基于LPV增益調度的風電機組控制驗證與仿真分析
鄧 英,周 峰,陳忠雷,田 德,高 尚(華北電力大學可再生能源學院,北京 102206)
?
基于LPV增益調度的風電機組控制驗證與仿真分析
鄧英,周峰,陳忠雷,田德,高尚
(華北電力大學可再生能源學院,北京 102206)
摘要:隨著風力發電機組裝機容量的持續增加,風力發電機組出力特性及其優化運行成為行業關注的熱點。針對湍流風下風電機組的動態響應特性,提出抑制風湍流的LPV增益調度控制方法。基于2 MW風電機組模型進行控制器設計,分別采用PI控制算法與LPV控制算法進行仿真計算。機組載荷的波動主要集中在風輪旋轉頻率1 P的倍頻上。仿真計算結果表明在不同風速下,機組顯示出不同的運行特性。在低風速時,塔影效應的作用較為顯著,在高風速時,湍流對載荷的影響較為明顯。相比于PI控制,LPV控制能夠跟隨機組運行狀態調整控制參數,能更好的抑制湍流對機組的影響。在16 m/s湍流風下,功率和齒輪箱低速軸轉矩在3P分量上分別降低了35.1%和41.8%。因此,在LPV控制下,齒輪箱的疲勞損傷降低了,發電機的功率波動減緩了。能夠增加風電機組的預期壽命,對電網也更加友好。
關鍵詞:風電機組;算法;模型;湍流;LPV增益調度;載荷控制
鄧英,周峰,陳忠雷,田德,高尚. 基于LPV增益調度的風電機組控制驗證與仿真分析[J]. 農業工程學報,2016,32(3):29-33.doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2016.03.005http://www.tcsae.org
Deng Ying, Zhou Feng, Chen Zhonglei, Tian De, Gao Shang. Verification and simulation analysis of wind turbine control based on linear parameter varying gain scheduling[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(3): 29-33. (in Chinese with English abstract)doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2016.03.005 http://www.tcsae.org
0 引 言
