Microwave-Assisted Hydrothermal Synthesis of Zinc Phosphates of Varying Dimensionality
HOU Hongjie, SONG Yu, 2, DONG Hui, TANG Yuwei
(1.School of Textile and Material Engineering, Dalian Polytechnic University, Dalian 116034, China) (2.School of Light Industry & Chemical Engineering,Dalian Polytechnic University, Dalian 116034, China)
1 Introduction
Since Stucky et al.[1]synthesized microporous zinc phosphates with zeolite like topologies for the first time, a variety of zinc phosphates with open frameworks of different dimensionalities, including one-dimensional (1D) chained structures[2-6], two-dimensional (2D) layered structures[5, 7-10]and a large number of three-dimensional (3D) open framework structures[5, 11, 12], have been synthesized and characterized. Generally these compounds were synthesized by hydrothermal/solvothermal methods in the presence of organic amines.
Microwave-assisted hydrothermal synthesis has been widely employed in many recent chemical reaction studies owing to its rapid heating, homogeneity, and higher yield[13-17].In a previous study, open-framework zinc phosphates were synthesized by microwave-assisted technique,and the morphologies of the products can be controlled by changing the synthesis conditions[18].
In this study, 1D chained structure, Zn(C3N2H4) HPO4(Compound Ⅰ), and 2D layered structure, Zn4P3O11(OH)·3C3N2H4(Compound Ⅱ), were obtained in the same reaction system under microwave heating. Pure compound Ⅱ has been successfully synthesized by using conventional hydrothermal method[5, 9]. The reaction conditions of compound Ⅰ and Ⅱ were investigated in detail, and the structures of the two zinc phosphate compounds were analyzed.
2 Experimental Section
A typical experiment was as follows: 1.23 g zinc acetate and 1.15 g imidazole were added into 7 ml deionized water, and stirred to form a transparent solution. Then 0.385 ml phosphoric acid was added drop by drop with vigorous stirring and a white precipitation formed. The molar composition of the mixture was 1.0(Zn(OAc)2) ∶1.0(H3PO4) ∶3.0(Imidazole) ∶70.0(H2O). The mixture was stirred for 1 h, then transferred into a 70 ml Teflon autoclave for microwave radiation heating under the reaction temperature for 30 min. After reaction, the solid products were washed with deionized water and dried at room temperature. The complete synthesis conditions and compositions of the products obtained by powder XRD analysis are presented in Table 1.

Table 1 Synthesis conditions and analysis for compounds

3 Results and Discussion
The framework structures of compoundⅠand compound Ⅱ were showed in Fig.1.

Fig.1 Polyhedral representation of framework structures along the a-direction: (a) compound Ⅰ, (b) compound Ⅱ
The structure of compound Ⅰ consists of ladders, which are formed by strictly alternating corner-sharing ZnO3N and PO3(OH) tetrahedra. The imidazole molecule is connected to the Zn center via the Zn-N bond and located between the ladders. The structure of compound Ⅱ is built up from the vertex-shared PO4, PO3(OH), ZnO4, ZnO2N2and ZnO3N tetrahedra. The imidazole molecule acts not only as a structure-directing agent but also as a ligand to Zn. Different from compound Ⅱ, the structure of compound Ⅰ does not consist of any Zn-O-Zn linkage. From Fig.1, it can be seen that the 4-membered ring is the basic structural building unit in these two zinc phosphate compounds. The effect of crystallization temperature was studied by varying the temperature from 140 ℃ to 200 ℃. Powder XRD and SEM were used to monitor the evolution of the products as the crystallization temperature increased (Fig.2a and Fig.3a~3e). It can be seen that pure compound Ⅰ was generated when the temperature was 140 ℃ or 160 ℃. However, the yield of product at 140 ℃ was lower than that in 160 ℃. When the crystallization temperature was raised up to 170 ℃, the powder XRD pattern shows a reflection peak of compound Ⅱ (2θ≈7.4°). As shown in SEM images, the external surfaces of crystals became rough (Fig.3b). The XRD pattern at 180 ℃ exhibits presence of both compound Ⅰ and Ⅱ. The morphology of the products is irregular and the crystal size of both compound Ⅰ and Ⅱ became smaller. When the reaction mixture was heated at 200 ℃,pure compound Ⅱ was obtained. The resulting crystals were aggregated and their sizes became larger and narrower.
Fig.2b and Fig.3c, Fig.3f~3h show the XRD patterns and SEM images of the zinc phosphates synthesized at 180 ℃ with different crystallization time. Pure compound Ⅰ was formed after the mixture was heated for 15 min. The presence of compound Ⅱ was observed when the crystallization time was increased to 20 min. The resulting crystals became larger obviously, but their morphology was poor. As the crystallization went on, the intensity of characteristic peaks of compound Ⅱ increased, while those of compound Ⅰ decreased. When the reaction time was extended to 90 min, pure compound Ⅱ was observed. The morphology of which is regular and uniform. The crystallinity of the product decreased slightly when the crystallization time was extended to 180 min. The transformation from compound Ⅰ to Ⅱ indicates that compound Ⅱ is more stable than compound Ⅰ. The reason might be there are much more Zn-N bonds in compound Ⅱ than in compound Ⅰ.

