior and evolved gases obtained from the sample during constant heating rate are analyzed by using the combination of thermal analysis and spectrometry.Meanwhile,the catalytic mechanism of nano-Fe2O3is investigated.
1 Experiment
In general,ADN exhibits plate or needle crystal which is easy to agglomerate and absorb moisture[3].In order to improve this situation,the spherification process of ADN were carried out in our laboratory.The catalyst of nano-iron oxide is used as-received without further purification.The granular Fe2O3has an average particle diameter of 30~50 nm and the purity is over 99.0%.
The thermal behavior of the sample is characterized by using TG-DSC-MS-IR(NETZSCH STA Instruments,449C).During the heating of the samples,the attendant mass loss and decomposition gases are analyzed simultaneously by using thermogravimetry-infrared spectrometry(TG-IR)and thermogravimetry-mass spectrometry(TG-MS). Samples consisting of 1 mg of either pure spherical ADN or an ADN/nano-Fe2O3mixture(100/0.1,100/1,100/3,100/5,or 50/50 mass ratio)are loaded into a sealed stainless steel cell,sealed under an argon flow rate of 60 mL/min is used as a purge gas in all analysis.All experiments are carried out at heating from 30 to 550 ℃ at 1,3,5,10 K/min.
ADN and catalyst are prepared by physically mixing them in the cells.They are sealed under atmospheric air and then heated from 30 to 550 ℃.During sample heating,the attendant mass loss and decomposition gases are simultaneously analyzed by using thermogravimetry-infrared spectrometry(TG-IR)and thermogravimetry-mass spectrometry(TG-MS).The evolved gases are transferred to the mass spectrometer,operating at an oven temperature of 220 ℃ in electron impact ionization mode.
2 Results and discussion
2.1 Thermal behavior of ADN/nano-Fe2O3 mixtures
The TG-DTA-DSC curves obtained from ADN and ADN/nano-Fe2O3samples heated at 10 K/min are shown in Fig.2.The endothermic peak that is observed at an onset temperature of about 93 ℃ is due to the melting of spherical ADN in each trial.One heat generation event is evident at 191.9 ℃ and the heat value is about 1.9 kJ/g.Generally,the thermal decomposition of ADN is believed to include two heat generation events in the range of approximately 150~260 ℃.The first exothermic peak is attributed to ADN decomposition and the second exothermic peak to the thermal decomposition of the AN produced by the decomposition of ADN,as shown in the reaction formula in Eq.(1)[12,17].AN is further decomposed to N2O and H2O subsequently,as shown in Eq.(2).For our processed ADN,it has only one exothermic peak,which shows that Eq.(1)and(2)are synchronized.The thermal decomposition of ADN begins at 158.8 ℃,and the maximum decomposition peak temperature is 191.9 ℃.
NH4N(NO2)2→NH4NO3+N2O
(1)
NH4NO3→N2O+2H2O
(2)
The DSC results for the ADN/nano-Fe2O3mixture indicate a lower onset temperature and an almost equal heat value at the exothermic event compared to pure ADN.The most significant exothermic of ADN/nano-Fe2O3mixture is observed at an earlier stage of decomposition about 183.6 ℃ and the thermal decomposition temperature begins at 148 ℃.In addition,the endotherm from the melting of ADN is observed at approximately 93 ℃ in each trial for pure ADN and ADN/nano-Fe2O3mixture.

Fig.2 TG-DTA-DSC results for pure AND and ADN/nano-Fe2O3 mixture
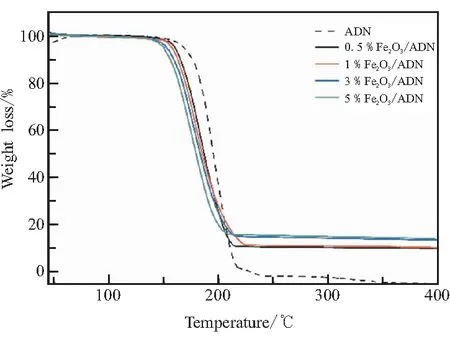
(a)TG curves

(b)DSC curves
TG-DSC results obtained for pure ADN and the ADN/nano-Fe2O3(100/0.1,100/1,100/3,100/5)mixtures are shown in Fig.3.In the case of the pure ADN,an exothermic event with mass loss that appears to be a collection of multiple exothermic peaks is observed from 159 ℃ to 214 ℃.
In contrast,in the case of the ADN/nano-Fe2O3mixture,the decomposition event onset with mass loss is lower than that for the case of pure ADN.Following the mass loss,some residue equal to the mass of nano-Fe2O3of the original sample mass is identified in the pan and the curves of the experiment data.In addition,the exothermic peak and corresponding heat release rates are affected significantly especially 5% nano-Fe2O3catalyst.

