牙鲆NPY的體外表達及體內檢測
王 倩, 譚訓剛 孫 威 尤 鋒 張培軍
(1. 中國科學院 海洋研究所, 實驗海洋生物學重點實驗室, 山東 青島 266071; 2. 中國科學院大學, 北京, 100049)
牙鲆NPY的體外表達及體內檢測
王 倩1,2, 譚訓剛1, 孫 威1, 尤 鋒1, 張培軍1
(1. 中國科學院 海洋研究所, 實驗海洋生物學重點實驗室, 山東 青島 266071; 2. 中國科學院大學, 北京, 100049)
神經肽Y (Neuropeptide Y, NPY)被普遍認為是一種重要的促食因子, 在調節魚類的攝食行為方面起著至關重要的作用。為進一步研究牙鲆NPY蛋白的生物學功能, 作者克隆了牙鲆NPY成熟肽序列(m-NPY)及含有信號肽的全長序列(f-NPY), 利用原核表達系統分別進行體外重組表達, 篩選出誘導劑IPTG最佳誘導濃度為0.8 mmol/L及最佳誘導時間3 h; 此外, 根據牙鲆NPY第49-64位氨基酸序列制備了多克隆抗體并通過Western blot驗證該多抗能夠有效檢驗重組NPY及牙鲆體內NPY的表達。研究結果為研究重組牙鲆NPY蛋白在牙鲆水產養殖產業中的應用及檢測提供了依據。
神經肽Y; 原核表達; 重組蛋白; 多克隆抗體
神經肽 Y(Neuropeptide Y, NPY)與結構肽 YY (peptide YY, PYY)、胰多肽(pancreatic polypeptide, PP)相似, 被認為屬于胰多肽家族[1]。NPY 廣泛存在于各種脊椎動物中, 多由 36個氨基酸組成, 且物種間高度保守[2]。NPY主要分布于中樞神經系統及外周神經系統中, 尤其在腦部含量很高。NPY以信號分子的形式參與到體內多種生理調節過程如血壓調節、交感神經系統節律、晝夜節律及攝食等[3]。金魚(Carassius auratus)中, 側腦室內注射NPY可顯著提高攝食量, 而加入NPY受體拮抗物可降低這種效應;禁食能夠引起NPY表達量的上升[4]。在其他魚類中如大鱗大麻哈魚(Oncorhynchus tshawytscha)、銀大馬哈魚(O.kisutch)、斑點叉尾 (Ictalurus punctatus)、冬鰩(Raja ocellata)、巴南牙鲆(Paralichthys orbignyanus)等中也發現禁食會使下丘腦中NPY mRNA的表達量增加[5-8]。通過腹腔注射將重組的NPY蛋白注射到羅非魚(Oreochromissp.)中, 可以促進其攝食量及體質量的增加[9]。因此NPY被認為是一種十分重要的攝食調控因子, 在調節魚類的攝食行為方面起著至關重要的作用。
牙鲆(Paralichthys olivaceus)是中國重要的海水養殖魚類之一, 生長率是養殖的重要指標之一, NPY的促進攝食作用可對提高牙鲆的生長率有重要意義。但是目前有關牙鲆 NPY生物學功能的研究主要集中在RNA水平[8,10-12], 蛋白水平的研究還未見報道。為進一步研究牙鲆 NPY的生物學作用, 本實驗在克隆牙鲆NPY基因的基礎上, 構建NPY原核表達質粒并進行體外原核表達; 根據牙鲆NPY蛋白序列制備了NPY多克隆抗體, 可有效地檢驗牙鲆內源 NPY, 從而為進一步研究牙鲆NPY蛋白的生物學功能提供依據。
1 材料和方法
1.1 試劑及抗體
