基于砂濾層內水體積分數瞬態模擬的反沖洗速度優選
李景海,蔡九茂,翟國亮,劉清霞,張文正
?
基于砂濾層內水體積分數瞬態模擬的反沖洗速度優選
李景海1,2,蔡九茂3,翟國亮3※,劉清霞1,張文正3
(1. 安陽工學院土木與建筑工程學院,安陽 455000; 2. 安陽市水資源管理委員會辦公室,安陽 455000; 3. 中國農業科學院農田灌溉研究所,新鄉 453002)
為了對石英砂濾層反沖洗過程水的體積分數波動規律進行分析,并確定合理的反沖洗速度范圍,該文采用數值模擬手段對濾層反沖洗過程水的體積分數進行三維動態模擬,采用Gambit軟件建立了石英砂過濾器的幾何模型,并對幾何模型進行了網格劃分,以Mixture模型做為反沖洗過程水的體積分數的數值模擬模型。以當量粒徑分別為1.06、1.2和1.5 mm的3種石英砂濾層為研究對象進行動態模型。為了驗證模擬結果的準確性,開展了室內模型試驗,并將模擬結果與試驗結果進行對比,結果顯示,水的體積分數的最大模擬誤差為5.64%,說明數值模擬結果是可信的。在使用模擬數據進行流場分析時,為了得出更具普遍性的結論,引入了反沖洗流化倍數的概念,最小反沖洗流化速度的倍數稱為反沖洗流化倍數。在此基礎上,分別分析了反沖洗流化倍數為1.1、1.3、1.5、1.7和1.9時,濾層高度分別為15、25和35 cm共3個橫截面上,反沖洗過程水的體積分數隨時間的變化規律。計算了水的體積分數的均值和標準偏差,分析了水的體積分數的均值和標準偏差隨隨反沖洗流化倍數的變化規律。在3個截面上水的體積分數均值基本相同的情況下,根據標準偏差的大小,判定濾層反沖洗的穩定性。由此得出,使反沖洗水的體積分數波動保持穩定的反沖洗流化倍數的臨界值為1.7。當反沖洗流化倍數范圍為1~1.7時,標準偏差適中,反沖洗效果理想。結果表明,對于均質石英砂濾層,反沖洗效果是否理想,決定因素是反沖洗流化倍數。該文可為砂過濾器的反沖洗運行機理提供參考。
灌溉;模型;計算機仿真;石英砂濾層;反沖洗;多相流
0 引 言
微灌技術是一項重要的節水灌溉技術[1-2],發展微灌技術是緩解水資源短缺的有效途徑[3]。微灌砂過濾器做為微灌系統的重要組成部分,對于微灌裝置的正常運行起著至關重要的作用。中國對微灌石英砂過濾器的研究始于20世紀90年代[4-7],迄今為止,在砂過濾器的過濾和反沖洗方面都開展了大量的試驗研究[8-11]。近幾年,基于計算流體動力學的數值模擬方法迅速發展[12-13],并逐步應用于旋流式過濾器[14]和網式過濾器的研究[15-17]。但對于砂過濾器的數值模擬較少,僅有個別文獻進行了二維模擬[18]。
