基因檢測在腦血管病精準醫療中的應用
折瀟 鄧艷春
基因檢測在腦血管病精準醫療中的應用
折瀟 鄧艷春
精準醫療是以個體化醫療為基礎、隨著基因檢測技術快速進步以及生物學信息和大數據科學交叉應用而發展起來的新型醫學概念與醫療模式.基因檢測技術是精準醫療的基礎.腦血管病是遺傳因素和環境因素相互作用的多因素疾病,其中遺傳因素發揮重要作用.本文擬從單基因遺傳病、基因多態性、藥物遺傳學研究和精準治療等方面闡述基因檢測在腦血管病精準醫療中的應用.
腦血管障礙; 基因; 綜述
精準醫療(PM)是以個體化醫療為基礎,隨著基因檢測技術迅速進步以及生物學信息和大數據科學交叉應用而發展起來的新型醫學概念與醫療模式.精準醫療采用現代遺傳技術、分子影像學技術、生物學信息技術,結合患者生活環境和臨床數據,實現精準疾病分類與診斷,制定個體化預防、診斷與治療方案,包括精確預測風險、精確診斷與分類、精確用藥、精確評價療效、精確預測預后等.美國"精準醫療計劃"已經明確首期任務是完成數百萬個體的基因組測序.因此,基因檢測技術作為采集患者信息和精準診斷與治療的依據,是精準醫療的支撐基礎.
《全國第三次死因回顧抽樣調查報告》顯示,腦血管病已經躍升至我國疾病死因的首位[1].急性腦血管病是單病種病殘率最高的疾病,其高發病率、高病殘率和高病死率給社會、家庭和患者帶來沉重負擔和巨大痛苦.腦血管病是遺傳因素和環境因素等相互作用的多因素疾病,遺傳因素起重要作用.本文擬從單基因遺傳病、基因多態性、藥物遺傳學研究、精準治療等方面介紹基因檢測在腦血管病精準醫療中的應用.
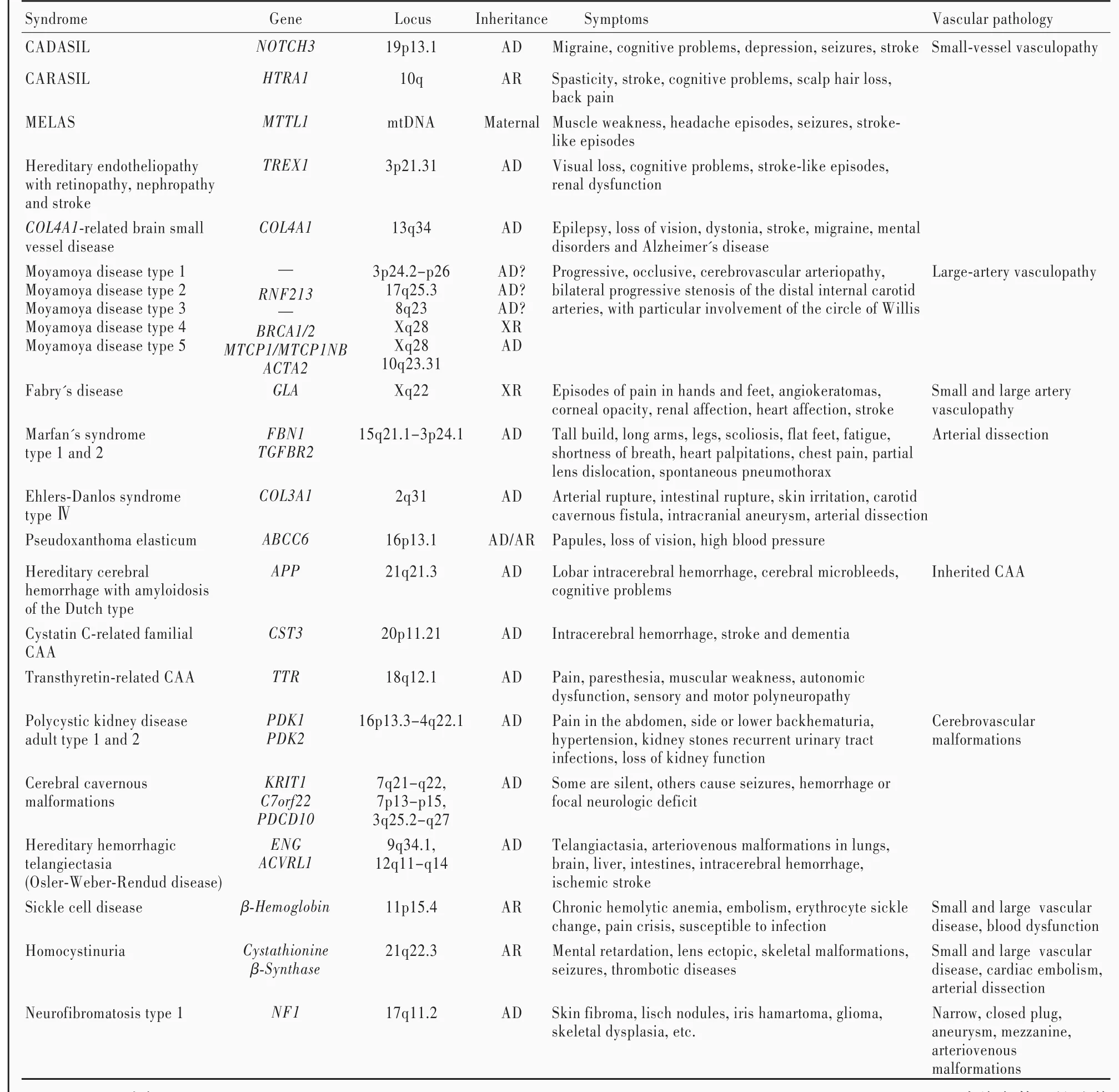
表1 單基因遺傳性腦血管病[3?5]Table 1. Monogenic hereditary cerebrovascular disease[3?5]
一、腦血管病相關單基因遺傳病
相關研究顯示,有30%~40%青年缺血性卒中患者無明確危險因素,其中一部分由單基因遺傳病所致[2].目前已發現多種單基因遺傳病可以導致腦血管病(表1)[3?5].對病因不明或某些特殊類型腦血管病,應行基因檢測以明確是否為單基因遺傳性腦血管病及其分型,從而制定個體化治療方案.
