體外培養的人惡性黑色素瘤球體細胞干細胞特性觀察
文輝才,眭云鵬,簡雪平,廖懷偉,馬麗,徐桂珍,劉燕平,萬珺
(南昌大學第一附屬醫院,南昌330006)
?
體外培養的人惡性黑色素瘤球體細胞干細胞特性觀察
文輝才,眭云鵬,簡雪平,廖懷偉,馬麗,徐桂珍,劉燕平,萬珺
(南昌大學第一附屬醫院,南昌330006)
目的觀察體外培養的人惡性黑色素瘤球體細胞的干細胞特性。方法利用無血清培養基培養人惡性黑色素瘤A375細胞系,獲得黑色素瘤球體細胞(球體組)和普通貼壁細胞(貼壁組)。采用Transwell小室檢測兩組細胞遷移能力。采用免疫熒光法檢測兩組細胞中的CD20、CD133。取BALB/c小鼠16只,分實驗組和對照組(各8只),于小鼠肩胛骨處皮下分別注射球體組、貼壁組細胞各1 mL(104個細胞),觀察并比較兩組細胞致瘤能力。6周后處死小鼠,取瘤。結果A375細胞接種于無血清培養基后,可見小的類圓形懸浮細胞球形成并逐漸變大,球內細胞連接緊密,折光性好。球體組細胞遷移能力及細胞中CD20、CD133表達強度均高于貼壁組。注射細胞6周后,實驗組小鼠均長出較大腫瘤,對照組小鼠均未見腫瘤生長。取實驗組小鼠的腫瘤組織行HE染色,病理診斷為惡性黑色素瘤。結論體外培養的人惡性黑色素瘤球體細胞具有干細胞特性,遷移能力和致瘤能力強,高表達免疫標記CD20、CD133,惡性黑色素瘤存在腫瘤干細胞。
黑色素瘤;腫瘤干細胞;無血清培養基
惡性黑色素瘤是起源于皮膚黑色素細胞的高度惡性腫瘤[1],其惡性程度高、易復發、進展快,手術、放療、化療等傳統治療方法療效均較差[2,3],需要尋找新的治療手段[4]。新近研究[5]發現,黑色素瘤細胞體外培養可形成球體細胞,球體細胞形成實驗可富集干細胞。2014年9月~2015年4月,我們以無血清培養基(SFM,由DMEM/F12、10 ng/mL bFGF、B27、20 ng/mL EGF組成)培養惡性黑色素瘤A375細胞系,分離、擴增出黑色素瘤球體細胞并觀察其干細胞特性,現報告如下。
1 材料與方法
1.1主要實驗材料人惡性黑色素瘤A375細胞系購自上海中國科學院細胞庫。BALB/c小鼠均為雌性,體質量18~20 g,4~6周齡,飼養于SPF級環境中。DMEM/F12(1∶1)細胞培養液,優級胎牛血清,0.25%胰酶消化液,B27,堿性成纖維細胞因子(bFGF),表皮生長因子(EGF),超低吸附培養板,超凈工作臺,CO2培養箱。
1.2惡性黑色素瘤球體細胞的獲取與培養A375細胞用含10%胎牛血清的DMEM/F12(1∶1)細胞培養液在37 ℃、5% CO2、飽和濕度條件下培養,當細胞融合達80%時,胰蛋白酶消化細胞,1∶2傳代。取貼壁培養的對數生長期A375細胞用PBS液清洗,胰酶消化,經臺盼藍染色并計數后重懸于SFM中,以1×104/mL接種于6孔超低吸附培養板,放入37 ℃、5% CO2、95%濕度的培養箱中培養。每隔1 d在每孔加入0.5 mL新鮮SFM。培養2周可形成球體細胞,球體細胞形成3~4 d后,收集細胞并機械吹打成單細胞懸液,重懸于SFM,按1∶3比例傳代培養,倒置顯微鏡下觀察細胞形態變化。將球體細胞納入球體組,貼壁細胞納入貼壁組。