數值模擬的方法可以大幅減少試驗量,還可以從微觀結構研究砂過濾器的運行機理,筆者采用分形理論[19-20]、多孔介質模型[21]和數值模擬方法[20,22]開展了一系列前期研究。為了減少模擬計算量,同時增加模擬的穩定性,并得出更具普遍性的結論,本文采用Eulerian-Eulerian模型的簡化形式Mixture兩相流模型,對石英砂濾層反沖洗過程中水的體積分數隨時間的變化過程進行了三維動態模擬,引入了反沖洗流化倍數的概念,根據水的體積分數波動特性,確定了保持水的體積分數穩定變化的臨界反沖洗流化倍數,為砂過濾器的反沖洗研究提供了技術支撐,為反沖洗性能參數的確定提供了參考。
1 石英砂濾層反沖洗試驗
試驗在中國農業科學院農田灌溉研究所進行。試驗用材料為石英砂濾層,采用粒徑范圍為1.0~1.18、1.18~1.4和1.4~1.7,當量粒徑分別為1.06、1.2和1.5 mm的3種濾層。試驗用模型裝置如圖1所示,過濾器采用透明有機玻璃管制作,有機玻管內徑200 mm、高1 200 mm,在其上每隔100 mm高度打孔,設為測壓取料孔,有機玻管下端安裝3個濾帽。石英砂濾料放置于過濾器內部,濾層孔隙率0.44,厚400 mm。試驗時,使用水池供水,采用渦輪流量計(LWGY-25)測流量,采用U型壓差計測量濾層內部壓差。
反沖洗試驗時,利用水泵將清水從反沖洗進水口注入過濾器模型,通過砂過濾器底部濾帽將水流分散并均勻作用于石英砂濾料,試驗過程中,記錄下每一個反沖洗速度對應的濾層膨脹高度,由膨脹高度計算出濾層水的體積分數。水的體積分數指在水與石英砂的混合物中,水的體積占混合物總體積的占比,計算如下[23-25]。
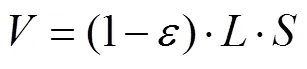
式中為水的體積分數;為石英砂的凈體積,可以由質量與密度的比值得到,m3;為濾層高度,m;為濾層截面面積,m2。
由式(1)得
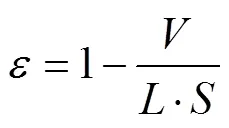
2 石英砂濾層反沖洗數值模擬
2.1 砂濾層反沖洗模擬模型
微灌石英砂濾層的反沖洗過程屬于復雜的固液多相流系統,因此,濾層反沖洗過程模擬需采用多相流模型。Mixture模型是Eulerian-Eulerian模型的簡化形式[26-28],該模型的收斂性和穩定性要優于Eulerian-Eulerian模型,且適用于顆粒相分布范圍比較廣泛的情況。而微灌石英砂濾層反沖洗過程與Mixture模型的適用條件十分吻合,因此采用Mixture模型模擬水與石英砂組成的固液兩相流,其中,水為連續相,石英砂為離散相。Mixture模型連續性方程為
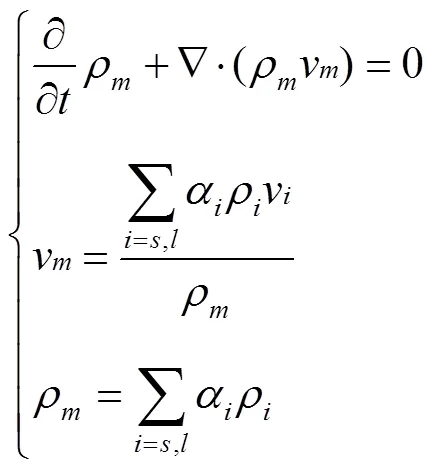
