基于MRI健康成人丘腦的形態測量
張華,謝興國,黃小華,肖如輝,白桂芹
( 1.川北醫學院人體解剖學教研室; 2.川北醫學院附屬醫院放射科,四川南充 637000)
?
基于MRI健康成人丘腦的形態測量
張華1,謝興國1,黃小華2,肖如輝2,白桂芹1
( 1.川北醫學院人體解剖學教研室; 2.川北醫學院附屬醫院放射科,四川南充637000)
【摘要】目的:探討MRI丘腦與毗鄰結構形態學變化規律和意義,為與丘腦形態改變相關的疾病提供線性測量指標方法:利用成人活體頭部MRI掃描資料,觀測丘腦及其毗鄰結構,分析各線性指標與丘腦面積、丘腦體積的相關性。結果:在斷層標本上采用單因素方差分析顯示:丘腦矢徑、丘腦寬、丘腦面積性差和側差未見顯著性差異;丘腦橫徑、丘腦長側差未見顯著性差異,但其性差差異性顯著( P<0. 05)。方差齊性檢驗后Pearson相關分析顯示:丘腦長與殼橫徑、殼矢徑、殼面積、尾狀核頭矢徑成正相關,丘腦寬與尾狀核頭矢徑負相關,丘腦矢徑、丘腦長與側腦室前角間距成負相關。在體積測量中標準化后各組樣本采用單因素方差分析顯示:丘腦體積、尾狀核頭橫徑、尾狀核頭矢徑及殼矢徑左、右側差異顯著(左側>右側,P<0. 05),其余各數據無顯著性差異。標準化后與丘腦體積相關程度最為密切的線性指標分別是丘腦橫徑、丘腦矢徑、丘腦長、丘腦寬(正相關)。結論:丘腦毗鄰結構參數與丘腦參數存在線性關系,其毗鄰結構的形態變化可作為研究丘腦形態變化的參考指標,丘腦橫徑、丘腦矢徑、丘腦長、丘腦寬可作為丘腦形態變化的初篩指標。
【關鍵詞】丘腦形態;線性指標;磁共振成像
網絡出版時間: 2016-3-4 10∶16網絡出版地址: http: / /www.cnki.net/kcms/detail/51.1254.R.20160304.1016.040.html
丘腦是間腦中最大的一部分,纖維聯系極為廣泛,是最大的皮質下接受站、中繼站以及信息管理的協調中樞。近年來,隨著醫學影像學技術特別是MRI技術的進步,許多學者研究并探討了丘腦的形態學變化與精神類疾病如精神分裂癥[1]、阿爾茨海默病[2]等疾病的關系。
以往研究多采用低場強MRI[3-4],分辨率不高;且邊界劃分標準不一,因此所獲結果大多相差較大。體積的手動測量耗時耗力且易受操作者主觀意識影響,因而不利于臨床推廣。因此本研究采用場強較高的GE 3.0 T核磁共振儀進行掃描,采用容積再現技術( volume render,VR)從冠狀位、水平位、矢狀位三個方位對丘腦進行觀測;研究丘腦等結構的線性指標與丘腦面積、體積的相關性,以期為相關疾病的診斷提供相關測值和形態學依據。
1 材料與方法
1.1斷面觀測