目前全球氣候變暖,以風能、太陽能為主的可再生能源快速發展。據CWEA統計,2014年中國(不包括臺灣地區),新增裝機容量2 335萬kW,累計裝機容量1.15億kW,兩項數據均居世界第一[1-2]。世界風電技術呈現如下特點:風電機組單機容量持續增大,設計和制造技術不斷提高,風電的優化運行成為行業關注的熱點。但是,風的湍流特性影響了風電機組發電運行和出力特性,因此,研究風湍流下風力發電機組發電出力特性,提出應對的控制策略,對提高風電機組發電量和運行壽命很有必要。
國標GB/T18451.1風電機組設計要求中,規定輪轂高度處的湍流強度,作為風力發電機組安全分級的重要參數;要求采用湍流風模型包括Von Karman、Kaimal和Mann譜等作為極端載荷與疲勞載荷的計算輸入[3-6]。風湍流作用造成了風電的波動性和間歇性,使風電設備制造和運行維護受到挑戰。國內外對風電機組控制做了大量的研究[7-8]。蔡繼峰、張宇[9]研究了Von Karman、Kaimal湍流風在載荷計算中的差異,并提出了葉片、輪轂和塔架的疲勞載荷的設計認證要求。風電機組單機容量的持續增大,風電機組塔架越來越高,葉片半徑越來越大,其可靠性受湍流的影響越來越顯著,Eggers等[10]指出風切變增加會引起風力發電機組葉片面外力矩增加,而湍流則是引起風力發電機組葉片振動扭矩和推力的主要原因。鄧英等[11-13]分析了極端湍流風下風力發電機組的設計載荷和葉尖距塔筒極限距離的響應特性。因此,風湍流是造成風電機組各部件疲勞損傷、可靠性降低和發電出力特性差的主要原因之一。常規的PI(proportional integral)控制用于線性時不變系統的調控,而風電機組中氣動系統是非線性的,且氣動系統的參數隨著運行狀態在時刻變化。以2 MW雙饋式風電機組為例,提出抑制風湍流的LPV(linear parameter varying)增益調度控制算法,仿真結果表明,LPV增益調度相比于常規的PI控制算法,可以有效的降低齒輪箱的疲勞載荷。
1 LPV控制算法
1.1LPV系統
線性變參數系統可以用來描述一個非線性系統[14]。開環LPV系統可描述為
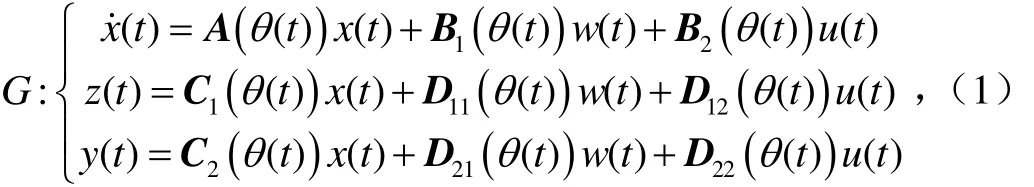
式中x表示狀態;w表示擾動;u表示控制輸入;z表示偏差輸出;y表示測量信號;θ(t)表示調度參數;t表示時間;A,B,C,D表示系數矩陣。
調度參數θ的邊界條件為

式中V表示調度參數變化率的集合,即系統的調度參數滿足(θ ,)∈Θ× V 。