式中分別代表固相與液相;為模擬時間,s;v為平均速度,m/s;ρ為混合相密度,m3/s;為相數;α(下同)為第相體積分數,無量綱量;v為第相速度,m/s;ρ為第相密度,m3/s。
Mixture模型兩相流的動量方程為
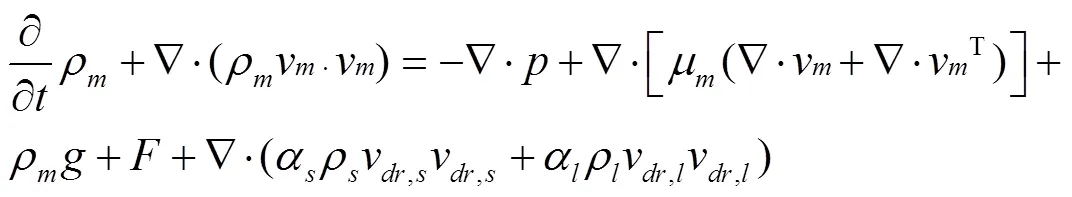
其中
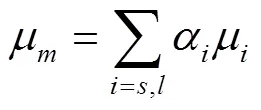

式中▽為拉普拉斯算子;為壓力,Pa;為體積力,Pa;μ為混合黏度,Pa·s;v,i為相的漂移速度,m/s。
固相與液相的相對速度v為
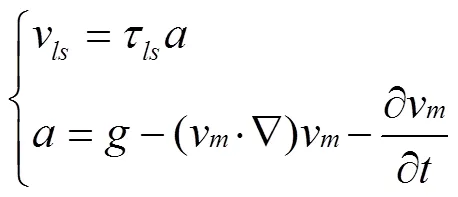
Manninen等[29]給出了馳豫時間τ的表達式
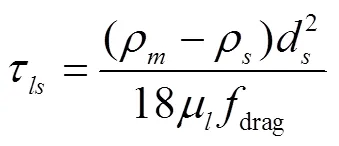
Schiller等[30]提出了曳力函數drag的表達式
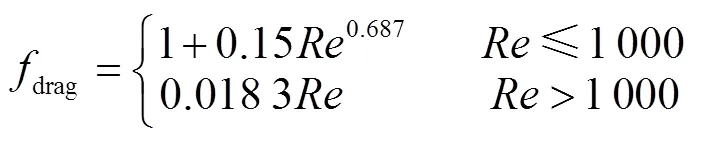
式中為雷諾數。
固相的體積分數方程為
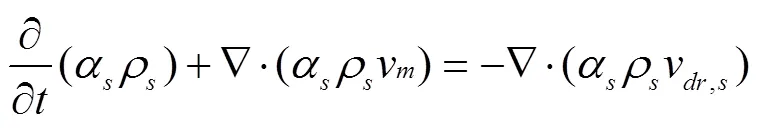
2.2 幾何模型及算法設置
采用Gambit軟件建立幾何模型,過濾器幾何模型與細部結構見圖2。

圖2 過濾器幾何模型
采用時間的二階隱式控制方程和瞬態求解器計算。采用Mixture多相流模擬模型,采用PC-SIMPLE算法求解壓力速度耦合方程,采用基于Green-Gauss的梯度方程進行空間離散化,動量、湍動能、湍流耗散率和體積分數方程均采用一階迎風格式,進口邊界設為速度進口,出口邊界設為壓力出口,并以速度進口對流場進行初始化。采用模擬軟件Fluent14.5進行數值計算,參數設置如表1。

表1 數值模擬參數
3 數值計算結果與分析
3.1 濾層水的體積分數的試驗驗證
根據入口的反沖洗流速,由CFD軟件計算出濾層水的體積分數,繪出水的體積分數隨反沖洗速度的變化關系圖并與試驗值進行對比,如圖3所示。由圖3可知,當濾層當量粒徑為1.06 mm時,濾層水的體積分數的最大誤差為4.62%;當濾層當量粒徑為1.2 mm時,濾層水的體積分數的最大誤差為5.38%;當濾層當量粒徑為1.5 mm時,濾層水的體積分數的最大誤差為5.64%。對比結果說明,濾層水的體積分數的試驗值與模擬值能夠較好地吻合,模擬結果準確可信。
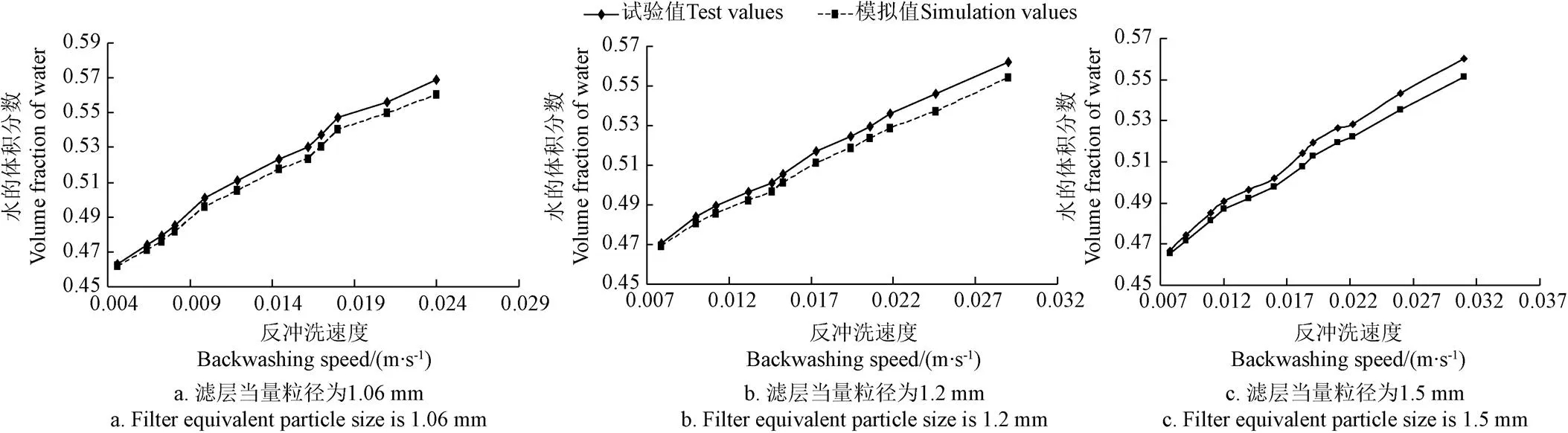
圖3 濾層水的體積分數模擬值與試驗值對比
以v表示濾層最小反沖洗流化速度,最小反沖洗流化速度的倍數稱為反沖洗流化倍數。對于當量粒徑為1.06、1.2和1.5 mm的濾層,選取1.1v、1.3v、1.5v、1.7v、1.9v5個反沖洗速度對濾層水的體積分數的變化規律進行分析。
