穩定期COPD患者營養狀況與肺功能水平的關系探討
劉麗芬沈陽市第四人民醫院呼吸內科,遼寧沈陽 110000
?
穩定期COPD患者營養狀況與肺功能水平的關系探討
劉麗芬
沈陽市第四人民醫院呼吸內科,遼寧沈陽110000
[摘要]目的探析穩定期慢性阻塞性肺病(COPD)患者的血清脂聯素濃度以及肺功能水平、COPD評估測試評分與患者營養狀況間的關系。方法分析2014年3月~2015年5月在我院呼吸內科接受治療的80例穩定期COPD患者(觀察組)的臨床資料。根據微型簡易營養評價精法(MNA-SF)問卷表將觀察組患者分成非營養不良組(觀察組1,29例)和營養不良組(觀察組2,51例)兩組。另外選取同期在我院接受體檢的39例健康者作為對照組。比較三組的基線資料以及脂聯素水平、肺功能水平、CAT評分,對上述三者與MNA-SF得分進行相關性分析。結果三組間的性別、年齡等無統計學差異(P>0.05),三組脂聯素水平有統計學差異(P<0.05),其中對照組的脂聯素水平最高,觀察組1最低;三組MNA-SF評分、肺功能以及CAT評分差異均有統計學意義(P<0.01),其中觀察組2的肺功能指標值最低,對照組最高;觀察組2的CAT評分明顯比觀察組1高。穩定期COPD患者脂聯素水平與MNA-SF不存在明顯的相關性;肺功能各指標與MNA-SF呈顯著正相關性(P<0.05);而MNA-SF得分與CAT得分呈顯著負相關(P<0.01)。結論穩定期COPD患者的肺功能水平和臨床癥狀的嚴重程度均與其營養狀況關系密切,故改善營養狀況可以有效提升患者的生活質量和預后情況;尚未明確脂聯素水平與營養狀況的關系。
[關鍵詞]慢性阻塞性肺病;簡易營養評價精法;脂聯素;肺功能;慢性阻塞性肺病評估測試
慢性阻塞性肺病(chronic obstructive pulmonary disease,COPD)屬于呼吸科的一種常見慢性疾病,致病率一直很高,給社會和經濟均造成了極大的負擔[1]。COPD的一種重要而常見的并發癥是營養不良,其可以與COPD互相促進對患者的預后及病程造成嚴重影響。然而,目前尚未明確COPD患者的營養不良的病理機制,其中糖脂代謝是誘發營養不良的一個重要因子,最近學者們開始關注新型的細胞因子—脂聯素,其與糖脂代謝作用有著密切關系[2]。本文旨在通過測定穩定期COPD患者的血清脂聯素濃度以及肺功能水平、COPD評估測試(COPD evaluation test,CAT)評分,探析上述三者與穩定COPD患者的營養狀況間的關系。
1 資料與方法
1.1一般資料
分析2014年3月~2015年5月在我院呼吸內科接受治療的80例穩定期COPD患者(觀察組)的臨床資料,根據患者的營養狀況將入選者分成觀察組1(非營養不良組,29例)和觀察組2(營養不良組,51例)兩組。另外選取同期在我院接受體檢的39例健康者作為對照組。三組間的性別、年齡等無統計學差異(P>0.05);而觀察組1與2兩組患者間的性別、年齡、BMI、吸煙比例及病程長短組間比較也均無統計學差異(P>0.05),具有可比性,見表1。入組標準:入選者均符合2013年慢性阻塞性肺疾病全球創議(The global initiative for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease,GOLD)指南關于COPD的相關診斷標準。排除標準:排除嚴重心、肝、腎功能受障者及結締組織病患者;最近有外科手術史或接受營養治療的患者;代謝異常性或消耗性疾病者;支氣管舒張試驗為陽性者;合并嚴重支氣管擴張以及支氣管哮喘者。
