Measurement and Correlation of Vapor-Liquid Equilibria for Hexamethyl Disiloxane + Vinyl Acetate System at 101.3 kPa
(張文林)*(杜威) MENG Nan(孟楠) SUN Ruyi(孫如意)2(李春利)
1School of Chemical Engineering, Hebei University of Technology, Tianjin 300130, China
2Shijiazhuang Newthreetalent Engineering, Co., Ltd, Shijiazhuang 050000, China
Measurement and Correlation of Vapor-Liquid Equilibria for Hexamethyl Disiloxane + Vinyl Acetate System at 101.3 kPa
ZHANG Wenlin(張文林)1,*, DU Wei(杜威)1, MENG Nan(孟楠)1, SUN Ruyi(孫如意)1,2and LI Chunli(李春利)1
1School of Chemical Engineering, Hebei University of Technology, Tianjin 300130, China
2Shijiazhuang Newthreetalent Engineering, Co., Ltd, Shijiazhuang 050000, China
Vapor-liquid equilibrium data of hexamethyl disiloxane + vinyl acetate system at 101.3kPa were measured by using double circulating vapor-liquid equilibrium still. The thermodynamic consistency of the VLE data was examined by Herrington method. Experimental data was correlated by non-random two-liquid (NRTL), Wilson and universal quasichemical (UNIQUAC) parameter models. All the models satisfactorily correlated with the VLE data. The result showed that the NRTL model was the most suitable one to represent experimental data satisfactorily. The system had a minimum temperature azeotrope at 345.71 K and the mole azeotropic composition was 0.0541.
vapor-liquid equilibria, vinyl acetate, hexamethyl disiloxane, determination, correlation
1 INTRODUCTION
Hexamethyl disiloxane (HMDSO, 1) is a significant chemical raw material used as silazane stock, silicon rubber, medicines, gas chromatography fixed fluid, analytical reagent, moisture repellent and so on. It is widely used in organic chemical industry and pharmaceutical chemicals.
Vinyl acetate (VAC, 2), a colorless liquid with a sweet smell of ether, is slightly soluble in water and soluble in alcohol, acetone, benzene, chloroform. It is used chiefly in the preparation of polyvinyl alcohol and synthetic fiber. Its single copolymer can be used in producing a variety of adhesive. Different properties of polymer composite materials are made of vinyl acetate with vinyl chloride, acrylonitrile, butenoate, acrylic and so on [1].
Nowadays along with the rapid development of pharmaceutical industry, hexamethyl disiloxane and some esters were used as intermediates solvents. Different esters were added to meet the different flow sheets. In order to protect the environment and save the cost, the liquid waste were need to separate by distillation. Vapor-liquid equilibrium data always need to be added gradually so as to meet the needs of distillation.
Up to now, there is few vapor-liquid equilibrium (VLE) data for those systems. Only the VLE data for hexamethyl disiloxane + ethyl acetate system had been determined [2]. In this work, isobaric VLE data for hexamethyl disiloxane (1) + vinyl acetate (2) system were investigated at 101.3 kPa. The results of the binary system were texted for thermodynamic consistency by Herington method. Meanwhile, the non-random two-liquid (NRTL) [3, 4, 5], universal quasichemical (UNIQUAC) [6, 7] and Wilson [8] equations were applied to fit with experimental data.
2 EXPERIMENTAL
2.1 Chemicals
Hexamethyl disiloxane (AR) supplied by Shanghai Nuotai Chemical Factory in China was further purified by distilling. Vinyl acetate (AR) was supplied by Tianjin Damao Reagent Factory in China.
All the chemicals had been analyzed by gas chromatography (GC) and no detectable impurity was observed. The properties of the experimental materials are shown in Table 1.
2.2 Apparatus and procedure
The double circulating still of modified Othmer type [9] was used to measure VLE data. The diagram for the still are shown in Fig. 1. It takes approximately 2 h to reach the stabilization of the system in study.
About 45 ml mixture of given content was put into the still. The equilibrium temperature was measured by a digital thermometer with an error of less than 0.1 K.