LPV系統所需要的控制器形式為
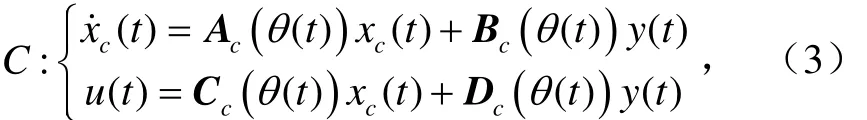
式中下標c表示控制器。
綜合開環系統和控制器得到閉環系統的狀態矩陣形式

式中下標lc表示閉環。
對于一個閉環系統,如果存在一個對稱矩陣X且
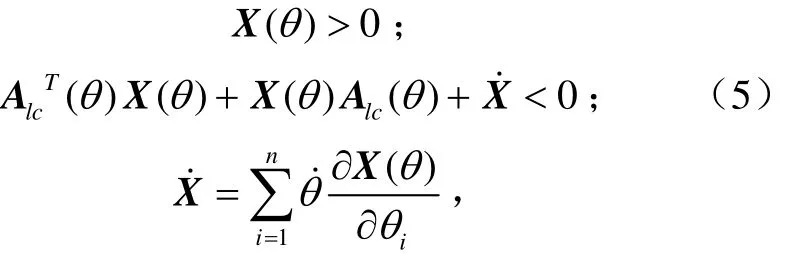
那么閉環系統系數矩陣Alc就是參數依賴二次穩定(PDQ,parameter dependent quadratic)。在零初始條件下,具有PDQ穩定的LPV系統,誘導2范數定義為
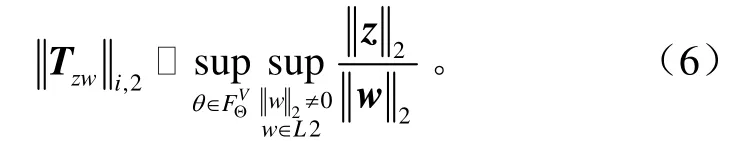
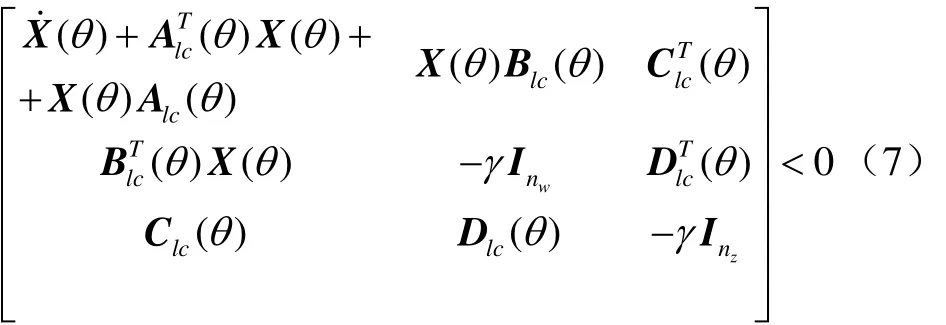
式中I表示單位矩陣。
1.2LPV控制器
這一節介紹LPV控制器的求解。為了簡化書寫,公式中不再標出調度參數θ。
閉環LPV系統的系數矩陣如下
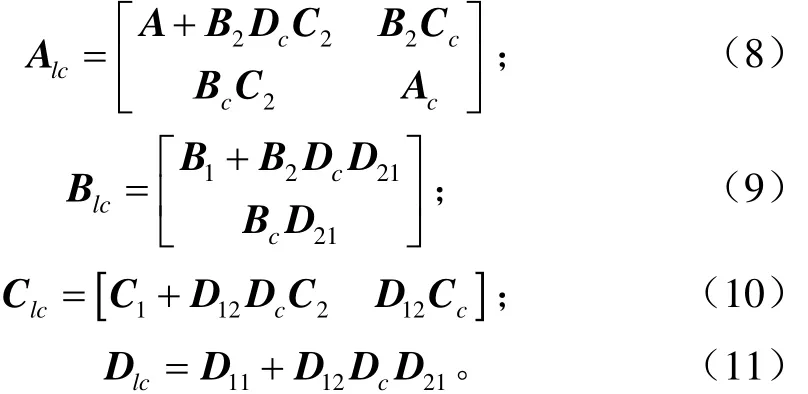
對于n×n維的開環系數矩陣A,選擇一個李雅普諾夫矩陣χ分割成如下形式

因為對稱矩陣滿足χχ-1=I,所以I?XY=NMT。X,Y以及誘導2范數的邊界γ滿足下列條件

式中NX是[C2D12]零空間的基,NY是[B2D21]T零空間的基,*表示無關項。在不等式約束條件下可求解得到X,Y,γ。
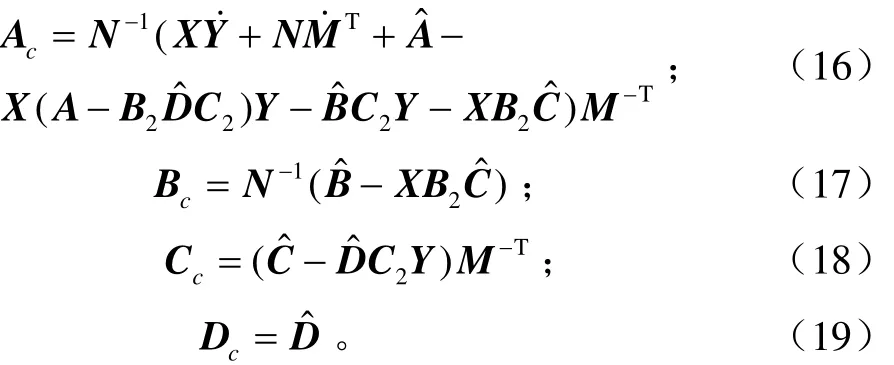
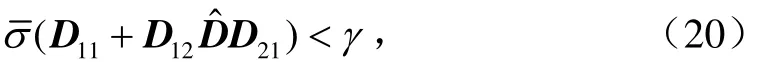
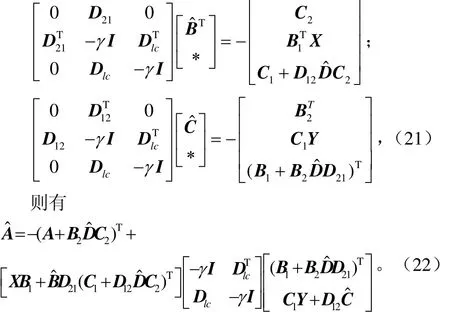
根據輔助系數矩陣與控制器矩陣系數矩陣的關系式(16)~(19)可得到控制器。
2 LPV增益調度算法的仿真分析
2.1風電機組的建模
實際中運行的風電機組安裝在吉林某風電場,機組主要參數如表1所示。
依據表1在風電機組仿真軟件Bladed中搭建模型。以平均風速15 m/s,湍流度0.155的Kaimal湍流模型作為風輸入,控制器為LPV控制。仿真計算結果與機組現場運行數據對比如圖1。
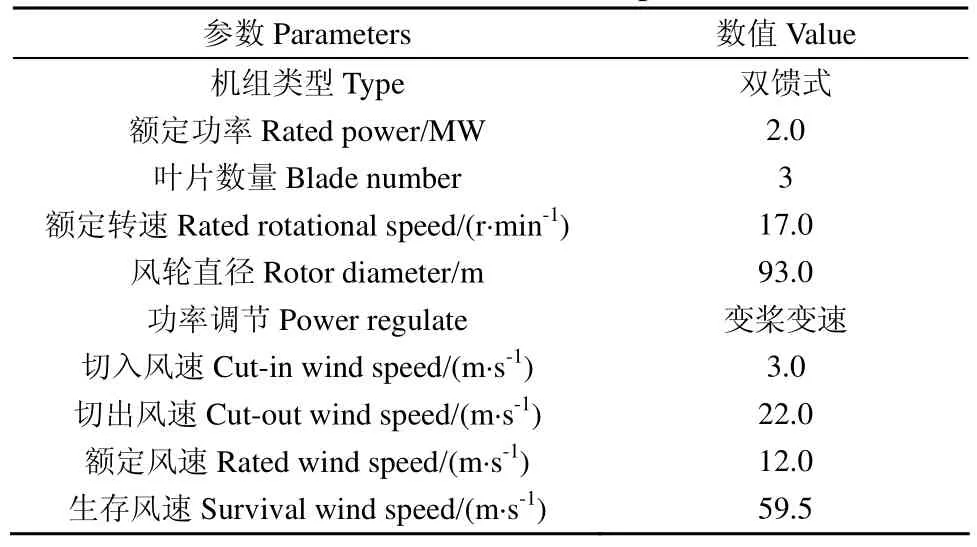
表1 2 MW風力發電機組總體參數表Table 1 2 MW wind turbine parameters
2.2控制器設計
根據風電機組各子系統的機理,得到整個機組的線性化模型[14]:

輸入量u有3個:v為風速,m/s;Tg為發電機需求轉矩,N·m;βd為需求槳距角,rad。其中風速作為擾動量輸入。
系數矩陣包含以下量

式中FT為風輪產生的軸向推力,影響塔架的前后運動。Tr為風輪產生的氣動轉矩,是傳動鏈主要傳遞的載荷,與發電功率息息相關。BT、Br、kT,V、kr,V、kT,β、kr,β分別為對應工作點(ω,β,V)下的偏導數。從式(26)可以看出,這幾個參數是隨著運行點在變化的。式(23)作為LPV開環系統,依據第2節的過程設計控制器。
2.3仿真結果驗證
從圖1中的響應曲線中可以看出,仿真計算的風速與實際中的風速基本一致。發電機功率:實測數據平均值為2 049 439 W,標準差16 189 W;仿真計算平均值為1 998 591 W,標準差13 279 W。發電機轉矩:實測數據平均值為11 222 N·m,標準差38.97 N·m;仿真計算平均值為11 245 N·m,標準差31.52 N·m。其中,實際機組的額定功率偏高,與標稱數據有偏差。從圖1中響應情況及標準差可以看出,LPV控制下的仿真計算結果與實際運行數據相似。因此,仿真軟件中所搭建的模型與實際機組相近。
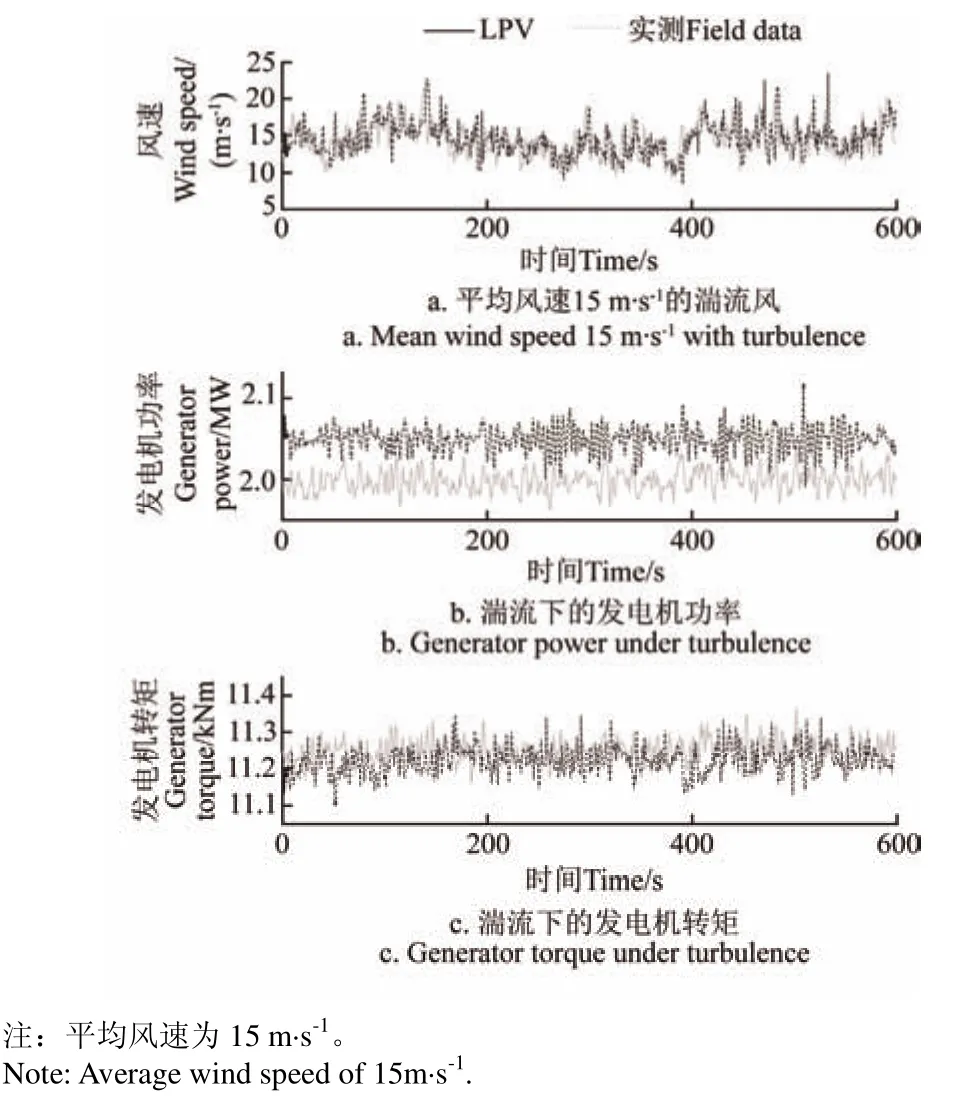
圖1 風電機組現場運行數據和仿真數據的對比Fig.1 Comparison between wind turbine field data and simulation data
分析實際運行機組的數據可知,由于湍流風的作用,發電機轉矩在11.1~11.35 kN·m間波動,波動的載荷在傳遞系統上產生疲勞損傷,同時影響了風電機組發電功率,功率波動最大達到3%。湍流引起的波動,會造成齒輪箱的疲勞損傷,電能質量也有所下降。
2.4機組運行的仿真結果分析
由于風電機組現場實測數據有限,不便于對比不同控制器的控制效果。仿真結果驗證了模型的仿真計算是可靠的,后續的仿真計算以常規的PI控制器作為基準,再以LPV控制算法編寫新的控制器。風電機組主要參數如表1所示,以標準IEC61400-1中的要求,設計表2中的2種風況為仿真計算的風輸入,將控制器加載到Bladed中進行仿真計算。
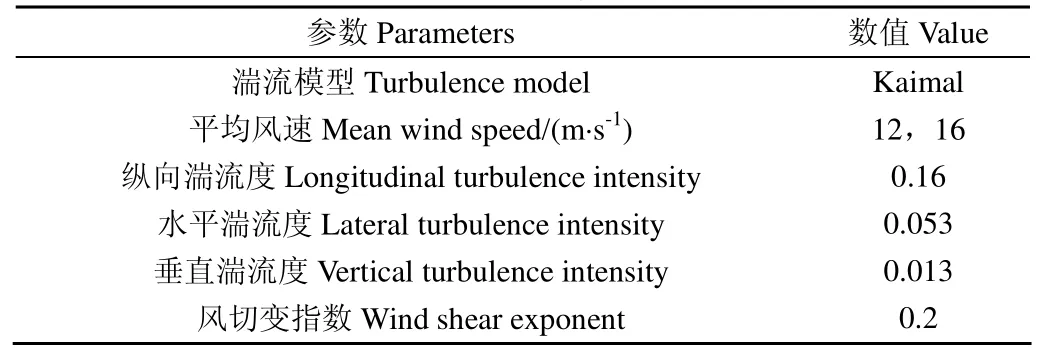
表2 仿真設計風況Table 2 Simulation design wind conditions
