關節鏡下肌腱固定術治療肱二頭肌腱近端病損
高慶峰 鄂剛 何耀華 張堯 趙金忠 皇甫小橋 沈繼 劉聞欣
?
關節鏡下肌腱固定術治療肱二頭肌腱近端病損
高慶峰1鄂剛1何耀華2張堯2趙金忠2皇甫小橋2沈繼2劉聞欣2
目的 探討關節鏡下通過肌腱固定術治療肱二頭肌腱近端病損的手術方法及臨床效果。方法 2010年1月至2012年6月關節鏡下通過肌腱固定術治療肱二頭肌腱近端病損49例,患者診斷明確,肱二頭肌長頭肌腱近端病損為其癥狀產生的主要原因,其中男性21例,女性28例。年齡37~60歲。分別記錄術前及最終隨訪時疼痛、活動范圍、前屈上舉肌力以及功能評分,并進行統計學分析。結果 所有患者術程順利,術后順利愈合并獲隨訪平均18(12~34)個月。術前Constant評分為平均39.4分,UCLA評分為平均15.4分;術后Constant評分為平均89.1分,UCLA評分為平均31.2分。術后與術前相比,在疼痛、活動范圍、屈肘、肌力及功能恢復方面差異均有統計學意義(P<0.05)。結論 關節鏡下通過肌腱固定技術治療肱二頭肌腱近端病損的臨床效果滿意。
肌腱固定術;肩關節;關節鏡;帶線錨釘
肱二頭肌長頭腱的近端病損會引起肩關節功能障礙和疼痛[1]。肱二頭肌長頭腱具有橫跨肩關節內外的特殊結構,其近端病損主要包括肱二頭肌腱炎、磨損或撕裂、肌腱半脫位以及脫位等[2]。肱二頭肌長頭腱的近端病損會導致患者肩關節活動范圍受限和前臂放射疼痛,嚴重影響患者的運動功能和生活質量。肱二頭肌腱的近端病損一旦確診通常需要手術治療。雖然文獻報道肌腱固定術和肌腱切斷術的治療效果差異無統計學意義,但很多學者認為<60歲及對功能和外觀要求較高的患者適于采用關節鏡下肌腱固定術[3-4]。傳統的治療方法為切開肌腱固定術,創傷大,患者康復困難且不易處理關節內的病變[5]。關節鏡下肌腱固定術創傷小,患者康復快,容易接受,在發達國家已成為治療肱二頭肌長頭腱的近端病損的首選治療方法,然而國內報道較少。本文著重介紹我科自2010年1月至2012年6月在關節鏡下采用縫合錨釘肌腱固定技術治療肱二頭肌腱患者49例的手術方法及臨床療效。
對 象 與 方 法
一、一般資料
納入標準:患者年齡均<60歲,術前體格檢查、X線及MRI檢查確診為肱二頭肌腱近端病損,保守治療無效,肱二頭肌腱近端病損為引起患者癥狀的主要原因。病例排除標準:肩關節其他疾病如神經病變等。本研究納入的病例為2010年1月至2012年6月采用帶線縫合錨釘肌腱固定術治療肱二頭肌腱近端病損的患者49例,其中男性21例,女性28例;其中肱二頭肌腱炎39例、撕裂5例、肌腱不穩2例、肌腱炎合并撕裂3例,均無明確外傷史。年齡35~60歲,均獲得臨床12個月以上隨訪,平均隨訪時間18(12~34)個月。
二、手術方法
患者采用側臥位,患肢外展40°,前屈15°,用大約4 kg重物作患肢縱向的牽引。常規消毒,鋪單后作肩關節后側入路,置入30°關節鏡鏡頭。首先進行術中的探查:肱二頭肌腱充血,炎癥嚴重,證實術前診斷明確;肩胛下肌腱完整,盂肱上、中、下韌帶存在,肩胛盂唇無撕裂,肩胛盂和肱骨頭的軟骨無剝脫,肩袖在肱骨的附著處完整。在后側入路觀察下,建立前側入路,通過前側入路置入刨削刀頭清理關節腔內肌腱周圍炎癥的滑膜組織,使視野更加清晰。切換入路到肩峰下,清除肩峰下有病變的滑囊組織,并進行肩峰成形術,以增大肩峰下間隙使空間增大暴露肩袖間隙。在后側入路監視下建立肩峰外側入路,到此三個主要關節鏡入路建立完畢。觀察入路和操作入路可以互換。在肩外側觀察入路下找到肩袖間隙,肱二頭肌腱就在肩袖間隙下方。在前側入路置入刨削刀頭清理肩袖間隙上方漂浮軟組織,以擴大視野方便操作。清理完畢后換用汽化電刀頭暴露肱二頭肌腱注意不要損傷肩袖組織(圖1,2)在暴露過程要切開橫韌帶。