還原石墨烯動態吸附磺胺嘧啶類抗生素的性能與機理研究
馬軍冠 趙傳起 李亞娟
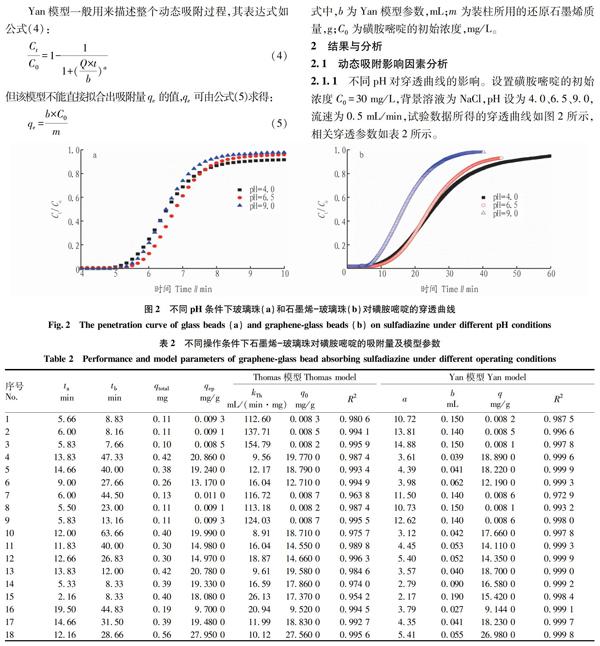
摘要 [目的]研究還原石墨烯動態吸附磺胺嘧啶類抗生素的性能與機理。[方法]利用熱沉積法制備出還原石墨烯-玻璃珠復合材料,并用其開展動態吸附磺胺嘧啶類抗生素的試驗研究,考察pH、背景液種類、流速、污染物濃度等影響因素對石墨烯吸附抗生素性能的影響,分別采用Thomas模型和Yan模型對試驗數據進行擬合。[結果]隨著流速和pH的升高,穿透時間縮短,吸附柱對磺胺嘧啶的吸附總量減小;而隨著背景液換為二價Ca.2+和磺胺嘧啶初始濃度的降低,穿透時間延長,吸附柱對磺胺嘧啶的吸附總量增大。Thomas模型和Yan模型均能夠較好地描述抗生素在石墨烯柱中的穿透曲線,2種模型擬合的結果與試驗得到的結果非常接近,但Yan模型的決定系數R.2更接近1,效果更好。[結論]該研究可為實際抗生素類污染水體的治理與修復提供科學依據。
關鍵詞 還原石墨烯;磺胺嘧啶;動態吸附;穿透曲線;動態吸附模型
中圖分類號 S181.3 文獻標識碼 A 文章編號 0517-6611(2018)23-0047-05
Abstract [Objective] The research aimed to study the performance and mechanism of dynamic adsorption of sulfadiazine antibiotics by graphene.[Method]The reduced grapheneglass bead composite was prepared by thermal deposition method,and the experimental study on dynamic adsorption of sulfadiazine antibiotics was carried out.The effects of pH,background liquid type,flow rate and pollutant concentration on the performance of graphene adsorption antibiotics were investigated.The Thomas data and Yan model were used to fit the experimental data.[Result]The sulfadiazine adsorptivity and the breakthrough time decreased with an increase in the pH value and flow rate.In contrast,the sulfadiazine adsorptivity increased and the breakthrough time prolonged when changing the ion species to bivalent Ca.2+ and decreasing the initial sulfadiazine concentration.Both the Thomas model and the Yan model could better describe the penetration curve of antibiotics in the graphene column.The results of the two model fittings were very close to those obtained by the experiment,but the decision coefficient R.2 of the Yan model was closer to 1,and the effect was better.[Conclusion] This study can provide a scientific basis for the treatment and restoration of actual antibiotic contaminated water bodies.
Key words Reduced graphene;Sulfadiazine;Dynamic adsorption;Breakthrough curve;Dynamic adsorption model
抗生素作為藥物可選擇性地抑制或影響生物功能而被廣泛使用。我國是抗生素生產大國,也是抗生素使用大國,我國城市污水中殘留的各類抗生素遠高于歐美國家。雖然水體中微量級抗生素通常不會造成急性毒性,但長期暴露在環境中會對生物存在慢性毒性的潛在可能,也可能會通過食物鏈富集作用對人體健康產生危害[1]。近年來研究表明,抗生素濫用、抗生素環境污染的真正危害在于加劇細菌耐藥性[2]。……