Table 1 Properties of the pure components
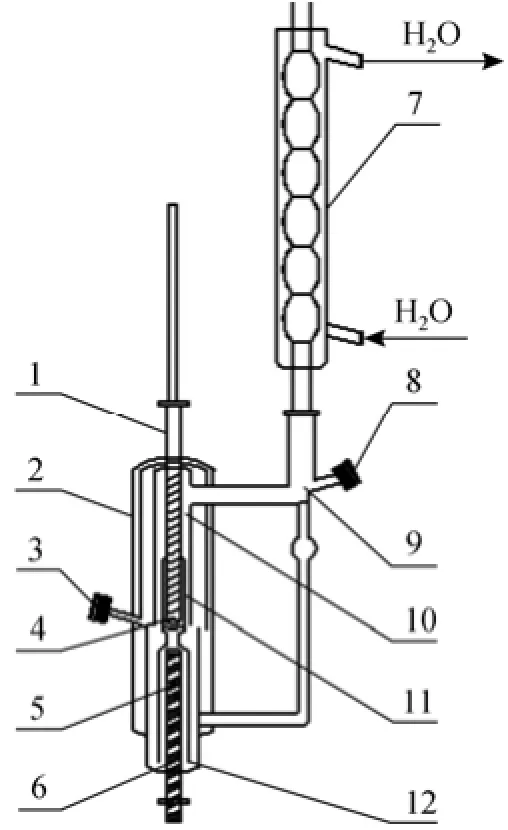
Figure 1 Circulating still1—thermometer casing; 2—vacuum thermal insulating jacket; 3—liquid-phase sample port; 4—liquid-phase sample reservoir; 5—boiling room; 6—inner heater tube; 7—vapor-phase condenser; 8—vapor-phase sample port; 9—vapor-sample reservoir; 10—vapor-phase separator room; 11—vapor-liquid riser; 12—vapor-liquid mixed room
2.3 Sample analysis
To determine the liquid and vapor samples, gas chromatography (GC3420A, Bei Fen Co.) was used with a 30 m long capillary column (HJ-OV-1701, 0.32 mm in diameter and 0.5 μm film thickness) and a hydrogen flame ionization detector (FID). The column, injector and detector temperatures were 353.15 K, 453.15 K and 453.15 K, respectively. The carrier gas was nitrogen (99.999% purity) at a constant flow rate of 30 ml·min?1. Hydrogen (99.99%) and compressed air were used at a constant flow rate of 30 and 300 ml·min?1, respectively. The injected sample was 0.2 μl. Each sample was analyzed at least thrice to ensure accuracy with an error within ±0.003. Then, the data was calibrated by series of standard mixtures, which are prepared by increasing 5 percent gravimetrically.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Experimental data