限制性內切酶(TaKaRa, 大連), T4 Ligase (Promega, 美國),PfuDNA 聚合酶(天根, 北京), 超低分子量蛋白質標準(Solarbio, 北京), Anti-His 抗體(天根, 北京), 辣根酶標記山羊抗小鼠 IgG(H+L)(中杉金橋, 北京), 辣根酶標記山羊抗兔 IgG(H+L)(中杉金橋, 北京)。
大腸桿菌BL-21(DE3)及質粒pPROEX? HTa由本實驗室保存。
1.2 NPY表達載體的構建
根據NCBI數據庫中公布的牙鲆NPYcDNA序列(GenBank 登錄號: AB055211.1), 分別設計全長NPY(f-NPY)及成熟肽NPY(m-NPY)的引物(表 1), 其中m-NPY的上游引物在 5′端根據 Kozak規則加入ACCATGGGA, 以提高轉錄和翻譯效率, 下游引物在5′端加入TCA進行翻譯的終止。使用Pfu高保真酶擴增目的片段, 插入pPROEX? HTa質粒的NcoI酶切位點并轉化大腸桿菌BL-21(DE3), 經LB+Amp培養基篩選陽性菌落, 提取質粒后分別以f-NPY-F/R和m-NPY-F/R為引物進行PCR鑒定并進行測序, 篩選到編碼框正確的陽性重組菌分別命名為f-NPY/ HTa、m-NPY/HTa。

表1 引物序列Tab.1 Sequences of primers
1.3 NPY重組蛋白的誘導表達及條件優化
挑取f-NPY/HTa、m-NPY/HTa單菌落于5 mL LB+ Amp培養基中37℃、200 r/min過夜培養, 次日以1%的接種量接于50 mL LB+Amp培養基中繼續培養至A600達到0.8, 此時取出1 mL培養液作為對照樣品T0, 然后向剩余培養基中加入誘導劑IPTG誘導重組蛋白的表達。
為確定誘導劑濃度對重組蛋白表達的影響, 設定IPTG濃度分別為0.6、0.8、1.0、1.5、2.0和3.0 mol/L,培養3 h后進行取樣。為確定誘導時間對重組蛋白表達量的影響, 固定IPTG 濃度為0.8 mmol/L, f-NPY取樣時間為分別為誘導后1、2、3、4和5 h; m-NPY取樣時間設置為誘導后3 h和4 h。
將樣品在6000 rpm離心5 min后棄上清, 用50 μL PBS和 50 μL 2×SDS-PAGE 樣品緩沖液重懸菌體,煮沸5 min后進行SDS-PAGE 檢測。f-NPY所用分離膠濃度為16%, 使用考馬斯亮藍R-250進行染色; m-NPY使用分離膠濃度為20%的Tricine-SDS-PAGE, 并使用考馬斯亮藍G-250進行染色。
1.4 Western blot分析
為進一步確認NPY重組蛋白的表達, 作者利用His表達標簽進行 Western blot分析。蛋白樣品由SDS-PAGE膠轉至硝酸纖維素濾膜, 以濃度為5%的脫脂奶粉進行封閉, 然后加入 1∶1000稀釋的Anti-His 抗體作為一抗室溫孵育1 h, PBST洗3x 5 min后, 加入 1∶1000稀釋的羊抗鼠二抗室溫孵育 1 h, PBST洗3x 5 min后用新鮮配制的DAB顯色液(0.2 g/L DAB, 0.1% H2O2)進行顯色。
1.5 NPY多克隆抗體檢測牙鲆內源NPY蛋白
