烏司他丁輔助治療重癥感染性休克的價值分析
李炬靈
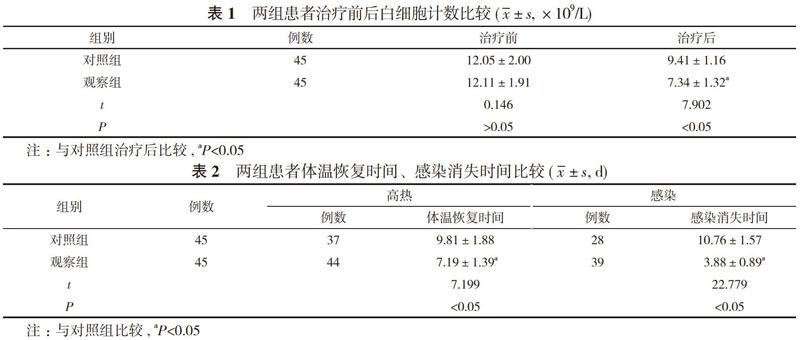
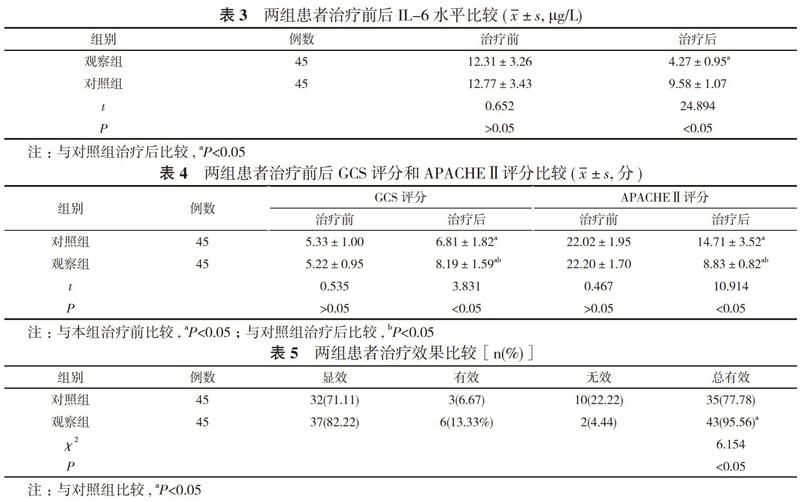
【摘要】 目的 探究臨床用烏司他丁輔助治療重癥感染性休克的治療效果。方法 90例重癥感染性休克患者, 隨機分為觀察組與對照組, 每組45例。對照組患者采用西醫常規治療, 觀察組患者在對照組基礎上聯合烏司他丁治療。比較兩組患者治療效果、體溫情況、感染情況以及治療前后白細胞計數、白細胞介素-6(IL-6)水平、格拉斯哥昏迷量表(GCS)評分、急性生理功能和慢性健康狀況評分系統Ⅱ(APACHEⅡ)評分。結果 治療后, 觀察組白細胞計數(7.34±1.32)×109/L低于對照組的(9.41±1.16)×109/L, 差異具有統計學意義(P<0.05)。治療后, 觀察組高熱、感染體征發生率分別為97.78%、86.67%, 均高于對照組的82.22%、62.22%, 差異具有統計學意義(P<0.05);觀察組體溫恢復時間、感染消失時間分別為(7.19±1.39)、(3.88±0.89)d, 均短于對照組的(9.81±1.88)、(10.76±1.57)d, 差異具有統計學意義(P<0.05)。觀察組患者血清IL-6為(4.27±0.95)μg/L低于對照組的(9.58±1.07)μg/L, 差異具有統計學意義(P<0.05)。觀察組患者GCS評分和APACHEⅡ評分較治療前均有所改善, GCS評分(8.19±1.59)分、APACHEⅡ評分(8.83±0.82)分均優于對照組的(6.81±1.82)、(14.71±3.52)分, 差異均具有統計學意義(P<0.05)。觀察組患者治療總有效率95.56%明顯高于對照組的77.78%, 差異具有統計學意義(χ2=6.154, P<0.05)。結論 烏司他丁具有較好的抗炎效果, 與西醫治療相結合可以提高臨床療效, 加快重癥感染性休克患者退熱速度, 縮短感染時間, 降低白細胞計數及血清IL-6水平, 改善GCS評分和APACHEⅡ評分, 臨床療效較好。
【關鍵詞】 烏司他丁;重癥感染性休克;白細胞水平;聯合治療
DOI:10.14163/j.cnki.11-5547/r.2020.12.002
【Abstract】 Objective? ?To investigate the therapeutic effect of ulinastatin in the treatment of severe septic shock. Methods? ?A total of 90 severe septic shock patients were randomly divided into observation group and control group, with 45 cases in each group. The control group was treated by conventional Western medicine, and the observation group was treated by ulinastatin on the basis of the control group. The therapeutic effect, body temperature recovery time , infection disappearance time, white blood cell count, interleukin-6 (IL-6) level, Glasgow coma scale (GCS) score, acute physiology and chronic health evaluation Ⅱ (APACHE Ⅱ) score were compared between the two groups. Results? After treatment, the white blood cell count (7.34±1.32)×109/L?of the observation group was lower than that of the control group (9.41±1.16)×109/L, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). After treatment, the body temperature recovery time and infection disappearance time of the observation group were (7.19±1.39) and (3.88±0.89) d, which were all shorter than those of the control group (9.81±1.88) and (10.76±1.57) d, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). After treatment, the serum IL-6 of the observation group was (4.27±0.95) μg/L, which was lower than that of the control group (9.58±1.07) μg/L,?and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). GCS score and APACHEⅡ score of the two groups were all better than those before treatment of the same group, and GCS score (8.19±1.59) points and APACHEⅡ score (8.83±0.82) points of the observation group were all better than those of the control group (6.81±1.82) and (14.71±3.52) points, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). The total effective rate of the treatment 95.56% of the observation group was obviously higher than that of the control group 77.78%, and the difference was statistically significant (χ2=6.154, P<0.05). Conclusion? Ulinastatin has a good anti-inflammatory effect. Combined with Western medicine, it can improve the clinical efficacy, accelerate the speed of fever reduction in severe septic shock patients, shorten the infection time, reduce the white blood cell count and serum IL-6 levels, improve the GCS score and APACHE Ⅱscore. The clinical efficacy is good.
綜上所述, 烏司他丁具有較好的抗炎效果, 與西醫治療相結合可以提高臨床療效, 加快重癥感染性休克患者退熱速度, 縮短感染時間, 降低白細胞計數及血清IL-6水平, 改善GCS評分和APACHEⅡ評分, 臨床療效較好。
參考文獻
[1] 吳然, 楊堃. 烏司他丁在重型顱腦損傷治療中的作用. 中國臨床神經外科雜志, 2019, 24(10):595-597, 601.
[2] 李欣, 張平, 曹琳. 烏司他丁聯合奧拉西坦對高血壓腦出血患者的臨床研究. 中國臨床藥理學雜志, 2019, 35(18):1982-1984.
[3] 黃康, 呂愛蓮, 何峻, 等. 血必凈聯合烏司他丁治療感染性休克臨床效果觀察. 臨床軍醫雜志, 2019, 47(9):1003-1004.
[4] 高靜, 劉磊, 王亮亮. 血必凈聯合烏司他丁治療感染性休克臨床觀察. 安徽中醫藥大學學報, 2019, 38(4):33-36.
[5] 方旭晨, 葉旭輝, 涂春蓮, 等. 連續血液凈化聯合烏司他丁治療膿毒癥休克療效觀察. 內科急危重癥雜志, 2018, 24(5):400-402.
[6] 齊英杰, 陳清閣. 烏司他丁聯合CRRT治療感染性休克效果分析. 中國急救醫學, 2018, 38(z2):280.
[7] 陳東嬌, 麥葉. 烏司他丁注射劑聯合血液凈化術治療重癥感染性休克患者的臨床研究. 中國臨床藥理學雜志, 2017, 33(21):2095-2097.
[8] 兀瑞儉, 鞏德成, 王強, 等. 烏司他丁聯合CRRT治療老年感染性休克患者臨床研究. 國際醫藥衛生導報, 2018, 24(21):3302-3304.
[9] 李曉蕾, 張連濤, 梁賢棟, 等. 參麥注射液聯合烏司他丁治療感染性休克患者臨床療效. 現代診斷與治療, 2019(14):2374-2376.
[10] 趙繼坤. 烏司他丁對感染性休克患者肝腎功能及血管外肺水指數的影響. 中國民康醫學, 2019, 31(19):16-18.
[11] 凌世諱. 生脈注射液聯合烏司他丁對感染性休克患者血清炎癥因子水平的影響. 臨床醫藥文獻電子雜志, 2018, 5(8):148-149.
[收稿日期:2020-01-03]