從時域可以看出,PI控制下,發電機的轉速轉矩有較大的波動,從而發電機的輸出功率也大幅度的波動。在不同風速下,氣動轉矩隨槳距角的變化率不一樣。因而針對不同運行點需要匹配的控制參數才能得到好的控制效果。相比于PI控制,LPV控制使得發電機的轉速轉矩更加平穩,從而可以輸出高質量的電能,同時機組的載荷波動也減緩,降低了疲勞損傷[15-16]。

圖2 12 m·s-1湍流風下發電機運行狀態Fig.2 Generator state at 12 m·s-1turbulence
從頻域觀察機組的運行狀態,機組風輪旋轉頻率(1P,one period)的3倍數對機組輸出特性的影響很大,LPV控制可以有效降低3倍頻的影響,從而穩定了功率輸出并降低了機組的疲勞。接近額定風速時,譜峰出現在機組風輪旋轉頻率的倍頻處。因此塔影效對機組的影響較為顯著,而湍流的影響不是很明顯,此時LPV控制主要作用在于改善塔影效應。而在高風速時,可以從PI控制的頻譜圖中看出,高頻分量占有較大比重,可知湍流的影響比較明顯,譜峰不再顯著的集中于機組風輪旋轉頻率的倍頻處。LPV控制降低了高頻的譜密度,即抑制了湍流引起的波動。
表3列出了16 m/s湍流下發電功率和齒輪箱低速軸的傅里葉級數展開量。3P分量在諧波分量中占有很大比例,應用LPV控制器后,功率譜中的諧波分量得到了抑制,尤其是3P分量降低了35.1%。同樣的,低速軸轉矩的3P分量降低了41.8%,而1P分量卻增加了33.8%,但占比較小,考慮整體效果,載荷波動是減緩的。因而LPV控制算法能有效降低載荷波動,進而減少齒輪箱的疲勞損傷。
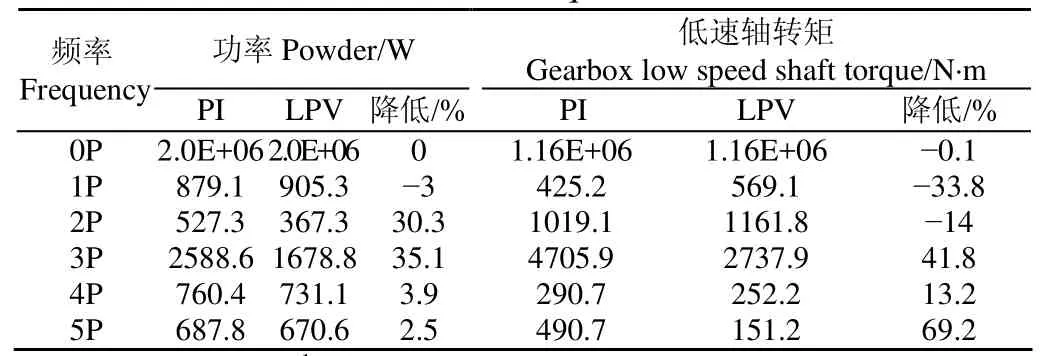
表3 發電機功率和齒輪箱低速軸轉矩波動情況Table 3 Fluctuations of generator power and gearbox low speed shaft torque
3 結 論
風電機組的是一個非線性系統,而風速是一個隨機性和波動性的輸入量,機組的運行狀態時刻在變化著,尤其是風輪部分受風速以及結構載荷耦合作用的影響,氣動性能時刻在變化。因而引入LPV增益調度控制算法,應用于風電機組控制。
1)根據風電機組運行參數的頻域分析,機組的載荷波動主要集中在3P的倍頻上,LPV增益調度控制能夠很好的抑制3P上的載荷,降低載荷中非常數分量即減少了載荷的波動。
2)載荷波動減緩了,齒輪箱的疲勞損傷降低,減少了需要維護的工作量,可以增加機組的預期壽命。并且發電功率也更加平穩,對于整個風電場而言,功率波動減小,對電網也更加友好。從整體而言,風電的度電成本可以有效的降低。