牙鲆多克隆抗體由天津賽爾生物技術有限公司合成, 多肽抗原序列為 YSALRHYINLITRQRY, 是牙鲆NPY的第49~64位氨基酸, 位于胰多肽超家族(PAH superfamily)結構域內。為檢測該抗體的有效性,作者取100尾24 hph (孵化后24 h) 的牙鲆仔魚, 加入50 μL PBS和50 μL 2×SDS-PAGE 樣品緩沖液煮沸5 min, 即可作為樣品與m-NPY誘導蛋白一起進行Western blot檢測。方法同1.4, 其中一抗為1∶500稀釋的NPY多克隆抗體, 二抗為1∶1000稀釋的羊抗兔抗體。另外, 以 1∶1000稀釋的Anti-His 抗體為一抗檢測m-NPY誘導樣品作為陽性對照。
2 結果
2.1 NPY表達載體構建
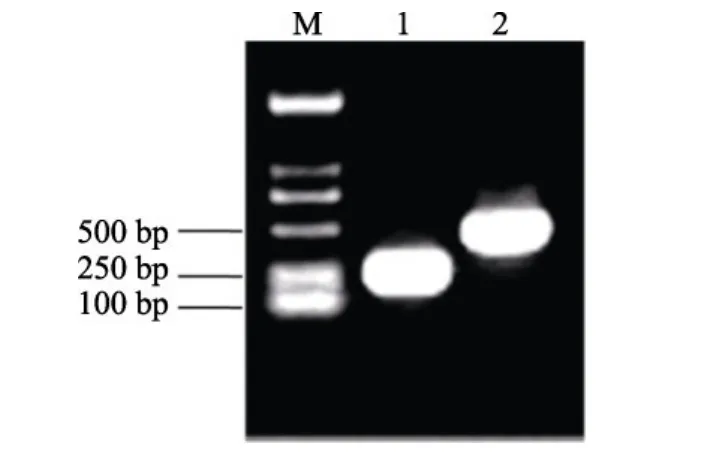
圖1 重組表達質粒m-NPY/HTa、f-NPY/HTa的鑒定Fig. 1 Identification of recombinant expression plasmid m-NPY/Hta and f-NPY/HTa
使用Pfu高保真酶擴增得到與預期大小相符的PCR片段, PCR產物回收后插入pPROEX? HTa質粒的NcoI酶切位點, 陽性重組質粒分別以f-NPY-F/ R和m-NPY-F/R為引物進行PCR擴增, 可以檢驗出各自的NPY條帶(圖1), 測序結果也表明克隆得到的為預期條帶, 插入方向正確且編碼框沒有發生改變,即成功獲得 NPY重組表達菌f-NPY/HTa、m-NPY/ HTa。
重組質粒插入的f-NPY為336 bp, 可編碼100個氨基酸, 加上 pPROEX? HTa質粒的融合標簽, 融合蛋白的分子量理論值為14 kDa;m-NPY為120 bp,可編碼40個氨基酸, 加上pPROEX? HTa質粒的融合標簽, 融合蛋白的分子量理論值為7 kDa。
2.2 NPY重組蛋白的誘導表達及條件優化
全長NPY重組蛋白f-NPY及成熟肽NPY重組蛋白m-NPY在E.coliBL21 (DE3)中表達為帶有組氨酸標簽的融合蛋白, 實驗發現在0.8 mmol/L IPTG、37℃條件下經過IPTG誘導后, f-NPY重組蛋白很快產生, 而對照樣品沒有該蛋白條帶。隨著誘導時間的延長, 重組蛋白的量不斷增加, 到3 h時, 重組蛋白表達量達到最大, 此后進入平臺期。因此將誘導時間定為3 h(圖2a)。在優化f-NPY誘導時間的基礎上, 設定了m-NPY誘導時間點為3 h和4 h, 實驗發現兩個取樣點 m-NPY的表達量沒有明顯變化, 因此同樣將誘導時間定為3 h(圖3a)。當培養溫度為37℃, 誘導時間為3 h時, 隨著IPTG濃度改變, f-NPY和m-NPY重組蛋白表達量變化均不明顯(圖2b, 圖3b), 因此采用較小濃度0.8 mmol/L作為表達的最佳誘導濃度。此外, Western blot以Anti-His鼠單克隆抗體為一抗, 結果顯示預期大小處有單一條帶顯色, 進一步確定了含有組氨酸標簽的重組蛋白的表達(圖2 c, 圖3 c)。
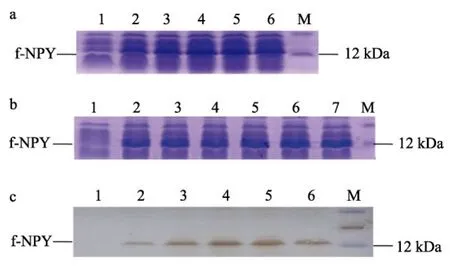
圖2 SDS-PAGE及Western blot檢測f-NPY重組蛋白的最佳表達條件Fig. 2 SDS-PAGE and western blot analysis of the optimal conditions for expression of recombinant f-NPY