The VLE data for the binary systems of hexamethyl disiloxane (1) + vinyl acetate (2) are measured at 101.3 kPa and shown in Table 2.
3.2 Thermodynamic consistency test
Since the equilibrium pressures were sufficiently low in the investigated system, the vapor phase could be considered as the ideal gas. The activity coefficients equation is simplified to

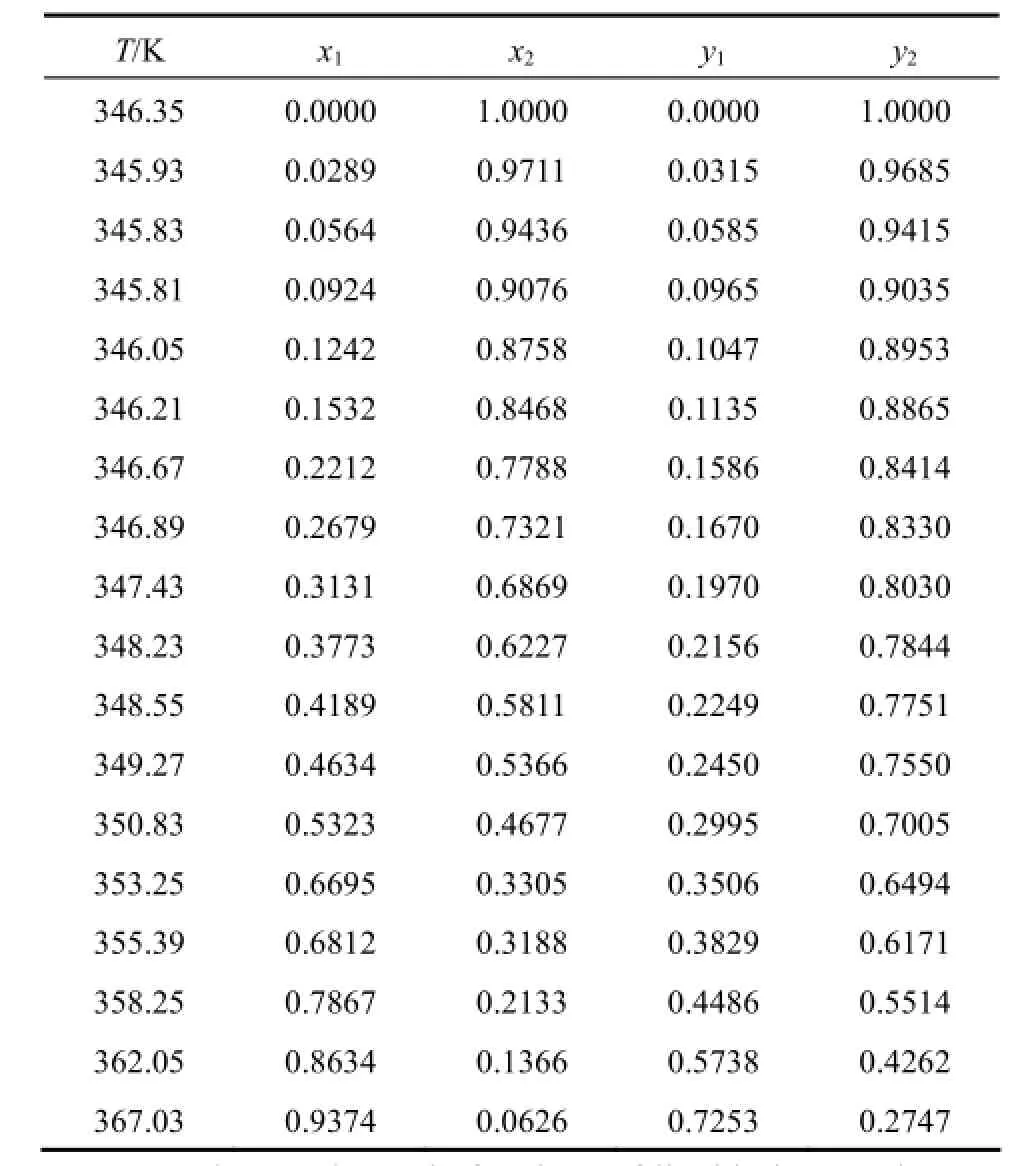
Table 2 VLE data of HMDSO (1) + VAC (2) at 101.3kPa
where γiis the activity coefficients of the component i; p is the total pressure;is the vapor pressure of pure component i; χiis the molar fraction of component i in the liquid phase; and yiis the molar fraction of component i in the vapor phase.
The vapor pressure of pure component is calculated by modified Antoine equation as follows: where a, b, c, d and e are specific coefficients of the components.
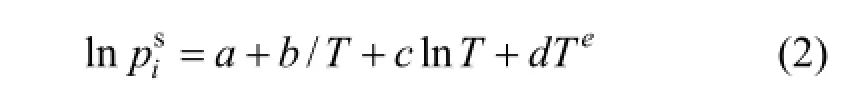

Table 3 Antoine equation parameters
The thermodynamic consistency of VLE data for the system was tested by Herington method. According to this method, D was 15.78, J was 11.64, and the check result D-J was 4.14 which was less than 10. Therefore, the VLE data passed the Herington test [10].