二、基因多態性與腦血管病
從遺傳因素角度看,絕大多數腦血管病為多基因遺傳病,與基因多態性密切相關.如果將腦血管病遺傳因素視為內因,高血壓、高脂血癥、糖尿病、高同型半胱氨酸血癥和血液成分異常等因素即為外因,外因通過內因發揮作用而誘發腦血管病[6].因此,我們可以從遺傳因素角度篩選可能的腦血管病高危人群,通過基因多態性分析,提示何種基因型個體更易發生腦血管病.如果對這些高危人群進行重點預防和早期抗高血壓、調脂、控制血糖等治療,可以有效降低腦血管病發病率.
1.腎素?血管緊張素基因多態性 (1)血管緊張素轉換酶(ACE)基因多態性:編碼血管緊張素轉換酶的基因根據其第16內含子是否存在長度287 bp的片段呈現插入(I)/缺失(D)多態性,即插入純合子型(II型)、缺失純合子型(DD型)和雜合子型(ID型)共3種基因型.D等位基因頻率與缺血性腦血管病發病率呈正相關[7],在亞洲人群中風險顯著增加,增加中國南方人群缺血性卒中易感性,但在白種人中的統計學結果不可靠[8].(2)血管緊張素原(AGT)基因多態性:AGT基因編碼區由5個外顯子和4個內含子組成,當位于第2外顯子第704位核苷酸胸腺嘧啶(T)被胞嘧啶(C)替代(c.704T>C),則導致第235位氨基酸由蛋氨酸突變為蘇氨酸(p.Met235Thr).根據等位基因的不同,AGT基因分為TT型、MT型、MM型.T等位基因可能增加中國北方漢族人群缺血性卒中風險[9].第174位氨基酸由蘇氨酸突變為甲硫氨酸(p.Thr174Met)增加亞洲人群缺血性卒中風險[10].
2.載脂蛋白基因多態性 (1)載脂蛋白E(ApoE)基因多態性:ApoE基因有6種常見基因型,即純合子型(E2/2型、E3/3型、E4/4型)和雜合子型(E2/3型、E2/4型、E3/4型),其中,E2和E4等位基因增加亞洲人群出血性腦血管病風險和中國北方漢族人群缺血性卒中風險,且增加高血壓易感性[11?12];E4等位基因增加缺血性卒中風險,故亞洲人群缺血性卒中發病率高于高加索人群[13?14].(2)對氧磷酶(PON)基因多態性:對氧磷酶是一種催化水解磷酸酯鍵的芳香酯酶,由355個氨基酸組成.在PON1 Gln192Arg多態性中,R等位基因增加缺血性卒中風險[15],尤其增加高加索人群缺血性卒中易感性[16].PON1 c.575A>G多態性和PON1 c.163T>A多態性可能與缺血性卒中風險增加有關[17].
3.β?纖維蛋白原基因多態性 纖維蛋白原(fibrinogen)是由α,β和γ共3對多肽鏈組成的糖蛋白,其中β鏈的合成是整個分子合成的限速步驟.研究顯示,β?fibrinogen基因突變是導致個體間血漿纖維蛋白原水平差異的重要遺傳因素,與腦血管病密切相關.目前已發現β鏈基因簇存在10個多態性位點.2014年的一項Meta分析顯示,β?fibrinogen c.455G>T多態性是缺血性卒中的易感因素[18].2015年的一項關于中國人缺血性卒中的Meta分析顯示,β?fibrinogen c.148C>T 和 c.?854G>A 多態性可能增加缺血性卒中易感性[19?20].