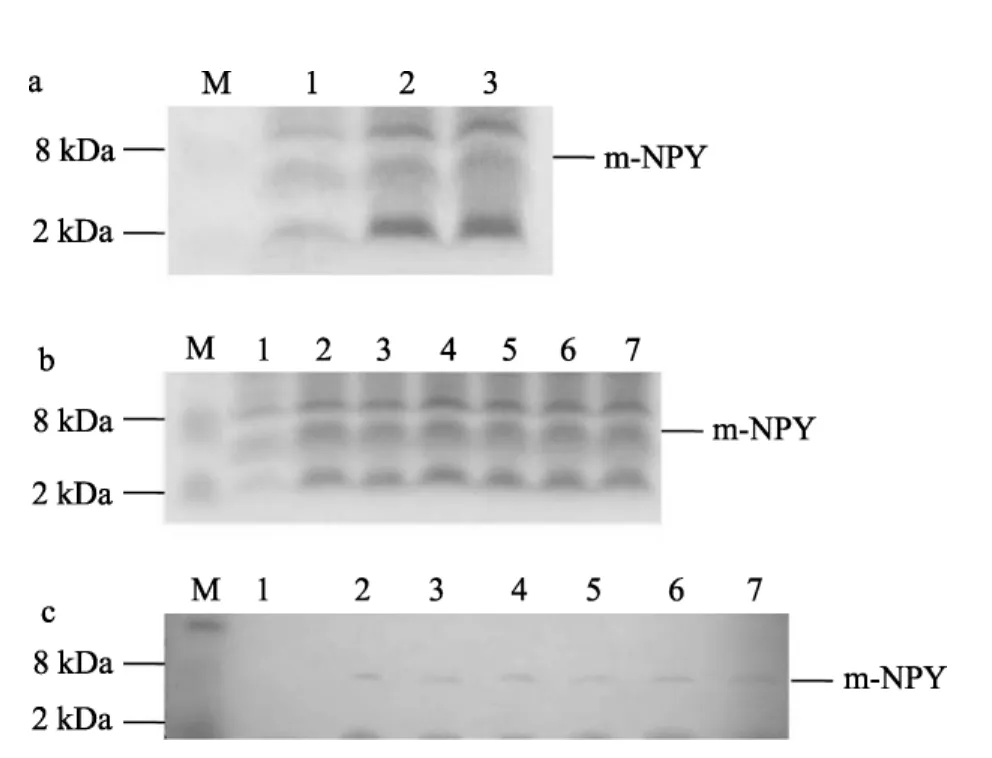
圖3 SDS-PAGE及Western blot檢測m-NPY重組蛋白的最佳表達條件Fig. 3 SDS-PAGE and western blot analysis of the optimal conditions for expression of recombinant m-NPY
2.3 牙鲆內源NPY蛋白的檢測
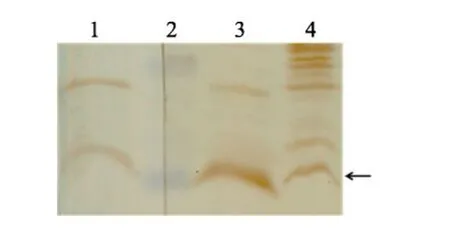
圖 4 多克隆抗體檢測牙鲆內源NPY表達Fig.4 Western blot analysis of the endogenous flounder NPY with the polyclonal antibody
為分析牙鲆體內NPY的表達, 作者根據NPY的部分氨基酸序列合成了多克隆抗體。實驗表明該抗體可以檢測到牙鲆仔魚樣品的 NPY表達(圖 4)。牙鲆 NPY蛋白的理論分子量約為 4 kDa, 比實驗中m-NPY重組蛋白略小, Western blot結果顯示合成的多抗可以在牙鲆仔魚樣品中檢測到約 4 kDa大小的條帶, 該條帶與兩種抗體處理的m-NPY大小接近。因此作者推論該合成的NPY多克隆抗體可以檢測出內源表達的NPY蛋白。
3 討論與結論
以往的研究表明, 牙鲆NPY蛋白的組成包括28個氨基酸的預測信號肽、36個氨基酸的成熟肽及32個氨基酸的C端延伸, 其成熟肽含有甘氨酸-賴氨酸-精氨酸加工位點, 與其他魚類的NPY有較高的保守性(鱸魚, 97.2%; 斑馬魚, 94.4%; 金魚, 91.7%)[10]。本研究分別克隆了牙鲆NPY兩種不同形式的基因片段, 全長NPY(f-NPY)及成熟肽NPY(m-NPY), 與NCBI數據庫中已有序列進行比對, 一致性均為100%, 并發現含有胰多肽超家族(PAH superfamily)結構域。將f-NPY及m-NPY分別插入到表達質粒pPROEXHTa的6xHis標簽之后, 利用大腸桿菌表達菌株BL 21(DE3)獲得重組蛋白。然后對重組蛋白的誘導條件進行了優化, 重組蛋白表達量的多少與誘導劑的濃度和誘導時間有密切關系, 而本實驗發現在選取的范圍內, 誘導劑濃度的變化對重組蛋白表達量的影響并不明顯, 主要影響因素是誘導時間。本實驗最終確定了IPTG 誘導濃度為0.8 mmol/L, 誘導時間為3 h, 為重組蛋白的大量培養表達提供了依據。
研究表明NPY促食的機制可能是其在室旁核中與Y1[13]或Y5[14]受體結合后傳出信號, 抑制交感神經興奮副交感神經, 并促進生長激素、促性腺激素[15]、促黃體生成素[16]等激素的釋放, 從而增加食欲和采食量并促進消化[17]。目前許多魚類物種中都克隆出了NPY并且驗證了其促食作用, 因而NPY在促進水產養殖業發展中有可觀的前景。在牙鲆中的研究還僅限于核酸水平, 而在機體內真正起作用的是蛋白。本實驗得到 NPY重組蛋白, 并制備了多克隆抗體,為在牙鲆中進一步研究其生物學功能提供了條件。
[1] Tatemoto K, Neuropeptide Y. Complete amino-acid-sequence of the brain peptide[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America-Biological Sciences, 1982, 79(18): 5485-5489.
