頸椎側位X線片評估退行性頸椎管狹窄的價值
林海等


【摘要】 目的 探討頸椎側位X線片測量評估退行性頸椎管狹窄的價值。
方法 收集近5年經健康體檢的正常人群作為研究對象,共200例,男性100例,女性100例。按研究對象的年齡分為兩組:青年組92例及中老年組108例。計算所有患者頸椎C3、C4、C5、C6、C7的椎管矢狀徑、椎體中矢徑、頸椎管率及有效頸椎管率。
結果 頸椎C3、C4、C5、C6、C7的椎管矢狀徑及椎體中矢徑兩組比較差異無統計學意義(P>0.05);而頸椎C4、C5、C6、C7兩組的頸椎管率比較差異有統計學意義(P<0.01);頸椎C3、C5、C6有效頸椎管率兩組比較差異有統計學意義(P<0.05或<0.01)。
結論 X線中有效頸椎管率用于診斷退行性頸椎管狹窄有較高價值,值得臨床推廣。
【關鍵詞】 頸椎側位片;X線;退行性變;頸椎管狹窄
中圖分類號:R681.504.454 文獻標識碼:A
【Abstract】 Objective To investigate value of cervical vertebra lateral X-ray in the evaluation of degenerative cervical spinal stenosis.
Methods 200 healthy people including 100 men and 100 women—who underwent physical examination in the the last five years—were selected as the object of study. All of them were divided into young group( 92 cases) and middle and old aged group (108 cases ) according their ages. Then, sagittal diameter of spinal canal, sagittal diameter of central vertebral body, rate of cervical spinal canal and rate of effective cervical spinal canal of cervical vertebra C3,C4,C5,C6 and C7 were calculated.
Results Differences of sagittal diameter of spinal canal and sagittal diameter of central vertebral body of cervical vertebra C3,C4,C5,C6 and C7 between the two groups were not statistically significant(P>0.05).However, differences of rate of cervical spinal canal of cervical vertebra C4,C5,C6 and C7 in both groups were statistically significant(P<0.01). In addition, differences of rate of effective cervical spinal canal of cervical vertebra C3, C5 and C6 were statistically significant between groups(P<0.05 or 0.01).
Conclusion Effective cervical spinal canal rate of X-ray has high value for the diagnosis of degenerative cervical spinal canal stenosis. Thus, it is worthy of promotion in clinic.
