乳腺非腫塊型病變的超聲臨床分析
余巧英
關(guān)鍵詞:乳腺非腫塊型病變;超聲反應(yīng);臨床價(jià)值
中圖分類號(hào):R445.1;R737.9 文獻(xiàn)標(biāo)識(shí)碼:B DOI:10?郾3969/j.issn.1001-0270.2019.02.10
Abstract: Objective: To evaluate the ultrasound reaction of breast non-mass lesions. Methods: Using retrospective analysis to analyze the total 50 patients who were diagnosed by routine examination from January 2018 to December 2018. Results: Among the 20 cases of non-mass breast lesions, 11 were malignant lesions(55%) and 9 were benign lesions(45%). Among them, 3 cases were invasive ductal carcinoma, 4 cases were intraductal carcinoma, 3 cases were lymphatic metastatic carcinoma, 1 case was fibrotic adenocarcinoma, 2 cases were lymphocytic leukemia, 2 cases were hyperplasia, 4 cases were adenopathy, and 1 case was inflammatory lesions. Among the 20 cases of non-mass breast lesions, 12 cases were lamellar hypoacoustic region(60%)and 8 cases were microcalcified schistose hypoechoic region(40%). The maximum diameter of lesions in the malignant group was 2.25±1.03(cm), and that was 3.09±1.02(cm) in the benign group; the proportion of microcalcification in the benign group was 77.8% and that in the malignant group was 27.3%. Abnormal axillary lymph node analysis, benign lesions was 9.1%, malignant lesions was 55.5%. Conclusion: The microcalcification in breast non-mass lesions has significant value in the diagnosis of intraductal carcinoma. The presence of axillary lymph node abnormality is useful in the differential diagnosis of benign and malignant lesions.
Key Words: Breast Non-mass Lesions; Ultrasound Reaction; Clinical Value