1.3惡性黑色素瘤細胞遷移能力檢測將含10%血清的DMEM/F12培養基按600 μL/孔加入到24孔板中,取出Transwell小室放入24孔板中,將貼壁組和球體組細胞在無血清DMEM/F12培養基重懸后加入未鋪膠的小室上層,置入37 ℃孵箱培養12 h,4%多聚甲醛固定20 min,結晶紫染色,用棉簽拭去小室上層細胞,清洗后置于顯微鏡下觀察。
1.4惡性黑色素瘤細胞免疫表型檢測分別將貼壁組和球體組細胞種植于蓋玻片上培養,等細胞爬滿蓋玻片后用4%多聚甲醛固定20 min,PBS洗3次,用0.3% Triton X-100室溫下穿孔,PBS洗3次,3% BSA室溫下封閉,加入熒光素標記的鼠抗人CD133、CD20抗體,DAPI染色,抗淬滅封片劑封片,在激光共聚焦顯微鏡下觀察、照相。
1.5惡性黑色素瘤細胞成瘤實驗取BALB/c小鼠16只,分實驗組和對照組,每組8只。在實驗組和對照組小鼠肩胛骨處皮下分別注射球體組、貼壁組細胞各1 mL(104個細胞)。觀察并比較兩組細胞致瘤能力。6周后處死小鼠,取瘤。
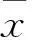
2 結果
A375細胞接種于無血清培養基后2~3 d,大部分細胞死亡崩解,少數細胞存活,懸浮生長,細胞逐漸變大,呈卵圓形或圓形,折光性好,一周后可見小的類圓形懸浮細胞球形成并逐漸變大,球內細胞連接緊密,無法區分細胞間界限,折光性好,新生的單個細胞常以“出芽”方式連接在球體表面。2周時細胞球體積達到最大。見圖1。
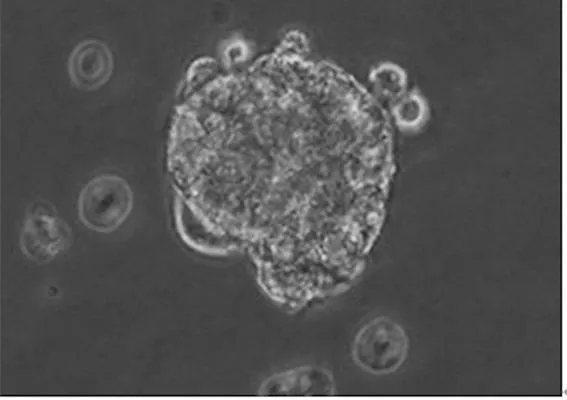
圖1 無血清懸浮培養黑色素瘤球體細胞(200×)
2.1球體細胞遷移能力球體組遷移細胞數目為(158.3±5.0)個/視野、貼壁組為(75.3±4.4)個/視野,兩組相比,P<0.05。
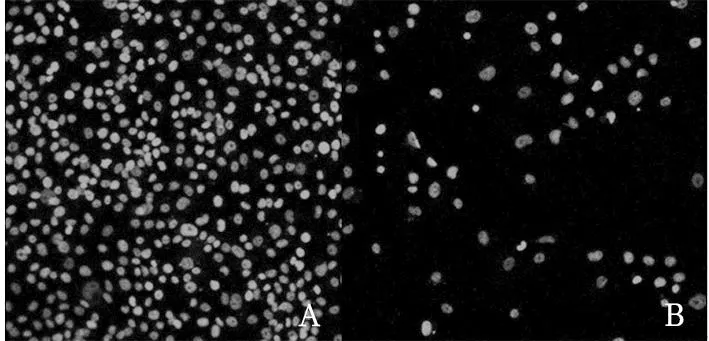
2.2球體細胞CD20、CD133表達情況球體組與貼壁組細胞中均檢測到CD20、CD133,且球體組細胞CD20、CD133表達強度高于貼壁組細胞。見圖2、3。
2.3球體細胞致瘤能力實驗組小鼠注射球體組細胞后2周看到有腫瘤凸起皮面,對照組小鼠未見腫瘤形成。注射細胞6周后,實驗組小鼠均長出較大腫瘤,對照組小鼠均未見腫瘤生長(見圖4)。取實驗組腫瘤組織,病理診斷為惡性黑色素瘤。
注:A為球體組細胞,B為貼壁組細胞。
圖2球體組與貼壁組細胞中CD20表達情況
注:A為球體組細胞,B為貼壁組細胞。
圖3球體組與貼壁組細胞中CD133表達情況
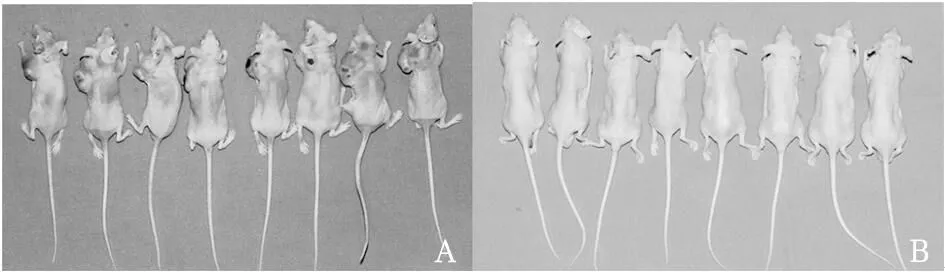
注:A為實驗組,B為對照組。
圖4實驗組與對照組小鼠注入細胞6周后瘤體形成情況
3 討論