1.1.1研究對象選取100例(男性50例,女性50例)經常規MR序列掃描證明無病變成年人,年齡17~60歲,平均年齡40歲,漢族,右利手,經簡易精神狀態量表檢查無異常。排除標準:有神經異常史、精神病家族史、酗酒或藥物依賴,有明顯醫學或神經病史、或有頭部外傷史等,過度肥胖或發育不良,其他不能完成心理測試者。
1.1.2掃描參數使用美國GE Signa HDxt 3. 0 T MRI系統,頭部正交8通道相控陣線圈,掃描野包含整個大腦。采用三維快速擾相梯度回波序列( threedimensional fast spoiled gradient-recalled,3D-FSPGR)獲得高分辨率軸位三維結構圖像,掃描參數: TR 8. 3 ms,TE 3. 3 ms,TI 400 ms,掃描視野( FOV) 24 cm× 24 cm,矩陣256×256,Nex 1,翻轉角( FA) 15°,層數156層,層厚1 mm,無間隔連續掃描。選取丘腦結構顯示較佳的MRI斷層圖像,傳入ADW4. 2圖像處理工作站進行觀測。
1.1.3數據測量選取丘腦及其毗鄰結構顯示較佳的室間孔層面,測量丘腦、尾狀核頭、殼等興趣結構的橫徑、矢徑和面積,側腦室前角間距等。為減少誤差,對所測結構測量3次并取其平均值。為消除頭顱個體差異影響,對測得的丘腦等全部原始數據經標準化處理。
1.2體積測量
1.2.1受試者42例經常規MR序列掃描證明無病變成年人(男性8例,女性34例),右利手,漢族,年齡17~60歲,平均年齡30歲,經簡易精神狀態量表檢查無異常。其排除標準同上。
1.2.2掃描參數使用GE 3.0T核磁共振儀對受試者行垂直于丘腦長軸的斜冠狀位掃描,3D BRAVO序列采集,參數為: TE 3. 2 ms,TR 8. 4 ms,TI 450 ms,掃描視野( FOV) 24 cm×24 cm,矩陣224×224,層厚1 mm,掃描連續無間隔。所得數據傳入ADW 4. 2圖像處理工作站。
1.2.3數據測量在工作站上于斜冠狀位逐層勾畫丘腦輪廓,得出單層面積,然后與層厚相乘得出單層體積,逐層體積相加即丘腦總體積。
線性測量指標包括:丘腦、尾狀核頭、殼等興趣結構的橫徑、矢徑,側腦室前角間距,顱腔上下徑、顱腔前后徑、顱腔左右徑。其中顱腔上下徑為正中矢狀位上經中腦導水管枕骨大孔后緣到頂骨板障間距,前后徑為正中矢狀位上胼胝體下緣前后顱骨板障間距,左右徑為水平位上過中腦導水管中點的左右顱骨板障間距。
為了消除個體頭顱大小的影響,所得數據均進行標準化。其公式為:

其中顱腔體積為顱腔上下徑、顱腔左右徑、顱腔前后徑之乘積。
1.2.4邊界劃分參照Nugent等[5-6]方法將丘腦邊界定義如下。前方以乳頭體和室間孔為界,后界為丘腦出現在穹窿交叉下方的層面。由于其腹前下方的核團與下丘腦相鄰,外側、上方、內側分別與內囊、側腦室以及第三腦室相鄰,因此上述四個方位的邊界可依此確定(圖1)。
1.3統計學分析
