The impact resistance of Kevlar woven fabrics impregnated with highly concentrated multiphase suspensions
Liu Jun Xiong Dangsheng
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Nanjing 210094, China
The impact resistance of Kevlar woven fabrics impregnated with highly concentrated multiphase suspensions
Liu JunXiong Dangsheng
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Nanjing 210094, China
The stab and puncture resistance of Kevlar woven fabrics impregnated with different kinds of highly concentrated multiphase suspensions was studied with self-made dual-catheter drop-hammer tester. The results showed that the shear thickening of multiphase particles was possibly based on hydrocluster and particle jamming mechanism; the introduction of alumina silicate fibre can remarkably improve the composite spike resistance, and multiphase particles co-strengthening can provide best protection effect; otherwise, the stab resistance increases weakly.
stab and puncture resistance; multiphase suspensions;armor protective materials;shear thickening;high strength fabric
1. Introduction
Conventional armor materials with high specific strength and stiffness is typically limited to chest and head protection, and little protection to those key components, including arms, legs, hands, and neck. optional ceramic tile inserts or fabric ply increase can improve protection against more lethal ballistic threats at the expense of increased weight of the armour but reduce mobility of the user, which actually raises the probability to be shot. In order to keep the flexibility without reducing the effective protection, many related studies were performed, such as thermoplastic coating[1], hard ceramic coating[2], fiber surface modification[3],fabric structure weaving[4, 5],particle blended spinning[6],fabric layer displacing[7], field responsive fluids strengthening[8-12]. Shear thickening fluids among field responsive fluids changes its properties according to the loading conditions and avoid the need for an external power source. Such behavior is a predominance of STFs product forming, and may also offer protection against different threats: high-speed bullet and low-speed stab[13],which attracts considerable attention.
STF is commonly considered as a non-Newtonian fluid which viscosity increases with the strain rate, but the question concerned the determination of any reliable dynamic viscosity diagrams is absent, and the construction of an adequate STF mathematical model is currently open[14]. The STF studies with standard rotational viscosimeters reveal complex (generally reversing) dependence of viscosity on strain rate[15]. Different suspension systems are usually shear-thicken by three different mechanisms - shearinduced formation of particle clusters flocculated by polymer bridging,hydrocluster formation, and particle jamming, which means the fluid viscosity with different interactions between particles can reveal complex (generally reversing) dependence of viscosity on strain rate[15]. This makes it really difficult to adjust the fluid shear thickening rheology when multimodal regulations are available. Most STFs of relevant literatures[12, 16-18]are diphase suspensions, and furthermore Al2O3particle and discontinuous alumina silicate fiber were introduced into SiO2/PEG suspension in this paper to study the microstructure change effects on impact resistance of impregnated Kevlar fabrics.
2.Experiments
2.1Materials
Al2O3particle(0.5um,Shanghai Chemical College Experimental Plant), SiO2particle(0.42um, Nanjing Materials Chemical Co., Ltd.) and discontinuousalumina silicate fiber(The continuous fiber was cut into pieceswith scissors and then grinded for 8 hours) were put as composite dispersing phases with volume concentration shown in table 1into the mixture of polyethylene glycol (PEG,MW 200) and ethanol with the ratio of 1 to 3 and then grinded by homogenization for several hours with a ball mill as dilute STF to be used.
Kevlar129(American DuPont Co., Ltd.)Plain woven fabric was cut into 12*22cm2layers and individually impregnated with the dilute STFs mentioned above and simultaneously irradiated by ultrasonic wave for several minutes. The fabrics were placed into the vacuum oven at 70 °C for 1h to evaporate the ethanol. Four layers of STF-treated fabrics were sealed together with polyethylene film as a sample for the impact resistant test. Kevlar fabric impregnated with the dilute STFs was abbreviated as STFKevlar subsequently.