Fig.2 XRD patterns of products with different reaction conditions: (a) different crystallization temperature, (b) different crystallization time and (c) different H2O/Zn(OAc)2 molar ratios
The syntheses of zinc phosphates with H2O/Zn(OAc)2molar ratios of 50, 70, 100 and 140 were conducted under similar conditions, respectively. The XRD patterns and SEM images of the products with different amounts of H2O are shown in Fig.2c and Fig.3c,Fig.3i,Fig.3j, respectively.When the H2O/Zn(OAc)2molar ratio was 50, Compound Ⅰ was obtained. However, the product was not pure, and the morphology of which was large and rough (Fig.3i). Two compounds coexisted when the H2O/Zn(OAc)2molar ratio increased to 70. Pure compound Ⅱ was obtained when the ratio increased to 100. Increasing this ratio to 140, the products did not change much. The pH value of the reaction mixture, which is affected by the content of H2O, might influence which products were formed.
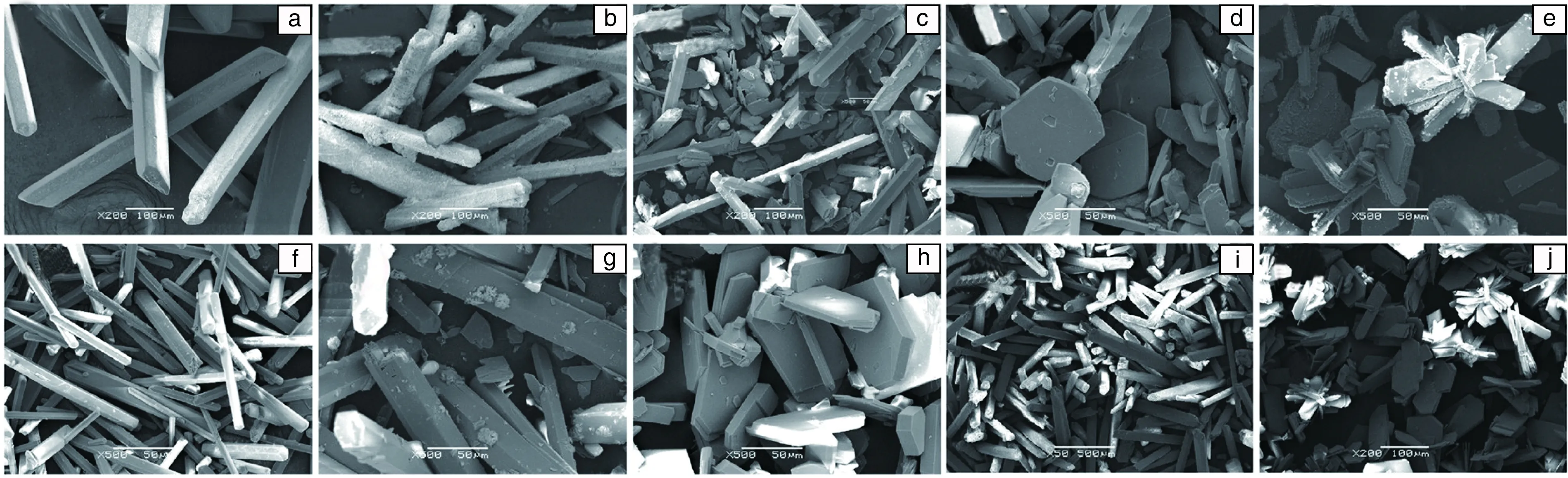