運用SPSS 22. 0統計軟件對所得數據進行分析處理,各樣本采用方差分析及Pearson相關分析。
2 結果
2.1丘腦的斷層數據
丘腦及毗鄰結構測值見表1-2。各組樣本采用單因素方差分析顯示:丘腦矢徑、丘腦寬、丘腦面積性差和側差未見顯著性差異;丘腦橫徑、丘腦長側差未見顯著性差異,但其性差具有統計學意義( P<0. 05)。方差齊性檢驗后利用Pearson相關分析顯示:丘腦長與殼橫徑、殼矢徑、殼面積及尾狀核頭矢徑成正相關,丘腦寬與尾狀核頭矢徑成負相關,丘腦矢徑、丘腦長與側腦室前角間距成負相關。更多分析見表3。
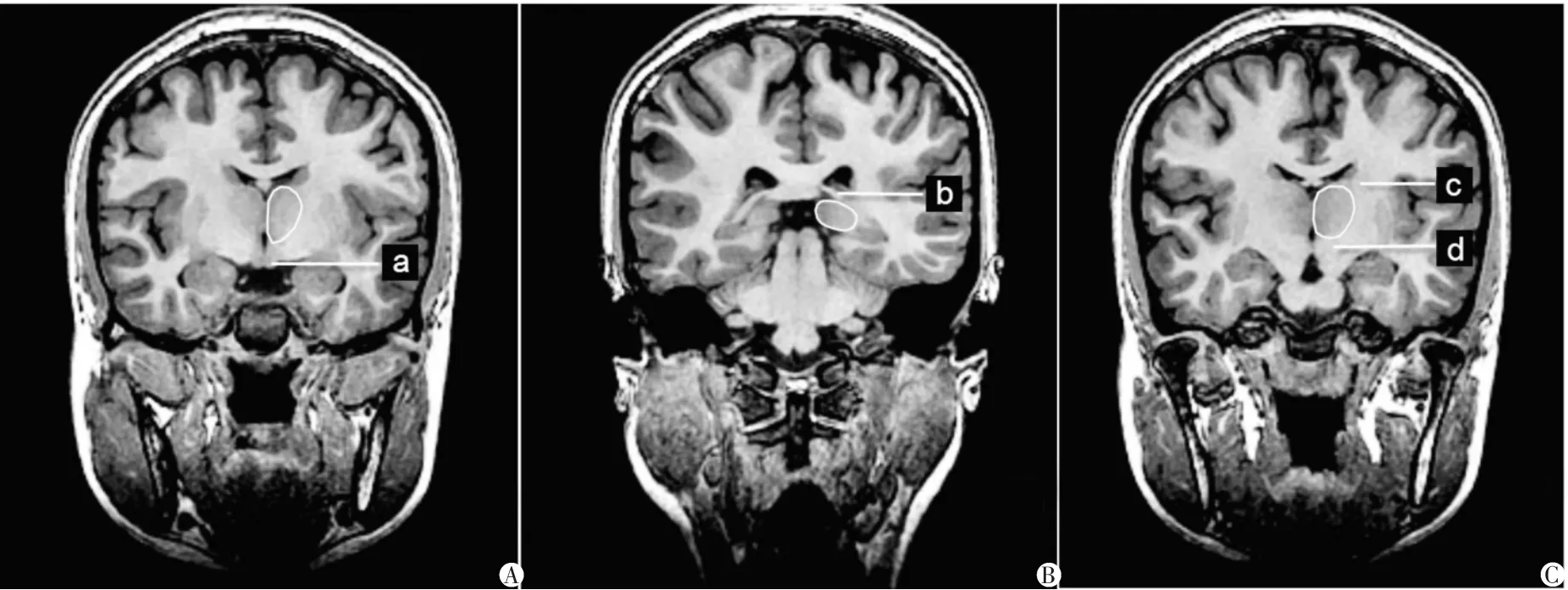

圖1 MRI斜冠狀位示健康成人丘腦邊界勾畫A. a為乳頭體; B. b為穹窿交叉; C. c為內囊,d為下丘腦。
2.2丘腦的體積數據
各組數據統計如表4-5所示,各組樣本采用單因素方差分析顯示:丘腦體積、尾狀核頭橫徑、尾狀核頭矢徑及殼矢徑左、右側差異顯著(左側>右側,P<0. 05),其余各數據未見顯著性差異。表6為Pearson相關性分析,結果顯示標準化后與丘腦體積相關程度最為密切的線性指標分別是丘腦橫徑、丘腦矢徑、丘腦長、丘腦寬(正相關)。
表1 丘腦的數據測量(±s)
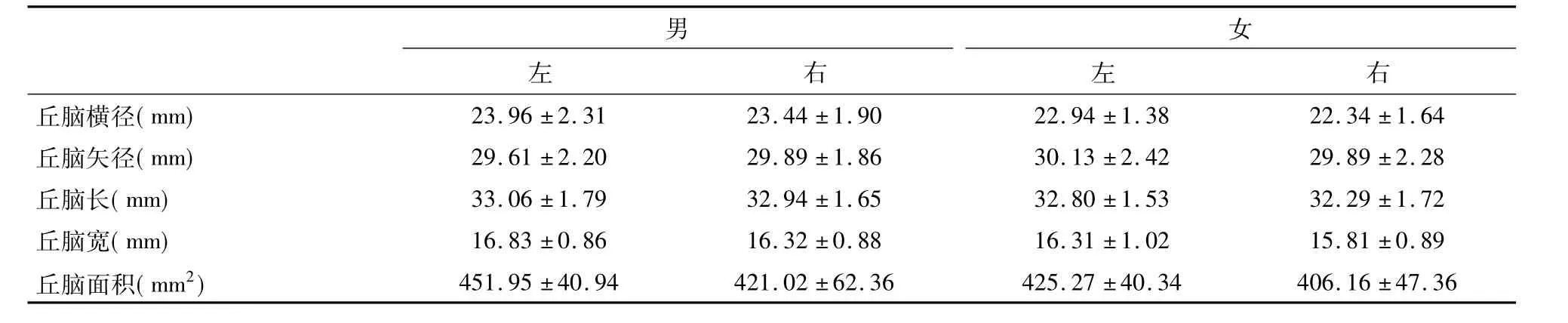
表1 丘腦的數據測量(±s)
男女左右左右丘腦橫徑( mm) 23.96±2.31 23.44±1.90 22.94±1.38 22.34±1.64丘腦矢徑( mm) 29.61±2.20 29.89±1.86 30.13±2.42 29.89±2.28丘腦長( mm) 33.06±1.79 32.94±1.65 32.80±1.53 32.29±1.72丘腦寬( mm) 16.83±0.86 16.32±0.88 16.31±1.02 15.81±0.89丘腦面積( mm2) 451.95±40.94 421.02±62.36 425.27±40.34 406.16±47.36
表2 丘腦毗鄰結構測量數據(±s)

表2 丘腦毗鄰結構測量數據(±s)
男女左右左右尾狀核頭橫徑( mm) 13.58±1.36 13.64±1.47 12.75±1.24 13.27±1.38尾狀核頭矢徑( mm) 22.40±1.84 22.14±2.04 20.77±1.99 20.59±2.30尾狀核頭面積( mm2) 155.75±22.36 148.79±20.64 140.82±19.40 142.34±23.24殼橫徑( mm) 13.71±1.71 13.28±2.60 13.26±2.26 12.03±1.95殼矢徑( mm) 37.89±3.40 38.10±3.63 35.38±3.69 34.26±3.41殼面積( mm2) 293.56±40.65 284.16±48.90 248.29±50.88 229.01±47.5側腦室前角間距( mm)34.31±3.45 32.17±2.59