4.同型半胱氨酸相關基因多態性 N5,10?亞甲基四氫葉酸還原酶(MTHFR)主要作用是在葉酸代謝通路中將MTHFR轉化為具有生物學功能的5?甲基四氫葉酸.MTHFR基因包含12個外顯子,編碼656個氨基酸殘基組成的蛋白質.MTHFR c.1298A>C多態性增加缺血性卒中風險,C等位基因是缺血性卒中重要危險因素[21],增加亞洲成年人群腦血管病風險[22].MTHFR c.677C>T多態性增加缺血性卒中風險[23],亦增加兒童缺血性卒中易感性[24].T等位基因是中國人群缺血性卒中的另一危險因素[25].胱硫醚β?合成酶(CBS)是同型半胱氨酸代謝關鍵酶,CBS c.833T>C多態性與腦卒中風險增加有關[26].
5.纖溶酶原激活物抑制物基因多態性 纖溶酶原激活物抑制物?1(PAI?1)是纖溶酶原系統主要調節因子,與纖溶酶原激活物結合后迅速失活而發揮抗纖溶作用.PAI?1是一種單糖蛋白,包含9個外顯子和8個內含子,編碼379個氨基酸.2014年的一項Meta分析顯示,中國人群PAI?1 4G/4G基因型可能是缺血性卒中的危險因素[27].亦有研究顯示,PAI?1基因多態性與腦血管病無關聯性[28].
6.凝血因子和血小板膜糖蛋白基因多態性 凝血因子Ⅴ(FⅤ)Leiden基因突變與靜脈血栓風險增加有關,但并未增加青年人群缺血性卒中風險[29].FⅦ c.807C>T多態性可能增加心房顫動患者腦卒中風險[30].既往研究顯示,F■基因多態性與腦血管病有關[31],但最新的Meta分析顯示二者無明顯關聯性,而增加白種人腦出血風險[32].血小板膜糖蛋白Ⅲa基因第33位氨基酸突變為脯氨酸是心源性和大血管源性缺血性卒中的危險因素[33].血小板膜糖蛋白Ⅰa c.807C>T多態性[34]和Ⅰb p.Met145Thr多態性和Koxak c.?5T>C多態性與缺血性腦血管病相關[32,35].
7.內皮型一氧化氮合酶基因多態性 內皮型一氧化氮合酶(eNOS)催化合成的一氧化氮可以通過對血小板聚集、白細胞黏附、平滑肌細胞增殖和遷移的抑制效應發揮保護作用.eNOS基因包含26個外顯子和25個內含子,編碼1203個氨基酸,基因型主要有:(1)第7外顯子c.894G>T突變,導致其編碼的第298位氨基酸由谷氨酸突變為天冬氨酸.(2)第4內含子的27個堿基重復序列不一致,重復4次者為A等位基因,重復5次者為B等位基因.(3)啟動子區c.?786T>C突變.2017年的一項Meta分析顯示,缺血性卒中與eNOS c.894G>T突變和4b/a基因多態性相關,而與c.?786T>C突變無顯著關聯性[36].亦有研究顯示,c.?786T>C突變與亞洲人群缺血性卒中有關[37?38],而4b/a基因多態性與高加索人群缺血性卒中無關聯性[39].
8.炎癥反應相關基因多態性 (1)白細胞介素(IL):2016年的一項Meta分析顯示,IL?6 c.174G>C和c.572G>C突變并未增加缺血性和出血性卒中易感性[40?41].IL?10 c.?1082A>G 突變增加亞洲人群缺血性卒中易感性[42],亦增加大血管病變和小血管病變易感性[22].腫瘤壞死因子?α(TNF?α)c.?238G>A突變與亞洲人群缺血性腦血管病風險增加有關,而c.?308G>A突變與其無關聯性[43?44].亦有相關研究顯示,TNF?α c.?308G>A突變與青年缺血性卒中相關[45].E?選擇素(E?slection)是黏附分子選擇素家族成員之一,在炎癥反應、動脈粥樣硬化致血栓形成過程中發揮重要作用.E?slection基因包含14個外顯子和13個內含子,AC基因型較AA基因型的缺血性卒中易感性更高[46],c.561A>C突變增加漢族人群缺血性卒中易感性[47].(2)磷酸二酯酶4D(PDE4D):主要作用是降解cAMP,而cAMP水平降低可以引起血管平滑肌細胞增殖和遷移,局部炎癥反應加劇,促進動脈粥樣硬化形成和斑塊不穩定性增加,PDE4D c.83T>C多態性與中國人群缺血性卒中易感性相關[48].(3)轉化生長因子β1(TGF?β1):系一種多效細胞因子,在缺血性腦血管病中具有抗炎癥反應作用.TGF?β1?c.509C>T多態性與轉化生長因子β1表達變化相關,T等位基因增加轉化生長因子β1總蛋白和活性蛋白水平;編碼區第10位氨基酸密碼子發生c.869T>C突變,使亮氨酸突變為脯氨酸,從而升高轉化生長因子β1表達水平.然而Meta分析顯示,目前尚無法得出c.869T>C多態性和c.509C>T多態性與缺血性卒中易感性相關的結論[49?50].(4)脂聯素(APN):系脂肪細胞分泌的細胞因子,干預機體糖和脂肪代謝途徑,具有明確的抗炎癥反應和抗動脈粥樣硬化作用.包含3個外顯子和2個內含子,c.45T>G多態性與北方漢族人群缺血性卒中易感性相關,GG基因型是北方漢族女性人群缺血性卒中的危險因素[51].
