大腸癌患者血清中硫氧還蛋白樣蛋白-2表達水平及臨床意義
陳細女
湖南省株洲市三三一醫院,湖南 株洲 412002
?
大腸癌患者血清中硫氧還蛋白樣蛋白-2表達水平及臨床意義
陳細女
湖南省株洲市三三一醫院,湖南株洲412002
目的:探討大腸癌患者血清中硫氧還蛋白樣蛋白-2(Txl-2)的表達及臨床意義。方法:采用酶聯免疫吸附法(ELISA)檢測82例大腸癌患者和25例健康對照者外周靜脈血清中Txl-2含量。結果:大腸癌患者血清中Txl-2含量明顯高于健康對照者(P<0.05);血清中Txl-2表達與大腸癌腫瘤分化程度、Dukes分期、淋巴結及遠處器官轉移、3年內復發情況密切相關,而與患者性別、年齡及腫瘤大小無明顯聯系(P>0.05)。結論:Txl-2表達與大腸癌生物學行為存在聯系,與大腸癌病情變化及預后密切相關(P<0.05),檢測血清中Txl-2的表達水平對于大腸癌的診斷、惡性程度及預后判斷具有良好的臨床應用價值。
大腸癌;血清Txl-2;酶聯免疫吸附法
結腸癌為全球高發的惡性腫瘤,發病危險因素主要包括肥胖、吸煙、運動量少和膳食中缺乏蔬果等,西方發達國家如歐洲和北美是大腸癌高發地區,大腸癌在歐美國家位居致死惡性腫瘤第二位[1-2]。在我國,大腸癌發病率也呈現逐漸上升的趨勢,篩選和鑒定大腸癌敏感標志物,對于早期診斷和準確判斷預后具有重要意義[3]。硫氧還蛋白樣蛋白2(Thioredoxin-like protein 2, Txl-2)是同時屬于硫氧還蛋白家族和核苷二磷酸激酶家族成員的蛋白[4],有研究報道Txl-2在大腸癌組織中存在高表達,且促進大腸癌的惡性進展,調控結腸癌細胞增殖、侵襲和凋亡抵抗等多種惡性生物學行為[5],但Txl-2在大腸癌患者血清中的表達情況及其與臨床特征間的關系尚未見明確報道。本研究則通過檢測大腸癌患者外周血中Txl-2的表達水平,分析其表達與大腸癌患者臨床病理參數的關系,探討其在大腸癌診斷及預后中的作用。
1 資料與方法
1.1一般資料選取2010年11月至2014年2月82例經病理學檢查確診為大腸癌的患者進入本研究,其中男性49例,女性33例;>60歲45例,≤60歲37例;腫瘤直徑>4cm 38例,≤4cm 44例;高分化8例,中分化53例,低分化21例;Dukes分期:A+B期40例,C+D期42例;有淋巴結轉移者45例,無淋巴結轉移者37例;有遠處器官轉移者33例,未見遠處器官轉移者49例;術后復查患者29例,其中3年內復發者16例,未復發者13例。選擇25例健康體檢者作為對照組。所有患者術前均未接受化療和放療,患者及健康對照組均簽署知情同意書。患者一般資料差異無統計學意義(P>0.05),具有可比性。
1.2檢測方法采集試驗對象外周靜脈血3mL,自然凝固后,3000rpm 離心5min,收集上層血清置-20℃儲存備用。Txl-2 ELISA檢測試劑盒購自上海聯世生物科技有限公司,具體檢測方法按試劑盒說明書進行。
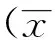
2 結果
2.1健康對照組與大腸癌患者組血清中Txl-2的表達差異采用ELISA方法對健康對照者和大腸癌患者血清中Txl-2含量進行檢測,Txl-2在大腸癌患者組血清中表達為(150.17±26.83)pg/mL,明顯高于健康對照者血清中含量(68.34±9.65)pg/mL,差異具有統計學意義(P<0.05)。見表1。

表1 健康對照組與大腸癌患者組血清中Txl-2的比較
注:與健康對照組比較,*P<0.05。
2.2Txl-2表達與大腸癌臨床病理特征的關系Txl-2在大腸癌患者血清中的表達水平與患者性別、年齡及腫瘤大小均無明顯相關(P>0.05);低分化大腸癌患者和Dukes C+D期患者血清中Txl-2的表達分別為(182.41 ± 11.65)pg/mL和(167.56±20.50)pg/mL,顯著高于中、高分化組(139.08±20.92)pg/mL及Dukes A+B組(133.62 ± 21.13)pg/mL,Txl-2在有淋巴結和遠處器官轉移組大腸癌患者血清中的表達均高于無淋巴結和遠處器官轉移者(P<0.05);另外,術后復查患者中,3年內有復發者血清中Txl-2的表達水平高于無復發者,差異具有統計學意義(P<0.05)。