暴露完畢后用器械把肌腱撥開暴露結節間溝(圖3)在結節間溝最狹窄處用打磨頭稍微打磨暴露新鮮骨床,然后在結節間溝內嵌入兩個縫合帶線錨釘,兩枚錨釘相距大約1~1.5 cm。利用穿線器在前側入路,使兩根PDS線中的一根穿過肌腱,另一根在肌腱下面穿過,將PDS線的一端拴住錨釘的縫合線,然后拉另一端使錨釘的縫合線穿過肌腱,在鏡下使用推結器打結(圖4,5)。固定完畢后切斷肌腱近端,切換入路到關節腔內清除肌腱病變殘端(圖6),術后閉合切口。

圖1肩袖間隙 圖2暴露肱二頭肌腱 圖3暴露結節間溝 圖4縫線穿過肌腱 圖5打結固定 圖6關節內清理肌腱殘端
三、術后評估
所有患者的疼痛評估和肩關節活動范圍評估包括前屈上舉、外旋、內旋,肩關節功能采用Constant-Murley評分[6]和美國加利福尼亞大學洛杉磯分校UCLA(university of California,Los Angeles)評分[7]進行評估。所有患者術后定期隨訪,術后6周、3個月、6個月及末次隨訪分別對其疼痛情況、肩關節活動范圍、前屈上舉的肌力以及功能進行評價,術后MRI復查。
四、術后處理
所有患者術后即刻進行頸腕吊帶固定,無痛前提下進行肘、腕及手部的主動活動。禁止主動屈肘6~8周,以使肌腱固定愈合,6~8周后,主動屈肘鍛煉慢慢進入康復措施,并強化直至術后3個月,術后3個月開始肌肉力量的恢復訓煉。
五、統計學分析
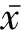
結 果
49例患者術后均順利康復,術后無感染,無傷口不愈合以及肩關節感覺異常等并發癥,術后患者對肩關節功能滿意(圖7),1例患者因劇烈運動,沒有進行預訂的康復鍛煉,仍存在疼痛。所有患者肘關節屈伸活動滿意,肌肉的形狀和輪廓與術前無變化,屈肘力量與健側相比普遍稍微下降但能滿足正常生活和運動需要。術前Constant評分為平均39.4分,UCLA評分為平均15.4分;術后Constant評分為平均89.1分,UCLA評分為平均31.2分。術后與術前相比,在疼痛、活動范圍、屈肘、肌力及功能恢復方面差異均有統計學意義(P<0.05)。即疼痛、活動范圍、屈肘、肌力及功能評分通過關節鏡手術治療差異均有統計學意義(表1,2)。
討 論

圖7男性患者,45歲,外傷至肱二頭肌腱長頭腱頑固性炎癥。A.術前核磁共振顯示肱二頭肌腱炎;B.術中探查顯示肌腱頑固性的炎癥;C.術后第1天核磁共振顯示固定牢靠;D.術后X線片;E.術后3個月時顯示肌腱已經愈合
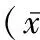
表1 本組患者術前與末次隨訪時UCLA評分結果比較±s)
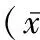
表2 本組患者術前與末次隨訪時Constant評分結果比較±s)
肱二頭肌腱的近端病損經常合并其他肩關節的病變[8]。所以術前應明確肱二頭肌腱近端病損為患者癥狀產生的主要病因。由于肱二頭肌腱長頭腱存在于肩袖間隙和結節間溝內,所以發生病變的主要原因就是長期的機械性的刺激導致肌腱和橫韌帶及喙肱韌帶的不斷摩擦。早期肌腱發生水腫和肌腱的無菌性炎癥,隨著病情發展肌腱磨損甚至發生斷裂,纖維鏡下會發現膠原纖維的萎縮,纖維蛋白壞死和大量纖維細胞的增生,至此肌腱病變已不可逆需要手術治療。患者一般會感到結節間溝區域持續的疼痛和強烈的壓痛,也有一部分患者疼痛區域模糊,大部分患者無明確的外傷史。本研究49例患者術前通過體格檢查、X線及MRI檢查確診為肱二頭肌腱的近端病損,術中關節鏡探查證實所有患者術前診斷明確。