9.其他 研究顯示,淋巴毒素α(LTα)c.?252G>A突變增加高加索人群缺血性卒中易感性[52],雌激素受體α(ERα)c.454?397T>C突變[53]、β2腎上腺素受體(β2AR)Gln27Glu多態性與缺血性卒中風險增加有關[54].
三、腦血管病藥物遺傳學研究
腦血管病預防藥物相關基因突變可能影響藥代動力學和藥效學,并增加不良事件風險.藥物遺傳學是腦血管病的重要研究領域.
1.重組組織型纖溶酶原激活物靜脈溶栓治療
一項納入497例缺血性卒中患者的重組組織型纖溶酶原激活物(rt?PA)靜脈溶栓研究結果顯示,IL?1β和血管性血友病因子(vWF)基因突變均與早期血管再通有關,vWF基因突變也與凝血因子Ⅷ(FⅧ)活性相關[55].α2巨球蛋白(α2M)c.669A>G多態性與rt?PA治療后出血性轉化有關[56].上述研究均表明遺傳學信息可能在未來用于預測缺血性卒中rt?PA治療反應,從而有助于rt?PA靜脈溶栓或替代療法如血管內治療的決策.
2.華法林或達比加群抗凝治療 編碼細胞色素P?450酶的CYP2C9基因突變影響華法林代謝,編碼維生素K環氧化物還原酶的VKORC1基因突變影響華法林敏感性[57].對2944例長期華法林抗凝治療的患者進行全基因組相關性研究(GWAS)顯示,羧酸酯酶1(CES1)次要等位基因與較低活性的達比加群代謝物水平相關,亦與達比加群治療后低出血風險相關[58].
3.抗血小板藥治療 抗血小板藥的臨床應用存在顯著個體差異.有5%~40%的缺血性卒中患者對阿司匹林治療無反應,4%~30%患者氯吡格雷療效欠佳[59].存在阿司匹林抵抗的患者常合并氯吡格雷抵抗.因此,了解基因型并選擇適宜藥物,可以決定治療效果.參與阿司匹林作用機制的各種基因發生遺傳變異性,可以導致活性藥物濃度差異,影響藥物療效.研究顯示,環氧合酶?1(COX?1)?1676A>G 突變[60]和 COX?2 ?765G>C 突變[61]均與阿司匹林抵抗相關.
4.他汀類調脂藥治療 他汀類調脂藥治療過程中,低密度脂蛋白膽固醇(LDL?D)每降低1 mmol/L,腦卒中相對風險降低約20%[62].肌肉病是他汀類調脂藥罕見且嚴重的并發癥,劑量增加或與某些藥物同時應用時風險增加.SLCO1B1基因突變使他汀類調脂藥導致肌肉病的相對風險增加[63].
5.戒煙 某些基因型與吸煙起止時間、數量和治療反應相關.某些基因涉及多巴胺再攝取和代謝,與吸煙成癮性相關或與尼古丁代謝相關[64].
四、精準醫療中應注意的問題
基因檢測有助于檢出更多的單基因遺傳性腦血管病,有助于發現腦血管病基因多態性易感位點,有助于在腦血管病危險因素出現前更早地預測腦血管病發生和發展機制,藥物代謝相關基因單核苷酸多態性(SNP)研究有助于檢測腦血管病藥物治療效果,從而提高腦血管病個體化預防、診斷與治療水平.然而,基因檢測僅是實現精準醫療的一種技術支持,要全面實現精準醫療還應注意以下問題:(1)基因檢測的臨床效度隨基因型的不同而異,這些不同基因型的改變可能對致疾病風險有不同的含義,其中一些變異可能有證據支持是明確的致病性突變,一些可能是無義突變,在人群數據庫中有超過5%的存在,另一些可能是臨床意義不明的突變.基因型與臨床表型關系的復雜性影響基因檢測的臨床效度.對于何種疾病患者應行何種基因檢測,最重要的考慮是對檢測結果呈陽性的患者能否進行有效干預.(2)隨著高通量基因檢測設備的廣泛應用,近年來檢測成本降低,基因數據量呈倍數增加.精準醫療的發展需建立高效、便捷的數據處理和共享系統,還應建立標準化、可重復和可追蹤的數據流.(3)目前的高通量基因檢測技術可以數字或字母序列形式快捷、準確地提供基因信息,但如何解讀基因檢測結果仍是絕大多數臨床醫師的難題.基因檢測從人工測序轉為數據分析,使很多醫師難以處理大規模數據,不能準確探尋基因與疾病、藥物選擇、患者之間關系.