3.3 Correlation of the system
For the binary system, the Wilson, NRTL and UNIQUAC equations were used to calculating theVLE data. Model parameters are obtained using the minimization of the objective function as followed:
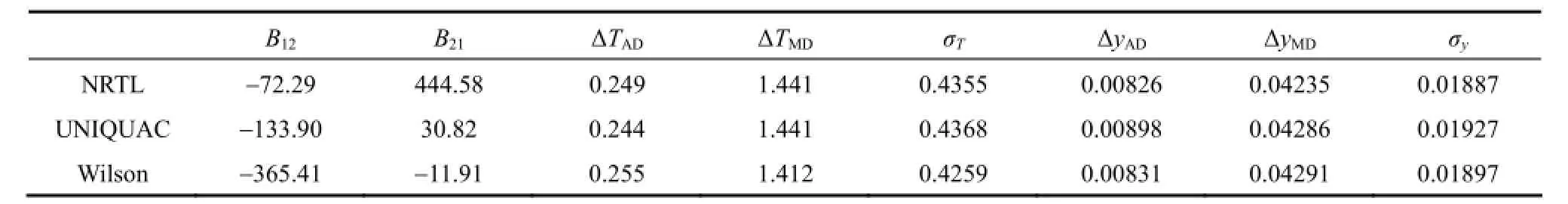
Table 4 Binary interaction parameters of NRTL, UNIQUAC and Wilson models
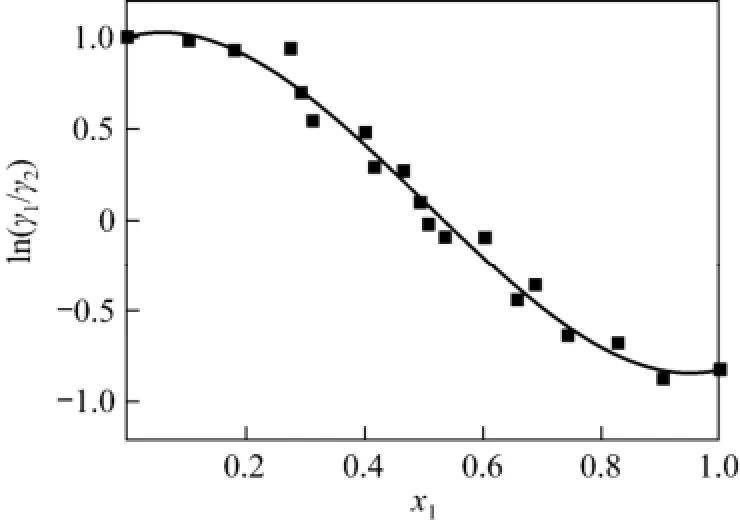
Figure 2 Herington test
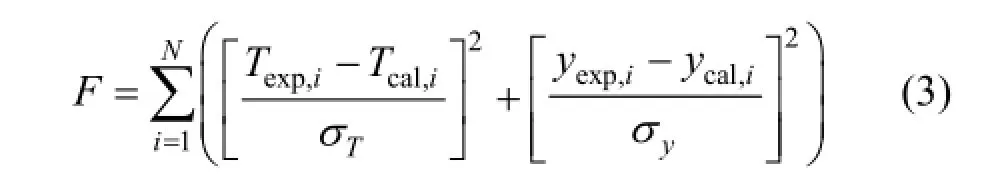
where N is the number of the data and σ is the standard deviation of the measured variables. In the calculations, the values of σ are set to 0.2 K for temperature and 0.005 for vapor phase composition.
The results of the calculated values of the equations binary parameters are shown in Table 4.
From Table 4, the average deviations in temperature are nearly the same. The NRTL average deviations in vapor phase composition are better than others. Fig. 3 compares the NRTL correlation values (α=0.3) [11, 12, 13] with the experimental T-χ-y data. The system has a minimum temperature azeotrope at 345.71 K and χ1=0.0541.
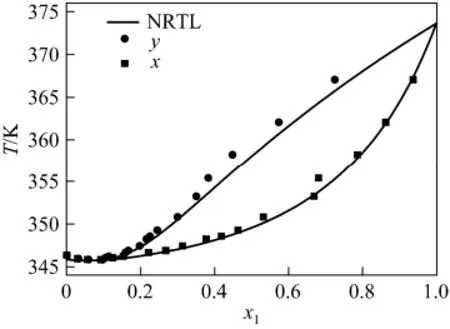
Figure 3 T-x-y diagram for HMDSO (1) + VAC (2)
4 CONCLUSIONS
Vapor-liquid equilibrium data for hexamethyl disiloxane + vinyl acetate system at 101.3 kPa were measured by using double circulating vapor-liquid equilibrium still. NRTL, UNIQUAC and Wilson model parameters were obtained with satisfactory correlation. The system had a minimum temperature azeotrope at 345.71 K and χ1=0.0541. Those data will be useful to distillation in organic chemical industry and pharmaceutical chemicals.
