黃芩苷抗哮喘作用與HMGB1/TLR4傳導(dǎo)通路的相關(guān)性研究
韓超 楊柳 張秋玲 梁慧玲 徐俊
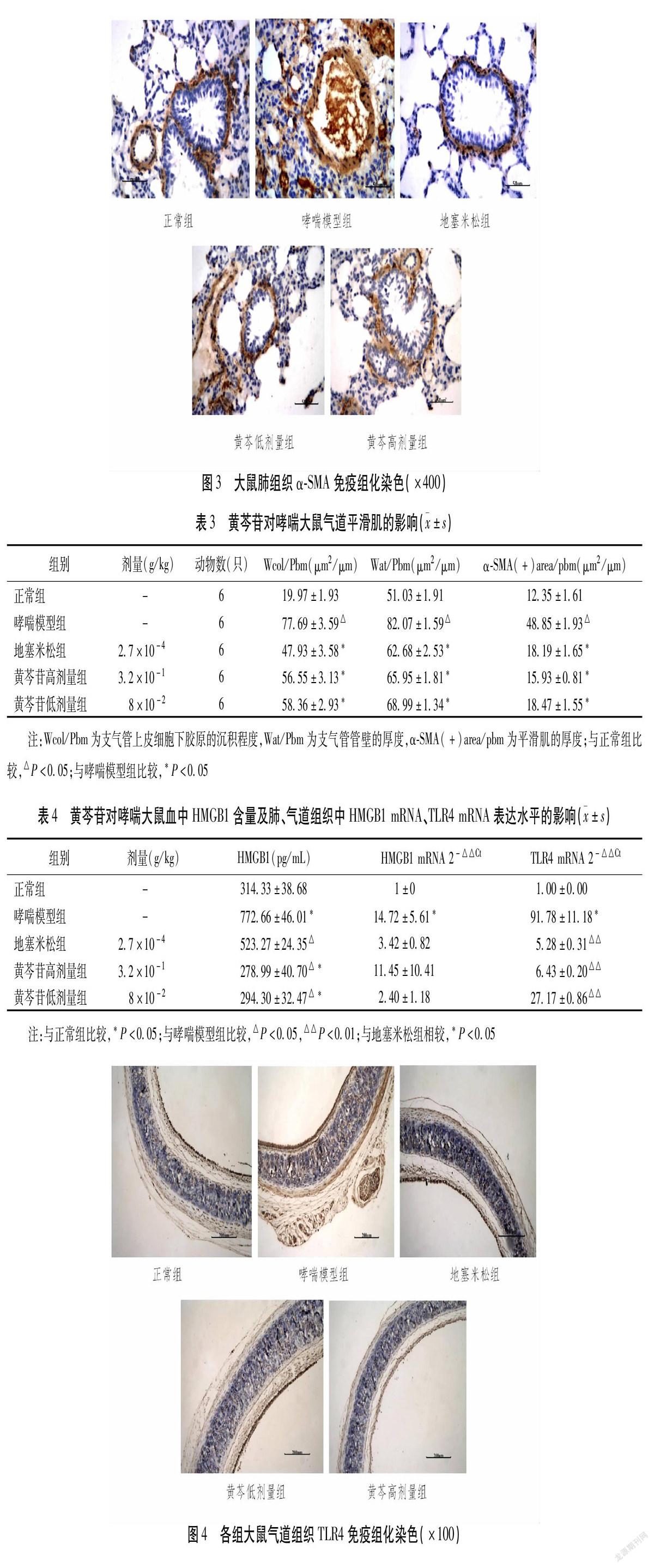
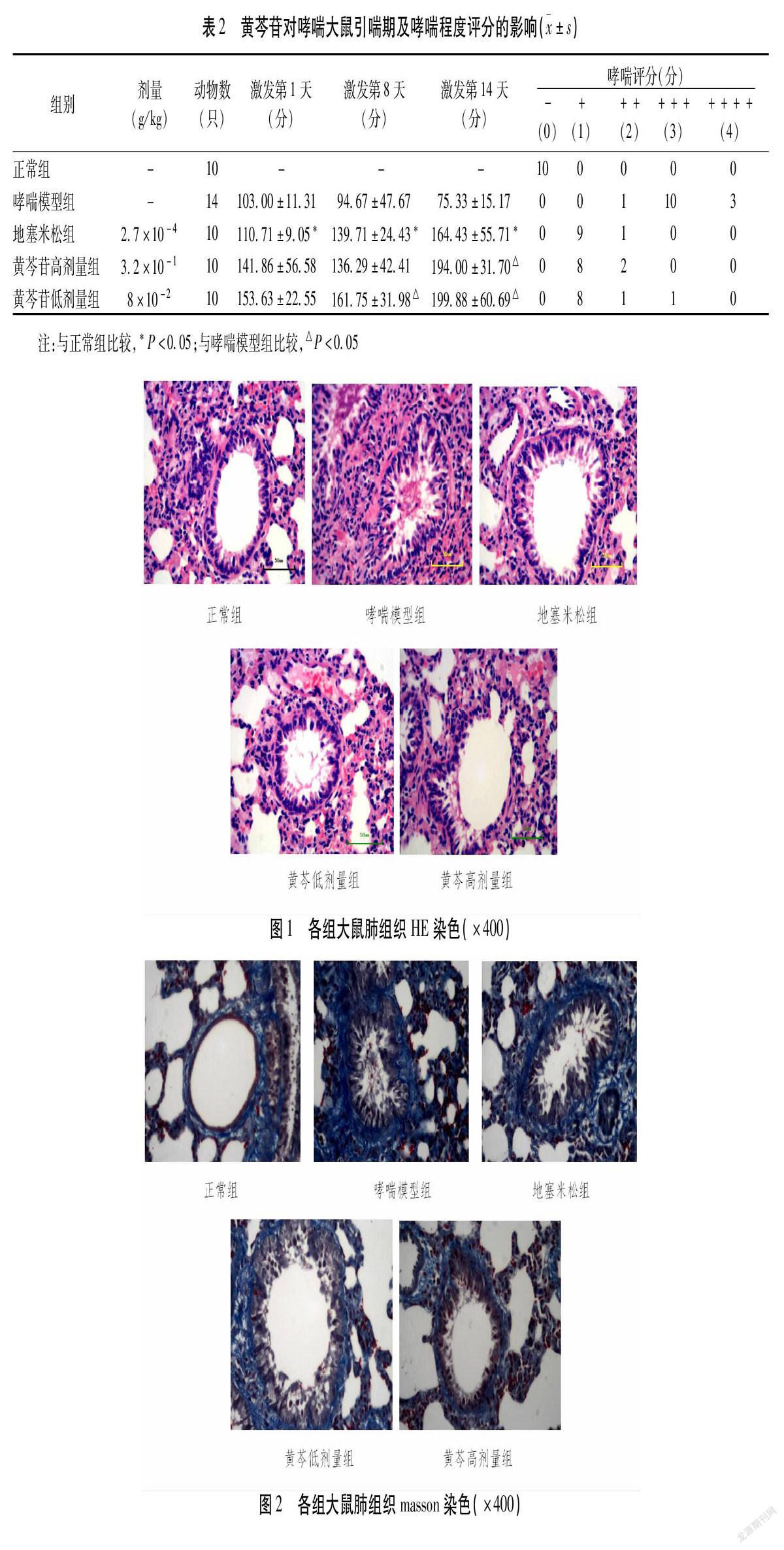

摘要 目的:研究黃芩苷對(duì)支氣管哮喘防治的作用及其可能的作用機(jī)制。方法:將54只SD大鼠按體質(zhì)量隨機(jī)分為正常組、哮喘模型組、地塞米松組及黃芩苷高、低劑量組。用卵清蛋白(OVA)誘發(fā)致敏大鼠建立支氣管哮喘的動(dòng)物模型,給予相應(yīng)藥物灌胃給藥4周,1次/d,其中正常組及哮喘模型組藥物以等量生理鹽水代替。用藥物干預(yù)性治療后,觀察各組藥物對(duì)大鼠的哮喘程度及哮喘潛伏期的影響。實(shí)驗(yàn)結(jié)束后,24 h內(nèi)處死大鼠,取材,測(cè)定并比較支氣管壁厚度、氣道上皮下膠原沉積程度;測(cè)定血中HMGB1濃度;免疫組織化學(xué)測(cè)定支氣管平滑肌中α-SMA和氣道組織TLR4的蛋白表達(dá);RT-PCR法測(cè)定肺組織HMGB1 mRNA表達(dá)變化。結(jié)果:黃芩苷可明顯改善病鼠的哮喘程度,延長(zhǎng)哮喘潛伏期(P<0.05~0.01);可有效減輕病鼠支氣管管壁增厚及氣道上皮下膠原沉積程度(P<0.05);明顯降低血漿中HMGB1的含量,肺組織中的HMGB1 mRNA表達(dá)呈下降趨勢(shì),但差異無統(tǒng)計(jì)學(xué)意義(P>0.05);可明顯降低氣道組織中的TLR4,氣管平滑肌中α-SMA的蛋白表達(dá)及TLR4 mRNA的表達(dá)水平(P>0.05)。結(jié)論:黃芩苷具有抗哮喘作用,其作用可能與其影響HMGB1/TLR4通路的信號(hào)傳導(dǎo)相關(guān)。
關(guān)鍵詞 黃芩苷;哮喘;地塞米松;哮喘潛伏期;傳導(dǎo)通路;大鼠
Abstract Objective:To study the effects of Baicalin on prevention and treatment of bronchial asthma and its possible mechanism.Methods:A total of 54 SD rats