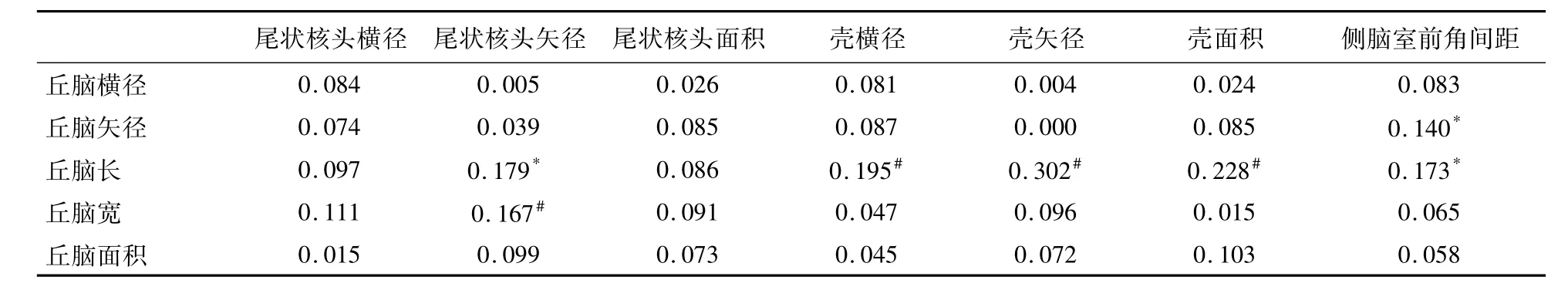
表3 丘腦與其毗鄰結構間的相關性分析
表4 丘腦的數據測量(±s)
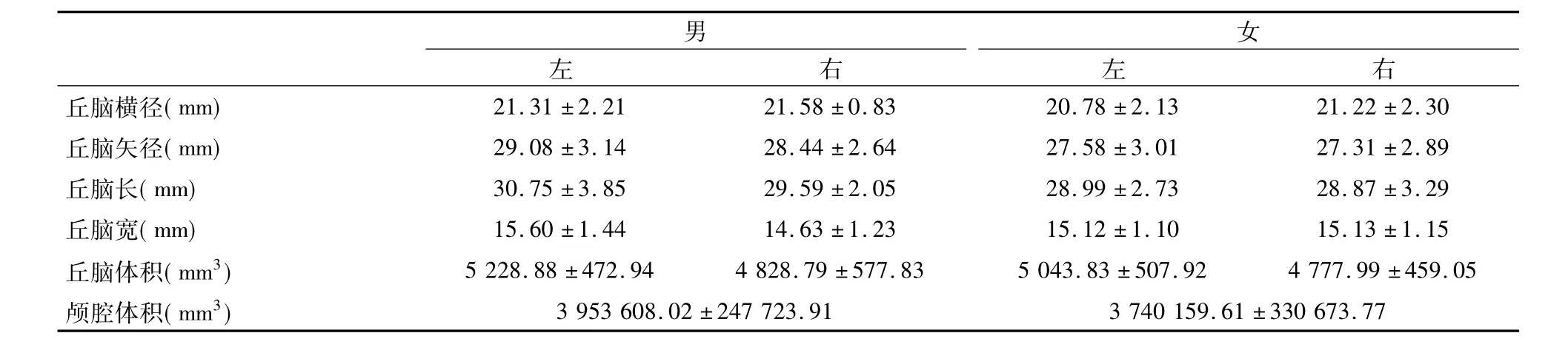
表4 丘腦的數據測量(±s)
男女左右左右丘腦橫徑( mm) 21.31±2.21 21.58±0.83 20.78±2.13 21.22±2.30丘腦矢徑( mm) 29.08±3.14 28.44±2.64 27.58±3.01 27.31±2.89丘腦長( mm) 30.75±3.85 29.59±2.05 28.99±2.73 28.87±3.29丘腦寬( mm) 15.60±1.44 14.63±1.23 15.12±1.10 15.13±1.15丘腦體積( mm3) 5 228.88±472.94 4 828.79±577.83 5 043.83±507.92 4 777.99±459.05顱腔體積( mm3) 3 953 608.02±247 723.91 3 740 159.61±330 673.77
表5 丘腦毗鄰結構測量數據(±s)

表5 丘腦毗鄰結構測量數據(±s)
男女左右左右尾狀核頭橫徑( mm) 13.37±1.30 14.57±1.16 13.04±1.39 14.77±1.25尾狀核頭矢徑( mm) 18.19±1.70 17.21±1.47 18.64±1.86 19.20±1.73殼橫徑( mm) 13.63±1.03 13.92±1.38 13.51±1.83 13.76±1.89殼矢徑( mm) 38.34±5.58 37.02±3.88 36.46±3.58 35.02±3.66側腦室前角間距( mm)31.11±2.74 29.60±1.90
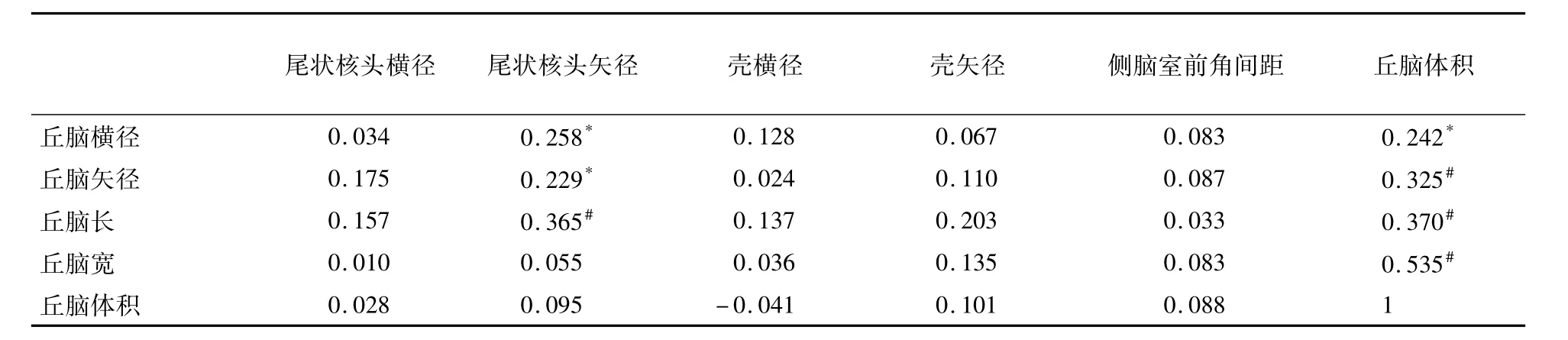
表6 丘腦與其毗鄰結構間的相關性分析
3 討論
3.1數據采集及分析
隨著年齡的增長,丘腦等顱內結構的體積均發生改變,尤其是在某些精神疾病的發生與發展過程中,丘腦的體積常發生變化。Pedro等[7]在研究中度阿爾茨海默病合并遺忘性輕度認知損傷時發現,在遺忘性輕度認知損傷中患者雙側丘腦出現萎縮。Batista等[8]在研究多發性硬化癥( multiple sclerosis,MS)時發現,與正常對照組相比,MS患者信息處理速度明顯減慢,丘腦等核團體積明顯減小。因此測量健康成人丘腦體積獲得其正常參考值對上述疾病等的臨床診斷和研究有著重要意義。