Fig.3 SEM images of products synthesized under different crystallization conditions
4 Conclusion
In this study, 1D chained zinc phosphate compound Ⅰ and 2D layered compound Ⅱ were synthesized successfully by microwave-assisted heating in the same reaction system. The reaction conditions have been investigated in detail and found that increasing the microwave radiation temperature or prolonging the reaction time, compound Ⅱ was obtained easily. Changing the content of H2O would affect the pH of the precursor solution, as well as the dimensionality of the resulting structures. We also found that the 4-membered ring is the basic structural building unit in the two structures of different dimensionalities, and believe the structures of compound Ⅰ and Ⅱ have some unknown relationships, which will be investigated further. Compared to conventional hydrothermal synthesis method, microwave heating method shows greater superiority which promoted the growth of crystals, lowered crystallization temperature and reduced crystallization time, thus saving energy.
[1] Harrison W T A, Gier T E, Moran K L,etal.ChemMater[J], 1991, 3(1):27-29.
[2] Harrison W T A, Phillips M L F.ChemMater[J], 1997, 9(8):1837-1846.
[3] Harrison W T A, Bricsak Z, Hannooman L,etal.JSolidStateChem[J],1998, 136(1):93-102.
[4] Chidambaram D, Neeraj S, Natarajan S,etal.JSolidStateChem[J], 1999, 147(1): 154-169.
[5] Ayi A A, Choudhury A, Natarajan S,etal.JMaterChem[J], 2001, 11(5):1181-1191.
[6] Zhong Y J, Chen Y M, Sun Y Q.CrystEngComm[J], 2005, 7(37):237-242.
[7] Neeraj S, Natarajan S, Rao C N R.ChemMater[J], 1999, 11(5):1390-1395.
[8] Harrison W T A, Bricsak Z, Hannooman L.JSolidStateChem[J], 1997, 134(1):148-157.
[9] Xing Y, Liu Y L, Shi Z,etal.JSolidStateChem[J], 2002, 163(2): 64-368
[10] Han Y D, Li Y, Yu J H,etal.EurJInorgChem[J], 2012, 2012(1):36-39.
[11] Song Y, Yu J H, Li Y,etal.EurJInorgChem[J], 2010, 2004(18):3718-3723.
[12] Wu J B, Yan Y, Liu B K,etal.ChemCommun[J], 2013, 49(44): 4995-4997.
[13] Zhang F, Zou X Q, Feng W,etal.JMaterChem[J], 2012, 22(48):25019-25026.
[14] Chen C J, Hu X L, Hu P,etal.EurJInorgChem[J], 2013, 2013(30): 5320-5328.
[15] Samadi-Maybodi A, Masoomeh P S.EurJInorgChem[J], 2014, 2014(7): 1204-1210.
[16] Song Y, Ding L, An Q D,etal.JSolidStateChem[J], 2013, 202(31): 300-304.
[17] Yang W, Song Y, Mu Y,etal.SolidStateSciences[J], 2014, 29(3): 41-47.
[18] Ding L, Song Y, Yang W,etal.JSolidStateChem[J], 2013, 204(8):356-361.