Vehicle routing problem for save fuel consumption
LIU+Hao+AI+Wen-wen
【Abstract】This study has extended a vehicle routing problem,by considering economy of fuel,and constructing a LF-VRP model,to obtain optimal fixed costs.Our objective was to minimize not only distance,but also the fuel consumption.A example were developed to solve the proposed models.It was found that our proposed models yielded better results than the traditional VRP models.
【Key words】VRP; Fixed costs; Fuel consumption
1 Introduction
With rapid development of economy and continuous improvement of people's living standard,especially under background of rapid development of global e-commerce,consumers seek more quality product,thus promoted development of logistics.Transport costs mainly refers to use of fuel cost of vehicles transporting goods,as international oil prices rising,fuel costs will gradually increase,ratio also will continue to increase.In recent years,National Development and Reform Commission have also unveiled a relevant policies,and actively promote transportation industry towards a low carbon emission reduction,direction of the development of environmental protection and energy saving[1].
In this paper,we from actual logistics business point of view,and consider vehicle fuel consumption.We refer to this problem as the Low Fuel-Vehicle Routing Problem(LF-VRP).
2 Method
The Vehicle Routing Problem(VRP) is central to road transportation planning and aims at routing a fleet of vehicles on a given network to serve a set of customers under side constraints[2].
2.1 Improve model
This study used Mehrsa Ehsani[3] proposed mechanical model,and we improve it.We only consider fuel consumed due to rolling resistance Ur,and aerodynamic resistance Ud, simplified model formula is:
Among it,F(xiàn) was fuel consumption;γk was fuel conversion efficiency;Cv was the fuel calorific value; ρk was fuel density.Where F can sum results by Fij which compute fuel consumption between two customers i and j.We find Fij is decided by three variable parameters Qi,dij,and vij.So this model can be written as:
In formula,we set G1dij=(CrgΦtλsrQ+0.5ρa(bǔ)AfCdφv2ij)evηm/Cvρkl is No-Load Fuel Consumption (N-LFC) by parameter vij and dij;and set G2Qidij=CrgΦtλsevηm/Cvρkl is Load-Dependent Fuel Consumption (L-DFC) by parameter Qi and dij。
2.2 Parameters
In our paper,we use Foton Aumark ISF 2.8,rQ=2500kg,Af=5m2,Ck=4t,Displacement 2.8L,fuel consumption is 8L/100km[4],and take best fuel consumption speed of 44km/h[2,5].we used other parameters in[3].So the model we studied only had two variable parameters Qi and dij,and we can estimated by following formula:
3 Computational analysis
In this section,we use a four-node instance to show differences between problems VRP and LF-VRP,and we also study effect of distance.
3.1 Relation
In LF-VRP model,there are three variable parameters Qi,vij and dij.If we ignored load change Qi=0,constant speed vij=v,LF-VRP is equivalent to VRP,which only one variable parameter dij.The proof is as follows:
Since G is constant,regardless of VRP.Therefore,fuel consumption model is equivalent to classic model of VRP,we prove that LF-VRP is VRP 's generalization.
3.2 Compare
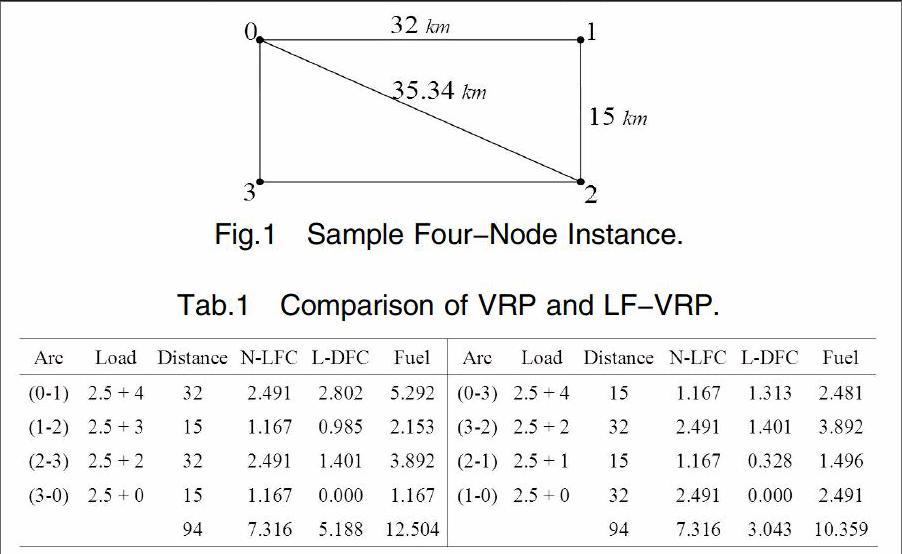
We consider four node network of Fig.1.We assume that there is a single vehicle based at node 0 to serve customers 1,2 and 3.we assume a uneven demand pattern as q1=1,q2=1 and q3=2(in t).