Table 1 Thermal characteristics of the decompositions of ADN and ADN/ nano-Fe2O3/ADN mixture obtained from DSC tests ℃
The dependence of the activation energies for thermal decomposition of ADN and the ADN/nano-Fe2O3mixture is shown in Fig.4 as reaction progress calculated from the DSC results at different heating rates by using the Friedman[18]method based on the equation:
(3)
whereαis the reaction progress,tis the time,kis the reaction rate constant,f(α)is the reaction model(a function of the reaction progress),Ais the pre-exponential factor,Ris the gas constant,andEais the activation energy.
In this study,αis determined from the ratio of the heat value at a given time to the total heat value of exothermic peakQt,as in Eq.(4)[19,20].
(4)
For a constantα,the relationship between ln(dα/dt)andT-1at several heating rates gives a straight line.The activation energy at eachαcan be calculated from its slope.
Fig.4 shows that the relation of ADN/nano-Fe2O3mixture activation energy toαshowes different behavior.TheEaof pure ADN increases from 115 kJ/mol(α=0.05)to 155 kJ/mol(α=0.5)and decreases until the end of reaction.On the other hand,theEaof ADN/nano-Fe2O3mixture is almost constant(120 kJ/mol).In addition,the ADN/nano-Fe2O3activation energy is generally lower when compared with the pure ADN for almost each value ofα.The observed thermal properties and activation energies indicate that the decomposition mechanism for ADN/nano-Fe2O3mixture is different from that ADN and the nano-Fe2O3promotes the thermal decomposition of ADN.

Fig.4 Activation energies associated with thermal decomposition of pure ADN and ADN/nano-Fe2O3 mixture
2.2 Thermal decomposition mechanism of ADN/nano-Fe2O3 mixtures
The gaseous species from a whole extent of thermal decomposition between pure ADN and ADN/nano-Fe2O3mixture are compared by TG-DTA-IR.The IR spectra of evolved gases from the decompositions of pure ADN and an ADN/nano-Fe2O3mixture acquired by using TG-DTA-IR at various time are shown in Fig.5,respectively.Basedon Fig.4(a),the decomposition gases evolved from heated ADN consisted of N2O(with peaks at 3500~3400,2250~2100 and 1350~1200 cm-1),NH2(1655~1590 cm-1),NO2(1650~1550 cm-1)and H2O(with broad peaks at 4000~3400 and 2100~1300 cm-1).From Fig.4(b),the evolved gases from the ADN/nano-Fe2O3mixture also consiste of N2O,NO2and H2O,and there is no different gaseous species from pure ADN.These results indicate that the species of evolved gases detectable by IR are unchanged when nano-Fe2O3is added to ADN.But the first detected gas for mixtures is earlier than that of pure ADN.

(a)Pure AND (b)ADN/nano-Fe2O3 mixture
The variations in evolved gases with temperature in the case of the ADN/nano-Fe2O3(50/50)mixture around the decomposition point of ADN are shown in Fig.6,as determined by TG-DTA-MS.In the case of pure ADN,an exothermic event with mass loss that appears to be a collection of multiple exothermic peaks is observed from 158 ℃.The mass loss between this point and 250 ℃ is 100 %,which means that the entire sample decompose to gaseous products.Gaseous products with mass/charge(m/z)ratios of 17(NH3)and 18(H2O or NH4+)are evidently generated simultaneously with the decomposition of the ADN.In addition,the main gas product throughout the reaction is NO(m/z=30),which is derived from ADN decomposition(Eq.(1)).Although,the peaks atm/z=42(N3),63(HNO3)are not observed,HNO3is consumed in the condensed phase reaction.The main gaseous products and related ion fragments in the maximum decomposition temperature range are HN3+(m/z=43),N2O(m/z=44),HN2O-(m/z=45),and NO2(m/z=46).
These results indicate that a portion of the ADN might react with the nano-Fe2O3to generate H2O(m/z=18).At slightly higher temperature ranges,gases withm/zvalues of 30,43,44,45 and 46 are also produced,demonstrating that H2O,N2O,and HN3+are generated during both ADN and AN decomposition.In the case of ADN/nano-Fe2O3mixture,the exothermic event with mass loss has its onset at a lower temperature(148 ℃)and appears more pronounced than that of the pure ADN.

(a)Pure AND (b)ADN/nano-Fe2O3 mixture
3 Conclusions
The thermal decomposition characteristics of ADN/nano-Fe2O3mixture are investigated by using TG-DSC,TG-DTA-IR,TG-DTA-MS.Present study reveals that the ADN has only one exothermic peak at 145~255 ℃,indicating the intermediate product ammonium nitrate and ADN decompose synchronously.The presence of nano-Fe2O3is found to increase the heat release and decrease the onset temperature and activation energy of exothermic events associated with ADN decomposition.Nano-Fe2O3also generates a significant exothermic reaction with the production of N2O in the vicinity of the nano-Fe2O3in the early stage of the decomposition process.The mass of nano-Fe2O3remaining following the reaction is equal to the amount originally added to the ADN,and nano-Fe2O3plays a catalytic role in the thermal decomposition of ADN.