3.2側差和性差
在斷層研究中顯示丘腦矢徑、丘腦寬、丘腦面積性差和側差未見顯著性差異;丘腦橫徑、丘腦長側差未見顯著性差異,但其性差具有統計學意義( P<0. 05)。手動測量丘腦體積等參數時顯示丘腦體積、尾狀核頭橫徑、尾狀核頭矢徑及殼矢徑左、右側差異顯著(左側>右側,P<0. 05)。Xie等[9]在研究健康青少年和兒童中性別、年齡及智力與腦干、丘腦的關系時發現,年齡的變化可預計丘腦的體積變化,在男性和女性中右側丘腦的體積明顯大于左側丘腦,且在女性中更明顯。在成人中,Sullivan等[10]研究顯示標準化后左、右側丘腦體積無性別差異。Keller等[11]在比較Freesurfer與體視學測量丘腦體積一致性時發現左、右側丘腦體積無差異。本研究與上述研究結果有偏差,出現差異的原因可能是掃描時采取的場強不同、邊界確定的解剖標志不一樣以及樣本量的不同等。
3.3相關性分析與臨床意義
丘腦是皮質-紋狀體-丘腦環的重要組成部分,與大腦皮質間、錐體外系間有往返纖維聯系。疾病的出現影響丘腦結構時,丘腦形態的變化可來自于相關結構的形態變化,也可由毗鄰結構形態變化引起。Lenglet等[12]研究發現,蒼白球、左側黑質與丘腦聯系緊密,底丘腦核也與丘腦存在聯系。deJong等[13]研究指出,在阿爾茨海默癥中除了有觀察到的海馬萎縮與認知功能降低之外,患者殼與丘腦的體積明顯減小。本研究斷層結果顯示丘腦長與尾狀核頭矢徑、殼橫徑、殼矢徑、殼面積成正相關,丘腦寬與尾狀核頭矢徑負相關,提示紋狀體的形態學變化可以作為研究丘腦形態學變化的參考指標。
側腦室擴大是精神分裂癥中最早出現的腦結構改變之一,其擴大的原因可能與疾病發生時臨近核團縮小有關。Gaser等[14]研究發現,精神分裂癥中側腦室擴大可能與丘腦萎縮特別是臨近中間核、相鄰皮層以及島皮質區域的萎縮相關。Horga等[15]研究表明,在精神分裂癥中側腦室的擴大與丘腦部分核團如丘腦枕等的體積減小有關。本研究采集部分相關線性指標,并與丘腦體積進行相關性分析,結果顯示:側腦室前角間距與丘腦體積相關性不顯著;丘腦橫徑、丘腦矢徑、丘腦長、丘腦寬與丘腦體積呈正相關,可以作為丘腦形態變化的初篩指標。因此在以后的研究中可以對側腦室進行整體研究,或許能發現其形態改變與丘腦形態改變的相關性。
參考文獻
[1]Kumari V,Gudjonsson GH,Raghuvanshi S,et al.Reduced thalamic volume in men with antisocial personality disorder or schizophrenia and a history of serious violence and childhood abuse[J].Eur Psychiatry,2013,28( 4) : 225-234.