肌腱固定術治療肱二頭肌腱近端病損取得了令人鼓舞的結果,目的意在重建肱二頭肌腱長頭肌腱的止點,清除病變肌腱,避免肌腱在結節間溝的摩擦從而達到治療的目的。許多文獻早已經報道了其廣泛的手術適應證[9-14]。在本研究中針對以下病變采取了肌腱固定術:(1)肌腱的頑固性炎癥,保守治療無效;(2)肌腱撕裂約超過直徑的25%;(3)肌腱完全脫位患者活動障礙;(4)合并肩袖損傷。肌腱切斷術雖然簡單易行也能減輕患者的疼痛,但肌腱切斷術會造成患者肌腱回縮畸形形成“大力水手征”,也有可能造成患者屈肘力量減弱和不明原因的持續性隱痛。本研究患者中年齡均<60歲且對功能美觀要求較高,所以均采取肌腱固定術治療。全關節鏡下肌腱固定術是從小切口聯合關節鏡的術式發展而來,主要是由于操作器械的發展和手術技能的提高。我們采用的是全關節鏡下雙縫合帶線錨釘固定肌腱的方法,帶線縫合錨釘可以達到肌腱固定需要的強度。Mazzocca 等[15]分別評估了關節內外的擠壓螺釘和縫線錨釘固定肌腱的生物力學測試,結果顯示兩種固定方法差異無統計學意義。雖然有尸體的生物力學研究顯示經骨的擠壓螺釘固定要強于帶線縫合錨釘的強度[16-17],但是在臨床研究中兩種固定方式愈后差異無統計學意義[18],而且還有擠壓螺釘固定失敗的報道[19-20]。采用帶線縫合錨釘還有其特定的優點:(1)可以同時縫合撕裂的肩袖,其操作技術及原理也與肩袖縫合相同;(2)在手術過程中使縫線穿過肌腱增加了固定的強度,可以達到早期鍛煉的要求;(3)術中應用了雙錨釘更增加了固定的強度。術中不需要鉆取骨隧道,避免了肩關節后方神經血管的損傷。我們在術中固定肌腱的位置與先前文獻報道的近胸大肌止點處1 cm左右的位置非常符合[21-22],近來也被尸體研究所證實此位置可以達到很好的生物力學[23]。
與傳統切開手術相比,關節鏡下肌腱固定術有許多優點:(1)鏡下對肌腱損傷程度可作出較全面、客觀、準確的評估;(2)可對盂肱關節腔進行全面檢查并可治療關節內可能聯合的損傷與病變;(3)鏡下操作避免了三角肌的剝離,對軟組織損傷小;(4)術后傷口恢復快,可以進行早期功能鍛煉;(5)關節鏡為微創手術理論上可以降低血管神經損傷并發癥的發生率;(6)術后瘢痕小,肩部較為美觀,患者易于接受。關節鏡下治療肱二頭肌腱的近端病損的原因分析如下:(1)采用關節鏡技術可徹底評估所有病損,在鏡下不僅能處理肩峰下問題,而且能同時處理盂肱關節內病變,最大限度緩解疼痛,改善功能;(2)肩峰下間隙廣泛的滑膜清掃,盡可能去除所有退變組織,最大限度避免這些退變組織影響治療效果。缺點為:(1)采用關節鏡技術手術難度大,需較長的學習曲線,并需要一些特殊的設備和器械;(2)術中在尋找肱二頭肌腱時還要避免損傷肩袖。本研究術中、術后均無明顯并發癥發生,但手術中應進行控制性降壓,盡量保持收縮壓在100 mmHg以下,以保持視野清楚。
本研究49例患者通過關節鏡下肌腱固定術取得了良好的臨床療效,1例患者術后仍然感覺嚴重疼痛,可能與此患者依從關系差,沒有按照康復計劃進行康復,因而療效較差。然而本研究納入病例數較少,隨訪時間較短,長期療效有待進一步的隨訪觀察。但近期顯著的臨床效果表明關節鏡下采用縫合錨釘固定技術治療肱二頭肌腱近端病損創傷小、恢復快、臨床效果滿意。總之,關節鏡下采用肌腱固定術治療肱二頭肌腱近端病損是一種較為理想的治療方法。
[1] Alpantaki K,Mclaughlin D,Karagogeos D,et al.Sympathetic and sensory neural elements in the tendon of the long head of the biceps[J].J Bone Joint Surg Am,2005,87(7):1580-1583.
