食管鱗狀細胞癌PRL-3及Intβ1表達分析及意義
成爭艷 雷龍春 楊旭峰 陳星
(四川省人民醫院城東病區 1.病理科;2. 胸外科,四川 成都 610101)
?
·論著·
食管鱗狀細胞癌PRL-3及Intβ1表達分析及意義
成爭艷1雷龍春1楊旭峰1陳星2
(四川省人民醫院城東病區 1.病理科;2. 胸外科,四川 成都 610101)
目的 研究促肝細胞再生磷酸酶-3(PRL-3)和整合素β1(Intβ1)在食管鱗狀細胞癌中的表達水平及差異,探討其臨床意義。方法 采用免疫組織化學法檢測40例食管癌患者食管癌組織,癌旁組織和正常組織中PRL-3 和Intβ1 蛋白的表達水平,利用Image Pro6.0圖像分析系統計算平均光密度值(MOD),分析其表達的差異。結果 PRL-3和Intβ1的表達,癌組織中均高于癌旁組織,正常組織中表達最低(P<0.05)。結論 PRL-3 和Intβ1在食管鱗狀細胞癌組織中表達增高,可作為參考指標判斷食管鱗狀細胞癌的浸潤、轉移和預后。
食管鱗狀細胞癌;免疫組化;促肝細胞再生磷酸酶3;整合素β1
食管癌發病率在世界范圍內居第8位[1],死亡率居第6位[2]。我國是食管癌高發地區, 其發病率和死亡率均明顯高于世界平均水平, 且無性別差異[3-4]。在集中高發區,食管癌標準化死亡率在10.34/10 萬~78.32/10萬,占高發縣全部惡性腫瘤死亡的11.69%~42.61%, 居城市和農村惡性腫瘤死亡率的第4位[5]。但是其發病的分子機制仍不清楚[6]。促肝細胞再生磷酸酶-3(phosphatase of regenerating liver-3, PRL-3)是一種蛋白酪氨酸磷酸酶,具有促進細胞的生長、浸潤與遷移的作用[7],Saha等[8]發現PRL-3與癌轉移密切相關。整合素β1(integrinβ1, Intβ1) 在腫瘤組織的浸潤轉移中因為可使細胞間的黏附能力下降而發揮作用[9]。目前PRL-3及Intβ1與食管癌的關系研究較少。本實驗通過檢測PRL-3和Intβ1在食管癌的表達,探討其關系,為臨床提供判斷食管癌浸潤和轉移的客觀有效指標。
1 資料與方法
1.1 臨床資料 收集四川省人民醫院城東病區2012年1月至2014年12月因食管鱗狀細胞癌手術切除治療的病理標本共40例。取癌組織及相應的癌旁組織(距腫瘤邊緣1.0 cm)、正常組織(距腫瘤邊緣5.0 cm)作為對照,所有標本均由病理診斷醫師HE切片,明確病理診斷。所有患者術前均未行放療或化療。
1.2 主要試劑 PRL-3單克隆抗體(美國Santa Cruz公司); Intβ1單克隆抗體(美國Santa Cruz公司)。
1.3 實驗方法 所有標本均經10%甲醛溶液固定,常規石蠟包埋,4 μm切片,按照免疫組化二步法檢測試劑盒說明進行操作,測定PRL-3和 Intβ1的表達。用0.01 mol/L PBS(pH7.4)代替一抗作為陰性對照。
