新型18F標記心肌灌注顯像劑的PET顯像實驗研究*
王道宇 牟甜甜 趙祚全* 郭 風 張現忠 方 緯
新型18F標記心肌灌注顯像劑的PET顯像實驗研究*
王道宇①牟甜甜②趙祚全①*郭 風①張現忠③方 緯①
目的:通過初步動物實驗,評價4-氯-2-叔丁基-5-[[6-[[4-(2-氟-18F-乙基)-1H-1,2,3-三唑-1-基]甲基]-2-吡啶基]甲氧基]-3(2H)-噠嗪酮(18F-FPTP2)用于心肌灌注發射型正電子斷層顯像(PET)的可能性。方法:采用18F-F-取代OTs前體的方法進行標記,通過HPLC非梯度洗脫進行純化,并通過HPLC確認標記化合物結構。中華小型豬經靜脈注射18F-FPTP2(37 MBq/15 kg),并于注射后2 min、10 min、20 min、30 min、40 min、50 min和60 min分別進行PET/CT掃描。結果:18F-FPTP2制備的總時間為70 min,未校正的放化產率為(25±7.2)%,放射化學純度>98%。PET研究表明,18F-FPTP2在中華小型豬中的心肌攝取隨時間的延長而增加,靶器官與非靶器官比值亦隨之增加。注射后2 min,心和(或)肝以及心和(或)肺放射性攝取比值分別為0.65±0.10和3.47±0.29。注射后60 min,心和(或)肝以及心和(或)肺放射性攝取比值分別為0.92±0.13和9.28±0.77。結論:18F-FPTP2能夠被心肌組織攝取而顯影清晰,但心和(或)肝放射性攝取比值需要進一步提高。
18F-FPTP2;噠嗪酮;心肌灌注;發射型正電子斷層顯像
[First-author’s address] Department of Nuclear Medicine,FuWai Hospital, National Center for Cardiovascular Diseases, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences,Beijing 100037, China.
心肌灌注顯像是臨床最常用的心血管核素顯像技術,在冠心病危險度分層、治療決策和預后評價中均發揮著重要的作用[1-2]。目前,臨床應用的心肌灌注顯像劑主要是99Tcm-MIBI、201Tl和99Tcmtetrofosmin,還有研究中的锝氮核類顯像劑,但均為發射型單光子斷層(single photon emission computed tomography,SPECT)顯像劑[3-5]。SPECT分辨率相對較低,目前難以實現心肌血流量的絕對定量評價[6]。
PET空間分辨率和時間分辨率均明顯優于SPECT,可以進行有效的組織衰減校正,實現心肌血流量的絕對定量。但目前的PET心肌灌注顯像劑都難以常規臨床應用,如15O-H2O和13N-NH3標記的核素半衰期很短,分別為2 min和10 min,必須同時配備現場回旋加速器,成本十分高昂。而82Rb不僅半衰期短(僅為75 s),而且心肌攝取低于15O-H2O和13N-NH3,且價格昂貴[7]。因此,開發新一代更為實用的PET心肌灌注顯像劑十分必要。
本研究合成的新型18F標記心肌灌注顯像劑18F-FPTP2,以18F作為標記核素,其半衰期適中(110 min),不依賴現場回旋加速器,可以在1 d內完成靜息和負荷顯像;18F的范德華半徑與氫類似,對標記化合物的生物活性影響很小。18F-FPTP2以心肌線粒體NADH-泛醌氧化還原酶(MC-I)為結合位點,有較強的特異性。故本研究將通過初步的小型豬實驗探討18F-FPTP2用于PET顯像的效能。
1 材料與方法
1.1 儀器與裝置
高效液相色譜儀島津LC-20AT(日本島津公司);Kromasil 100-5 C18半制備反相色譜柱250 mm×10 mm (瑞典AkzoNobel公司);Biograph 64 PET/CT(德國西門子公司);RM-905a放射性活度計(中國計量科學研究院)。
1.2 材料與試劑
