低溫脅迫對水稻幼苗葉片生理生化特性的影響
王亞男 范思靜
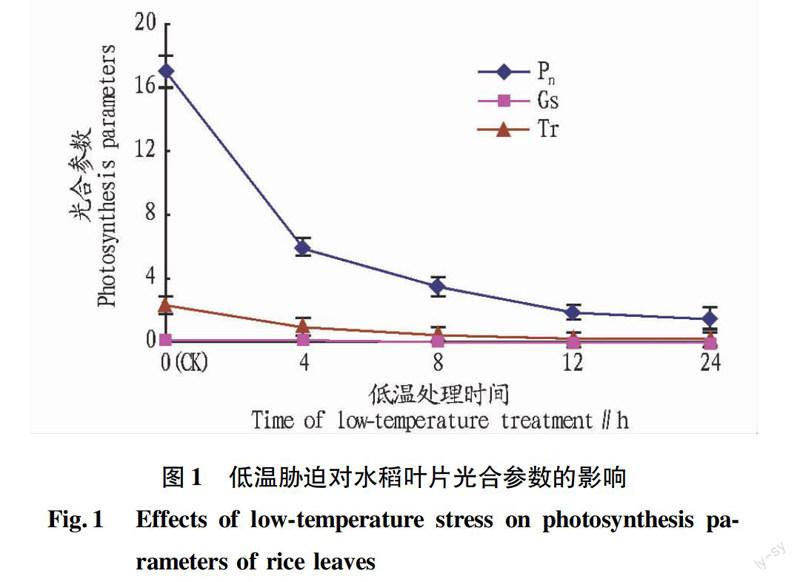
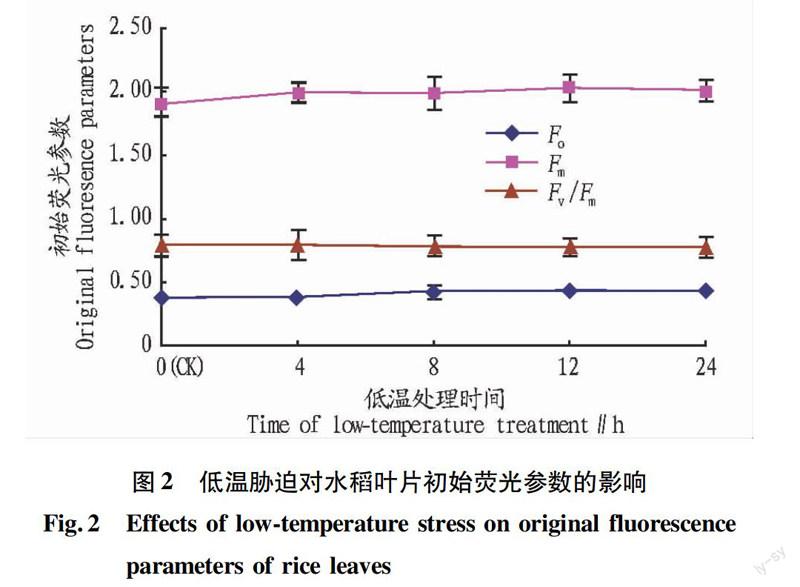

摘要[目的]研究低溫脅迫對水稻葉片生理生化特性的影響。[方法]以水稻品種兩優5916為試驗材料,研究低溫脅迫過程中水稻幼苗葉片的光合參數、葉綠素熒光參數、抗氧化系統酶活和丙二醛含量的變化。[結果]低溫脅迫下,水稻的凈光合效率、氣孔導度與蒸騰速率均明顯下降,葉綠素熒光參數光合系統 Ⅱ 最大潛在光化學效率(Fv/Fm)與光化學轉換的實際量子效率(ФPSⅡ)也顯著降低,初始最小熒光(Fo)與光合系統 Ⅱ 非調控能量耗散系數(ФNO)升高。對抗氧化系統酶活的測定結果表明,在低溫處理過程中水稻幼苗葉片的抗氧化系統SOD、POD、CAT酶活呈先升高后降低的趨勢,丙二醛含量則逐步升高。[結論]在低溫脅迫下,水稻對光能的吸收轉換效率降低,而蒸騰速率與氣孔導度的降低導致葉片凈光合速率的降低,由于葉片抗氧化系統酶活的降低以及MDA含量的增加,葉片光合系統 Ⅱ 受到了不可逆的損傷。
關鍵詞水稻;低溫冷害;光合作用;葉綠素熒光參數;抗氧化系統
中圖分類號S501文獻標識碼A文章編號0517-6611(2017)05-0008-02
Abstract[Objective] To study the effects of lowtemperature stress on the physiological and biochemical characteristics of rice seedling leaves. [Method] Taking rice cultivar Liangyou 5916 as test materials, the changes of photosynthesis parameters, chlorophyll fluorescence parameters, enzyme activities of antioxidant system and MDA content in the process of lowtemperature stress were studied. [Result] Under lowtemperature stress, the net photosynthesis rate, stomatal conductance and transpiration rate obviously decreased, and chlorophyll fluorescence parameters Fv/Fm, ФPSⅡ obviously decreased, but Fo and ФNO increased. The determination results of the activities of SOD, POD and CAT enzymes firstly increased and then decreased, MDA content gradually increased. [Conclusion] Under lowtemperature stress, photochemical conversion efficiency decreased, the net photosynthesis rate decreased by the decrease of stomatal conductance and transpiration rate. PSⅡ was damaged because enzymes activities of antioxidant system decreased and MDA content increased.
Key wordsRice;Cold damage;Photosynthesis;Chlorophyll fluorescence parameters;Antioxidant system
基金項目安徽省科技攻關計劃項目(1501031111)。
作者簡介王亞男(1983—),女,安徽青陽人,農藝師,碩士,從事作物遺傳育種研究。
收稿日期2016-12-24
水稻在前期育苗生產過程中常常會遭遇低溫的影響,導致苗期遭遇冷害,水稻生長緩慢或停滯[1-3]。研究表明,當環境溫度低于10 ℃時,水稻的生理代謝過程就會受到傷害,如膜透性增加、葉綠素合成受到抑制、引起光合作用系統對光能的吸收轉換與利用效率降低,直接影響水稻幼苗的生長[4]。……