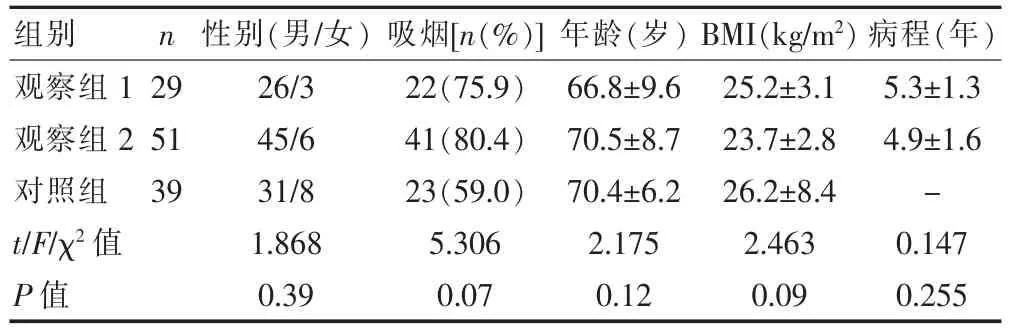
表1 三組基線資料的比較
1.2方法
簡易營養評價精法(Short-form Mini-Nutritional Assessment,MNA-SF):測量入選對象的凈身高、體重,分別精確至0.5 cm、0.5 kg。計算每位受試者的體質量指數(Body Mass Index,BMI)。根據MNA-SF問卷表將觀察組患者分成非營養不良組(觀察組1,29例)和營養不良組(觀察組2,51例)兩組。對照組同樣也接受MNA-SF評分。
1.3觀察指標
1.3.1測量脂聯素水平清晨空腹抽取患者5 mL靜脈血,于25℃下靜置30 min,以3 000 r/min的速度離心15 min后,將血清分離出并注入試管,加蓋塞緊,保存于-70℃的冰箱內待測;采用酶聯免疫吸附法(Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay,ELISA)法檢測,采用美國RB公司生產的DRE10017試劑盒,按照說明書嚴格執行操作步驟。
1.3.2肺功能測定QUAP.PFT3型COSMED肺功能儀(意大利)。技術員在測試前需向受試者詳細講解檢查要求以及具體的操作流程,由同一技術員操作完成所有的操作,確保每次的檢測結果均可靠準確,檢測的肺功能指標包括第1秒用力呼氣容積(forced expiratory volume in one second,FEV1)、FEV1%在預計值中所占的百分值(FEV1%pred)以及用力肺活量(forced vital capacity,FVC)和FEV1/FVC值,反復測量3次并選取最理想的值。
1.3.3臨床癥狀的評估COPD評估測試(COPD evaluation test,CAT)評分表以問卷調查的形式對患者的臨床病情嚴重程度進行評估,按照得分情況對患者病情的嚴重程度進行判斷。CAT問卷評分表主要包括8個問題,即患者的咳嗽、咳痰、睡眠、胸悶、情緒、精力這6項主觀指標,再加上運動耐力以及日常運動影響這2項評估運動耐受力的指標。患者按自身實際情況對各條項目做出相應0~5分的評分,CAT總分范圍為0~40分。CAT分值越高,提示COPD影響越大。
1.4統計學方法
采用SPSS19.0統計學軟件進行分析。計量資料以均數±標準差(±s)表示,采用t檢驗,多組間比較采用單因素方差分析,計數資料比較采用χ2檢驗,P<0.05為差異有統計學意義。
2 結果
2.1MNA-SF得分、血清脂聯素水平、肺功能以及CAT分數
三組脂聯素水平有統計學差異(P<0.05),其中對照組的脂聯素水平最高,觀察組1最低;三組MNA-SF評分、肺功能以及CAT評分差異均較顯著(P<0.01),其中觀察組2的肺功能指標值最低,對照組最高;觀察組2的CAT評分明顯比觀察組1高。見表2。
表2 三組MNA-SF得分、血清脂聯素水平、肺功能以及CAT分數比較(±s)
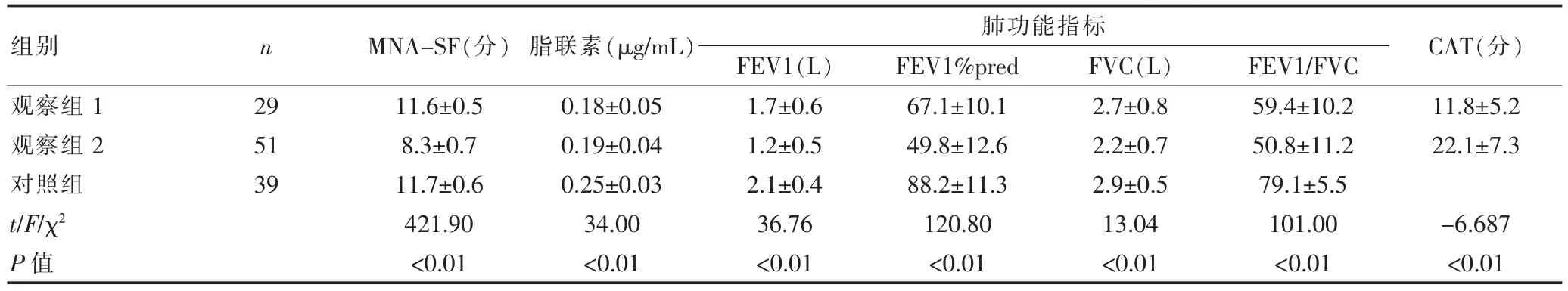
表2 三組MNA-SF得分、血清脂聯素水平、肺功能以及CAT分數比較(±s)
