調胃承氣湯對腸源性膿毒癥大鼠免疫功能的影響
趙鋒利 王澍欣 羅苑苑 鄭述銘 陳靜 趙馥 冼紹祥


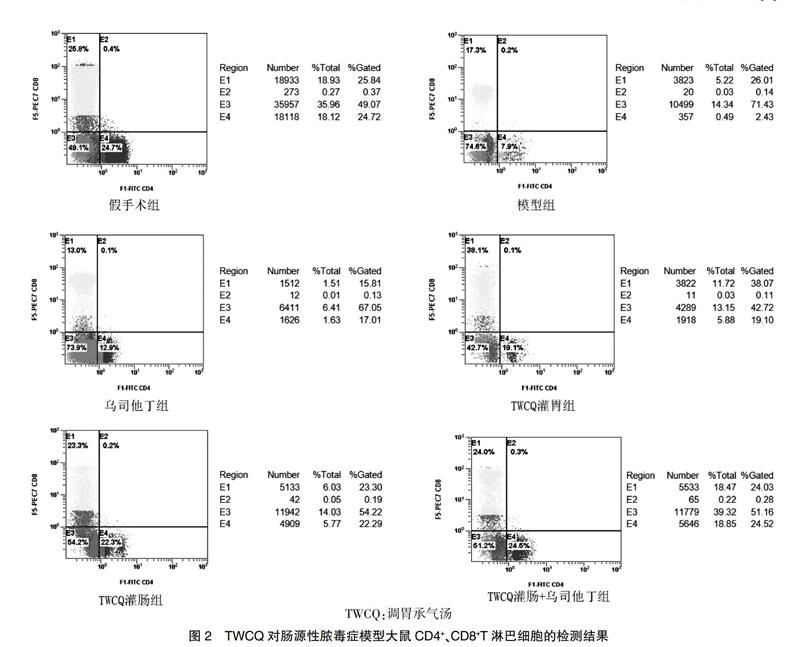
[摘要] 目的 觀察調胃承氣湯(TWCQ)對腸源性膿毒癥大鼠免疫功能的影響。 方法 將60只SPF級雄性SD大鼠按體重隨機分為假手術組、模型組、烏司他丁組(30 000 U/kg)、TWCQ灌胃組(9.45 g生藥/kg)、TWCQ灌腸組(9.45 g生藥/kg)和TWCQ灌腸+烏司他丁組(n = 8),在造模后2、10、24 h分別給藥,烏司他丁經腹腔注射給藥,TWCQ根據組別分別通過灌胃途徑和灌腸途徑給藥,在24 h結束實驗。用酶聯免疫吸附測定法(ELISA)檢測血清中白細胞介素10(IL-10)和腫瘤壞死因子α(TNF-α)水平,流式細胞儀檢測小腸系膜中CD4+和CD8+T淋巴細胞水平,并在光鏡下觀察小腸HE染色結果。 結果 與假手術組比較,模型組大鼠小腸系膜中CD4+/CD8+T淋巴細胞數的比例明顯下降(P < 0.05),血清IL-10水平降低,TNF-α水平升高(P < 0.05),小腸可見明顯的病理性損傷;與模型組比較,TWCQ治療組大鼠小腸系膜中CD4+/CD8+T淋巴細胞數的比例明顯上升(P < 0.05),血清IL-10水平升高,TNF-α水平降低(P < 0.05),并且模型小腸的損傷程度明顯改善;與TWCQ灌胃組比較,TWCQ灌腸組的治療效果更為明顯(P < 0.05)。 結論 TWCQ具有改善腸源性膿毒癥大鼠模型CD4+/CD8+T淋巴細胞比例、降低免疫炎癥的功能,且灌腸療法要優于灌胃療法。
[關鍵詞] 調胃承氣湯;腸源性膿毒癥;免疫功能;淋巴細胞
[中圖分類號] R631.2? ? ? ? ? [文獻標識碼] A? ? ? ? ? [文章編號] 1673-7210(2019)06(b)-0018-05
Influence of Tiaowei Chengqi Decoction on the immunologic function of rats with gut-derived sepsis
ZHAO Fengli1? ?WANG Shuxin2? ?LUO Yuanyuan1? ?ZHENG Shuming1? ?CHEN Jing1? ?ZHAO Fu1? ?XIAN Shaoxiang3
1.Intensive Care Unit, the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangdong Province, Guangzhou? ?510405, China; 2.Acupuncture Department, the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangdong Province, Guangzhou? ?510405, China; 3.the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangdong Province, Guangzhou? ?510405, China
[Abstract] Objective To observe the influence of Tiaowei Chengqi Decoction (TWCQ) on the immunologic function of rats with gut-derived sepsis. Methods Sixty SPF male SD rats were randomly divided into sham operation group, model group, Ulinastatin group (30 000 U/kg), TWCQ gavage group (9.45 g/kg), TWCQ enema group (9.45 g/kg) and TWCQ enema + Ulinastatine group according to their body weight (n = 8). After modeling for 2, 10, 24 h, Ulinastatine was administered by intraperitoneal injection, respectively. TWCQ was administered by gastric way and enema way respectively according to different groups, and the experiment was completed at 24 hours. The levels of serum interleukin 10 (IL-10) and tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) were detected by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), the levels of CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocyte in mesentery of small intestine were detected by flow cytometry, and the results of HE staining in small intestine were observed under light microscope. Results Compared with sham operation group, the proportion of CD4+/CD8+ T lymphocyte in mesentery of small intestine in rats of model group was decreased significantly (P < 0.05), the level of IL-10 was reduced and TNF-α was improved significantly (P < 0.05), and the pathological damage of small intestine could be seen obviously. Compared with model group, the proportion of CD4+/CD8+ T lymphocyte in mesentery of small intestine in rats of TWCQ treatment group increased significantly (P < 0.05), the level of IL-10 was improved and TNF-α was reduced significantly (P < 0.05), and the damage degree of model small intestine was improved obviously. Compared with TWCQ gavage group, the therapeutic effect of TWCQ enema group was more obvious (P < 0.05). Conclusion TWCQ has the function of improving the proportion of CD4+/CD8+ T lymphocyte and reducing immunologic function in model rats with gut-derived sepsis, and enema therapy is superior to gavage therapy.
[Key words] Tiaowei Chengqi Decoction; Gut-derived sepsis; Immunologic function; Lymphocyte
腸源性膿毒癥是一種由腸道感染引發的全身性反應,主要包括引起宿主免疫功能失調,并最終導致多器官功能障礙[1]。腸源性膿毒癥是ICU常見的危重病,其病情發展迅速,臨床救治難度大,每年全世界患病人數超過數百萬,病死率已超過膿毒癥患者數量的四分之一,并且這一數據逐年上升[2-3]。腸源性膿毒癥的發病機制主要包括腸黏膜機械屏障破壞、自身抵抗力下降及腸道微生態環境失衡[4-6]。盡管腸源性膿毒癥的致病因素是多方面的,但機體對腸源性膿毒癥的免疫反應將決定病情的走向,并且,過度而持久的炎性反應嚴重降低機體免疫功能,進一步加重病情[7-8]。同時,由于腸黏膜的破壞,經灌胃給藥途徑的藥物生物利用度降低,而直腸黏膜血流豐富,利于藥物的吸收,臨床上常采用灌腸給藥來提高療效[9]。……