[2] Busconi BB,Deangelis N,Guerrero PE.The proximal biceps tendon:Tricks and pearls[J].Sports Med Arthrosc,2008,16(3):187-194.
[3] Osbahr DC,Diamond AB,Speer KP.The cosmetic appearance of the biceps muscle after long-head tenotomy versus tenodesis[J].Arthroscopy,2002,18(5):483-487.
[4] Patton WC,Mccluskey GM.Biceps tendinitis and subluxation[J].Clin Sports Med,2001,20(3):505-529.
[5] Crenshaw AH,Kilgore WE.Surgical treatment of bicipital tenosynovitis [J].J Bone Joint Surg Am,1966,48(8):1496-1502.
[6] Constant CR,Murley AH.A clinical method of functional assessment of the shoulder[J].Clin Orthop Relat Res,1987(214):160-164.
[7] Ellman H,Hanker G,Bayer M.Repair of the rotator cuff.End-result study of factors influencing Reconstruction[J].J Bone Joint Surg Am,1986,68(8):1136-1144.
[8] Neviaser TJ.The role of the biceps tendon in the impingement syndrome[J].Orthop Clin North Am,1987,18(3):383-386.
[9] Walch G,Nové-Josserand L,Boileau P,et al.Subluxations and dislocations of the tendon of the long head of the biceps[J].J Shoulder Elbow Surg,1998,7(2):100-108.
[10] Pfahler M,Branner S,Refior HJ.The role of the bicipital groove in tendopathy of the long biceps tendon[J].J Shoulder Elbow Surg,1999,8(5):419-424.
[11] Froimson AI,O I.Keyhole tenodesis of biceps origin at the shoulder[J].Clin Orthop Relat Res,1975,(112):245-249.
[12] Dines D,Warren RF,Inglis AE.Surgical treatment of lesions of the long head of the biceps[J].Clin Orthop Relat Res,1982,164:165-171.
[13] Becker DA,Cofield RH.Tenodesis of the long head of the biceps brachii for chronic bicipital tendinitis:long-term results[J].J Bone Joint Surg Am,1989,71(3):376-381.
[14] Berlemann U,Bayley I.Tenodesis of the long head of biceps brachii in the painful shoulder:improving results in the long term[J].J Shoulder Elbow Surg,1995,4(6):429-435.
[15] Mazzocca AD,Bicos J,Santangelo S,et al.The biomechanical evaluation of four fixation techniques for proximal biceps tenodesis[J].Arthroscopy,2005,21(11):1296-1306.
[16] Ozalay M,Akpinar S,Karaeminogullari O,et al.Mechanical strength of four different biceps tenodesis techniques[J].Arthroscopy,2005,21(8):992-998.
[17] Golish SR,Caldwell PE 3rd,Miller MD,et al.Interference screw versus suture anchor fixation for subpectoral tenodesis of the proximal biceps tendon:a cadaveric study[J].Arthroscopy,2008,24(10):1103-1108.
[18] Millett PJ,Sanders B,Gobezie R,et al.Interference screw vs.suture anchor fixation for open subpectoral biceps tenodesis:Does it matter?[J].BMC Musculoskelet Disord,2008,9(1):121.
[19] Nho SJ,Reiff SN,Verma NN,et al.Complications associated with subpectoral biceps tenodesis:Low rates of incidence following surgery[J].J Shoulder Elbow Surg,2010,19(5):764-768.
[20] Koch BS,Burks RT.Failure of biceps tenodesis with interference screw fixation[J].Arthroscopy,2012,28(5):735-740.
[21] Mazzocca AD,Rios CG,Romeo AA,et al.Subpectoral biceps tenodesis with interference screw fixation[J].Arthroscopy,2005,21(7):e1-896.
[22] Provencher MT,LeClere LE,Romeo AA.Subpectoral biceps tenodesis[J].Sports Med Arthrosc,2008,16(3):170-176.