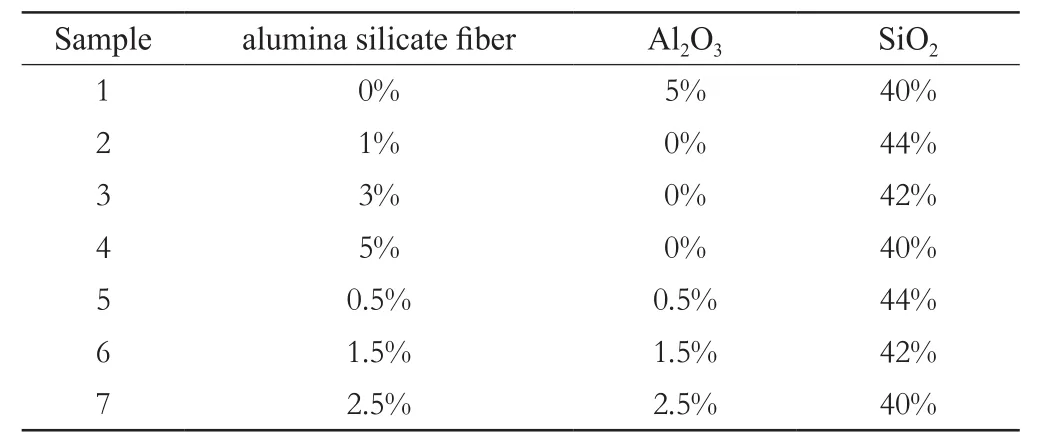
Table 1 volume concentration of different STFs
2.2Dynamic impact resistance test
Thedynamic impact resistance test was carried on a self-made dualcatheter drop-hammer tester shown in Fig.1 based on American NIJ-0115.00 standard and Chinese GA 68-2008 standard. The specimens were placed on top of the backing material. The impact mass was mounted to a specific height and then released to puncture the specimens. The drop height was set 0.3 m for each sample and the weight of knife and spike impactors was both 2.38 kg.
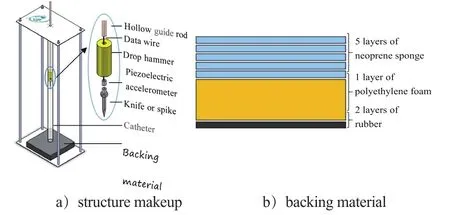
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of impact resistance tester
3.Results and discussion
3.1Particle diameter of different suspensions

Table 2 Average particle diameter of different suspensions
The average particle diameter in different suspensions was determined by dynamic light scattering as shown in table 2. The results showed that the average particle diameter ranged from 5.35∽6.72μm, suggesting that decades of different particles were held together by hydroxy groups to form particle clusters. The coexisting of different particles could increase the size of particle clusters in 3 dimensions, when sample 5, 6, 7 were contrasted with sample 2, 3, 4. The introduction of alumina silicate fiber and its increase concentration had a bigger effect on enlarging the size of particle clusters.
3.2Spike resistance of different STF-Kevlar systems
Spike resistance of backing material, neat Kevlar fabric and STFKevlar impregnated with 7 types of suspensions was explored, as shown in Table 3.
Form Table 3, we could see that spike resistance properties of STF-Kevlar are better than backing material and neat Kevlar fabric. Comparing sample 3-7 to sample 1 and 2, the introduction of multiphase particles obviously improves the spike-resistance of STF-Kevlar, and the increasing volume concentration of alumina silicate fiber results in more improvement of spike resistance than that of Al2O3(sample 3,4, 6, 7). These changes may base on two mechanisms: one is that the existing of multiphase particles changes particle aggregating way in STFs under spike impact, namely from hydrocluster mode to hydrocluster and particle jamming mode, which improves the probabilities of particle collision and friction exhibiting strong strain stiffening of the elastic moduli and strain thickening of the loss moduli behavior[15, 19], resulting in a higher resistance by the coated fabric against the spike when trying to push aside (windowing) and pull out the yarns[16], and the other is that the introduction of alumina silicate fiber increases stress transmission under impact.