3.2 濾層橫截面水的體積分數的波動規律分析
在濾層中由低到高依次選取高度為15、25和35 cm的3個橫截面,繪制3種濾層,5個反沖洗速度對應的水的體積分數隨時間的變化關系曲線,如圖4~圖6所示。
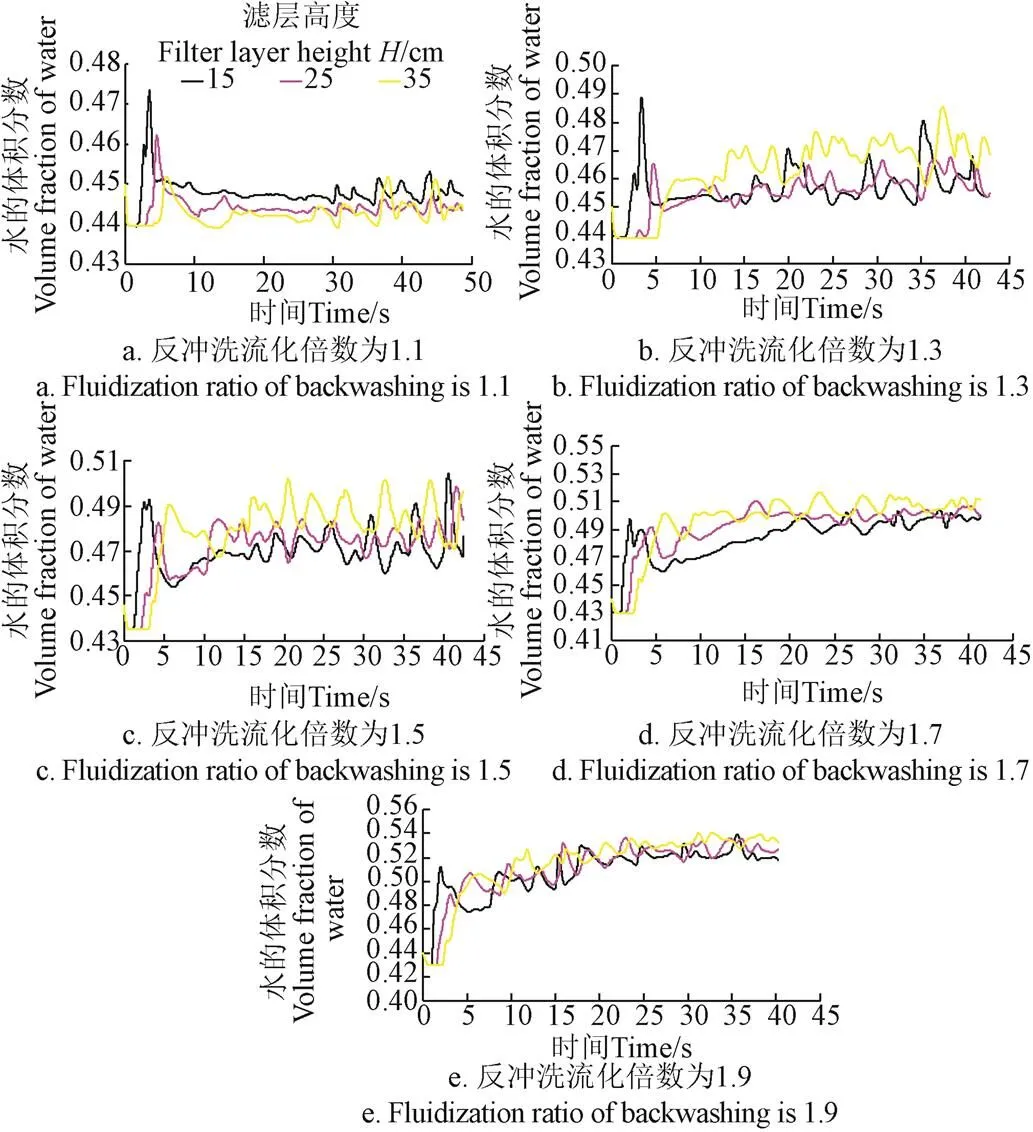
注:最小反沖洗流化速度的倍數稱為反沖洗流化倍數。
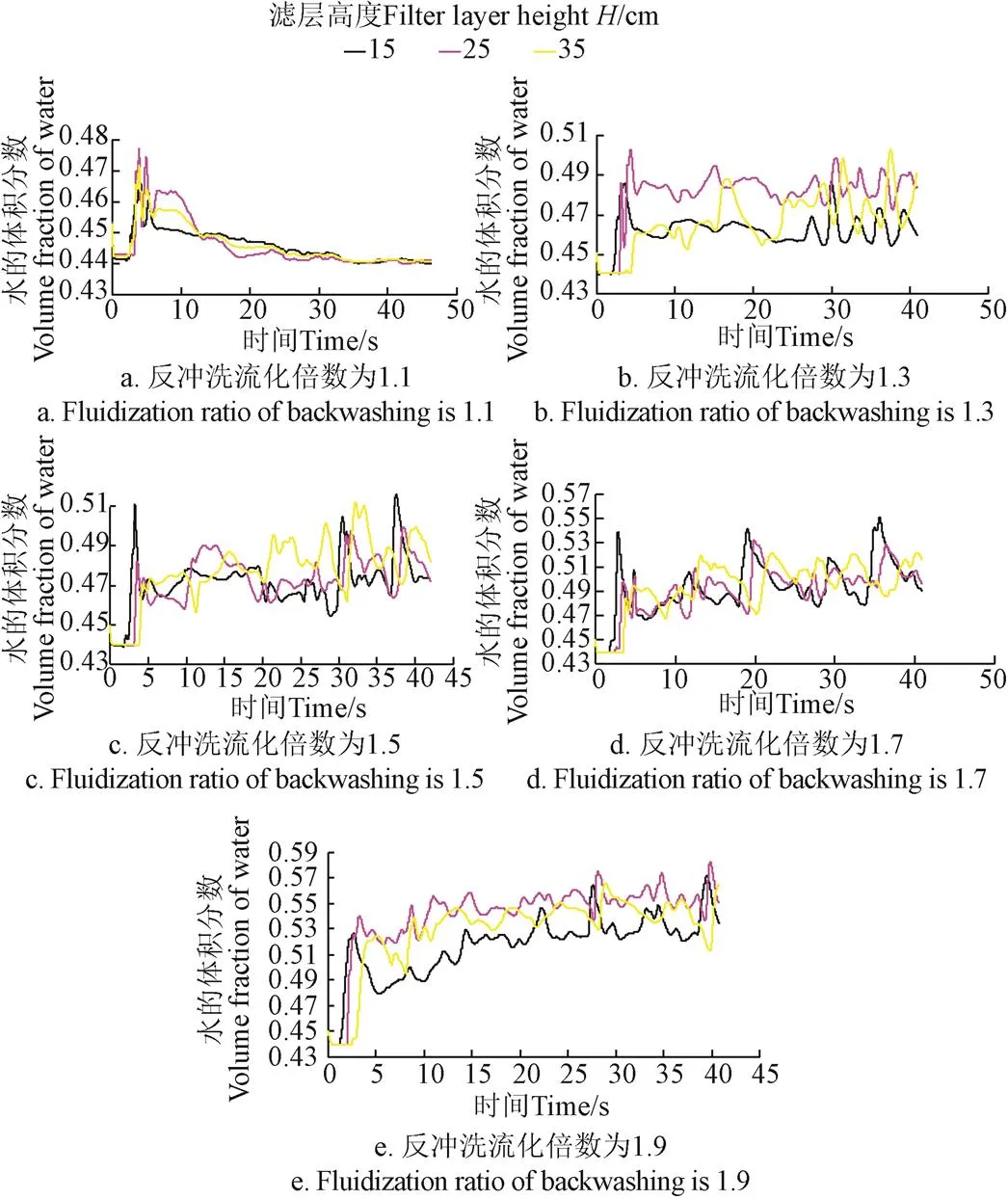
圖5 不同濾層高度水的體積分數隨時間變化關系曲線(當量粒徑為1.2 mm)
由圖4-圖6可知,在反沖洗的初始階段,水流剛進入濾層,水的體積分數在濾層的自然堆積狀態做短暫停留,然后由自然堆積狀態迅速提高到最高點,之后又在極短時間內下降,經過幾個周期的波動逐漸穩定至某一固定值,并圍繞這一固定值上下波動。造成這種現象的原因是,在反沖洗的初期,石英砂濾層處于自然堆積狀態,水的體積分數相應較小,水流通過濾層時,遇到較大阻力,水流的沖擊導致濾層迅速膨脹,從而水的體積分數迅速增大,由于水流空隙的增加,水流速度則隨之減小,水流對石英砂顆粒的攜帶作用隨之減小,石英砂由上升迅速回落,濾層水的體積分數又達到最小值。經過這個短暫的突變過程后,濾層水的體積分數與水流速度逐漸相適應并穩定下來。

圖6 不同濾層高度水的體積分數隨時間變化關系曲線(當量粒徑為1.5 mm)
為了對濾層水的體積分數波動規律進行深入分析,計算每種濾層每個截面水的體積分數的平均值,繪出水的體積分數均值隨反沖洗速度的變化關系圖(圖7)。由圖7可知,隨著反沖洗速度的增加,水的體積分數均值呈增加趨勢。但對于同一反沖洗速度,不同的濾層高度上水的體積分數均值基本相同,這說明,單純從均值看,水的體積分數在整個濾層內分布比較均勻。
計算每種濾層每個截面水的體積分數的標準偏差,繪出水的體積分數的標準偏差隨反沖洗速度的變化關系圖(圖8)。由圖8可知,隨著反沖洗速度的增加,水的體積分數的標準偏差呈增加趨勢,說明在均值穩定的情況下,水的體積分數的波動幅度呈增加趨勢。當濾層反沖洗流化倍數達到1.7時,標準偏差急劇變大,說明濾層開始變得不穩定。
由此可知,石英砂濾層臨界反沖洗流化倍數為1.7。當反沖洗流化倍數大于1.7時,水的體積分數的均值雖然仍然穩定,但由于標準偏差增大,水的體積分數出現極大值和極小值的情形增多,水的體積分數的極小值出現表明石英砂濾層出現局部堆積,對于反沖洗是不利的。當反沖洗流化倍數范圍為1~1.7時,反沖洗效果是理想的。
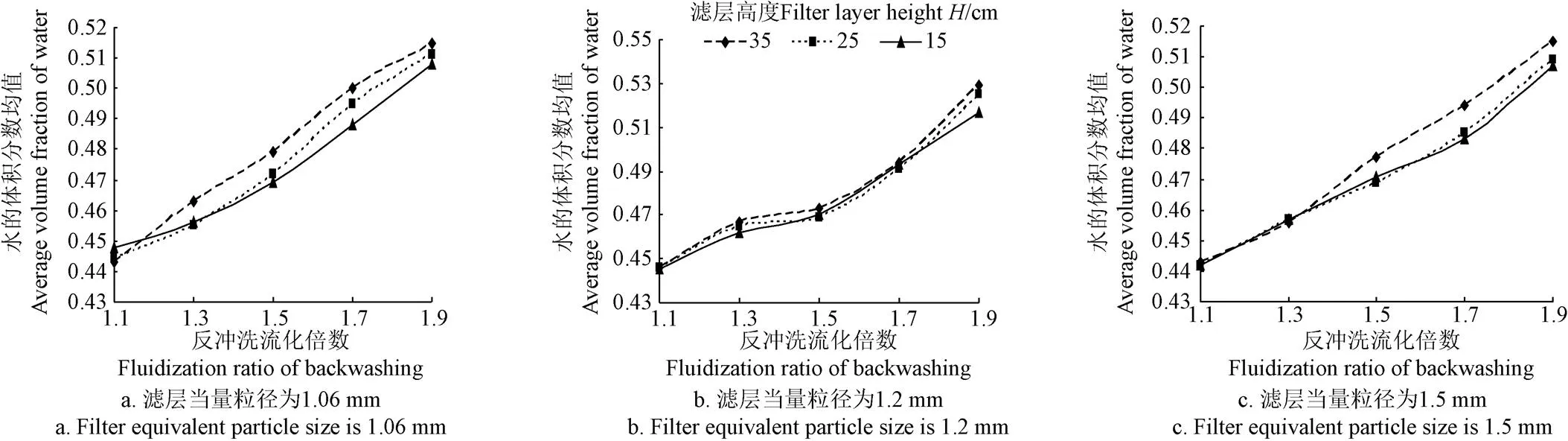
圖7 不同濾層高度水的體積分數均值隨反沖洗流化倍數的變化關系曲線