觀察組1觀察組2對照組t/F/χ2P值29 51 39 11.6±0.5 8.3±0.7 11.7±0.6 421.90 <0.01 0.18±0.05 0.19±0.04 0.25±0.03 34.00 <0.01 1.7±0.6 1.2±0.5 2.1±0.4 36.76 <0.01 67.1±10.1 49.8±12.6 88.2±11.3 120.80 <0.01 2.7±0.8 2.2±0.7 2.9±0.5 13.04 <0.01 59.4±10.2 50.8±11.2 79.1±5.5 101.00 <0.01 11.8±5.2 22.1±7.3 -6.687 <0.01組別 n MNA-SF(分)脂聯素(μg/mL) FEV1(L) FEV1%pred FVC(L) FEV1/FVC肺功能指標 CAT(分)
2.2相關性分析
脂聯素水平、肺功能指標以及CAT得分與MNASF得分行線性相關分析結果(表3),提示穩定期COPD患者脂聯素水平與MNA-SF不存在明顯的相關性;肺功能各指標與MNA-SF呈顯著正相關(P<0.05);而MNA-SF得分與CAT得分呈顯著負相關(P<0.01)。
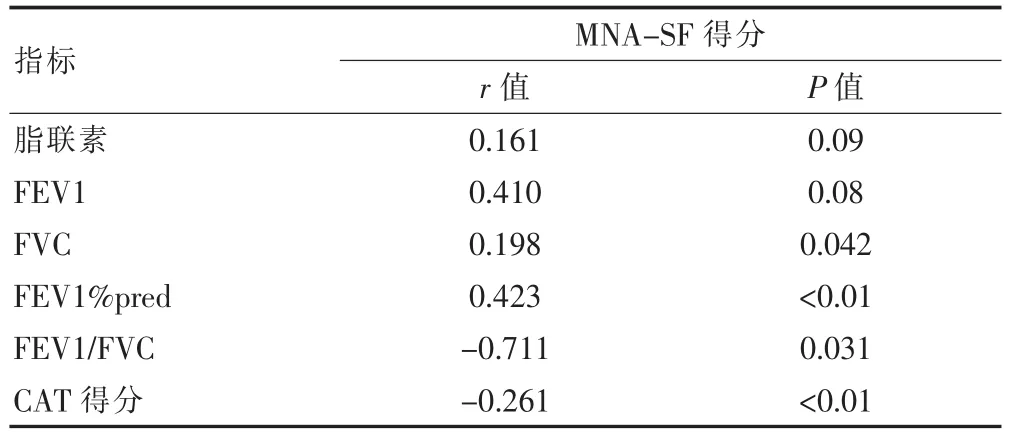
表3 穩定期COPD患者脂聯素水平、肺功能指標以及CAT得分與MNA-SF得分相關性分析
3 討論
慢性阻塞性肺病(chronic obstructive pulmonary disease,COPD)屬于慢性氣道炎癥性疾病之一,主要表現是肺部炎癥以及體重降低、代謝異常等肺外表現[3]。有資料顯示,COPD患者發生營養不良的幾率達24%~60%[4]。本實驗發現穩定期COPD患者中63.75%的患者營養不良,而營養不良是COPD患者預后的一個獨立危險因子[5],對患者的預后以及生活質量均構成了嚴重影響。COPD患者合并營養不良的病理機制較為復雜,不僅與藥物治療、食欲減退、高碳酸血癥、低氧血癥及感染等所導致的新陳代謝變化有關,還與體內多種細胞因子相關,其中血清脂聯素扮演了重要角色[6]。
有學者發現血清脂聯素濃度與腰臀圍、體質百分比呈顯著負相關,其在炎癥反應發生時可以代償性上升[7]。有資料顯示,COPD患者的誘導痰和血清中的脂聯素濃度均比正常健康者高,且脂聯素水平隨營養不良程度的加重而升高[8];有學者指出,排除吸煙因素,穩定期COPD患者的血清脂聯素水平比正常健康者高,重度以及重度以上的阻塞者比輕中度者高[9]。但是另外一些報道稱COPD患者的血清脂聯素濃度低于正常者,同時急性加重期患者的脂聯素水平比穩定期患者低[10]。本研究發現,穩定期COPD患者的血清脂聯素水平低于對照組,觀察組2(營養不良組)比觀察組1(非營養不良組)高,但是組間無統計學差異(P>0.05)。目前對于穩定期COPD患者體內脂聯素水平變化的報道各異,推測原因為COPD屬于慢性氣道炎癥之一,患者普遍合并高碳酸血癥、低氧血癥、高碳酸血癥,上述癥狀均可以對脂聯素的分泌和表達進行有效抑制,且促炎因子白介素-6(Interleukin-6,IL-6)和腫瘤壞死因子(tumor necrosis factors,TNF)可以對脂肪細胞的分泌作用(分泌脂聯素)進行有效抑制[11],此外,煙草刺激會使血清脂聯素濃度下降[12],故雖然血清脂聯素濃度在肥胖患者中較偏瘦患者顯著上升,但是由于受到上述因子的影響,研究結果會有所不同,尚需進一步研究血清脂聯素水平的變化。