Fig. 5(a) shows the dynamic loads results of neat Kevlar fabric and STF-Kevlar fabric composite for spike threats at the drop height of 0.3m. As seen in the fig. 5(a), the neat Kevlar fabric exhibits about 40% higher loading than the backing material, and STF-Kevlar exhibits not much improvement resistance than the neat.
由上述方程容易看出,無論哪種模型得到的均方末端距都與統計單元數目的一次方成正比,而單元數目恰恰與分子量是線性相關的,因此均方末端距與分子量呈線性正比關系.用均方末端距除以鏈的分子量就可以得到一個能表征分子鏈剛柔性的特征參數——分子無擾尺寸:
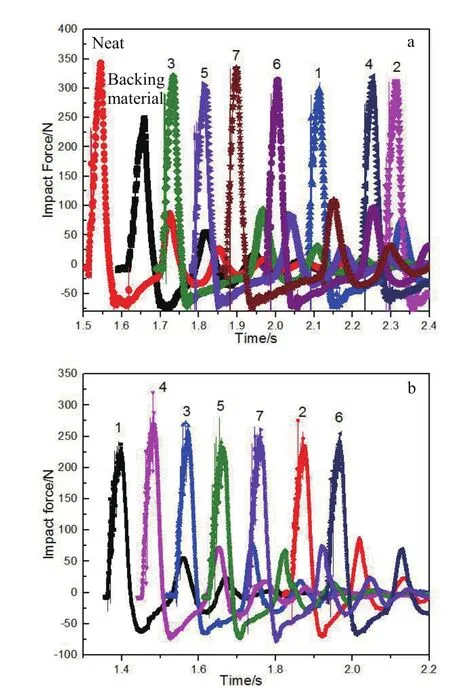
Fig. 2 Dynamic loads for the impact tests of neat and STF-Kevlar composite targetsfor (a) spike, and (b) knife
3.3Stab resistance of different STF-Kevlar systems
Stab resistance of backing material, neat Kevlar fabric and STF-Kevlar impregnated with 7 types of suspensions was explored, as shown in Table 4. stab resistance properties of STF-Kevlar show little difference from that of neat Kevlar fabric. As shown in fig. 2(b), the stab resistances of sample 3,4,6 and 7 are a little larger than that of sample 1, 2 and 5, showing that the introduction of higher concentration alumina silicate fiber has a better effect on improving the stab resistance of STF-Kevlar than Al2O3.