因此,基因檢測只有與生物學信息和臨床表型相結合,才能被理解和正確使用.目前由于數據科學到生物學信息和醫學的脫節,使得如何解讀基因檢測結果成為下一步工作的關鍵[65].
[1]Chen Z.The third review of national death causes report.Beijing:Peking Union Medical College Press,2008:10?17[.陳竺.全國第三次死因回顧抽樣調查報告.北京:中國協和醫科大學出版社,2008:10?17.]
[2]Jacobs BS,Boden?Albala B,Lin IF,Sacco RL.Stroke in the young in the Northern Manhattan stroke study.Stroke,2002,33:2789?2793.
[3]Lindgren A.Stroke genetics:a review and update.J Stroke,2014,16:114?123.
[4]Francis J,Raghunathan S,Khanna P.The role of genetics in stroke.Postgrad Med J,2007,83:590?595.
[5]Della?Morte D,Pacifici F,Rundek T.Genetic susceptibility to cerebrovascular disease.Curr Opin Lipidol,2016,27:187?195.
[6]Dang XY, Zhang JJ. Research progress of hereditary cerebrovascular disease.Zhonghua Nao Ke Ji Bing Yu Kang Fu Za Zhi(Dian Zi Ban),2015,5:35?40[.黨相玉,張敬軍.遺傳性腦血管病研究進展.中華腦科疾病與康復雜志(電子版),2015,5:35?40.]
[7]Stankovic S,Stankovic A,Asanin M,Jovanovic?Markovic Z,AlavanticD,Majkic?Singh N.Angiotensin Ⅰ ?converting enzyme gene polymorphism and activity in patients with ischemic stroke.EJIFCC,2011,21:108?117.
[8]Zhao J,Qin X,Li S,Zeng Z.Association between the ACE I/D polymorphism and risk of ischemic stroke:an updated meta?analysis of 47 026 subjects from 105 case?control studies.J Neurol Sci,2014,345:37?47.
[9]Wang B,Guo Q,Peng Y,Lu J,Singh B,Hua B.Association of AGT M235T and ACE I/D polymorphisms with the risk of ischemic stroke:meta?analysis in Han Chinese population.J Neurol Sci,2012,320:79?84.
[10]Ou Z,Chen H,Liu G,Li C,Lin S,Lin J.Association between angiotensinogen T174M polymorphism and ischemic stroke:a meta?analysis.J Res Med Sci,2015,20:619?623.
[11]Tzourio C,Arima H,Harrap S,Anderson C,Godin O,Woodward M,Neal B,BousserMG,Chalmers J,Cambien F,MacMahon S.APOE genotype,ethnicity,and the risk of cerebral hemorrhage.Neurology,2008,70:1322?1328.
[12]Wang B,Zhao H,Zhou L,Dai X,Wang D,Cao J,Niu W.Association of genetic variation in apolipoprotein E and low density lipoprotein receptor with ischemic stroke in Northern Han Chinese.J Neurol Sci,2009,276:118?122.
[13]Kumar A,Kumar P,Prasad M,Misra S,Kishor Pandit A,ChakravartyK.Association between apolipoprotein ε 4 gene polymorphism and risk of ischemic stroke:a meta?analysis.Ann Neurosci,2016,23:113?121.
[14]Gu L,Su L,Chen Q,Liang B,Qin Y,Xie J,Wu G,Yan Y,Long J,Wu H,Tan J,Dou W,Chen W,Wu P,Wang J.Association between the apolipoprotein E gene polymorphism and ischemic stroke in Chinese populations:new data and meta?analysis.Exp Ther Med,2013,5:853?859.
[15]Liu H,Xia P,Liu M,Ji XM,Sun HB,Tao L,Mu QW.PON gene polymorphisms and ischaemic stroke:a systematic review and meta analysis.Int J Stroke,2013,8:111?123.
[16]Banerjee I.Relationship between Paraoxonase 1(PON1)gene polymorphisms and susceptibility of stroke:a meta?analysis.Eur J Epidemiol,2010,25:449?458.
[17]Dahabreh IJ,Kitsios GD,Kent DM,Trikalinos TA.Paraoxonase 1 polymorphisms and ischemic stroke risk:a systematic review and meta?analysis.Genet Med,2010,12:606?615.
[18]Gu L,Wu G,Su L,Yan Y,Long J,Tan J,Liang B,Guo X,Huang G.Genetic polymorphism of beta?fibrinogen gene?455G/A can contribute to the risk of ischemic stroke.Neurol Sci,2014,35:151?161.
[19]Wu G,Cai H,Cai H,Chen Z,Tan L,Qi H,Cai Y.Effect of the?148C/T,448G/A,and ?854G/A polymorphismsoftheβ ?fibrinogengene on the risk ofischemic stroke in Chinese population.J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis,2015,24:1577?1590.