【Key words】 cervical vertebra lateral radiograph; X-ray; degeneration; cervical spinal canal stenosis
近幾年隨著醫學影像學快速發展,X線頸椎攝片技術和圖像有了很大提高。X線對顯示頸椎退行性變如骨質增生、頸椎前凸消失、椎體后緣雙邊影、椎間孔變窄、韌帶鈣化等效果極好[1]。頸椎退行性變是頸椎由于年齡、磨損等因素逐步導致血運障礙引起。因此本次研究的目的為探討頸椎側位X線片測量評估退行性頸椎管狹窄的意義。
1 資料與方法
1.1 病例選擇
收集近5年來我院進行健康體檢的正常人群作為本次研究的對象,共200例,男性100例,女性100例。按研究對象的年齡分為兩組:青年組92例及中老年組108例。青年組年齡18~39歲,平均(32.8±7.8)歲,男性44例,女性48例。中老年組年齡大于40歲,平均(51.6±9.6)歲,男性56例,女性52例。所有研究對象均簽訂知情同意書,保密知情書。
1.2 入選標準
(1)體檢資料完整;(2)每個研究對象能配合醫務人員,自愿參與本次研究。
1.3 排除標準
(1)生命體征不平穩的患者;(2)有各種急性、慢性感染,嚴重肝、腎功能不全,惡性腫瘤,自身免疫性疾病者,有藥物過敏、惡性心律失常者;(3)所有研究對象無頸及肩部痛、運動異常癥狀;(4)患者既往無頸椎骨折、脫位、頸椎強直、頸椎管狹窄者。
1.4 測量方法endprint
參考文獻[2]測量頸椎各節段椎管矢狀徑、椎體中矢徑及相鄰下端椎體矢狀徑(不包括向椎體前方突出的骨嵴)。根據測量結果,計算頸椎C3、C4、C5、C6、C7的頸椎管率及有效頸椎管率。頸椎管率=椎管矢狀徑/椎體中矢徑;有效頸椎管率=(椎管矢狀徑+椎體中矢徑-退變椎體矢狀徑)/退變椎體矢狀徑。頸椎各節段參數測量方法示意圖見圖1。
1.5 評價指標
比較兩組不同頸椎節段的椎管矢狀徑、椎體中矢徑、頸椎管率及有效頸椎管率。
1.6 統計學方法
將資料錄入SPSS 18.0統計學軟件,所有計量資料符合正態分布,采用均數±標準差(±s)表示,兩組均數的比較采用t檢驗,計數資料采用頻數表示,組間比較用χ2檢驗,P<0.05為差異有統計學意義。
2 結 果
2.1 所有對象觀察指標結果
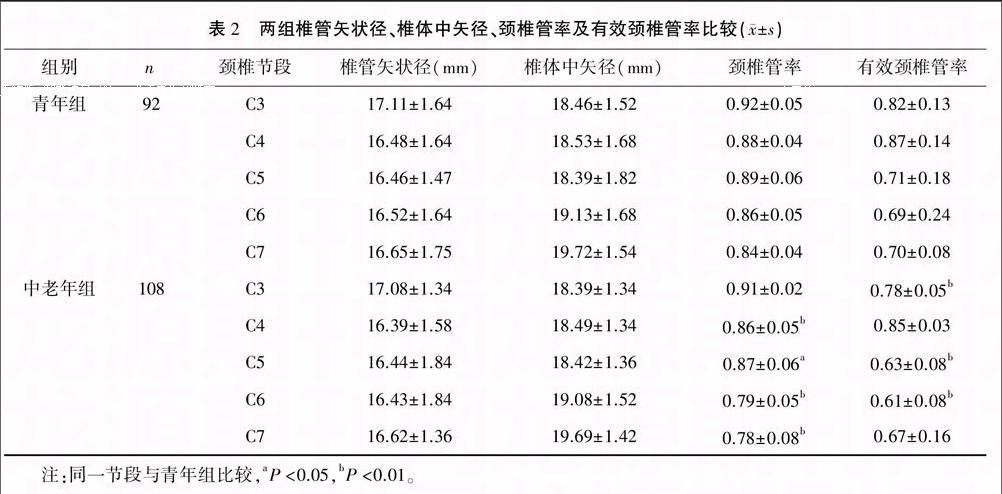
200例患者椎管矢狀徑、椎體中矢徑、頸椎管率及有效頸椎管率結果見表1。
2.2 兩組椎管矢狀徑、椎體中矢徑、頸椎管率及有效頸椎管率比較
青年組和中老年組頸椎C3、C4、C5、C6、C7的椎管矢狀徑與椎體中矢徑差異無統計學意義(P>0.05);兩組頸椎C4、C5、C6、C7的頸椎管率差異有統計學意義(P<0.05或<0.01);兩組頸椎C3、C5、C6有效頸椎管率差異有統計學意義(P<0.01)。見表2。
3 討 論
傳統用于測量頸椎管狹窄的方法依靠X線上測量椎管矢狀面直徑或椎體中矢徑,但本次研究發現青年組和中老年組頸椎C3、C4、C5、C6、C7的椎管矢狀徑及椎體中矢徑差異無統計學意義(P>0.05),即椎管矢狀徑和椎體中矢徑不能很好地反映椎體退變情況。我們分析認為,椎管矢狀徑和椎體中矢徑在臨床使用中準確性受到照射距離、暗盒距離、性別、放射醫生等因素的影響,因此對于鑒別生理性頸椎管狹窄臨床價值不大[3,4]。