[23] Denard PJ,Dai X,Hanypsiak BT,et al.Anatomy of the biceps tendon:implications for restoring physiological Length-Tension relation during biceps tenodesis with interference screw fixation[J].Arthroscopy,2012,28(10):1352-1358.
(本文編輯:李靜)
高慶峰,鄂剛,何耀華,等.關節鏡下肌腱固定術治療肱二頭肌腱近端病損[J/CD].中華肩肘外科電子雜志,2015,3(1):24-29.
Arthroscopic tenodesis in the treatment of long head of biceps tendon lesions
GaoQingfeng,EGang,HeYaohua,ZhangYao,ZhaoJinzhong,HuangfuXiaoqiao,ShenJi,LiuWenxin.
DepartmentofOrthopaedics,KailuanGeneralHospital,Tangshan063000,China
HeYaohua,Email:heyaohua@vip.163.com
Background The purpose of this study is to evaluate operative technique and clinical results of Arthroscopic Biceps Tenodesis for proximal lesion of the long head of biceps tendon.Methods Inclusion criteria:patient was younger than 60 years old; confirmed diagnosis of proximal lesion of biceps brachii tendon; conservative treatment was failed; biceps tendon lesion was supposed to be the main cause of shoulder symptoms.Exclusion criteria:other shoulder diseases such as neuropathy.From January 2010 to June 2012,49 patients underwent arthroscopic biceps Tenodesis for proximal lesion of long head of biceps tendon using suture anchor technique.There were 21 males and 28 females.Thirty-nine cases were diagnosed as bicipital tendinitis; 5 cases as tendon tear; 2 cases as biceps tendon instability and tendinitis with tears in 3 cases.Operatiive technique:patients were positioned in lateral decubitus position with 40 degrees of abduction,15 degrees of flexion and 4KG longitudinal traction.The viewing portal was routine posterior portal.Arthroscopic gleno-humeral joint examination was performed.Biceps lesion was confirmed after examination.Anterior working portal was established and debridement was performed if necessary.Then scope was transferred to subacromial space.Anterior lateral portal was then established.Subacromial decompression and anterior acromioplasty was done.Rotator interval was opened to identify biceps tendon.Inter-tuberosity groove was opened along biceps tendon.Two suture anchors were screwed into the narrowest part of the groove.Tenodesis was performed by the two suture anchors.The scope was transferred into joint again and intra-articular part of biceps tendon was removed under direct visualization.The portals were closed routinely.Rehabilitation protocol:all patients were protected in shoulder immobilizer.Pain free range of motion was allowed immediately after operation.Active flexion of elbow was not allowed until 6-8 weeks after operation.Then after,active flexion of elbow began to exercise gradually.Strengthening exercise began from 3 months after operation.Patients were followed up at 6 weeks,3 months,6 months and final review.Pain and range of motion was evaluated at each time.Shoulder function was evaluated according to Constant-Murley score and UCLA score (University of California,Los Angeles score).The preoperative and postoperative scores was analyzed by the paired t test using SPSS 13.0 statistical software,all the data was expressed by Mean ± SD.P<0.05 was statistical significant difference level.Results The mean follow-up time was 18 months (12-34 months).29 patients were well recovered without complications.They were satisfied with their shoulder function.Only 1 patient had residual pain because of uncontrolled active exercise during rehabilitation.All patients were satisfied with their elbow function.No pop-eye deformity was found.The strength of elbow flexion was slightly decreased compared with the healthy side.The preoperative Constant score was 39.4 on average,the average UCLA score was 15.4; after operation,the average Constant score was 89.1,the average UCLA score was 31.2.This means that the arthroscopic biceps tenodesis can improve pain relief,range of motion,elbow flexion,muscle strength,functional score significantly.Conclusion Arthroscopic biceps tenodesis is a convenient technique.Patients suffered from biceps problems can benefit from this procedure.
Biceps tenodesis;Shoulder joint;Arthroscopic;Suture anchors
10.3877/cma.j.issn.2095-5790.2015.01.006
院級特色專業——肩關節運動損傷專科(1687)
063000唐山,開灤總醫院骨科1;200233上海交通大學附屬第六人民醫院關節鏡外科2
何耀華,Email:heyaohua@vip.163.com
2014-12-05)