[20]Zhang XF,Luo TY.Association between the FGB gene polymorphism and ischemic stroke:a meta?analysis.Genet Mol Res,2015,14:1741?1747.
[21]Kang S,Wu Y,Liu L,Zhao X,Zhang D.Association of the A1298C polymorphism in MTHFR gene with ischemic stroke.J Clin Neurosci,2014,21:198?202.
[22]Zhang MJ,Hu ZC,Yin YW,Li BH,Liu Y,Liao SQ,Gao CY,Li JC,Zhang LL.A meta?analysis of the relationship between MTHFR gene A1298C polymorphism and the risk of adult stroke.Cerebrovasc Dis,2014,38:425?432.
[23]LiP,Qin C.Methylenetetrahydrofolatereductase(MTHFR)gene polymorphisms and susceptibility to ischemic stroke:a meta?analysis.Gene,2014,535:359?364.
[24]Sarecka?Hujar B,Kopyta I,Pienczk?Reclawowicz K,Reclawowicz D,Emich?Widera E,Pilarska E.The TT genotype of methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase 677C>T polymorphism increases the susceptibility to pediatric ischemic stroke:meta?analysis of the 822 cases and 1552 controls.Mol Biol Rep,2012,39:7957?7963.
[25]Zhu XY,Hou RY,Pan XD,Wang YC,Zhang ZS,Guo RY.Association between the methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase(MTHFR)gene C677T polymorphism and ischemic stroke in the Chinese population:a meta?analysis.Int J Neurosci,2015,125:885?894.
[26]Ding R,Lin S,Chen D.The association of cystathionine β synthase(CBS)T833C polymorphism and the risk of stroke:a meta?analysis.J Neurol Sci,2012,312:26?30.
[27]Cao Y,Chen W,Qian Y,Zeng Y,Liu W.Plasminogen activator inhibitor?1 4G/5G polymorphism and ischemic stroke risk:a meta?analysis in Chinese population.Int J Neurosci,2014,124:874?881.
[28]Adamski MG,Turaj W,Slowik A,Wloch?Kopec D,Wolkow P,Szczudlik A.A?G?4G haplotype of PAI?1 gene polymorphisms ?844 G/A,HindⅢ G/C,and ?675 4G/5G is associated with increased risk ofischemic stroke caused by smallvessel disease.Acta Neurol Scand,2009,120:94?100.
[29]Hamedani AG,Cole JW,Cheng Y,Sparks MJ,O'Connell JR,Stine OC,Wozniak MA,Stern BJ,Mitchell BD,Kittner SJ.FactorⅤleiden and ischemic stroke risk:the Genetics of Early Onset Stroke(GEOS)study.J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis,2013,22:419?423.
[30]Roldán V,Marín F,González?Conejero R,García?Honrubia A,Martí S,Alfaro A,Valdés M,Corral J,Lip GY,Vicente V.FactorⅦ ?323 decanucleotide D/Ipolymorphism in atrial fibrillation:implications for the prothrombotic state and stroke risk.Ann Med,2008,40:553?559.
[31]Ma J,Li H,You C,Liu Y,Ma L,Huang S.Blood coagulation factor■?A subunit Val34Leu polymorphisms and intracerebral hemorrhage risk:a meta?analysis of case?control studies.Br J Neurosurg,2015,29:672?677.
[32]Li B,Zhang L,Yin Y,Pi Y,Yang Q,Gao C,Fang C,Wang J,Li J.Lack of evidence for association between factor■?A Val34Leu polymorphism and ischemic stroke:a meta?analysis of 8800 subjects.Thromb Res,2012,130:654?660.
[33]Floyd CN,Ellis BH,Ferro A.The PlA1/A2 polymorphism of glycoproteinⅢa as a risk factor for stroke:a systematic review and meta?analysis.PLoS One,2014,9:E100239.
[34]Wu G,Xi Y,Yao L,Su L,Yan Y,Li M,Gu L.Genetic polymorphism ofITGA2 C807T can increase the risk of ischemic stroke.Int J Neurosci,2014,124:841?851.
[35]Maguire JM,Thakkinstian A,Sturm J,Levi C,Lincz L,Parsons M,Whyte S,Attia J.Polymorphisms in platelet glycoprotein 1balpha and factorⅦ and risk of ischemic stroke:a meta?analysis.Stroke,2008,39:1710?1716.
[36]Kumar A,Misra S,Kumar P,Prasad K,Pandit AK,Chakravarty K,Kathuria P,Gulati A.Association between endothelial nitric oxide synthase gene polymorphisms and risk of ischemic stroke:a meta?analysis.Neurol India,2017,65:22?34.
[37]NiuPP,YangG,ZhengBK,GuoZN,JinH,YangY.Relationship between endothelial nitric oxide synthase gene polymorphisms and ischemic stroke:a meta?analysis.Acta Neurol Scand,2013,128:202?212.