NOMENCLATURE
MWmolecular mass, g·mol?1
N number of the data
p total pressure, MPa
pccritical pressure, MPa
psvapor pressure of pure component i, MPa
i
T temperature, K
Tbnormal boiling point, K
Tccritical temperature, K
χimolar fraction of component i in the liquid phase
yimolar fraction of component i in the vapor phase
γiactivity coefficients of the component i
σ standard deviation of the measured variables
REFERENCES
1 Cheng, N.L., Solvents Handbook, Chemical Industry Press, Beijing (2002). (in Chinese)
2 Zhang, W.L., Meng, N., Sun, R.Y., “Determination and correlation of vapor-liquid equilibrium data for the ethyl acetate + hexamethyl disiloxane system at 101.3 kPa”, J. Chem. Eng. Data, 56, 5078-5080 (2011).
3 Wilson, G. M., “Vapor-liquid equilibium. XI. A new expression for the excess free energy of mixing”, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 86 (6), 127-130 (1964).
4 Renon, H., Prausnitz, J.M., “Local compositions in thermo-dynamic excess function for liquid mixtures”, AIChE J., 14, 135-144 (1968).
5 Deng, D.S., Wang, R.F., Zhang, L.Z., “Vapor-liquid equilibrium measurements and modeling for ternary system water + ethanol + 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate”, Chin. J. Chem. Eng., 19 (4), 703-708 (2011).
6 Abrams, D., Prausnitz, J. M., “Statistical thermodynamics of liquid mixtures: A new expression for Gibbs energy of partly or completely miscible system”, AIChE J., 21, 116-128 (1975).
7 Gong, X.C., Lu, Y.C., Luo, G.S., “Phase equilibrium calculations inmixtures containing caprolactam with a UNIFAC model”, Chin. J. Chem. Eng., 18 (2), 286-291 (2010).
8 Susial, P., Sosa-Rosario, A., Rios-Santana, R., “Vapour-liquid equilibrium with a new ebulliometer: ester + alcohol system at 0.5 MPa original research article”, Chin. J. Chem. Eng., 18 (6), 1000-1007 (2010).
9 Zhang, W.L., Hou, K.H., Mi, G.J., “Study on isobaric VLE data for the binary system of thiophene and octane”, J. Chem. Eng. Chin. Univ., 21 (06), 911-913 (2007).
10 Abobott, M.M., Van-Ness, H.C., Theory and Problems of Thermodynamics, McGraw-Hill, New York (1972).
11 Zhang, W.L., Hou, K.H., Mi, G.J., “Liquid-liquid equilibria of ternary systems sulfide + octane + solvents at different temperatures”, J. Chem. Eng. Data, 53, 2275-2281 (2008).
12 Wang, X.Q., Zhuang, X.L., Yun, S.S., “Measurement and correlation of vapor-liquid equilibrium for a cyclohexene-cyclohexanol binary system at 101.3 kPa original research article”, Chin. J. Chem. Eng., 19 (3), 484-488 (2011).
13 Walas, S.M., Phase Equilibria in Chemical Engineering, Butterworth, Boston (1985).
Received 2012-07-12, accepted 2012-11-23.
* To whom correspondence should be addressed. E-mail: ctstzwl@hebut.edu.cn
 Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering2014年2期
Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering2014年2期
- Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering的其它文章
- Kinetics of Glucose Ethanolysis Catalyzed by Extremely Low Sulfuric Acid in Ethanol Medium*
- Synthesis of Sub-micrometer Lithium Iron Phosphate Particles for Lithium Ion Battery by Using Supercritical Hydrothermal Method
- Hydrogenation of Silicon Tetrachloride in Microwave Plasma
- Effects of Solvent and Impurities on Crystal Morphology of Zinc Lactate Trihydrate*
- Large-eddy Simulation of Ethanol Spray-Air Combustion and Its Experimental Validation*
- Kinetic and Thermodynamic Studies of Acid Scarlet 3R Adsorption onto Low-cost Adsorbent Developed from Sludge and Straw*