1.4 結果判定 PRL-3 及Intβ1以胞質中出現棕黃色信號為陽性細胞。每張切片高倍鏡下隨機選取5~6個視野拍照,采用Image Pro6.0圖像分析系統分析測量平均光密度值(mean optical density,MOD),進行各組比較。
1.5 統計學方法 采用SPSS 17.0統計軟件對數據進行分析,多組間均數比較采用單因素方差分析(ANOVA),用Pearson分析相關性,P<0.05為差異有統計學意義。
2 結果
2.1 PRL-3的蛋白表達情況和MOD比較 免疫組化檢測40例人食管癌組織、癌旁組織及正常組織中PRL-3表達情況結果顯示,食管癌組織中PRL-3有27例(67.5% )陽性(圖1A),而相應的40例癌旁組織有15例(37.5%)陽性表達,且陽性細胞均集中在不典型增生區域的細胞質中(圖1B);正常組織中PRL-3有13例(32.5%)散在陽性(圖1C)。MOD結果顯示,PRL-3表達總趨勢為癌組織>癌旁組織>正常組織,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05),見表1。
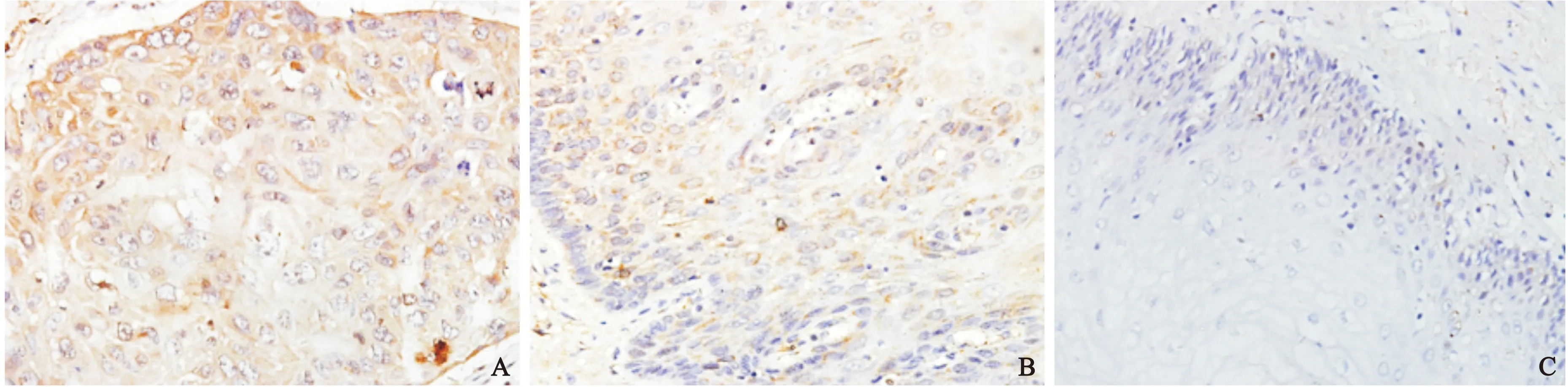
圖1 不同組織中PRL-3蛋白表達情況(×400)
注:與正常組比較,①P<0.05, ②P<0.05
2.2 Intβ1的蛋白表達情況和MOD比較 食管癌組織中Intβ1有29例(72.5%)陽性(圖2A),而相應的40例癌旁組織有16例(40%)陽性表達(圖2B),正常組織中有15例(37.5%)散在陽性表達(圖3C)。MOD結果顯示,Intβ1表達總趨勢為癌組織>癌旁組織>正常組織,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05)(表2)。
2.3 PRL-3和Intβ1表達的相關性 癌組織和癌旁組織中PRL-3 和Intβ1表達呈正相關關系(r=0.412,P=0.024;r=0.446,P=0.049);在正常組織中PRL-3和Intβ1表達無相關性(r=-0.137,P=0.563)。
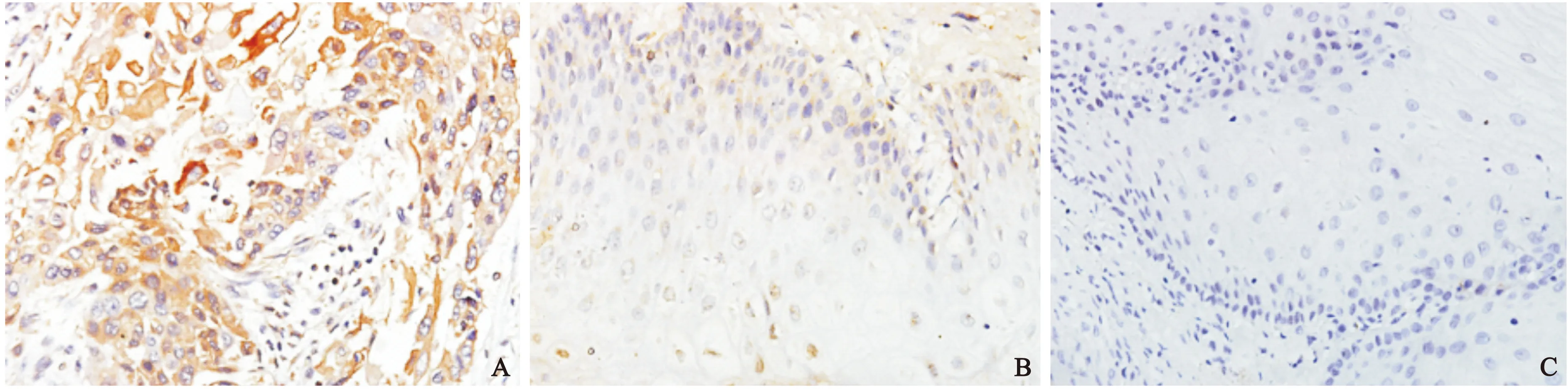
圖2 不同組織中Intβ1蛋白表達情況(×400)
注:與正常組比較,①P<0.05,②P<0.05。
3 討論
肝再生磷酸酶家族包含3個亞型,即PRL-1、PRL-2、 PRL-3,編碼基因分別位于染色體6q12、1p35、8q24.3上。其是一類獨特的核蛋白酪氨酸磷酸酶,含有完全相同的蛋白質酪氨酸磷酸酶催化位點序列。研究表明PRLs,特別是PRL-3在多種腫瘤的發生、增殖及侵襲中起作用[10-11]。目前已發現PRL-3在乳腺癌、卵巢癌、結直腸癌及胃癌等惡性腫瘤中表達升高,同時發現表達水平越高,腫瘤惡性程度越高,淋巴結及其它轉移灶的表達水平明顯高于原發灶及正常組織[12-14]。Guo等[15]將PRL-3高表達的CHO細胞注入小鼠體內,全部誘導出形成肺轉移瘤,并且有20%的小鼠合并出現肝轉移瘤,而注入PRL-3突變失活的對照組小鼠則無轉移性腫瘤形成。本實驗通過免疫組化檢測了食管鱗狀細胞癌及癌旁組織,正常食管黏膜組織中PRL-3的表達情況,結果表明在食管鱗狀細胞癌中PRL-3 蛋白的表達明顯高于癌旁組織及正常組織,說明高表達的PRL-3 可能在食管鱗狀細胞癌發生中起作用。