4.Conclusions
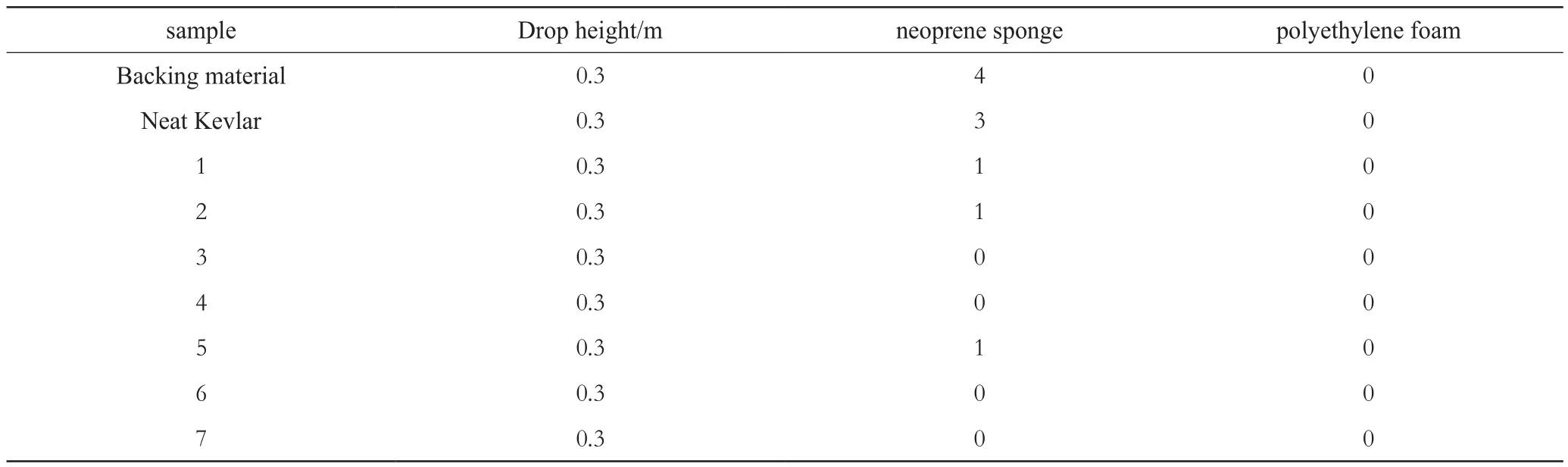
Table 3 Number of penetration layersof different STF-Kevlar systems under spike impact
The dynamic impact resistance of Kevlar fabrics impregnated withSTFs against knife and spike threats were investigated. In the suspensions processed by ball milling and ultrasonic dispersion, decades of different particles form a large quantity of particle clusters; The introduction of alumina silicate fiber and its increase concentration had a bigger effect on enlarging the size of particle clusters. The spike resistance of STF-Kevlar improves obviously than neat Kevlar fabric, and the stab resistance of STFKevlar shows little increase than neat Kevlar fabric.
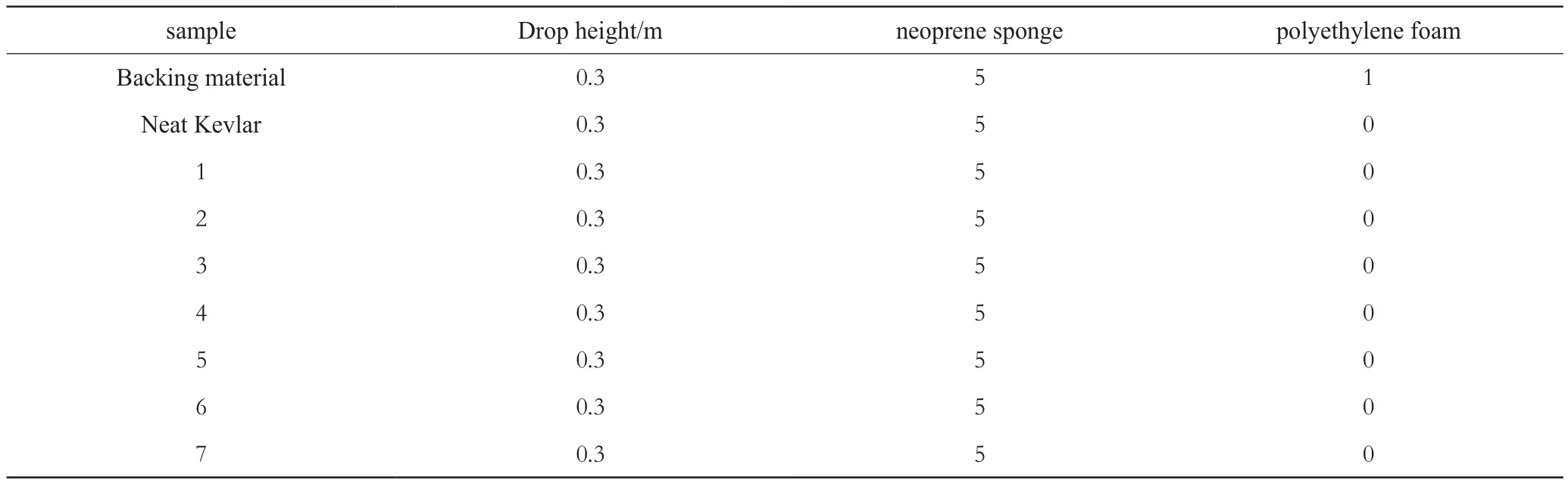
Table 4 Number of penetration layersof different STF-Kevlar systems under spike impact
Acknowledgement
This work is financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 11172142).
