基于大數(shù)據(jù)的區(qū)域慢病綜合管理平臺的設(shè)計與應(yīng)用實踐
蘇逸飛 王穎 殷偉東 丁臘春 張偉
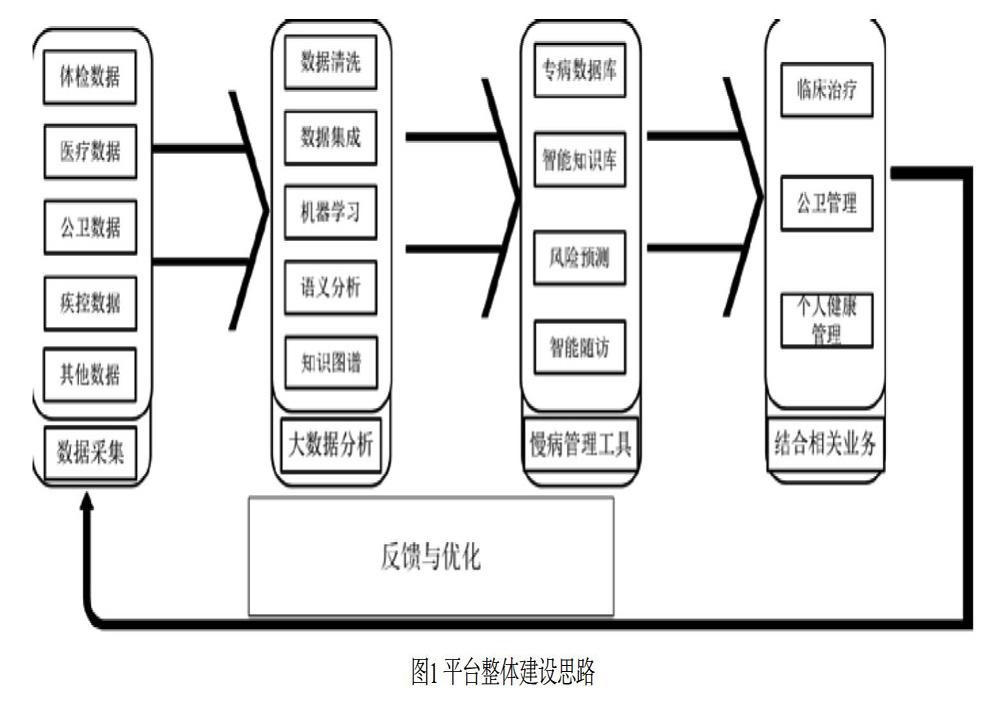
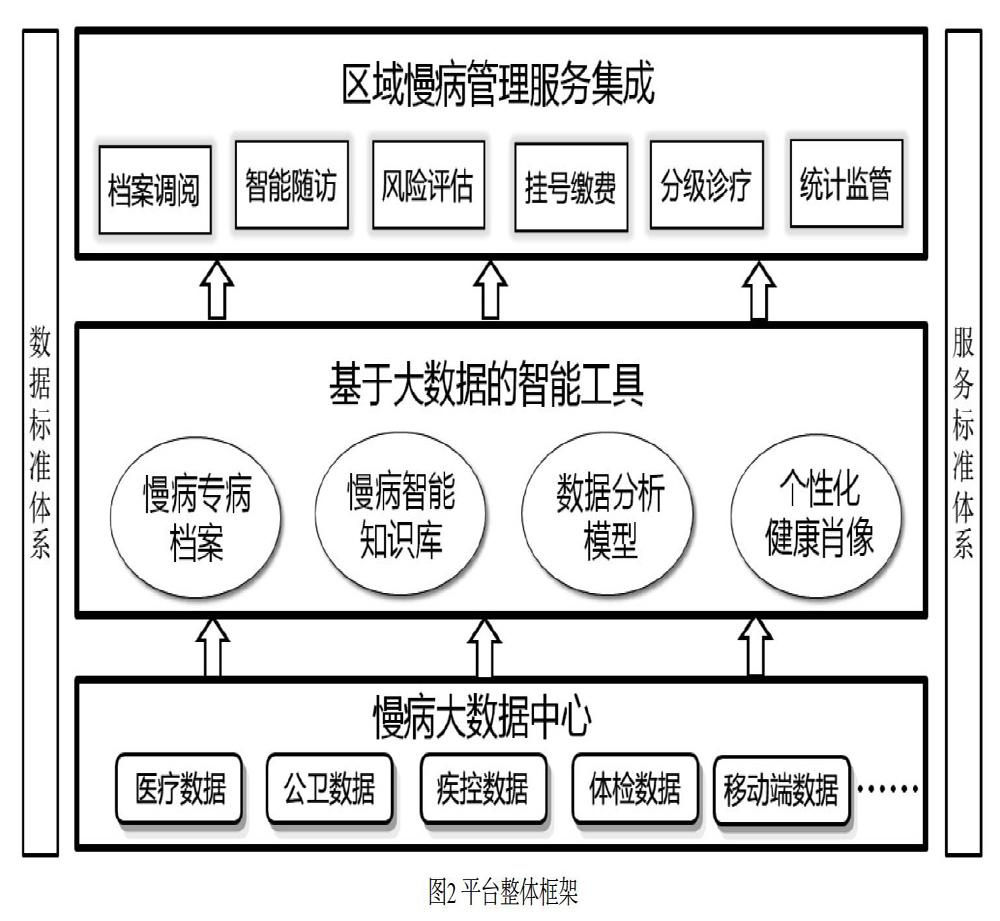
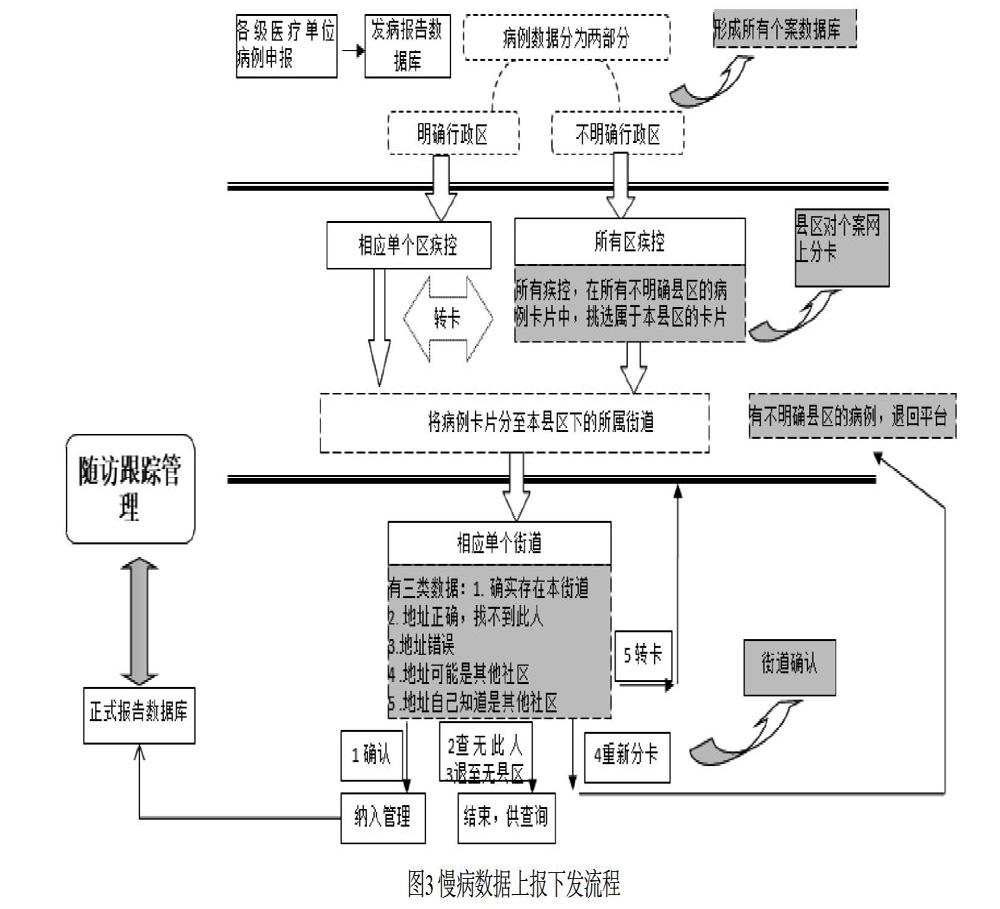
摘? ?要:文章設(shè)計并應(yīng)用了基于大數(shù)據(jù)的區(qū)域慢病綜合管理平臺,匯總了南京區(qū)域內(nèi)各醫(yī)療衛(wèi)生機構(gòu)的醫(yī)療健康數(shù)據(jù),通過大數(shù)據(jù)、人工智能等技術(shù)研究,建立了專病檔案調(diào)閱、知識庫、管理系統(tǒng)等慢病管理工具等,并在現(xiàn)有的醫(yī)療、公共衛(wèi)生管理中,應(yīng)用慢病管理工具并反饋相關(guān)應(yīng)用效果,形成了數(shù)據(jù)采集、分析、應(yīng)用與反饋優(yōu)化的閉環(huán)式。平臺實現(xiàn)了區(qū)域內(nèi)慢病相關(guān)數(shù)據(jù)的共享,強化了各醫(yī)療衛(wèi)生業(yè)務(wù)之間的聯(lián)動,提高了各醫(yī)療衛(wèi)生機構(gòu)的管理服務(wù)能力,有利于對慢病患者的長期跟蹤和多維度管理。
關(guān)鍵詞:大數(shù)據(jù);人工智能;區(qū)域慢病管理