18F-F-由北京宣武醫院提供;標記前體PTP-2OTs由廈門大學公共衛生學院提供;參考物質19F-FPTP2由廈門大學公共衛生學院提供;Kryptofix2.2.2.(K222) (美國Sigma-Aldrich公司)。
1.3 實驗方法
1.3.118F-FPTP2的制備
18F-FPTP2制備路線具體步驟如下:用0.3 ml K2CO3水溶液(1 mg/0.3 ml)和1 ml K222的乙腈溶液(13 mg/1 ml)的混合液將18F-F-從QMA柱淋洗至10 ml西林瓶中。110 ℃氮氣吹干后,加入0.5 ml無水乙腈蒸發至干。將2 mg PTP-2OTs溶于1 ml無水乙腈,加至反應瓶中,90 ℃密封反應20 min。反應結束后冷卻至室溫,將反應液注入C18反相半制備柱,收集保留時間為10~11 min的組分,加入40 ml水稀釋后,過Sep-Pak C18小柱。用0.5 ml乙醇將小柱上吸附的放射性淋洗至西林瓶中,并加入9.5 ml水混勻,即為5%的18F-FPTP2乙醇溶液。①HPLC條件:A相為水,B相為乙腈;②洗脫條件:0~30 min, 55%A(如圖1所示)。

圖1 18F-FPTP2制備路線示圖
1.3.218F-FPTP2 PET的顯像研究
選擇5只體重約15 kg的中華小型豬,靜脈注射氯胺酮(25 mg/kg)和安定(1.1 mg/kg)進行麻醉。然后將小型豬俯臥于PET/CT檢查床上,靜脈注射體積為2 ml,活度為37 MBq的18F-FPTP2溶液(溶于5%乙醇溶液中)。
PET/CT掃描分別于注射后2 min、10 min、20 min、30 min、40 min、50 min和60 min進行。先進行CT低劑量掃描,掃描條件為:管電壓120 kV,CareDose4D管電流50 mAs,準直為24 mm×1.2 mm,旋轉時間0.5 s,螺距為1.2,斷層厚度3 mm。用于心臟部位定位及進行衰減校正,然后行PET 8 min。影像采集結束后進行OSEM重建,4次迭代,8個子集。像素單元為128×128,重建放大倍數為2.0,短軸圖像層厚為3 mm。勾畫心肌、肝和肺的“感興趣”區,自動得到上述器官的標準化攝取值(standard uptake value,SUV),計算各時間點的心和(或)肝以及心和(或)肺的放射性SUV比值。
2 結果
2.118F-FPTP2的放化產率及放射化學純度
從18F-F-起,包括HPLC純化在內的制備時間為70 min,未校正的放化產率為(25±7.2)%。產物的放化純>98%,比活度約為30 GBq/μmol。放射性峰的保留時間為10.5 min,和相應的參考物質19F-FPTP2的保留時間10.3 min一致,表明所制備的標記物為18F-FPTP2(如圖2所示)。
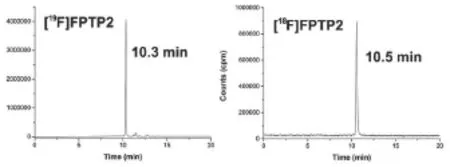
圖2 18/19F-FPTP2的HPLC圖譜
2.218F-FPTP2 PET的應用研究
18F-FPTP2在中華小型豬心肌中的初始攝取較低,但隨著時間的延長,心肌攝取明顯增加。18F-FPTP2在各時間點的肺攝取均很低,注射后2 min、10 min、20 min、30 min、40 min、50 min和60 min的心和(或)肺比值分別為3.47±0.29、4.10±0.46、4.57±0.38、6.10±0.59、7.17±0.87、8.01±1.01和9.28±0.77。與此同時,18F-FPTP2在肝部有著顯著的初始攝取,隨著時間的延長,肝的放射性有一定的清除,但60 min后攝取仍較高。注射后2 min、10 min、20 min、30 min、40 min、50 min和60 min心臟與肝臟的比值分別為0.65±0.10、0.56±0.09、0.58±0.07、0.69±0.09、0.71±0.11、0.79±0.10和0.92±0.13(如圖3所示)。