整合素作為粘附分子五大家族成員之一,它可以調節細胞之間及細胞與胞外基質(extracellular matarix, ECM)的粘附而發揮作用[16]。Intβ1是介導ECM信號的主要細胞表面受體,其與配體結合后有促進細胞黏附、增殖和遷移等作用。研究表明, Intβ1表達升高除了影響腫瘤細胞與基質的粘附,從而使腫瘤細胞更具有侵襲性,Intβ1還可以影響腫瘤細胞ERK,AKT等基因的表達,從而與腫瘤細胞的增殖、基因轉導、凋亡等生物學行為有密切關系[17-19]。本實驗根據蛋白水平檢測Intβ1的表達,結果表明,在食管鱗狀細胞癌中Intβ1 蛋白在原發灶中的表達明顯高于癌旁組織及正常組織,證明Intβ1的高表達可能與食管鱗狀細胞癌黏附,侵襲增強有關。
PRL-3和Intβ1將各種細胞外信號傳遞至細胞內主要依靠MAPK信號通路[14];有研究顯示,PRL-3通過Intβ1-ERK1/2-MMP-2信號傳導通路促進Intβ1的表達[20]。因此,其共同作用下促使腫瘤組織的侵襲性、活動性和轉移能力增強。本實驗結果顯示,在蛋白表達水平癌組織和癌旁組織中PRL-3 和Intβ1表達均呈正相關,說明其機制PRL-3可能通過活化通路提高Intβ1表達,從而增強細胞間質侵襲和轉移的能力。
4 結論
在食管鱗狀細胞癌中PRL-3和Intβ1的高表達,聯合檢測可能作為腫瘤標志物來判斷食管鱗狀細胞癌的發生發展、浸潤和轉移,也有望成為治療腫瘤的靶點。
[1]Parkin DM, Pisani P, Ferlay J. Estimates of the worldwide incidence of 25 major cancers in 1990[J]. Int J Cancer, 1999, 80(6): 827- 841.
[2]Pisani P, Parkin DM, Bray F,etal. Estimates of the worldwide mortality from 25 cancers in 1990[J]. Int J Cancer, 1999, 83(1): 18-29.
[3]段紀俊, 陳萬青, 張思維.中國惡性腫瘤死亡率的國際比較[J].中國社會醫學雜志, 2009, 26(6): 377- 378.
[4]赫捷, 邵康.中國食管癌流行病學現狀,診療現狀及未來對策[J].中國癌癥雜志,2011,21 (7): 501-504.
[5]王國清, 魏文強,喬友林.食管癌篩查和早診早治的實踐與經驗[J].中國腫瘤, 2010, 19(1): 4-8.