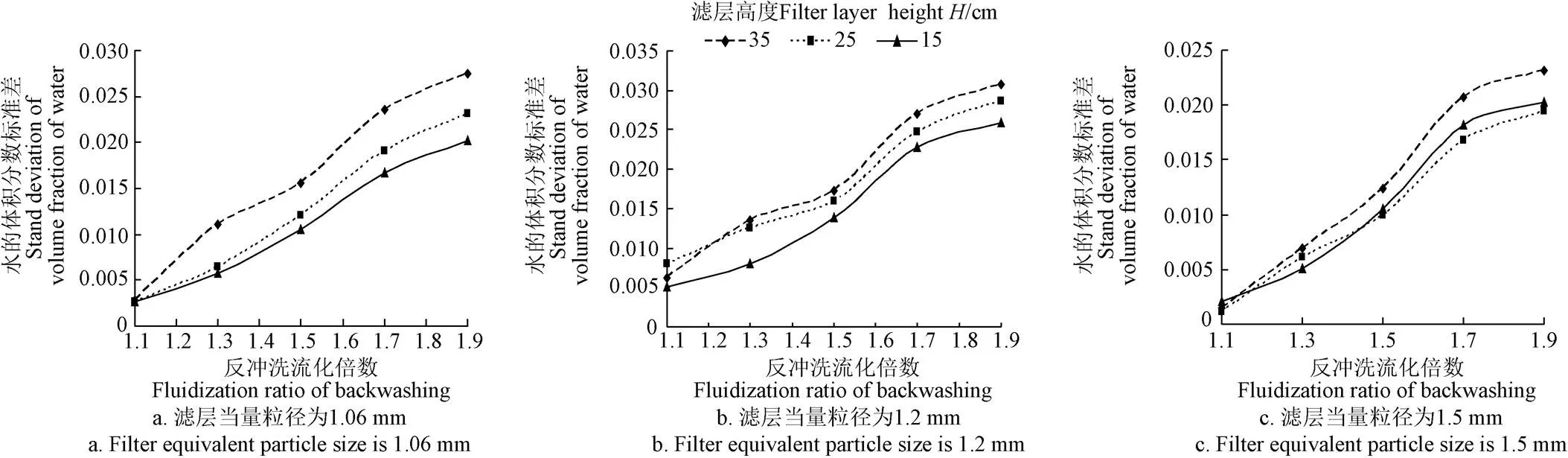
圖8 不同濾層高度水的體積分數標準偏差隨反沖洗流化倍數的變化關系曲線
4 結論與討論
1)采用Mixture模型作為反沖洗模擬模型,建立了以水為液相、以石英砂為固相的Mixture兩相流模型的控制方程、馳豫時間方程和曳力函數。
2)對濾層反沖洗過程水的體積分數的變化進行了瞬態模擬,并且通過室內試驗對模擬結果進行了驗證,水的體積分數的最大模擬誤差為5.64%,表明數值模擬結果準確可信。
3)分析了反沖洗過程水的體積分數的變化規律,通過對水的體積分數均值和標準偏差的分析,確定了使水的體積分數波動保持穩定的臨界反沖洗流化倍數。結果表明,石英砂濾層臨界反沖洗流化倍數為1.7,當反沖洗流化倍數范圍為1~1.7時,反沖洗效果是理想的。反沖洗流化倍數與濾層粒徑無關,反沖洗效果是否理想,決定因素是臨界反沖洗流化倍數。
多相流動態數值模擬對于計算工具的要求非常高,為了將模擬計算的工作量控制在一定范圍,筆者在對石英砂濾層反沖洗過程進行模擬時,設定的時間步長為0.01 s,每步迭代次數為10次,保證了計算過程能夠收斂,并能反映出濾層反沖洗的大致規律,但模擬結果精度較低。下一步的研究中,應采用計算速度更快的計算工具,設定小于0.001 s的時間步長,每步迭代次數不少于20次,從而增加模擬精度,得出水的體積分數更準確的波動規律、動態云圖和臨界反沖洗速度等模擬結果。
[1] 黃修橋,高峰,王景雷,等. 節水灌溉發展研究[M]. 北京:科學出版社,2014:5-7.
[2] 謝新民,張海慶,尹明萬,等. 水資源評價及可持續利用規劃理論與實踐[M]. 鄭州:黃河水利出版社,2003:231-234.
[3] 李久生,王迪,栗巖峰. 現代灌溉水肥管理原理與應用[M].鄭州:黃河水利出版社,2008:161-165.
[4] 董文楚. 微灌用砂過濾器的過濾與反沖洗[J]. 中國農村水利水電,1996(12):15-20.
Dong Wenchu. On filtering and inverse washing of sandy filter in micro-irrigation[J]. China Rural Water and Hydropower, 1996(12): 15-20. (in Chinese w ith English abstract)
[5] 董文楚. 微灌用過濾砂料選擇與參數測定[J]. 噴灌技術,1995(2):42-46.