COPD患者肺功能由于營養不良而受到損傷,合并營養不良的COPD患者的第1秒用力呼氣容積(forced expiratory volume in one second,FEV1)、用力肺活量(forced vital capacity,FVC)、每分鐘最大通氣量(maximal voluntary ventilation,MVV)和呼氣峰值流速(peak expiratory flow,PEF)均比非營養不良患者低[13]。本研究發現營養不良的穩定期COPD患者的肺功能水平低于非營養不良患者。有學者認為穩定期COPD患者中非營養不良患者和正常健康者的COPD評估測試(CAT)評分低于營養不良者。2013年慢性阻塞性肺疾病全球創議(The global initiative for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease,GOLD)指南推薦采用CAT評分對COPD患者臨床癥狀進行評估,理由是CAT簡單且實用,能快速掌握患者的生活質量和病情情況[14]。本文發現觀察組2的CAT評分分值明顯高于觀察組1,提示穩定期COPD患者自身的營養狀況與其肺功能水平及臨床表現關系密切,且患者肺功能水平越低,越容易出現營養不良,此外營養不良會進一步降低肺功能水平,使臨床病情及表現加重,病程延長,最終使COPD患者致死率上升[15]。
綜上所述,COPD患者如果營養不良,不僅會使其臨床癥狀加重,還會使其肺功能水平降低,給患者造成了極大地不良影響,故提示穩定期COPD患者的營養水平可以顯著改善其生活質量和預后。迄今為止,治療COPD患者的治療效果仍然不夠理想,探尋敏感的療效評估指標和更有效的治療手段是目前的主要研究方向。本文尚未能證實血清脂聯素水平與穩定期COPD患者的營養狀況間的關系,還需進一步擴大樣本容量進行深入研究。
[參考文獻]
[1] Nowak C,Sievi NA,Clarenbach CF,et al. Accuracy of the hospital anxiety and depression scale for Identifying depression in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients[J]. Pulm Med,2014,2014:973858.
[2] Carolan BJ,Kim YI,Williams AA,et al. The association of adiponectin with computed tomography phenotypes in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease[J]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med,2013,188(5):561-566.
[3]余偉鵬.慢性阻塞性肺病患者血清炎癥因子與肺功能相關性探討[J].臨床肺科雜志,2012,17(4):725-726.
[4]李雪英.慢性阻塞性肺病相關肺動脈高壓與炎癥反應[J].臨床肺科雜志,2014,19(5):900-902.