1 臨床數(shù)據(jù)和方法
1.1 基本資料
對(duì)我院于2018年1月-2018年12月期間,所收治的經(jīng)常規(guī)確診的患者共20例予以分析,20例患者中,最大年齡81歲,最小年齡37歲,中位年齡(52.7±25.8)歲。
1.2 方法
患者保持仰臥位或者側(cè)臥位,采用超聲檢查的形式對(duì)乳腺病灶位置進(jìn)行測(cè)量。
1.3 統(tǒng)計(jì)學(xué)分析
本次研究的所有數(shù)據(jù)均行SPSS17.0軟件處理。
2 結(jié)果
2.1 腫塊型乳腺病變反應(yīng)分析
20例非腫塊型乳腺病變反應(yīng)中,惡性病變11例(55%),良性病變9例(45%)。其中3例為浸潤(rùn)性導(dǎo)管癌、4例為導(dǎo)管內(nèi)癌、淋巴轉(zhuǎn)移性低分化癌3例、纖維性腺癌1例、淋巴細(xì)胞性白血病2例、增生2例、腺病4例、炎性病變1例。
20例非腫塊型乳腺病變中,12例為片狀低回聲區(qū)域(60%),8例為微鈣化片狀低回聲區(qū)域(40%)。
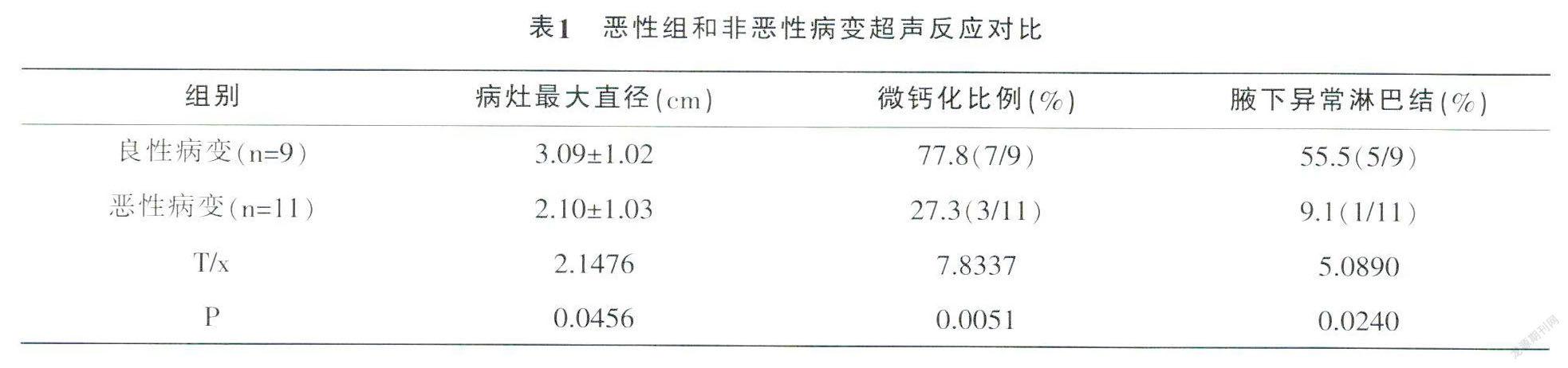
2.2 惡性組和非惡性病變超聲反應(yīng)對(duì)比
惡性組和非惡性病變超聲反應(yīng)對(duì)比:惡性組和非惡性組病灶最大直徑統(tǒng)計(jì)學(xué)意義存在,微鈣化比例分析不存在差異性(P>0.05),詳情見(jiàn)表1。
3 討論
在對(duì)乳腺癌患者進(jìn)行診斷的過(guò)程中,通過(guò)檢查形式將其分成非腫塊型病變以及腫塊型病變,超聲較為顯著的特點(diǎn)是腫塊型病變,但是病變位置的部分結(jié)構(gòu)模糊不清楚,因此漏診情況極易發(fā)生[1-3]。
綜上所述,在當(dāng)前超聲設(shè)備不斷發(fā)展的過(guò)程中,圖像分辨率也逐漸清晰,乳腺內(nèi)多數(shù)腫塊病變可以測(cè)定出來(lái)[4]。腫塊型是最為典型的超聲反應(yīng),但是一部分乳腺癌病變出現(xiàn)彌漫反應(yīng),所以,對(duì)微鈣化的出現(xiàn)需要高度注意。在高頻超聲不斷應(yīng)用的過(guò)程中,可出現(xiàn)數(shù)量越來(lái)越多的非腫塊型超聲病變。但是在對(duì)腋下是否出現(xiàn)異常淋巴結(jié)狀態(tài)時(shí),仍然需要影像學(xué)方法進(jìn)行診斷和判別[5,6]。
參考文獻(xiàn):
[ 1 ]范賓.乳腺區(qū)段切除治療乳腺良性腫塊的臨床應(yīng)用[J].中國(guó)醫(yī)藥指南,2016,14(36):66-66.
[ 2 ]趙永生.改良乳腺區(qū)段切除術(shù)治療乳腺良性腫塊的臨床療效分析[J].中國(guó)醫(yī)藥指南,2017,15(4):66-67.
[ 3 ]李曄,王知力.非腫塊型乳腺病變的超聲診斷[J].解放軍醫(yī)學(xué)院學(xué)報(bào),2015,36(9):957-959.
[ 4 ]陶斯翠,談雯,王娜等.乳腺非腫塊型病變的超聲臨床探討[J].中國(guó)繼續(xù)醫(yī)學(xué)教育,2016,8(13):64-65.
[ 5 ]吳曉燕.乳腺非腫塊型病變的超聲診斷[J].中國(guó)現(xiàn)代藥物應(yīng)用,2015,9(13):80-80.
[ 6 ]馮聰.乳腺非腫塊型病變的超聲診斷分析[J].中國(guó)衛(wèi)生標(biāo)準(zhǔn)管理,2017,8(3):125-126.