[2]Ryan NS,Keihaninejad S,Shakespeare TJ,et al.Magnetic resonance imaging evidence for presymptomatic change in thalamus and caudate in familial Alzheimer’s disease[J].Brain,2013,136 ( Pt 5) : 1399-1414.
[3]Vassal F,Coste J,Derost P,et al.Direct stereotactic targeting of the ventrointermediate nucleus of the thalamus based on anatomic 1. 5-T MRI mapping with a white matter attenuated inversion recovery ( WAIR) sequence[J].Brain Stimul,2012,5( 4) : 625-633.
[4]馬帥,陳楠,秦媛,等.中國健康成人丘腦體積與年齡的相關性[J].中國醫學影像技術,2012,( 1) : 19-22.
[5]Nugent AC,Luckenbaugh DA,Wood SE,et al.Automated subcortical segmentation using FIRST: test-retest reliability,interscanner reliability,and comparison to manual segmentation[J].Hum Brain Mapp,2013,34( 9) : 2313-2329.
[6]Focke NK,Trost S,Paulus W,et al.Do manual and voxel-based morphometry measure the same? A proof of concept study[J].Front Psychiatry,2014,5: 39.
[7]Pedro T,Weiler M,Yasuda CL,et al.Volumetric brain changes in thalamus,corpus callosum and medial temporal structures: mild Alzheimer’s disease compared with Amnestic mild cognitive impairment[J].Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord,2012,34 ( 3-4) : 149-155.