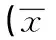
表2 Txl-2表達與大腸癌臨床病理特征的關系 ±s)
3 討論
Txl-2在2003年被首次報道[4],全長編碼330個氨基酸,N端有一個硫氧還蛋白(Thioredoxin,Trx)結構域,為硫氧還蛋白家族的新成員,Trx系統與谷胱甘肽系統一起,將生物體內眾多蛋白質半胱氨酸殘基保持在還原狀態,是細胞內重要的氧化還原調節系統[6],同時,Trx家族參與多種腫瘤惡性生物學行為,Moon等的研究表明,Trx-1可促進結腸癌細胞生長,在結腸癌細胞HT-29中抑制Trx-1的表達可導致細胞周期阻滯,從而抑制細胞增殖[7],Ramanathan 等的研究結果顯示,PX-12作為Trx-1的抑制劑,已進入臨床Ⅱ期研究,與化療聯合用于治療實體瘤患者,具有良好的應用前景[8];Trx家族成員還可以參與黏附分子和整合素相關的信號通路,促進腫瘤細胞增殖、侵襲,在腫瘤的發生發展中有重要作用[9]。Txl-2的C末端有一個核苷二磷酸激酶(Nucleoside diphosphate kinase,NDPK)結構域,為nm23家族的新成員。目前nm23家族在細胞發育中的作用尚未完全清楚,但是其在腫瘤中的作用卻被廣泛關注,nm23-H1可促進神經母細胞瘤、胰腺癌等的轉移,并且與腫瘤的分期密切相關[10-12],nm23-H2則是潛在的肝細胞癌致癌因子[13]。另外,Qu等的研究報道表明,Txl-2可通過氧化還原平衡及NF-kB信號通路調控腫瘤細胞的增殖和轉移[14],構建Txl-2 siRNA載體,穩定轉染入SW620細胞,獲得Txl-2表達抑制的細胞株;對其功能學進行研究發現,下調Txl-2的表達能夠顯著抑制結腸癌細胞的無限增殖、凋亡抵抗和侵襲轉移等惡性表型[15]。
本研究結果顯示,大腸癌患者血清中Txl-2表達為(150.17±26.83)pg/mL,其表達水平明顯高于健康對照者血清中含量(68.34±9.65)pg/mL(P<0.05),而且,Txl-2在低分化組患者血清中的表達顯著高于中、高分化組(P<0.05),說明Txl-2與大腸癌的惡性程度呈現正相關;Dukes A+B期和Dukes C+D期患者血清中Txl-2表達分別為(133.62±21.13)pg/mL和(167.56±20.50)pg/mL,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05),表明隨著大腸癌臨床分期的進展,Txl-2表達逐漸升高,Txl-2可能參與了大腸癌的發展。伴淋巴結轉移及遠處器官轉移患者血清中Txl-2分別為(166.57±19.68)pg/mL和(173.56±16.65)pg/mL,均高于無淋巴結及遠處器官轉移患者(130.23±20.03)pg/mL和(134.42±20.00)pg/mL,(P<0.05)。而這些結果提示,Txl-2參與了結腸癌的發展,可能在腫瘤生長、侵襲轉移方面發揮重要作用。對術后復查患者血清中Txl-2進行檢測,復查患者血清中Txl-2水平與術前相比有所下降,且3年內無復發者血清中Txl-2表達較有復發者也存在降低趨勢(P<0.05),同時,對大腸癌患者血清中Txl-2的表達與臨床病理特征的分析比較與組織中的檢測結果相一致[4]。
本研究結果表明,Txl-2在大腸癌患者血清中呈現高表達,其表達水平與患者體內腫瘤負荷程度密切相關,在治療過程中,測定Txl-2水平有助于對大腸癌患者進行療效評定、腫瘤復發監測和預后判斷,同時也為大腸癌的靶向治療提供新的思路和理論依據。
[1]Center MM, Jemal A, Smith RA, et al. Worldwide variations in colorectal cancer [J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2009, 59 (6):366-378.