腫瘤干細胞具有很強的分化潛能和自我更新能力,具有耐藥性,是腫瘤增殖、轉移、復發的重要原因[6,7]。Fang等[8]用人胚胎干細胞的培養基培養原代惡性黑色素瘤細胞,發現約20%的惡性黑色素瘤細胞能形成懸浮腫瘤球,這些懸浮球體細胞具有可塑性[9],能在適當培養條件下分化成多種類型的細胞,如骨細胞[10]、軟骨細胞[11]、脂肪細胞[12]等。Mansur等[13]從惡性黑色素瘤中分離出表達CD133的細胞亞群,并發現所有的CD133陽性細胞均可在NOD/SCID小鼠體內成瘤,而CD133陰性細胞則不能成瘤。上述研究成果提供了惡性黑色素瘤干細胞存在的直接證據。
腫瘤干細胞研究的首要工作是分離出腫瘤干細胞[14]。最新研究[15]證實,含EGF和bFGF的SFM可分離出各種實體瘤的腫瘤干細胞。我們利用含EGF、bFGF和B27添加劑的SFM分離人惡性黑色素瘤A375細胞系的腫瘤干細胞,結果顯示,A375細胞在SFM中能夠形成球體細胞,延長培養時間,球體細胞數量可增多、體積增大,證實無血清環境能刺激腫瘤干細胞分裂增殖。
腫瘤細胞遷移性越強,轉移能力也就越強[16]。我們通過Transwell小室檢測球體組與貼壁組細胞的遷移能力,結果顯示球體組細胞遷移能力明顯強于貼壁組。CD20是B細胞表面常見的標志物,CD20陽性的黑色素瘤細胞具備腫瘤干細胞的特征。CD133廣泛存在于實體瘤干細胞表面,為腦腫瘤、結腸癌、急性粒細胞性白血病的腫瘤起始細胞表面標志物。球體組細胞與貼壁組細胞均可表達CD20、CD133,且球體組細胞表達強度更高,這進一步表明黑色素瘤A375細胞中存在腫瘤干細胞,其遷移能力更強。我們將兩種細胞分別注入BALB/c小鼠皮下,發現注射細胞6周后實驗組小鼠均成瘤,而對照組小鼠無一成瘤,取實驗組小鼠腫瘤組織行HE染色,均證實為惡性黑色素瘤,這提示富集干細胞的球體細胞比普通貼壁細胞具有更強的致瘤能力。我們認為,無血清培養的人惡性黑色素瘤球體細胞具有干細胞特性,遷移能力和致瘤能力強,惡性黑色素瘤存在腫瘤干細胞。這為惡性黑色素瘤的治療提供了新的研究方向。
[1] 許磊,李文鹿,成雨生,等.口腔頜面部惡性黑色素瘤39例臨床分析[J].實用口腔醫學雜志,2013,29(6):803-806.
[2] 郜亮,馮向先.Toll樣受體4在惡性黑色素瘤中的表達及其介導腫瘤免疫逃逸的機制[J].中華實驗外科雜志,2015,32(6):1387-1390.
[3] 蔡媛,蔡云,王楠斌,等.上腭原發惡性黑色素瘤伴乳腺轉移的臨床病理特征及文獻復習[J].臨床與實驗病理學雜志,2013,29(5):486-489.
[4] 岳冬麗,韓交玲,關方霞,等.腫瘤干細胞的研究進展及臨床意義[J].鄭州大學學報(醫學版),2013,48(1):1-8.
[5] Simoes BM,Alferez D,Howell S,et al.The role of steroid hormones in breast cancer stem cells[J].Endocr Relat Cancer,2015,35(7):87-93.
[6] Zhao Z,Li S,Song E,et al.The roles of ncRNAs and histone-modifiers in regulating breast cancer stem cells[J].Protein Cell,2015,27(6):809-813.