由于3個葉片上的風速是不一樣,集中變槳并不能有效的平衡3個葉片間的載荷差距,后續的研究可以考慮應用獨立變槳,可望進一步改善機組的出力特性。
[參考文獻]
[1] 中國可再生能源學會風能專業委員會(CWEA). 2014年中國風電裝機容量統計[J]. 風能,2015,6(2):36-49.
[2] 祁和生,沈德昌. 2009-2010年國內外風電產業發展報告[R].中國農機工業學會風能設備分會,2011.
[3] IEC61400-1 third edition 2005-08, Wind Turbine– Part 1: Design requirement[S].
[4] IEC 61400-1 Amd.1 Ed. 3.0 en: 2010 Amendment 1, Wind turbines Part 1: Design requirements[S].
[5] IEC61400-12-1 Ed.1, Wind turbine-Part 12-1: Power performance measurements of electricity producing wind turbines[S].
[6] Mann J. The spatial structure of neutral atmospheric surface-layer turbulence[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1994, 273: 141-168.
[7] Pao L Y, Johnson K E. Control of wind turbines[J]. Control Systems, IEEE, 2011, 31(2): 44-62.
[8] Song Y D, Li P, Liu W, et al. An overview of renewable wind energy conversion system modeling and control[J]. Measurement and Control, 2010, 43(7): 203-208.
[9] 蔡繼峰,張宇. Kaimal和Von Karman湍流譜模型在風電機組載荷計算中的差異[J]. 風能,2012,3(3):80-84.
[10] Eggers A J, Digumarthi R, Chaney K. Wind shear and turbulence effects on rotor fatigue and loads control[C]//2003 Wind Energy Symposium, American Society of Mechanical Engineers, 2003: 225-234.
[11] Deng Ying, Xie Ting, Zhang Guoqiang, et al. Blade tip deflection calculations and safety analysis of wind turbine[C]// IET Renewable Power Generation Conference, 2013.
[12] 鄧英,周峰,田德,等. 不同風湍流模型的風電機組載荷計算研究[J]. 太陽能學報,2014(12):2395-2400. Deng Ying, Zhou Feng, Tian De, et al. Research on load calculation of wind turbine for different wind turbulence model[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2014(12): 2395-2400. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 何偉. 湍流風場模擬與風力發電機組載荷特性研究[D].北京:華北電力大學,2013. He Wei. Research on Turbulent Wind Field Simulation and Load Characteristics of Wind Turbines[D]. Beijing: North China Electric Power University, 2013. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] Bianchi F D, De Battista H, Mantz R J. Wind Turbine Control Systems: Principles, Modelling and Gain Scheduling Design[M]. Springer Science & Business Media, 2006.