[5]沈琴.不同方式給氧對慢性阻塞性肺病患者氧合和營養攝入的影響[J].臨床肺科雜志,2012,17(5):967-968.
[6] Shukla SD,Sohal SS,Mahmood MQ,et al. Airway epithelial platelet-activating factor receptor expression is markedly upregulated in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease[J]. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis,2014,(9):853-861.
[7] Boutou AK,Nair A,Douraghi-Zadeh D,et al. A combined pulmonary function and emphysema score prognostic index for staging in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [J]. PLo S One,2014,9(10):e111109.
[8] Yuan Y,Jiang H,Kuang J,et al. Genetic variations in ADIPOQ gene are associated with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease[J]. PLo S One,2012,7(11):e50848.
[9] Brusik M,Ukropec J,Joppa P,et al. Circulatory and adipose tissue leptin and adiponectin in relationship to resting energy expenditure in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease[J]. Physiol Res,2012,61(5):469-480.
[10] Breyer MK,Rutten EP,Vernooy JH,et al. Gender differences in the adipose secretome system in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease(COPD):A pivotal role of leptin[J]. Respir Med,2011,105(7):1046-1053.
[11] Bianco A,Mazzarella G,Turchiarelli V,et al. Adiponectin:An attractive marker for metabolic disorders in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease(COPD)[J]. Nutrients,2013,5(10):4115-4125.
[12] Rubinsztajn R,Przybylowski T,Maskey-Warzechowska M,et al. Effect of exacerbation frequency on body composition and serum ghrelin and adiponectin concentrations in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [J]. Pol Arch Med Wewn,2014,124(7-8):403-409.
[13] Tse HN,Tseng CZ. Update on the pathological processes,molecular biology,and clinical utility of N-acetylcysteine in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease[J]. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis,2014,(9):825-836.
[14] Ghebre MA,Bafadhel M,Desai D,et al. Biological clustering supports both "Dutch" and "British" hypotheses of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol,2015,135(1):63-72.
[15] Pinto JM,Martin-Nogueras A,Nations M. Illness experiences of persons with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease:Self-perceived efficacy of home-based pulmonary rehabilitation[J]. Cad Saude Publica,2014,30(6):1270-1280.
The correlation between the nutritional status and lung function in patients with COPD
LIU Lifen
Department of Respiratory Medicine,the Fourth People's Hospital of Shenyang City,Shenyang 110000,China
[Abstract]Objective To analyze the relationship between the levels of adiponectin,lung function,CAT scores of COPD patients and the nutriture of patients. Methods Clinical data of patients with slationary phase COPD(observe group)received treatment in our hospital from March 2014 to May 2015 was retrospectively analyzed, and divided into two groups according to MNA-SF scores,non-nutriture group(observe group 1,29 cases)and nutriture group(observe group 2,51 cases). 39 healthy persons at the same time were chosen at our hospital as the control group. The general information,the levels of adiponectin,lung function,CAT scores of patients in three groups were compared. The relationship between the levels of adiponectin,lung function,CAT scores and MNA-SF scores were correlatively analyzed. Results There was no statistical difference in gender,age,BMI,smoking and the levels of adiponectin in three groups (P>0.05). The level of adiponectin in control group was the highest,and it was the lowest in observe group 1. The MNA-SF scores,lung function and CAT scores of patients in three groups had statistical differences(P<0.01). The level of lung function in observe group 2 was the lowest,and it was the highest in control group. The CAT scores in observe group 2 were higher than those in observe group 1. The level of adiponectin in patients with slationary phase COPD had no obvious correlation with MNA-SF scores. The indexes of lung function had positive correlation with MNA-SF scores(P<0.05). The CAT scores had negative correlation with MNA-SF scores(P<0.05). Conclusion The level of lung function and the severity of clinical symptoms have close correlation with the nutriture of patients. Improving the nutriture can effectively promote the quality of life and prognosis of patients. The relationship between the level of adiponectin and the nutriture is still not certain.
[Key words]Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease(COPD);Short-form mini-nutritional assessment(MNA-SF);Adiponectin;Lung function;Assessment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease(CAT)
收稿日期:(2015-09-18)
[中圖分類號]R563.3
[文獻標識碼]B
[文章編號]1673-9701(2016)01-0026-04