[2] Hoyle C H V. Neuropeptide families and their receptors: evolutionary perspectives[J]. Brain Research, 1999, 848(1-2): 1-25.
[3] Larhammar D. Evolution of neuropeptide Y, peptide YY and pancreatic polypeptide[J]. Regulatory Peptides, 1996, 62(1): 1-11.
[4] Lopez-Patino M A. Neuropeptide Y has a stimulatory action on feeding behavior in goldfish (Carassius auratus)[J]. European Journal of Pharmacology, 1999, 377(2-3): 147-153.
[5] Silverstein J T. Neuropeptide Y-like gene expression in the salmon brain increases with fasting[J]. Gen Comp Endocrinol, 1998, 110(2): 157-165.
[6] Silverstein J T, Plisetskaya E M. The effects of NPY and insulin on food intake regulation in fish[J]. American Zoologist, 2000, 40(2): 296-308.
[7] Mac Donald E, Volkoff H. Neuropeptide Y (NPY), cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript (CART) and cholecystokinin (CCK) in winter skate (Raja ocellata): cDNA cloning, tissue distribution and mRNA expression responses to fasting[J]. General and Comparative Endocrinology, 2009, 161(2): 252-261.
[8] Campos V F. Identification, tissue distribution and evaluation of brain neuropeptide Y gene expression in the Brazilian flounderParalichthys orbignyanus[J]. Journal of Biosciences, 2010, 35(3): 405-413.
[9] Carpio Y. Cloning, expression and growth promoting action of Red tilapia (Oreochromissp.) neuropeptide Y[J]. Peptides, 2006, 27(4): 710-718.