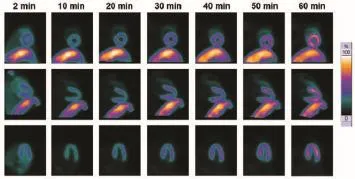
圖3 18F-FPTP2 PET在中華小型豬中的顯像圖
3 討論
目前,新型PET心肌灌注顯像藥物的研發在國際上受到高度關注。由于18F被認為是較為理想的標記核素,因此,國內外的心肌灌注顯像新藥研究主要集中于18F標記的化合物。主要包括兩類化合物。
(1)親脂性陽離子結構化合物。其原理是利用線粒體跨膜電位進入心肌細胞線粒體,分為季銨鹽和季膦鹽兩種結構。季銨鹽類化合物以羅丹明衍生物18F-FERhB[8-9]為代表,但其結構中的酯鍵容易水解造成該化合物在血清中不穩定,因此后續研究較少。季膦鹽的代表性結構是18F標記三苯膦類化合物18F-FBnTP,其心肌攝取較高,血液和肺本底低,在心肌缺血動物模型實驗中取得了較為滿意的顯像結果[10-12]。但該標記物在肝臟中代謝較慢,影響了早期成像和心肌圖像質量,同時標記過程較為復雜,放射化學產率僅為6%,不利于臨床推廣。
(2)NADH-泛醌氧化還原酶(MC-I)抑制劑類似物。MC-I抑制劑類顯像藥物通過與線粒體中MC-I的特異性結合而在心肌中富集,代表性結構是以MC-I抑制劑噠嗪酮為母體,制備得到的18F-BMS-747158-02[13-18]。其在心肌攝取、靶與非靶比值等方面均優于201Tl和99Tcm-MIBI[19]。動物模型PET顯示具有較高的心肌攝取和心肌滯留,心肌攝取量與血流量呈正比[20]。18F-BMS-747158-02已進入三期臨床試驗,但肝部清除相對較慢,最佳顯像時間為注射后60 min,且制備較為復雜,仍需要改進[21]。
本研究的前期研究表明:18F-FPTP2具有穩定性佳、放化產率高的特點,在小鼠中具有良好的心肌攝取和較高的靶與非靶比值,值得對其進行進一步研究[22]。同時,18F-FPTP2的HPLC純化方法為梯度洗脫,所用HPLC需要配備雙泵,但許多自動化合成模塊所配備的HPLC只有單泵。為了更適于臨床研究和推廣,本研究中簡化了HPLC的純化方式,將原有的梯度洗脫變為非梯度洗脫,從而降低了對HPLC配置的要求。同時,本研究還將HPLC的出峰時間由原來的18.3 min提前至10.5 min,顯著縮短了制備和質量控制的時間,提高了未校正的放射化學產率。
中華小型豬行PET的顯像結果與前期小鼠實驗相比有所不同。在小鼠生物分布研究中,18F-FPTP2具有很高的初始心肌攝取,注射后2 min為(39.70±2.81)%ID/g,滯留注射后60 min心肌滯留率為51%。而在中華小型豬行PET的顯像中,心肌初始攝取較低,但隨著時間延長,心肌攝取顯著增加。在小鼠生物分布實驗中18F-FPTP2在肝中的初始攝取很低,注射后2 min僅為(4.87±1.35)%ID/g。而在小型豬實驗中,肝部攝取在注射后2~60 min期間始終攝取較高,造成這種差異的原因可能是由于動物種屬的不同。這種現象也曾出現在其他標記物的研究中[23]。18F-FPTP2是否能在其他種屬大動物(犬、靈長類)中具有更好的生物性能,仍待后續研究。
標記化合物的肝攝取高,通常與其脂溶性較高有關。在后續研究中可以對標記物結構進行一定調整,適當降低其脂溶性,以期能得到性能更好的心肌灌注顯像劑。
[1]Klocke FJ,Baird MG,Lorell BH,et al.ACC/ AHA/ASNC Guidelines for the clinical use of cardiac radionuclide imaging—executive summary:a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines(ACC/AHA/ASNC committee to revise the 1995 Guidelines for the clinical use of cardiac radionuclide imaging)[J]. Circulation,2003,108(11):1404-1418.