Dong Wenchu. The material selection and parameter determination of sand filter in micro irrigation[J]. Sprinkler Irrigation Technology, 1995(2): 42-46. (in Chinese w ith English abstract)
[6] 翟國亮,陳剛,趙武,等. 微灌用石英砂濾料的過濾與反沖洗試驗[J]. 農業工程學報,2007,23(12):46-50.
Zhai Guoliang, Chen Gang, Zhao Wu, et al. Experimental study on filtrating and backwashing of quartz sand media in micro-irrigation filter [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2007, 23(12): 46-50. (in Chinese w ith English abstract)
[7] 翟國亮,馮俊杰,鄧忠,等. 微灌用砂石過濾器反沖洗參數試驗[J]. 水資源與水工程學報,2007,18(1):24-28.
Zhai Guoliang, Feng Junjie, Deng Zhong, et al. Parameters experiment of backwashing on sandy filter in micro- irrigation[J]. Journal of Water Resources & Water Engineering, 2007, 18(1): 24-28. (in Chinese w ith English abstract)
[8] 馮俊杰,翟國亮,鄧忠,等. 微灌過濾器用水壓驅動反沖洗閥啟閉機構的力學計算[J]. 農業機械學報,2007,38(12):212-214.
Feng Junjie, Zhai Guoliang, Deng Zhong, et al. Mechanical calculation of opening and closing mechanism of back flushing valve driven by hydraulic pressure[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Machinery, 2007, 38(12): 212-214. (in Chinese w ith English abstract)
[9] 鄧忠,翟國亮,仵峰,等. 微灌過濾器石英砂濾料過濾與反沖洗研究[J]. 水資源與水工程學報,2008,19(2):34-37.