[38]Yao YS,Chang WW,Jin YL,He LP.An updated meta?analysis of endothelial nitric oxide synthase gene: three well?characterized polymorphisms with ischemic stroke.Gene,2013,528:84?92.
[39]Guo X.Endothelial nitric oxide(eNOS)gene G894T and VNTR polymorphisms are closely associated with the risk of ischemic stroke development for Asians:meta?analysis of epidemiological studies.Mol Biol Rep,2014,41:2571?2583.
[40]Kumar P,Yadav AK,Kumar A,Sagar R,Pandit AK,Prasad K.Association between Interleukin?6 (G174C and G572C)promoter gene polymorphisms and risk of ischaemic stroke:a meta?analysis.Ann Neurosci,2015,22:61?69.
[41]Kumar P,Misra S,Kumar Yadav A,Kumar A,Sriwastva M,Prasad K.Relationship between interleukin?6(?174G/C and ?572C/G)promoter gene polymorphisms and risk of intracerebral hemorrhage:a meta?analysis.Pulse(Basel),2016,4:61?68.
[42]Jin J,Li W,Peng L,Chen J,Li R,Wu P,Tan S.Relationship between interleukin?10 ?1082A/G polymorphism and risk of ischemic stroke:a meta?analysis.PLoS One,2014,9:E94631.
[43]Niu YM,Weng H,Zhang C,Yuan RX,Yan JZ,Meng XY,Luo J.Systematic review by multivariate meta?analyses on the possible role of tumor necrosis factor?α gene polymorphisms in association with ischemic stroke.Neuromolecular Med,2015,17:373?384.
[44]Kumar P,Misra S,Kumar A,Pandit AK,Chakravarty K,Prasad K.Association between tumor necrosis factor?α(?238g/a and ?308g/a)gene polymorphisms and risk of ischemic stroke:a meta?analysis.Pulse(Basel),2016,3:217?228.
[45]Gu L,Wu G,Long J,Su L,Yan Y,Chen Q,Xie J,Hu Y.The role of TNF?α 308G>A polymorphism in the risk for ischemic stroke.Am J Med Sci,2013,345:227?233.
[46]Roy S,Das S,Danaboina R,Sharma V,Kaul S,Jyothy A,MunshiA.Association ofE?selectin gene polymorphism(S128R) with ischemic stroke and stroke subtypes.Inflammation,2014,37:599?603.
[47]Zhao DX,Feng J,Cong SY,Zhang W.Association of E?selectin gene polymorphisms with ischemic stroke in a Chinese Han population.J Neurosci Res,2012,90:1782?1787.
[48]Liu X,Zhu R,Li L,Deng S,Li Q,He Z.Genetic polymorphism in PDE4D gene and risk ofischemic stroke in Chinese population:a meta?analysis.PLoS One,2013,8:E66374.
[49]Peng L,Li P,Chen J,Yan K,Huo F,Han L,Li C,Tan S,Jiang X.Association between transforming growth factor?beta 1 T869C polymorphism and ischemic stroke:a meta?analysis.PLoS One,2013,8:E67738.
[50]Kumar P,Kumar A,Srivastava MK,Misra S,Pandit AK,Prasad K.Association of transforming growth factor beta?1?509c/t gene polymorphism with ischemic stroke:a meta analysis.Basic Clin Neurosci,2016,7:91?96.
[51]Chen XL,Cheng JQ,Zhang RL,Liu JP,Li XX,Tong YQ,Geng YJ. Study on the relationship between polymorphism of adiponectin gene and risk ofischemic stroke among Han population in the northern parts of China.Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi,2010,31:129?132[.陳小良,程錦泉,張仁利,劉建平,李曉霞,童葉青,耿藝介.脂聯素基因多態性與北方漢族人群缺血性腦卒中易感性關系研究.中華流行病學雜志,2010,31:129?132.]
[52]Kumar P,Misra S,Kumar A,Kishor Pandit A,Chakravarty K,Prasad K.Association between lymphotoxin alpha(?252G/A and?804C/A)gene polymorphisms and risk of ischemic stroke:a meta?analysis.Acta Neurol Taiwan,2016,25:10?17.
[53]Li BH,Zhang LL,Yin YW,Pi Y,Guo L,Yang QW,Gao CY,FangCQ,WangJZ,XiangJ,LiJC.Association between estrogen receptor alpha c.454?397T>C and c.454?351A>G and ischemic stroke risk:a systematic review and meta?analysis.Mol Biol Rep,2012,39:9331?9338.
[54]Kumar A,Prasad M,Kumar P,Yadav AK,Pandit AK,Kathuria P.Association between beta adrenergic receptor polymorphism and ischemic stroke:a meta?analysis.J Stroke,2015,17:138?143.