[2]Berman DS,Hachamovitch R,Shaw LJ,et al. Roles of nuclear cardiology,cardiac computed tomography,and cardiac magnetic resonance: noninvasive risk stratification and a conceptualframework for the selection of noninvasive imaging tests in patients with known or suspected coronary artery disease[J].J Nucl Med,2006,47(7):1107-1118.
[3]Baggish AL,Boucher CA.Radiopharmaceutical agents for myocardial perfusion imaging[J].Circ ulation,2008,118(16):1668-1674.
[4]Bu L,Li R,Jin Z,et al.Evaluation of99mTcNMPO as a new myocardial perfusion imaging agent in normal dogs and in an acute myocardial infarction canine model:comparison with99mTc-Sestamibi[J].Mol Imaging Biol,2011, 13(1):121-127.
[5]Fang W,Liu Y,Zhu L,et al.Evaluation of99mTcN-15C5 as a new myocardial perfusion imaging agent in normal dogs and canines with coronary stenosis[J].Nucl Med Commun, 2008,29(9):775-781.
[6]Zhang WC,Fang W,Li B,et al.Experimental study of [99mTc(PNP5)(DBODC)]+as a new myocardial perfusion imaging agent[J]. Cardiology,2009,112(2):89-97.
[7]Lalonde L,Ziadi MC,Beanlands R.Cardiac positron emission tomography:current clinical practice[J].Cardiol Clin,2009,27(2):237-255.
[8]Heinrich TK,Gottumukkala V,Snay E,et al. Synthesis of fluorine-18 labeled rhodamine B:a potential PET myocardial perfusion imaging agent[J].Appl Radiat Isot,2010,68(1):96-100.
[9]Gottumukkala V,Heinrich TK,Baker A,et al. Biodistribution and stability studies of [18F] Fluoroethylrhodamine B,a potential PET myocardial perfusion agent[J].Nucl Med Biol,2010,37(3):365-370.
[10]Madar I,Ravert HT,Du Y,et al.Characterization of uptake of the new PET imaging compound18F-fluorobenzyl triphenyl phosphonium in dog myocardium[J].J Nucl Med,2006,47(8):1359-1366.
[11]Madar I,Ravert H,Dipaula A,et al.Assessment of severity of coronary artery stenosis in a canine model using the PET agent18F-fluorobenzyl triphenylphosphonium:comparison with99mTctetrofosmin[J].J Nucl Med,2007,48(6):1021-1030.
[12]Higuchi T,Fukushima K,Rischpler C,et al. Stable delineation of the ischemic area by the PET perfusion tracer18F-fluorobenzyl triphenyl phosphonium after transient coronary occlusion[J].J Nucl Med,2011,52(6):965-969.
[13]Yu M,Guaraldi M,Kagan M,et al.Assessment of18F-labeled mitochondrial complex I inhibitors as PET myocardial perfusion imaging agents in rats,rabbits,and primates[J].Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging,2009,36(1):63-72.
[14]Yalamanchili P,Wexler E,Hayes M,et al. Mechanism of uptake and retention of18F-BMS-747158-02 in cardiomyocytes:a novel PET myocardial imaging agent[J].J Nucl Cardiol,2007,14(6):782-788.
[15]Yu M,Guaraldi MT,Mistry M,et al.BMS-747158-02:a novel PET myocardial perfusion imaging agent[J].J Nucl Cardiol,2007,14(6): 789-798.
[16]Huisman MC,Higuchi T,Reder S,et al.Initial characterization of an18F-labeled myocardial perfusion tracer[J].J Nucl Med,2008,49(4):630-636.
[17]Higuchi T,Nekolla SG,Huisman MM,et al. A new18F-labeled myocardial PET tracer: Myocardial uptake after permanent and transient coronary occlusion in rats[J].J Nucl Med,2008, 49(10):1715-1722.