First,we examine gap of fuel between this model and combined fuel consumption.For example,in order to a distance of 94km,combined fuel consumption is about 7.52L,and no-load vehicle fuel consumption in this model is 7.316L,gap is 0.204L.It is felt that this model can effectively simulate actual vehicle when fuel consumption amount.
The distance-minimizing objective VRP yields two optimal tours,(0,1,2,3,0) and (0,3,2,1,0) of length 94km.In terms of fuel,however,former tour consumes 12.504L whereas latter requires 10.359L.Not surprisingly,a weighted load-minimizing objective of LF-VRP yields latter tour as optimal solution,with a saving of 20.71% in consumption with respect to former.
3.3 Analysis
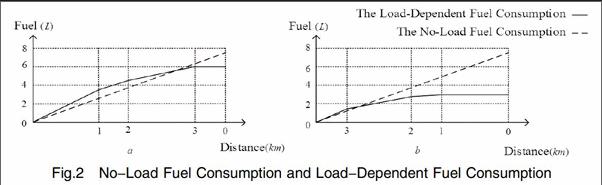
Reference to above two examples,we can clearly demonstrate advantages of this model,and differences from model of the VRP.We examine role of three key characteristics of LF-VRP model:(a) No-Load Fuel Consumption,(b)Load-Dependent Fuel Consumption.
From Fig.2,a and b were given by Section 3.2.We observe following tendency: As expected,the higher demand deviation,the higher weighted distance savings achieved by consideration of LF-VRP model.In other words,when cargo weight has an important contribution to overall objective,the higher the deviation of the required customer quantities,the stronger effectiveness of LF-VRP model on minimizing weighted distance objective.
4 Conclusions
The examined problem,called Low Fuel-Vehicle Routing Problem(LF-VRP),is best suited for heavy-duty transportation logistics activities where transported cargo weight significantly contributes to gross weight of vehicles.Contrary to classic distance objective,LF-VRP calls for minimization of product of total distance travelled and gross weight carried along this distance.The aforementioned objective function is capable of producing sensible solution structures which take into account variation of vehicle load along designed trips.In addition,LF-VRP objective provides a basis for minimizing total energy requirements of vehicle fleet and consequently total fuel consumption.Thus,LF-VRP constitutes an optimization model which is appropriate for cases where environmental consequences of transportation activities are taken into consideration.
【References】
[1]Mehrsa E,Abbas A,Dawud F.Modeling of vehicle fuel consumption and carbon dioxide emission in road transport[J].Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2016(53):1638-1648.
[2]Bektas T,Laporte G.The Pollution-Routing Problem[J].Transportation Research Part B 2011(45):1232-1250.
[3]Mehrsa E,Abbas A,Dawud F.Modeling of vehicle fuel consumption and carbon dioxide emission in road transport[J].Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2016,(53):1638-1648.
[4]FOTON official website.http://aumark.foton.com.cn/.
[5]Emmanouil E Z,Christos D T,Chris T K.Load-dependent vehicle routingproblem and its pick-up and delivery extension[J].Transportation Research Part B 2015(71):158-181.
[責(zé)任編輯:湯靜]