Deng Zhong, Zhai Guoliang, Wu Feng, et al. Study on the filtration and backwashing for the quartz filter in micro- irrigation[J]. Journal of Water Resources & Water Engineering, 2008, 19(2): 34-37. (in Chinese w ith English abstract)
[10] 趙紅書. 微灌用石英砂濾料的過濾與反沖洗性能研究[D].北京:中國農業科學院,2010.
Zhao Hongshu. Performance of Filtration and Flushing of Quartz Sand Media for Micro-irragation[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2010. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 張文正. 微灌砂濾層氣水反沖洗與過濾的試驗研究[D]. 北京:中國農業科學院,2013:1-5.
ZhangWenzheng. Experiment Research of Air Water Backwashing and Filtration of Sand Layer in Micro- irrigation[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2013: 1-5. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] ANSYS Inc. ANSYS FLUENT User’s Guide[M]. Pittsburgh: ANSYS Inc, 2011: 301-309.
[13] ANSYS Inc. ANSYS FLUENT Theory Guide[M]. Pittsburgh: ANSYS Inc, 2011: 486-192.
[14] 宋輝智,塔娜,王全喜,等. 溢流管插入深度及圓柱段高度對旋流式過濾器沉沙效果的影響[D]. 內蒙古:內蒙古農業大學,2012:3-7.
Song Huizhi, Ta Na, Wang Quanxi, et al. Overflow Pipe Insertion Depth and the Cylindrical Section Height of Cyclone Filter Settling Effect[D]. Inner Mongolia: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2012: 3-7. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 王新坤,高世凱,夏立平,等. 微灌用網式過濾器數值模擬與結構優化[J]. 排灌機械工程學報,2013,31(8):719-723.
Wang Xinkun, Gao Shikai, Xia Liping, et al. Numerical simulation and structure optimization of screen filter in micro-irrigation[J]. Journal of Drainage and Irrigation Machinery Engineering, 2013, 31(8): 719-723. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 王棟蕾,宗全利,劉建軍,等. 微灌用自清洗網式過濾器自清洗結構流場分析與優化研究[J]. 節水灌溉,2011,12:5-8.
Wang Donglei, Zong Quanli, Liu Jianjun, et al. Flow analysis and structure optimization of Self cleaning nets filter for micro-irrigation[J]. Water Saving Irrigation, 2011, 12: 5-8. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 宗全利,鄭鐵剛,劉煥芳,等. 滴灌自清洗網式過濾器全流場數值模擬與分析[J]. 農業工程學報,2013,29(16):57-65.
Zong Quanli, Zheng Tiegang, Liu Huanfang, et al. Numerical simulation and analysis on whole flow field for drip self-cleaning screen filter[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2013, 29(16): 57-65. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 劉文娟. 石英砂過濾器過濾及反沖洗特性的實驗研究與數值模擬[D]. 北京:中國農業科學院,2014:35-38.
Liu Wenjuan. Experimental Study and Numerical Simulation of Filtration and Backwashing Characteristics of Quartz Sand Filter[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2014: 35-38. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 李景海,劉清霞,黃修橋,等. 微灌石英砂濾層流態特性與分形阻力模型參數確定[J]. 農業工程學報,2015,31(13):113-119.
Li Jinghai, Liu Qingxia, Huang Xiuqiao, et al. Flow state characteristics and fractal model parameters determination of quartz sand filter layer used in micro-irrigation[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2015, 31(13): 113-119. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 李景海. 微灌石英砂濾層清潔壓降分形阻力模型與反沖洗數值模擬[D]. 北京:中國農業科學院,2016:70-81.
Li Jinghai. Fractal resistance Model of Clean Pressure Drop and Numerical Simulation of Backwashing Process of Quartz Sand Filter Layer in Micro-irrigation[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2016: 70-81. (in Chinese with English abstract).
[21] 李景海,劉清霞,黃修橋,等. 微灌石英砂濾層清潔壓降計算參數確定與分析[J]. 灌溉排水學報,2016,35(11):24-28.
Li Jinghai, Liu Qingxia, Huang Xiuqiao, et al. Determination and analysis of the calculation parameters for the cleaning pressure drop of quartz sand filter layer used in Micro-Irrigation[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 2016, 35(11): 24-28. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 李景海,翟國亮,黃修橋,等. 微灌石英砂過濾器反沖洗數值模擬與流場分析[J]. 農業工程學報,2016,32(9):74-82.
Li Jinghai, Zhai Guoliang, Huang Xiuqiao, et al. Numerical simulation and flow field analysis of backwashing of quartz sand filter in micro irrigation[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2016, 32(9): 74-82. (in Chinese with English abstract).
[23] 董文楚. 微灌用砂過濾器水力性能研究[J]. 噴灌技術,1996(1):7-14.
Dong Wenchu. Study on the hydraulic performance of sand filter in micro irrigation[J]. Sprinkler Irrigation Technology, 1996(1):7-14. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 董文楚. 微灌用砂過濾器堵塞與反沖洗效果研究[J]. 武漢水利電力大學學報,1996,29(6):30-34.
Dong Wenchu. Study on the clogging and backflushing coefficieng of the sand filters for micro-irrigation[J]. J. Wuhan Univ. of Hydr. & Elec.Eng., 1996, 29(6): 30-34. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 馬俊. 球床多孔介質通道高速區流動特性研究[D]. 黑龍江:哈爾濱工程大學,2010:19-20.