[2] Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, et al. Cancer statistics, 2007 [J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2007,57:43-66.
[3] Deschoolmeester V, Baay M, Specenier P, et al. A review of the most promising biomarkers in colorectal cancer: one step closer to targeted therapy [J]. Oncologist, 2010, 15: 699-731.
[4] Sadek CM, Jiménez A, Damdimopoulos AE, et al. Characterization of human thioredoxin-like 2. A novel microtubule-binding thioredoxin expressed predominantly in the cilia of lung airway epithelium and spermatid manchette and axoneme [J]. J Biol Chem, 2003,278(15):13133-13142.
[5] 盧瑗瑗. 結直腸癌相關抗原MC3-Ag的鑒定和功能研究[D]. 西安:第四軍醫大學,2011.[6] Lillig CH, Holmgren A. Thioredoxin and related molecules--from biology to health and disease[J]. Antioxid Redox Signal, 2007,9(1):25-47.
[7] Moon MS, Kim JS, Kim TL, et al. Polyamine depletion partially reduces the radiation induced cell death via cell cycle delay mediated by thioredoxin[J]. Cell Biol Toxicol, 2006,22:137-147.
[8] Ramanathan RK, Abbruzzese J, Dragovich T, et al. A randomized phase II study of PX-12, an inhibitor of thioredoxin in patients with advanced cancer of the pancreas following progression after a gemcitabine-containing combination[J]. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol, 2011,67(3):503-509.
[9] Yamawaki H, Pan S, Lee RT, et al. Fluid shear stress inhibits vascular inflammation by decreasing thioredoxin-interacting protein in endothelial cells[J]. J Clin Invest, 2005,115(3):733-738.
[10]Roymans D, Willems R, Van Blockstaele DR, et al. Nucleoside diphosphate kinase (NDPK/NM23) and the waltz with multiple partners: possible consequences in tumor metastasis[J]. Clin Exp Metastasis, 2002,19(6):465-476.
[11] Hailat N, Keim DR, Melhem RF, et al. High levels of p19/nm23 protein in neuroblastoma are associated with advanced stage disease and with N-myc gene amplification[J]. J Clin Invest, 1991,88(1):341-345.
[12] Conery AR, Sever S and Harlow E. Nucleoside diphosphate kinase Nm23-H1 regulates chromosomal stability by activating the GTPase dynamin during cytokinesis[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2010, 107: 15461-15466.
[13] Lee MJ, Xu DY, Li H,et al. Pro-oncogenic potential of NM23-H2 in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Exp Mol Med, 2012, 44: 214-224.
[14] Qu Y, Wang J, Ray PS,et al. Thioredoxin-like 2 regulateshuman cancer cell growth and metastasis via redox homeostasisandNF-kappaB signaling[J]. J Clin Invest, 2011, 121: 212-225.
[15] Lu Y, Zhao X, Li K , et al. Thioredoxin-like protein 2 is overexpressed in colon cancer and promotes cancer cell metastasis by interaction with Ran[J]. Antioxid Redox Signal, 2013, 19(9):899-911.
(編輯:程鵬飛)
Serum of Patients with Colorectal Thioredoxin-like Protein 2 Expression and Clinical Significance
CHEN Xinv
Hunan Zhuzhou 331 Hospital,Zhuzhou 412002,China
Objective To investigate the serum of patients with colorectal thioredoxin-like protein -2 (Txl-2) expression and clinical significance. Methods Using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) to detect 82 cases of colorectal cancer patients and 25 healthy controls peripheral vein serum Txl-2 content. Results The serum of patients with colorectal Txl-2 were significantly higher than healthy controls (P<0.05); Txl-2 expression in serum and tumor differentiation degree of colorectal cancer, Dukes stage, lymph node and distant metastasis, recurrence within 3 years They are closely related(P<0.05), but not with sex, age and tumor size had no significant contact (P>0.05). Conclusion Txl-2 expression and the biological behavior of colorectal cancer there is a link, is closely related to changes in condition and prognosis of colorectal cancer, the expression levels of serum Txl-2 for diagnosis, degree of malignancy and prognosis of colorectal cancer have a good clinical application value.
Colorectal Cancer; Serum Txl-2; ELISA
2016-05-10
陳細女(1970-),女,漢族,研究方向為腫瘤內科。E-mail:136498164@qq.com
R446.11
A
1007-8517(2016)16-0093-03