20世紀有學者使用X線測量頸椎C3至頸椎C7的各節段椎管矢狀徑及椎體中矢徑,并以兩者比值定義為頸椎管率。經過循證醫學的發展,已經證實該指標具有科學性,如當頸椎管率小于0.75時,對診斷發育性頸椎管狹窄有較好實用性[5]。我們研究以頸椎管率作為參考指標,結果顯示雖然青年組和中老年組頸椎C3、C4、C5、C6、C7的椎管矢狀徑與椎體中矢徑差異無統計學意義(P>0.05),但兩組頸椎C4、C5、C6、C7的頸椎管率差異有統計學意義(P<0.01)。頸椎管率由椎體矢狀徑與椎管矢狀徑決定,頸椎管率變小見于病理性椎管狹窄和生理退變性狹窄。前者的原因是當椎間管狹窄時,相應椎體骨關節端增生,引起椎體矢狀徑距離增大,致該層面椎管率變小。而生理退變性狹窄是由于年齡增大,出現骨關節退變、骨質增生使椎間孔縮小,對鄰近椎動脈推移壓迫使其狹窄改變[6]。雖然頸椎管率克服了椎管矢狀徑與椎體中矢徑的缺陷,提高了攝影誤差,但仍難避免放大系數對測量的誤差,而且研究指出椎體中矢徑不會隨年齡增長而變大,因此將頸椎管率用于診斷退行性頸椎管狹窄仍有一定疑問[7]。
有效頸椎管率是有效骨性椎管矢狀徑與退變椎體矢狀徑之比。在臨床實際運用中即頸髓在頸椎管內實際占有空間的反映。我們將有效頸椎管率作為參考指標時,發現青年組和中老年組頸椎C3、C5、C6差異有統計學意義,即相對于頸椎管率,有效頸椎管率更能反映年齡導致的頸椎生理退變性狹窄,隨著年齡增長,有效頸椎管率在逐步變小。
目前臨床上診斷退行性頸椎管狹窄的金標準是核磁共振,其優點是能清晰顯示骨、軟骨及周圍組織三維結構,但核磁共振價格昂貴,基層醫院不能開展,限制了其在臨床上的使用。而X線操作簡單,價格低廉,在臨床中使用廣泛。因此將X線中有效頸椎管率用于診斷退行性頸椎管狹窄有較高的臨床推廣價值。
參 考 文 獻
[1] Hassan KM,Sahni H,Jha A,et al.Clinical and radiological profile of Hirayama disease: a flexion myelopathy due to tight cervical dural canal amenable to collar therapy[J].Ann Indian Acad Neurol, 2012,15(2): 106-112.
[2] Hou C,Han H,Yang X, Xu X,et al.How does the neck flexion affect the cervical MRI features of Hirayama disease[J].Neurol Sci,2012,33(5):1101-1105.
[3] 孫 宇,張鳳山,王少波,等.平山病的外科治療以及近期療效觀察——附 18例臨床病例分析[C].中國康復醫學會第十一次全國頸椎病學術會議論文集,2009:285-286.
[4] Sang-Hun Lee,Ki-Tack Kim,Kyung-Soo Suk,et al.Assessment of pedicle perforation by the cervical pedicle screw placement using plain radiographs:a comparison with computed tomography[J].Spine,2012,37(4):280-285.
[5] Huppert J,Beaurain J, Steib JP,et al.Comparison between single-and multi?level patients: clinical and radiological outcomes 2 years after cervical disc replacement[J].Eur Spine J,2011, 57(8):759-763.
[6] 劉景堂,劉興炎,唐天駟,等.下頸椎椎弓根螺釘內固定相關參數的解剖學和影像學測量[J].中國脊柱脊髓雜志,2009,19(7):535-539.
[7] Wang XN,Cui LY,Liu MS,et al. A clinical neurophysiology study of Hirayama disease[J].Chin Med J,2012,125(6):1115-1120.
(收稿日期:2014-11-27 修回日期:2015-02-08)
(編輯:潘明志)endprint