[18]Sherif HM,Saraste A,Weidl E,et al.Evaluation of a novel18F-labeled positron-emission tomography perfusion tracer for the assessment of myocardial infarct size in rats[J].Circ Cardiovasc Imaging,2009,2(2):77-84.
[19]Maddahi J,Berman D,Taillefer R,et al.Phase 2 clinical comparison of flurpiridaz F-18 injection PET and SPECT myocardial perfusion imaging for diagnosis of coronary artery disease[J].J Nucl Med,2011,61:469-477.
[20]Nekolla SG,Reder S,Saraste A,et al.Evaluation of the novel myocardial perfusion positronemission tomography tracer18F-BMS-747158-02:comparison to13N-ammonia and validation with microsphere in a pig model[J].Circulati on,2009,119(17):2333-2342.
[21]Maddahi J,Czernin J,Lazewatsky J,et al. Phase I,first-in-human study of BMS747158,a novel18F-labeled tracer for myocardial perfusion PET:dosimetry,biodistribution,safe ty,and imaging characteristics after a single injection at rest[J].J Nucl Med,2011,52(9): 1490-1498.
[22]Mou T,Zhao Z,Zhang P,et al.Synthesis and bio-evaluation of new18F-labeled pyridaben analogues with improved stability for myocardial perfusion imaging in mice[J].Chem Biol Drug Des,DOI:10.1111/cbdd.12499.
[23]Zhao Z,Yu Q,Mou T,et al.Highly efficient one-pot labeling of new phosphonium cations with fluorine-18 as potential PET agents for myocardial perfusion imaging[J].Mol Pharmace ut,2014,11(11):3823-3831.
The preliminary experimental study of a novel 18F-labeled myocardial perfusion imaging agent for PET imaging
WANG Dao-yu, MU Tian-tian, ZHAO Zuo-quan, et al
China Medical Equipment,2015,12(6):50-53.
Objective: To preliminarily evaluate the potential of 2-tert-butyl-4-chloro-5-((6-((4-(2-[18F]fluroethyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl)methyl)-2-pyridinyl)methoxy)-3(2H)-pyridazinone ([18F]FPTP2) as a myocardial perfusion imaging agent, by animal positron emission tomography(PET) imaging. Methods: [18F]FPTP2 was prepared by substituting tosyl of precursor with18F, purified and confirmed by HPLC. [18F] FPTP2 (37 MBq/15 kg) was injected into Chinese mini-swines intravenously by a venous catheter. The cardiac PET scans were performed at 2, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 and 60 min after injection. Results: The total radio-synthesis time was 70 min, radiochemical yield was 25±7.2% without correction. The radiochemical purities (RCP) were >98% after purification. In PET imaging study, the heart uptake and target-to-nontarget uptake ratios increased with time. The heart/liver and heart/lung ratios were 0.65±0.10 and 3.47±0.29 at 2 min post injection, 0.92±0.13 and 9.28±0.77 at 60 min post injection respectively. Conclusion: Although the higher uptake of [18F]FPTP2 were shown in myocardium, the heart/liver ratio still need to be improved in future study.
[18F]FPTP2; Pyridazinone; Myocardial perfusion; Positron emission tomography imaging
王道宇,男,(1970- ),大專,主管技師。中國醫學科學院 國家心血管病中心 阜外心血管病醫院核醫學科,從事核醫學工作。
1672-8270(2015)06-0050-04
R817.4
A
10.3969/J.ISSN.1672-8270.2015.06.016
2015-04-02
國家自然科學基金(81301251)“新型氟-18標記的噠嗪酮類心肌灌注顯像劑的研制及PET顯像實驗研究”
①中國醫學科學院 國家心血管病中心 阜外心血管病醫院核醫學科 北京 100037
②首都醫科大學附屬北京安貞醫院核醫學科 北京 100029
③廈門大學公共衛生學院分子影像暨轉化醫學研究中心 福建 廈門 361102
*通訊作者:418zhaozuoquan@163.com