Abstract: This paper designs and applies the regional chronic disease comprehensive management platform based on big data, and summarizes the medical and health data of various medical and health institutions in Nanjing region. Chronic disease management tools are established such as special disease file access, knowledge base, management system, etc. Through the research of big data, artificial intelligence and other technologies, chronic disease management tools are applied in existing medical and public health management and feeds back relevant information Application effect, forming a closed-loop of data collection, analysis, application and feedback optimization. The platform realizes the sharing of chronic disease related data in the region, strengthens the linkage between medical and health services, improves the management and service ability of medical and health institutions, and is conducive to the long-term tracking and multi-dimensional management of chronic disease patients.
Key words: big data; artificial intelligence; regional chronic disease management
1 引言
隨著我國社會經(jīng)濟的快速發(fā)展,人口的老齡化以及導(dǎo)致慢性非傳染性疾病(本文簡稱慢病)的各種行為危險因素(吸煙、飲酒、缺乏體育鍛煉等)在人群中的強度不斷增加,慢病已成為我國多數(shù)地區(qū)的主要健康問題。據(jù)統(tǒng)計,我國居民慢病死亡占總死亡人數(shù)的比例高達86.6%,造成的疾病負擔(dān)已占總疾病負擔(dān)的70%以上,已成為影響國家經(jīng)濟社會發(fā)展的重大公共衛(wèi)生問題[1]。
《“健康中國2030”規(guī)劃綱要》《“健康江蘇 2030”規(guī)劃綱要》與《中國防治慢性病中長期規(guī)劃(2017-2025)》相繼發(fā)布,我國慢病防控事業(yè)也迎來了新的機遇與挑戰(zhàn)。如何提高人均健康期望壽命,開展重大慢病高危人群篩查和干預(yù),阻止、延緩發(fā)病或降低致殘率,已成為保障全民健康的重點工作之一。隨著大數(shù)據(jù)、人工智能技術(shù)的不斷發(fā)展,匯集和分析真實世界全人群的多維醫(yī)療衛(wèi)生數(shù)據(jù),以此輔助和支撐區(qū)域慢病管理業(yè)務(wù)的開展,已具備了實踐的可行性[2,3]。……