[10] Kurokawa T, Suzuki T. Development of neuropeptide Y-related peptides in the digestive organs during the larval stage of Japanese flounder,Paralichthys olivaceus[J]. General and Comparative Endocrinology, 2002, 126(1): 30-38.
[11] Volkoff H. Aspects of the hormonal regulation of appetite in fish with emphasis on goldfish, Atlantic cod and winter flounder: Notes on actions and responses to nutritional, environmental and reproductive changes[J]. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology a-Molecular & Integrative Physiology, 2009, 153(1): 8-12.
[12] Campos V F. Neuropeptide Y gene expression around meal time in the Brazilian flounderParalichthys orbignyanus[J]. Journal of Biosciences, 2012, 37(2): 227-232.
[13] Zukowska-Grojec Z. Neuropeptide Y: an adrenergic cotransmitter, vasoconstrictor, and a nerve-derived vascular growth factor[J]. Adv Pharmacol, 1998, 42: 125-128.
[14] Flynn M C. Feeding response to neuropeptide Y-related compounds in rats treated with Y5 receptor antisense or sense phosphothio-oligodeoxynucleotide[J]. Physiol Behav, 1999, 66(5): 881-884.
[15] Peng C. Neuropeptide Y stimulates growth-hormone and gonadotropin-Ii secretion in the goldfish pituitary -involvement of both presynaptic and pituitary cell actions[J]. Endocrinology, 1993, 132(4): 1820-1829.
[16] Cerda-Reverter J M. Energetic dependence of NPY-induced LH secretion in a teleost fish (Dicentrarchus labrax)[J]. American Journal of Physiology-Regulatory Integrative and Comparative Physiology, 1999, 277(6): 1627-1634.
[17] Mccarthy H D. Megestrol-acetate stimulates food and water-intake in the rat effects on regional hypothalamic neuropeptide-Y concentrations[J]. European Journal of Pharmacology, 1994, 265(1-2): 99-102.
(本文編輯: 譚雪靜)
Expression of recombinant flounder NPY proteinin vitroand detection of endogenous NPY in flounder
WANG Qian1,2, TAN Xun-gang1, SUN Wei1, YOU Feng1, ZHANG Pei-jun1
(1. Experimental Marine Biology Laboratory, Institute of Oceanology, Chinese, Academy of Sciences, Qingdao 266071, China; 2. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049, China)
Apr., 24, 2013
Neuropeptide Y; prokaryotic expression; recombinant protein; polyclonal antibody
Neuropeptide Y (NPY) plays a key role in regulation of food intake in fish, which is essential for aquaculture. In order to investigate the effects of NPY on olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus), two types of flounder NPY gene, full length NPY (f-NPY) with signal peptide and mature peptide NPY (m-NPY) without the signal, were cloned into expression vector pPROEXTMHTa and expressed inE.coliBL21 (DE3) respectively. The recombinant NPY proteins were induced by IPTG. The optimal concentration of IPTG was 0.8 mmol/L and the optimal induction time was 3 h. In addition, the NPY polyclonal antibody was prepared according to its amino acid sequence. Western blot analysis confirmed that both the recombinant NPY and the flounder endogenous NPY protein could be detected by the polyclonal antibody. In summary, our study will provide basis for further study on the application of recombinant olive flounder NPY in aquaculture.
Q78
A
1000-3096(2014)04-0015-05
10.11759/hykx20130424003
2013-04-24;
2013-10-16
國家863計劃資助項目(2012AA092203); 國家自然科學基金資助項目(31128017); 國家科技基礎條件平臺建設運行項目-水產種質資源平臺運行服務(2006DKA30470017)
王倩(1987-), 女, 山東曲阜人, 博士生, 主要從事海洋生物學研究, 電話: 0532-82898559, E-mail: ameliaxing@163.com; 譚訓剛, 通信作者, 副研究員, 電話: 0532-82898559, E-mail: tanx@ qdio.ac.cn; 尤鋒, 通信作者, 研究員, 電話: 0532-82898561, E-mail: youfeng@qdio.ac.cn