References
[1] Ahmad M R, Ahmad W Y W, Salleh J,et al. Effect of fabric stitching on ballistic impact resistance of natural rubber coated fabric systems[J]. Materials & Design, 2008, 29(7): 1353-1358.
[3] LaBarre E D, Calderon-Colon X, Morris M,et al. Effect of a carbon nanotube coating on friction and impact performance of Kevlar[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2015, 50(16): 5431-5442.
[4] Walter T R, Subhash G, Sankar B V,et al. A Novel Method for Dynamic Short-Beam Shear Testing of 3D Woven Composites[J]. Experimental Mechanics, 2013, 53(3): 493-503.
[5] Pankow M, Quabili A, Yen C-F. Hybrid Three-Dimensional (3-D) Woven Thick Composite Architectures in Bending[J]. JOM, 2014, 66(2): 255-260.
[6] Jacob K I, Cook F L, Thadhani N,et al. Demand Activated Toughening in Garments[R]. City, November 2005.
[7] Monteiro S, Louro L, Trindade W,et al. Natural Curaua Fiber-Reinforced Composites in Multilayered Ballistic Armor[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2015, 46(10): 4567-4577.
[8] Bettin G, Deshmukh S S, Mckinley G H. Active controlled energy absorber using responsive fuids[P]. United States, 20070107778. 2007.
[9] Deshmukh S S, McKinley G H. Adaptive energy-absorbing materials using field-responsive fluid-impregnated cellular solids[J]. Smart Materials and Structures, 2007, 16(1): 106-113.
[10] Hasanzadeh M, Mottaghitalab V. The Role of Shear-Thickening Fluids (STFs) in Ballistic and Stab-Resistance Improvement of Flexible Armor[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2014, 23(4): 1182-1196.
[11] Liu J, Xiong D S. The Stab-resistant characteristics of Kevlar woven fabrics impregnated with monodisperse concentrated suspension[J]. BULLETIN OF THE CHINESE CERAMIC SOCIETY, 2010(01): 184-187.
[12] Liu J, Xiong D S, Xiong H C. The Stab-resistant characteristics of Kevlar woven fabrics impregnated with a colloidal shear thickening fuid[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Science and Technology (Natural Science),2010(02): 271-274.
[13] Kalman D P, Merrill R L, Wagner N J,et al. Effect of particle hardness on the penetration behavior of fabrics intercalated with dry particles and concentrated particle-fluid suspensions[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2009, 1(11): 2602-2612.
[14] Lomakin E V, Mossakovsky P A, Bragov A M,et al. Investigation of impact resistance of multilayered woven composite barrier impregnated with the shear thickening fluid[J]. Archive of Applied Mechanics, 2011, 81(12):2007-2020.
[15] Khandavalli S, Rothstein J. Large amplitude oscillatory shear rheology of three different shear-thickening particle dispersions[J]. Rheologica Acta,2015, 54(7): 601-618.
[16] Baharvandi H R, Khaksari P, Kordani N,et al. Analyzing the quasistatic puncture resistance performance of shear thickening fluid enhanced p-aramid composite[J]. Fibers and Polymers, 2014, 15(10): 2193-2200.
[17] Kordani N, Vanini A. Optimizing the ethanol content of shear thickening fluid/fabric composites under impact loading[J]. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 2014, 28(2): 663-667.
[18] Liu J, Xiong D S. The Stab-resistant characteristics of Kevlar woven fabrics impregnated with monodisperse concentrated suspension[J]. BULLETIN OF THE CHINESE CERAMIC SOCIETY.
[19] Ewoldt R, Winter P, Maxey J,et al. Large amplitude oscillatory shear of pseudoplastic and elastoviscoplastic materials[J]. Rheologica Acta, 2010,49(2): 191-212.
Liu Jun, doctoral candidate, Email:xingzhitianxia@163.com. Corresponding author: Xiong Dangsheng, PhD, Professor; E-mail:xiongds@163.com.