[55]Fernández?Cadenas I,Del Río?Espínola A,Giralt D,Domingues?Montanari S,Quiroga A,Mendióroz M,Ruíz A,Ribó M,Serena J,Obach V,Freijo MM,Martí?Fábregas J,Delgado P,Montaner J.IL1B and VWF variants are associated with fibrinolytic early recanalization in patients with ischemic stroke.Stroke,2012,43:2659?2665.
[56]del Río?Espínola A,Fernández?Cadenas I,Giralt D,Quiroga A,Gutiérrez ?Agulló M,Quintana M,Fernández ?álvarezP,Domingues ?Montanari S,Mendióroz M,Delgado P,Turck N,Ruíz A,Ribó M,Castellanos M,Obach V,Martínez S,Freijo MM,Jiménez?Conde J,Cuadrado?Godia E,Roquer J,Chacón P,Martí?Fábregas J, Sánchez JC; GRECOS Investigators;MontanerJ.A predictiveclinical?genetic modelof tissue plasminogen activator response in acute ischemic stroke.Ann Neurol,2012,72:716?729.
[57]Meschia JF.Pharmacogenetics and stroke.Stroke,2009,40:3641?3645.
[58]ParéG,Eriksson N,LehrT,Connolly S,Eikelboom J,Ezekowitz MD,Axelsson T,Haertter S,Oldgren J,Reilly P,Siegbahn A,Syvanen AC,Wadelius C,Wadelius M,Zimdahl?GellingH,YusufS,Wallentin L.Geneticdeterminantsof dabigatran plasma levels and their relation to bleeding.Circulation,2013,127:1404?1412.
[59]Wang BX,Li YS.Study on genetic mechanism associated with aspirin and clopidogrel resistance.Zhonghua Lao Nian Xin Nao Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi,2014,16:1002?1003[.王寶祥,李焰生.阿司匹林和氯吡格雷抵抗相關的遺傳學機制研究.中華老年心腦血管病雜志,2014,16:1002?1003.]
[60]Li XL,Cao J,Fan L,Ye L,Cui CP,Wang YZ,Liu L,Li B,Wu RJ,Zhou FC,Zhang JH.Genetic polymorphisms of HO?1 and COX?1 are associated with aspirin resistance defined by light transmittance aggregation in Chinese Han patients.Clin Appl Thromb Hemost,2013,19:513?521.
[61]Xu ZH,Jiao JR,Yang R,Luo BY,Wang XF,Wu F.Aspirin resistance:clinical significance and genetic polymorphism.J Int Med Res,2012,40:282?292.
[62]Amarenco P,Labreuche J.Lipid management in the prevention of stroke:review and updated meta?analysis of statins for stroke prevention.Lancet Neurol,2009,8:453?463.
[63]SEARCH Collaborative Group;Link E,Parish S,Armitage J,Bowman L,Heath S,Matsuda F,Gut I,Lathrop M,Collins R.SLCO1B1 variants and statin?induced myopathy:a genomewide study.N Engl J Med,2008,359:789?799.
[64]Carlsten C,Burke W.Potential for genetics to promote public health:genetics research on smoking suggests caution about expectations.JAMA,2006,296:2480?2482.
[65]Su X.Gene detection opens up a new area for precision medicine,which causes subversive revolution in medical field.Zhongguo Yi Yao Ke Xue,2015,4:1?6[.蘇暄.基因檢測掀開精準醫療帷幕,帶來醫學領域顛覆性革命.中國醫藥科學,2015,4:1?6.]
Application of gene detection in precision medicine of cerebrovascular disease
ZHE Xiao1,DENG Yan?chun21Department of Neurology,the First Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Medical University,Xi'an 710077,Shaanxi,China
2Department of Neurology,Xijing Hospital,the Fourth Military Medical University of Chinese PLA,Xi'an 710032,Shaanxi,China
DENG Yan?chun(Email:yanchund@fmmu.edu.cn)
Precision medicine(PM),a new type of medical concept and model which based on personalized medicine,is developed with the fast progress of genetic detection technology and the cross?application of biological information and large data science.Genetic detection technology is the basis of PM.Cerebrovascular disease is a multifactorial disease,in which genetic factors play an important role in the pathogenesis.This paper intends to discuss the application of gene detection technology in the PM of cerebrovasculardisease,includingsingle gene genetic disease,genetic polymorphism,drug genetics research and precision treatment.
Cerebrovascular disorders; Genes; Review
This study was supported by 2010 Science and Research Special Project of Shaanxi Provincial Education Department(No.2010JK811)and Science and Technology Project of Lianhu District,Shaanxi Province,China(No.K2011-024).
10.3969/j.issn.1672?6731.2017.07.005
陜西省教育廳2010年專項科學研究項目計劃(項目編號:2010JK811);陜西省西安市蓮湖區科技計劃項目(項目編號:K2011-024)
710077西安醫學院第一附屬醫院神經內科(折瀟);710032西安,第四軍醫大學西京醫院神經內科(鄧艷春)
鄧艷春(Email:yanchund@fmmu.edu.cn)
2017?06?24)