[8]Batista S,Zivadinov R,Hoogs M,et al.Basal ganglia,thalamus and neocortical atrophy predicting slowed cognitive processing in multiple sclerosis[J].J Neurol,2012,259( 1) : 139-146.
[9]Xie Y,Chen YA,De Bellis MD.The relationship of age,gender,and IQ with the brainstem and thalamus in healthy children and adolescents: a magnetic resonance imaging volumetric study[J].J Child Neurol,2012,27( 3) : 325-331.
[10]Sullivan EV,Rosenbloom M,Serventi KL,et al.Effects of age and sex on volumes of the thalamus,pons,and cortex[J].Neurobiol Aging,2004,25( 2) : 185-192.
[11]Keller SS,Gerdes JS,Mohammadi S,et al.Volume estimation of the thalamus using freesurfer and stereology: consistency between methods[J].Neuroinformatics,2012,10( 4) : 341-350.
[12]Lenglet C,Abosch A,Yacoub E,et al.Comprehensive in vivo mapping of the human basal ganglia and thalamic connectome in individuals using 7T MRI[J].PLoS One,2012,7( 1) : e29153.
[13]de Jong LW,van der Hiele K,Veer IM,et al.Strongly reduced volumes of putamen and thalamus in Alzheimer’s disease: an MRI study[J].Brain,2008,131( 12) : 3277-3285.
[14]Gaser C,Nenadic I,Buchsbaum BR,et al.Ventricular enlargement in schizophrenia related to volume reduction of the thalamus,striatum,and superior temporal cortex[J].Am J Psychiatry,2004,161 ( 1) : 154-156.
[15]Horga G,Bernacer J,Dusi N,et al.Correlations between ventricular enlargement and gray and white matter volumes of cortex,thalamus,striatum,and internal capsule in schizophrenia[J].Eur Arch of Psychiatry Clin Neurosci,2011,261( 7) : 467-476.
(學術編輯:翟昭華)
論著
Morphological study of the thalamus in health human on MRI
ZHANG Hua1,XIE Xing-guo1,HUANG Xiao-hua2,XIAO Ru-hui2,BAI Gui-qin1
( 1.Department of Anatomy,North Sichuan Medical College; 2.Department of Radiology,Affiliated Hospital of North Sichuan Medical College,Nanchong 637000,Sichuan,China)
【Abstract】Objective: To explore the morphological variations and the relationship between the structures around the thalamus and the thalamus,and provide linear indices for thalamus morphological change-related diseases.Methods: Exploring the relationship between the structures around the thalamus and the thalamus.Results: On sectional images the gender difference and lateral difference are not significant on the area,the sagittal diameter and the width of the thalamus; the gender difference of the thalamus is significant whereas the lateral difference of the transverse diameter is not.The length of the thalamus is positively related to the sagittal diameter,the transverse diameter,the area of the putamen and the sagittal diameter of the caudate nucleus head ( P<0. 05).The indice positively related to width of the thalamus is the sagittal diameter of the caudate nucleus head ( P<0. 05).There is a negative relationship between the sagittal diameter of the caudate nucleus head and the width of the thalamus ( P<0. 05).The distance between the anterior horns was negatively related to the sagittal diameter and the length of the thalamus ( P<0. 05).After normalization,the lateral difference is significant on the volume of the thalamus,the sagittal diameter and sagittal diameter of the putamen,and transverse diameter of the caudate nucleus head ( left>right,P<0. 05).The indices which mostly related with the volume of the thalamus are the transverse diameter,the sagittal diameter,the length,the width of the thalamus.Conclusion: There is a linear relationship between the structures around the thalamus and the thalamus,the morphological changes of these structures could be used as linear indices to the thalamus.The transverse diameter,the sagittal diameter,the length,the width of the thalamus could be used as preliminary screening indices for morphological changes of the thalamus.
【Key words】Thalamic morphology; Linear indices; MRI
作者簡介:張華( 1986-),男,碩士,助教。通訊作者:謝興國,E-mail: xgxiejp@163.com
基金項目:川北醫學院科研發展計劃項目( CBY-13-A-QN36)
收稿日期:2015-03-02
doi:10. 3969/j. issn. 1005-3697. 2016. 01.20
【文章編號】1005-3697( 2016) 01-0073-05
【中圖分類號】R322.81
【文獻標志碼】A