[6]Kashyap MK, Marimuthu A, Kishore CJ,etal. Genomewide mRNA profiling of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma for identification of cancer biomarkers [J]. Cancer Biol Ther, 2009, 8(1): 36-46.
[7]Stephens BJ, Han H, Gokhale V,etal. PRL phosphatases as potential molecular targets in cancer[J]. Mol Cancer Ther, 2005, 4(11): 1653-1661.
[8]Saha S,Bardelli A,Buckhaults P,etal.A phosphatase associated with metastasis of colorectal cancer[J]. Science,2001, 294(5545):1343-1346.
[9]Yang J, Dai C, Liu Y. A novel mechanism by which hepatocyte growth factor blocks tubular epithelial to mesenchymal transition[J]. J Am Soc Nephrol,2005,16(1):68-78.
[10] Bessette DC, Qiu D, Pallen CJ. PRL PTPs: mediators and markers of cancer progression [J]. Cancer Metastasis Rev, 2008, 27(2): 231-252.
[11] AI-Aidaroos AQ, Zeng Q. PRL-3 phosphatase and cancer metastasis [J]. J Cell Biochem,2010,111(5):1087-1098.
[12] Ren T, Jiang B, Xing X,etal. Prognostic significance of phosphatase of regenerating liver-3 expression in ovarian cancer [J]. Pathol Oncol Res,2009,15(4):555-560.
[13] Mayinuer A,Yasen M,Mogushi K,etal. Upregulation of protein tyrosine phosphatase type IVA member 3(PTP4A3/PRL-3)is associated with tumor differentiation and a poor prognosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma [J]. Ann Surg Oncol,2013,20(1):305-317.
[14] Bilici A, Ustaalioglu BB, Yavuzer D,etal. Prognostic significance of high phosphatase of regenerating liver-3 expression in patients with gastric cancer who underwent curative gastrectomy [J]. Dig Dis Sci,2012, 57(6):1568-1575.[15] Guo K, Li J, Tang JP,etal.Catalytic domain of PRL-3 plays an essential role in tumor metastasis:formation of PRL-3 tumors inside the blood vessels [J].Cancer Biol Ther,2004,3(10):945-951.
[16] Hood JD, Cheresh DA. Role of integrins in cell invasion and migration [J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2002, 2(2):91-100.
[17] Yao ES, Zhang H, Chen YY,etal. Increased beta1 integrin is associated with decreased survival in invasive breast cancer[J]. Cancer Res, 2007, 67(2): 659- 664.
[18] Hazlehurst LA, Argilagos RF, Dalton WS. Beta1 integrin mediated adhesion increases Bim protein degradation and contributes to drug resistance in leukaemia cells[J]. Br J H aematol, 2007, 136(2): 269-275.
[19] Kobel M, Pohl G, Schmitt WD,etal. Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase is required for migration and invasion of placental site trophoblastic tumor [J]. Am J Pathol, 2005,167(3):879-885.
[20] Peng LR, Xing XF, Li WJ,etal. PRL-3 promotes the motility, invasion, and metastasis of LoVo colon cancer cells through PRL-3-integrin β1-ERK1/2 and-MMP2 signaling [J]. Molecular Cancer,2009, 28:110-112. doi:10.1186/1476-4598-8-110.
Expression of phosphatase of regenerating liver-3 and integrin β1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
CHENG Zhengyan1,LEI Longchun1,YANG Xufeng1,et al
(1.DepartmentofPathology,EastenDistrict,SichuanAcademyofMedicalSciences&SichuanProvincial>People′sHospital,Chengdu610101,China;2.DepartmentofThoracicSurgery,EastenDistrict,SichuanAcademyofMedicalSciences&SichuanProvincialPeople′sHospital,Chengdu610101,China)
Objective To study expression levels and differences of phosphatase of regenerating liver-3 and integrinβ1 protein in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, and explore its clinical significance. Methods PRL-3 and Intβ1 expression level of esophageal cancer tissue, tissue adjacent to carcinoma and normal tissues were detected by analysis of the differences in expression. Results The protein expressions of PRL-3 and Intβ1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma were higher than that in the adjacent non-tumor tissues. The protein expressions of PRL-3 and Intβ1 were lowest in normal esophageal tissues. Conclusion PRL-3 and Intβ1 may be used as tumor markers in progression, invasion and metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; Immunohistochemistry; Phosphatase of regenerating liver-3; Integrin β1
R 365;R 735.1
A
10.3969/j.issn.1672-3511.2016.11.005
2016-04-06;編輯: 張文秀)

