西部六省居住用地與工業用地的集聚變化態勢研究
張宇 鄧春磊
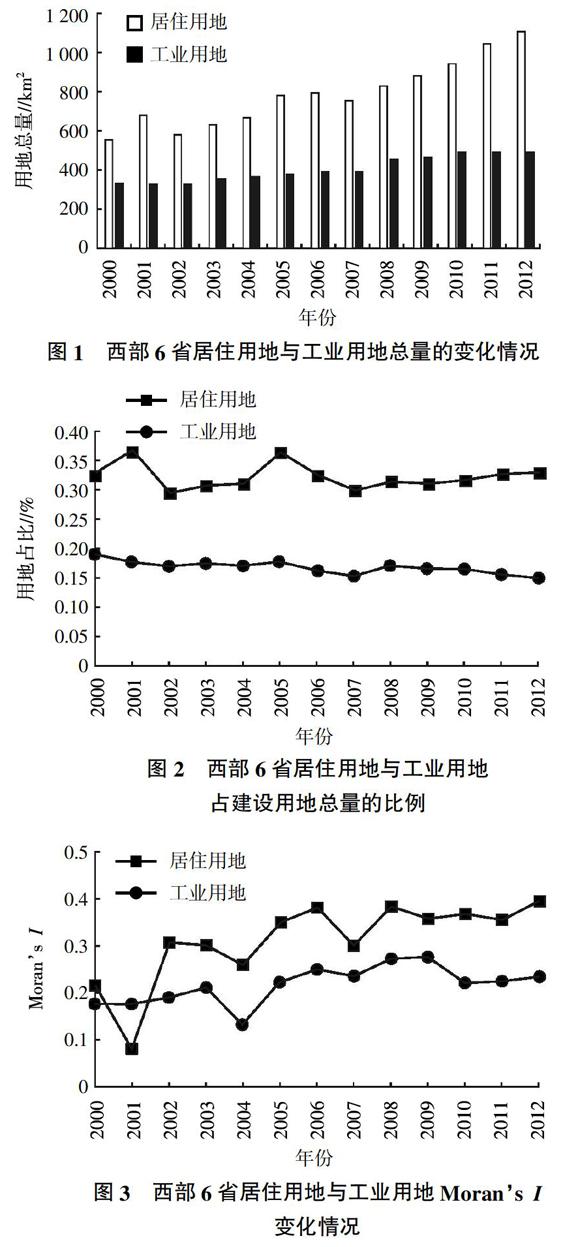

摘要:采用空間自相關和空間回歸模型等空間計量方法,選取中國西部6省86個縣(市)為單元對2000—2012年居住用地與工業用地時空變化的空間格局進行分析并對集聚變化原因進行測算。結果表明,①2000—2012年西部6省的居住用地Morans I指數從0.22上升為0.40,空間集聚正在逐步增強;工業用地則從0.18上升為0.23,相對居住用地集聚現象偏弱。②從城市空間格局考察居住用地與工業用地集聚變化態勢,HH類型及LL類型的變化最為顯著,多出現在內蒙古。③城市建設用地面積、國民生產總值、第三產業占GDP的比重及公共用地面積對居住用地在空間上集聚影響最為顯著;人均國民收入、工業產值、交通用地面積及人口數量對工業用地在空間上集聚影響最為顯著。
關鍵詞:居住用地;時空變化;空間分析;空間回歸
中圖分類號:F124.5;U412.1+4 文獻標識碼:A 文章編號:0439-8114(2018)08-0130-06
DOI:10.14088/j.cnki.issn0439-8114.2018.08.032
Study on the Aggregation and Change of Residential and Industrial Land
in Six Western Provinces
ZHANG Yu,DENG Chun-lei
(College of Public Administration,Hohai University,Nanjing 211100,China)
Abstract: Spatial autocorrelation and spatial regression models were used to analyze the spatial and temporal changes of residential and industrial land from 2000 to 2012 of 86 counties and cities in 6 western provinces of China. Results showed that,①The Moran's I index of residential land in the six western provinces changed from 0.22 to 0.40 in 2000-2012,the spatial agglomeration gradually increased, the industrial land was increased from 0.179 to 0.230,and the relative residential land was weakly clustered. ②From the urban spatial analysis of residential land and industrial agglomeration trend,HH type and LL type had the most significant change, mostly in the province of Inner Mongolia. ③The urban construction land area, gross national products,the proportion of tertiary industry to GDP and the public land area had the most significant impact on the spatial agglomeration of residential land. The per capita national income,industrial output value, traffic land area and population size had the most impact of significant spatial agglomeration on residential land.
Key words: residential land; spatial and temporal change; spatial analysis; spatial regression
在中國快速而持續的城市化進程中,土地供給扮演的支撐與制約角色越來越明顯,據中國土地勘測規劃院的統計,西部地區住宅用地增速快于中東部地區,2009—2013年,全國城鎮住宅用地增幅為18.8%,基本與城鎮土地面積總體增幅(18.2%)持平,但西部地區34.0%的增幅明顯高于全國總體增幅,中部地區和東部地區分別為16.0%和15.1%。而據《中國城市建設統計年鑒》數據,2009—2012年,中國西部工業用地則減少了79.73 km2。工業化和城市化進程的加快使中國逐漸步入以資源環境約束加大為主要特征的矛盾突顯期,尤其是西部地區居住用地及工業用地面臨越來越大的空間、環境和社會壓力,因而研究建設用地中比重最大兩類用地的集聚模式及變化過程對于快速城鎮化的西部地區來說非常重要。……