[7] Ambrosini G,Sawle AD,Musi E,et al.BRD4-targeted therapy induces Myc-independent cytotoxicity in Gnaq/11-mutatant uveal melanoma cells[J].Oncotarget,2015,35(30):325-330.
[8] Fang D,Nguyen TK,Leishear K,et al.A tumorigenic subpopulation with stem cell properties in melanomas[J].Cancer Res,2005,65(20):9328-9337.
[9] Roux J,Pages C,Malouf D,et al.BRAF inhibitor rechallenge in patients with advanced BRAF V600-mutant melanoma[J].Melanoma Res,2015,29(5):89-93.
[10] Figueiredo CR,Matsuo AL,Azevedo RA,et al.A novel microtubule de-stabilizing complementarity-determining region C36L1 peptide displays antitumor activity against melanoma in vitro and in vivo[J].Sci Rep,2015,5(20):143-150.
[11] Stanojevic I,Miller K,Kandolf-Sekulovic L,et al.A subpopulation that may correspond to granulocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells reflects the clinical stage and progression of cutaneous melanoma[J].Int Immunol,2015,30(8):85-90.
[12] Charepalli V,Reddivari L,Radhakrishnan S,et al.Anthocyanin-containing purple-fleshed potatoes suppress colon tumorigenesis via elimination of colon cancer stem cells[J].J Nutr Biochem,2015,31(9):75-80.
[13] Mansur AT,Demirci GT,Ozel O,et al.Acral melanoma with satellitosis,disguised as a longstanding diabetic ulcer: a great mimicry[J].Int Wound J,2015,51(9):65-70.
[14] Tsao CY,Sabbatino F,Cheung NV,et al.Anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic activity of GD2 ganglioside-specific monoclonal antibody 3F8 in human melanoma cells[J].Oncoimmunology,2015,4(8):e1023975.
[15] Naldi L,Cazzaniga S.Are All Screening Programmes Created Equal? The Case of Melanoma[J].Dermatology,2015,41(6):165-170.
[16] Haymaker CL,Wu RC,Ritthipichai K,et al.BTLA marks a less-differentiated tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte subset in melanoma with enhanced survival properties[J].Oncoimmunology,2015,4(8):e1014246.
Stem cell characteristics of human malignant melanoma sphere cells cultured in vitro
WEN Huicai,SUI Yunpeng,JIAN Xueping,LIAO Huaiwei,MA Li,XU Guizhen,LIU Yanping,WAN Jun
(The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University,Nanchang 330006,China)
ObjectiveTo observe the stem cell properties of human malignant melanoma cells cultured in serum-free medium.MethodsHuman malignant melanoma A375 cell line was cultured in serum-free medium,and the melanoma sphere cells (sphere group) and common adherent cells (adherent group) were obtained.Cell migration was detected using Transwell chamber.CD20 and CD133 were detected by immunofluorescence.Sixteen BALB/c mice were divided into the experimental group and control group (8 rats in each group),and the sphere cells and the adherent cells of 1 mL (104) were injected into the mouse shoulder blade by subcutaneous injection in the sphere and the adherent groups,respectively.The tumor cells were observed and compared between the two groups.Six weeks later,the mice were killed to obtain the tumor tissues.ResultsA375 cells were seeded in serum-free medium,visible small round ball suspension cells formed and gradually becomes larger,the ball inside the cells were closely connected with good refraction.The cell migration ability and the expression intensity of CD20 and CD133 in the sphere group were higher than those in the adherent group.After 6 weeks of injection,the mice in the experimental group had a large tumor,and no tumor growth was found in the control group.The tumor tissues of the experimental group were stained with HE,and the malignant melanoma was pathologically diagnosed.ConclusionsHuman malignant melanoma cells cultured in serum-free medium have the characteristics of stem cells with high migration ability and tumorigenesis.High expression of immune markers CD20,CD133 is found and malignant melanoma exists in the tumor stem cells.
melanoma; tumor stem cells; serum-free medium
江西省科技支撐計劃項目(2010BSA14600)。
文輝才(1973-),男,醫學博士,副主任醫師,副教授,碩士生導師,主要研究方向為皮膚體表腫瘤、器官再造,改臉型。E-mail: whcjxmc@163.com
10.3969/j.issn.1002-266X.2016.19.007
R739.5
A
1002-266X(2016)19-0022-03
2015-12-14)