[15] Shirazi F A, Grigoriadis K M, Viassolo D. Wind turbine integrated structural and LPV control design for improved closed-loop performance[J]. International Journal of Control, 2012, 85(8): 1178-1196.
[16] Cao G, Grigoriadis K M, Nyanteh Y D. LPV control for the full region operation of a wind turbine integrated with synchronous generator[J]. The Scientific World Journal, 2015, ID 638120. http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/638120
Verification and simulation analysis of wind turbine control based on linear parameter varying gain scheduling
Deng Ying, Zhou Feng, Chen Zhonglei, Tian De, Gao Shang
(Renewable Energy School, North China Electric Power University, Beijing 102206, China)
Abstract:With the installed capacity of wind turbines increasing, the wind turbine output characteristics and optimal operation obtain much more concerns in the industry. This paper discusses the influence of wind turbulence on the performance of wind turbines. Wind turbine is a complex nonlinear system. Due to structure load coupling, wind variation and pitch actions, the parameters of aerodynamic subsystem are changing with operation state. Usually, PI (proportional integral) control algorithm is satisfied for a linear time invariant system. To obtain better performance, a nonlinear system needs an advanced control algorithm. To address this issue, we propose a linear parameter varying (LPV) gain scheduling control to mitigate the influence of wind turbulence on wind turbine performance. At different wind speed with variable pitch and rotor speed, the LPV control can adjust feedback gain to satisfy the changing operation point. First, we introduce the stability of LPV system and LPV controller design process. Once the stability conditions are reached, the closed-loop system is stable. Then, we derive a control model with a 2 MW wind turbine based on an actual double-fed induction generator. The input is a recommended turbulence model, Kaimal. In order to check the simulation model, the field data are compared with simulation results. The generator power and torque have similar statistic characteristics. So the model is suitable for simulation and the simulation results are credible. According to the analysis of field data, wind turbulence has a great impact on wind turbine performance, such as fatigue damage of gearbox and decreasing power generation efficiency. Therefore the economic benefits are reduced in the entire lifetime of wind turbine. Simulation results of LPV control algorithm and PI control algorithm are obtained by the software Bladed under 12 and 16 m/s wind turbulence, respectively. In time domain, the generator speed and torque are varying due to the wind turbulence. The amplitude of fluctuations under PI controller is bigger than that under LPV controller. However, the differences are not significant. To illustrate the characteristics of wind turbulence affecting wind turbine performance, the simulation results are also analyzed in frequency domain. Through spectrograms, it is observed that the peaks are concentrated on multiple rotational frequencies. The primary components are multiple 3P frequencies. Therefore, decreasing the components of multiple 3P frequencies can mitigate load fluctuation. At rated wind speed, the tower shadow effect is dominant in the load fluctuations of wind turbine. However, at high wind speed, the fluctuation does not occurs only on multiple rotational frequencies, so the turbulence has bigger influence on wind turbine performance compared with the situation at rated wind speed. In the simulation, the wind speed is 16 m/s and the turbulence intensity is 0.16; compared with PI controller, the fluctuations of gearbox’s low speed shaft torque and power are reduced by 41.8% and 35.1% respectively on 3P frequency by LPV controller. Less load fluctuation on shaft torque leads to less fatigue damage on gearbox. Also smooth power output is friendly to the grid. Therefore, the proposed control algorithm can alleviate the influence of wind turbulence and enhance the performance of wind turbine, which can bring lower wind energy cost and longer wind turbine lifetime.
Keywords:wind turbines, algorithms; models; wind turbulence, linear parameter varying gain scheduling, load control
作者簡介:鄧英,女,教授,主要從事風電機組控制方面的研究。北京華北電力大學,102206。Email:dengying@ncepu.edu.cn
基金項目:國家高技術研究發展計劃(863計劃)(2011AA05A104)
收稿日期:2015-06-10
修訂日期:2015-11-12
中圖分類號:TM614
文獻標志碼:A
文章編號:1002-6819(2016)-03-0029-05
doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2016.03.005