Ma Jun. Research on the High Speed Fluid Flow in Pebble-Bed Porous Channel[D]. Heilongjiang: Harbin Engineering University, 2010: 19-20. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 賀靖峰. 基于歐拉-歐拉模型的空氣重介質流化床多相流體動力學的數值模擬[D]. 北京:中國礦業大學,2012:25-26.
He Jingfeng. Numerical Simulation of Multiphase Fluid Dynamic in Air Dense Medium Fluidized Bed Based on Euler-Euler Model[D]. Beijing: China University of Mining and Technology, 2012:25-26. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] 賀靖峰,趙躍民,何亞群,等. 基于Euler-Euler模型的空氣重介質流化床密度分布特性[J]. 煤炭學報,2013,38(7):1277-1282.
He Jingfeng, Zhao Yuemin, He Yaqun, et al. Distribution characteristic of bed density in air dense medium fluidized bed based on the Euler-Euler model[J]. Journal of Coal Science & Engineering,2013, 38(7): 1277-1282. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] He Jingfeng, He Yaqun, Zhao Yuemin, et al. Numerical simulation of the pulsing air separation field based on CFD[J]. International Journal of Mining Science and Technology, 2012, 22(2): 201-207.
[29] Manninen M, Taivassalo V, Kallio S. On the Mixture Model for Multiphase Flow[M]. VTT publications 288:Technical Research Centre of Finland,1996: 52-60.
[30] Schiller L, Naumann Z. A drag coefficient correlation[J]. Z.Ver.Deutsch Ing.. 1935, 77: 318-320.
Optimization of backwashing speed based on transient simulation of water volume fraction in sand filter layer
Li Jinghai1,2, Cai Jiumao3, Zhai Guoliang3※, Liu Qingxia1, Zhang Wenzheng3
(1.,455000,; 2.455000; 3.,,453002)
The volume fraction of water is an important parameter which affects the backwashing effect of quartz sand filter layer. In order to analyze flow field of the volume fraction of water and to determine the reasonable range of backwashing speed in the backwashing process of quartz sand filter layer, numerical simulation method was used in this paper to simulate the dynamic process of the volume fraction of water in the filter layer. For this, the geometric model of quartz sand filter was established and the mesh division of the geometric model was carried out through Gambit software. Because the backwashing process of quartz sand filter layer is a solid-liquid multiphase flow system composed of water and quartz sand, we can conclude that the mixture model is suitable for the numerical simulation of the volume fraction of water by comparing the applicability of the current multiphase flow numerical simulation models such as Eulerian model, mixture model and VOF (volume of fluid ) model. At the same time, because the backwashing process of quartz sand filter layer is both a dynamic and a stable process, the transient simulation solver was adopted. The simulation objects were 3 kinds of quartz sand filter layers whose thickness was all 400 mm, and the equivalent particle diameter was 1.06, 1.2 and 1.5 mm respectively. In order to verify the reliability of simulation results, laboratory experiments of backwashing were conducted with the 3 different quartz sand filter layers in Farmland Irrigation Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, which is located in Xinxiang City, Henan Province, China. The parameters such as the backwashing speed and the total height of the filter layers were measured during the experiments. And the simulation results were compared with the experimental results. Comparison results showed that the maximum simulation error of the volume fraction of water was 5.64%. It was proved that the numerical simulation results were reliable. When the flow field of the volume fraction of water was analyzed with the simulation data, in order to draw a more general conclusion, the concept of fluidization ratio of backwashing was introduced. On this basis, 3 cross-sections, whose heights were 15, 25 and 35 cm respectively, were selected in each filter layer and the fluctuation rule of the volume fraction of water on the sections with time was analyzed when the fluidization ratio of backwashing was 1.1, 1.3, 1.5, 1.7 and 1.9 respectively. Then the mean and the standard deviation of the volume fraction of water were calculated. And their variation trend with the backwashing speed of quartz sand filter layer was analyzed. In the condition that the volume fraction of water in the 3 cross-sections is basically the same, the stability of filter layer can be determined according to the standard deviation. Therefore, it was concluded that the critical value of the fluidization ratio of backwashing was 1.7 for these 3 filter layers. It is said that the standard deviation is modest and the backwashing effect is ideal when the range of the fluidization ratio of backwashing is 1-1.7. The results showed that the fluidization ratio of backwashing decided whether the backwashing effect was ideal. The research results above provide not only a theoretical basis but also a technical support for the operation of the sand filter in the process of backwashing.
irrigation; models; computersimulation; quartz sand filter layer; backwashing; multiphase flow
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.02.011
S275.6
A
1002-6819(2018)-02-0083-07
2017-08-14
2017-11-04
“十三五”國家重點研發計劃(2016YFC0400202)
李景海,博士,高級工程師,主要從事微灌過濾器及水資源配置研究。Email:649923670@qq.com
翟國亮,研究員,博導,主要從事節水灌溉設備研究。 Email:275580557@qq.com
李景海,蔡九茂,翟國亮,劉清霞,張文正. 基于砂濾層內水體積分數瞬態模擬的反沖洗速度優選[J]. 農業工程學報,2018,34(2):83-89. doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.02.011 http://www.tcsae.org
Li Jinghai, Cai Jiumao, Zhai Guoliang, Liu Qingxia, Zhang Wenzheng. Optimization of backwashing speed based on transient simulation of water volume fraction in sand filter layer[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2018, 34(2): 83-89. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.02.011 http://www.tcsae.org