were randomly divided into a normall group,an asthma model group,a dexamethasone group,baicalin high and low dose groups by weight.Animal model of bronchial asthma was induced by ovalbumin (OVA).The corresponding drugs were given by orally intragastric administration once a day for 4 weeks.The normal group and the asthma model group were replaced by same volume of normal saline (NS).The effects on asthmatic degree and the latent period of asthma of each rats group were observed after treatment.After the experiment,the rats were killed within 24 h for collection of materials.The thickness of bronchial wall,the degree of collagen deposition in airway,the concentration of HMGB1 in blood,the expression of α-SMA in bronchial smooth muscle and TLR4 in airway were measured by immunohistochemistry.The expression of HMGB1 mRNA in lung tissue was determined by RT-PCR method.Results:Baicalin high and low dose groups could obviously improve the asthmatic degree and prolong the latent period of asthma (P<0.05-0.01),and could effectively reduce the thickness of bronchial wall and the degree of subcutaneous collagen deposition in airway (P<0.05).The content of HMGB1 in plasma was significantly decreased,and the expression of HMGB1 mRNA in lung tissue was decreased,but there was no significant difference (P>0.05).The protein expression of α-SMA and TLR4,the expression of TLR4 mRNA in tracheal smooth muscle were significantly decreased (P>0.05).Conclusion:Baicalin has an effect of anti-asthmatic,which may be related to its influence on signal transduction of the HMGB1/TLR4 pathway.
Key Words Baicalin;Asthma;Dexamethasone;Asthma latency;Conduction pathway;Rat
中圖分類號(hào):R285.5文獻(xiàn)標(biāo)識(shí)碼:Adoi:10.3969/j.issn.1673-7202.2019.06.012
黃芩苷(Baicalin)是植物黃芩的主要有效成分之一,具有清熱解毒、抗炎、抗變態(tài)反應(yīng)等多方面的藥理作用[1]。近年來隨著國(guó)內(nèi)外對(duì)黃芩苷研究的不斷深入,其越來越多的作用如抗氧化、免疫調(diào)節(jié)、促細(xì)胞凋亡等多作用被發(fā)現(xiàn)。高遷移族蛋白B1(High Mobility Group Box 1,HMGB1)是一種高度保守的核蛋白,為重要的內(nèi)源性炎性反應(yīng)遞質(zhì),既是早期炎性反應(yīng)的觸發(fā)因子,又是晚期炎性反應(yīng)的啟動(dòng)因子[2]。……

